20 January 2025 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Indian cryptography research gears up to face the quantum challenge
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
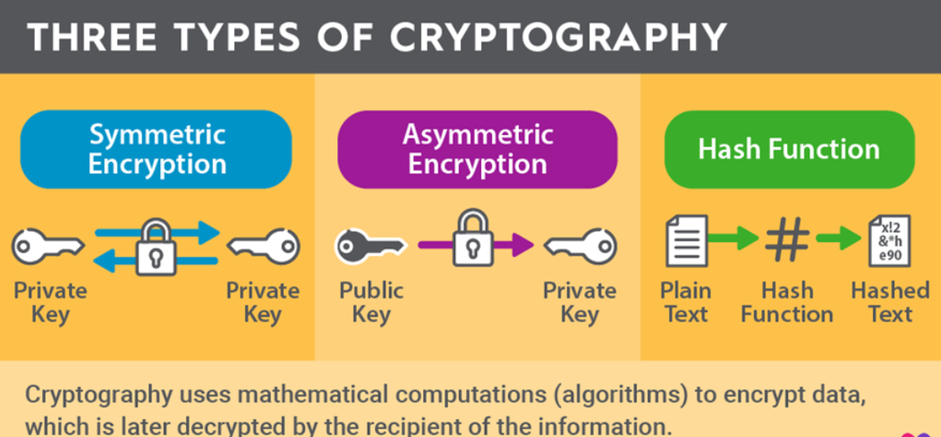
Introduction to Cryptography
- Cryptography is a technique used to secure information by converting plain text into unreadable ciphertext.
- Its main goal is to ensure system security and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- The practice of sending secret messages has existed since ancient times, with notable historical examples such as Julius Caesar’s cipher and the Enigma system used during World War II.
| The Importance of Cryptography |
|
Challenges and Slow Progress
- Cryptography is a slow-moving field due to its complexity and the close connection between complexity theory and cryptography.
- Research in India focuses on areas like communication complexity, proof complexity, and algebraic coding theory, aiming to enhance security.
Cryptography Keys and Their Function
- The core of cryptosystems is the key, which is a secret value used for encrypting or decrypting data.
- Modern systems, like public-key cryptography, use two keys: a public one shared with the sender and a private one kept by the receiver.
- One-way functions are used to make encryption easy but decryption very difficult without the key.
Emerging Research and Challenges
- Two disruptive research areas in cryptography are homomorphic encryption, which allows computations on encrypted data, and quantum-resistant cryptography, which ensures systems can withstand quantum computing threats.
- Indian researchers are making progress in these areas, and the government is funding cryptography research, including the National Quantum Mission and quantum communication developments.
Future of Cryptography in India
- India is advancing in cryptography research, particularly in quantum communication and data security, with government support and collaboration from various institutions.
- The importance of encryption will grow as sensitive data continues to increase, especially in cloud storage.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of cryptography in modern data security systems. Analyze the potential impact of quantum computing on existing cryptographic methods and India’s progress in this field. (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. Annual calendar, at least 100 sittings every year must in Parliament: O’Brien
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Topic: GS2 – Indian Polity |
| Context |
|
Issues Associated with Short Notice for Parliament Sessions
Inadequate Preparation Time:
- Short notice leaves lawmakers with little time to prepare for crucial debates and discussions.
- This can lead to superficial scrutiny of bills and motions, affecting the quality of legislative work.
Reduced Accountability and Scrutiny:
- With insufficient time, Parliament members are unable to hold the government accountable effectively.
- Parliamentary debates on national issues are rushed, reducing the chances for detailed examination.
Impact on Members’ Engagement:
- Short session notices disrupt MPs’ schedules, especially those with constituency commitments.
- Lack of preparation time affects both the members and their ability to represent the people they serve effectively.
Public Distrust:
- Unpredictable parliamentary schedules erode public trust in the functioning of the government.
- Citizens expect transparency, and sudden session announcements may raise concerns about the legislative process being manipulated.
Legislative Disorganization:
- When sessions are not planned in advance, there’s a lack of structured business, affecting the prioritization of critical national issues.
- Lack of a predictable calendar results in chaotic and disorganized parliamentary proceedings.
Way Forward: Structured Parliamentary Calendar
Introducing an Annual Parliamentary Calendar:
- The government should publish an annual calendar for Parliament, enabling all stakeholders to plan ahead.
- This can include expected session dates, discussion topics, and important legislative matters.
Mandating Minimum 100 Parliamentary Sessions:
- To ensure proper legislative functioning, at least 100 sittings per year should be conducted.
- This ensures that there’s adequate time for legislation, debates, and holding the government accountable.
Improved Session Planning:
- The planning should allow for a sufficient gap between sessions, giving members enough time for preparation and constituency work.
- A predictable session structure also improves the quality of debates and deliberations.
Conclusion
- By establishing a predictable calendar, Parliament can become more accountable, transparent, and better equipped to serve the public’s interests.
| Practice Question: Critically analyze the issues arising from short notice announcements for Parliament sessions. Suggest a way forward to improve the functioning and accountability of Parliament through a structured annual calendar.(150 Words /10 marks) |
3. Abetment of suicide charges should not be ‘mechanically’ invoked: SC
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained – Page No. – 12)
| Topic: GS2 – Polity |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
About Section 306 of IPC
- Section 306 of IPC deals with the Abetment of suicide whereas the same provision has been covered under Section 108 of the Bhartiya Nyaya Sanhita, 2023(BNS).
- It states that if any person commits suicide, whoever abets the commission of such suicide, shall be punished with imprisonment of either description for a term which may extend to ten years, and shall also be liable to fine.
Sensitizing Investigation Agencies and Courts in Abetment of Suicide Cases
- The Supreme Court cautioned against the misuse of the provision (Section 306 of the IPC) to satisfy the immediate emotions of a deceased’s family, stressing that only genuine cases meeting the legal threshold should lead to prosecution.
- The Court highlighted the abuse of process in cases lacking adequate evidence of abetment.
Legal Framework for Abetment of Suicide
- Section 306 IPC criminalizes abetment of suicide, which is defined under Section 107 IPC as acts of instigation, conspiracy, or intentional aiding.
- Prosecution under this section requires proof of direct instigation or acts that leave the deceased with no alternative but to die by suicide.
- Punishment includes up to 10 years of imprisonment and a fine. However, conviction rates remain low at 17.5% in 2022, highlighting challenges in proving intent and direct abetment.
The Supreme Court’s Intervention in the Bank Manager Case
- In the case of a bank manager accused of abetting a borrower’s suicide, the Supreme Court discharged the manager, stating that mere allegations of harassment for loan recovery do not meet the threshold for abetment.
- It criticized trial courts for framing charges mechanically and stressed the need for a practical approach in evaluating evidence.
- The Court reiterated that casual exchanges or hyperboles should not be misconstrued as instigation to suicide.
Higher Standard for Proof in Workplace-Related Cases
- The Supreme Court has set a higher bar for proof in abetment of suicide cases stemming from workplace or official relationships.
- In cases like M Mohan v State (2011) and Ude Singh v State of Haryana (2019), the Court emphasized that prosecution requires evidence of direct incitement or a continuous course of conduct that left the deceased with no alternative but suicide.
- It clarified that indirect acts or vague allegations without proof of intent do not suffice for prosecution.
Conclusion
- The Court has repeatedly cautioned against unnecessary prosecutions under Section 306 IPC, highlighting the need for evidence-based investigations and judicial prudence.
- A balance must be struck between protecting genuine victims and preventing misuse of the law, which could otherwise lead to undue harassment of accused individuals.
- Sensitization of investigating agencies and trial courts is critical to ensure fair application of the law.
| What is the Statistics Related to Suicide in India? |
|
| Practice Question: Critically analyze the challenges in prosecuting abetment of suicide cases under Section 306 of the IPC. Discuss the role of the judiciary in ensuring a balance between preventing misuse of the law and delivering justice to genuine victims. (150 Words /10 marks) |
4. Spike in Olive Ridley Turtle Deaths Along Tamil Nadu Coast Sparks Conservation Concerns
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained- Page No. – 12)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
What are Olive Ridley Turtles?

- These turtles are carnivores and get their name from their olive-coloured carapace.
- They are best known for their unique mass nesting called Arribada, where thousands of females come together on the same beach to lay eggs.

- Habitat:
- They are found in warm waters of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian oceans.
- Odisha’s Gahirmatha Marine Sanctuary is known as the world’s largest rookery (a colony of breeding animals) of sea turtles.
- Protection Status:
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule 1
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I
Causes of Turtle Deaths
- The deaths are primarily attributed to bycatch from commercial fishing operations.
- Olive ridley turtles, needing to surface for air, asphyxiate when trapped in fishing nets.
- This year, the spike in deaths may be due to an increased presence of fish near turtle gathering areas, attracting more trawlers.
- Post-mortem reports confirmed signs of suffocation, such as lesions on lungs, bulging eyes, and swollen necks.
Need for Mitigation Measures
- Experts emphasize the urgent need to enforce the use of Turtle Excluder Devices (TEDs) in fishing nets to allow turtles to escape.
- A comparative analysis of fish catch trends could also help identify patterns contributing to the deaths.
- Strict monitoring and regulation of fishing activities near nesting sites are essential to protect these vulnerable turtles.
The Nesting Season and Conservation Efforts
- Olive ridley turtles nest along India’s east and west coasts, with mass nesting sites in Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu.
- Females lay 100-110 eggs per nest, which hatch after 45-60 days. To protect eggs from predation and human disturbance, hatcheries are established by Forest Departments.
- Hatchlings are released safely into the sea, ensuring their survival.
Conclusion
- The alarming deaths of olive ridley turtles in Tamil Nadu underscore the need for stringent conservation measures, including enforcement of TEDs, regulation of fishing practices, and increased public awareness.
- Protecting these turtles is vital for maintaining marine biodiversity and ecological balance.
| Operation Olivia |
|
|
PYQ: Which one of the following is the national aquatic animal of India? (2015) (a) Saltwater crocodile (b) Olive ridley turtle (c) Gangetic dolphin (d) Gharial Ans: C |
| Practice Question: Analyze the causes behind the recent surge in olive ridley turtle deaths along Tamil Nadu’s coast. Discuss the impact of commercial fishing practices on turtle populations and suggest measures to mitigate such fatalities. (150 Words /10 marks) |
5. Raman Research Institute faculty honored with the Gates-Cambridge Impact Prize 2025
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2094287®=3&lang=1 )
| Context |
|
Gates-Cambridge Impact Prize:
- The Gates-Cambridge Impact Prize is awarded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
- It celebrates the contributions of Gates-Cambridge Scholars who have made significant global impacts.
- The prize is part of the 25th anniversary celebration of the Gates-Cambridge Scholarship program.
- It highlights individuals whose work embodies the spirit of science and global progress.
- The prize acknowledges achievements across various fields, including science, technology, and global health.
- Winners are selected for their vision, leadership, and dedication to addressing humanity’s most pressing issues.
- The prize aims to inspire future generations to contribute to global change.
Prelims Facts
1. Water hyacinth threatens the livelihoods of fishers on Kenyan lake
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Context |
|
Water Hyacinth:
- It is an invasive aquatic plant native to the Amazon Basin in South America.
- Characteristics: Floats on water, has large, glossy green leaves, purple flowers.
- Spread: Grows rapidly, forming dense mats that block sunlight, affecting aquatic life.
- Environmental Impact: Reduces oxygen levels, hampers fish populations, and affects water quality.
- Economic Impact: Disrupts water transport, fishing, and agriculture.
- Control Methods: Mechanical removal, biological control (using insects), chemical treatments.

Places in News: Lake Naivasha
- Lake Naivasha is a popular freshwater lake in Kenya.
- It has been affected by the invasive water hyacinth for over 10 years.
- The hyacinth has reduced fish populations, impacting the livelihoods of fishermen.
- Previously, fishermen caught up to 90 kg of fish daily, but now it’s only 10-15 kg.
- The lake faces economic losses due to the hyacinth invasion, affecting fishing, transport, and tourism sectors.
2. SVAMITVA Scheme: Unlocking Economic Potential in Rural India through Property Cards
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained- Page No. – 12)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
The SVAMITVA Scheme

- The SVAMITVA scheme (Survey of Villages and Mapping with Improvised Technology in Village Areas) is an initiative launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in 2020.
- It aims to provide a legal property record to rural households, empowering them with property cards for their homes and land.
- The scheme utilizes advanced technologies like drones and GIS-based mapping to survey rural properties, benefiting rural residents by enabling access to financial services, facilitating land taxation, and aiding rural planning.
Benefits of the SVAMITVA Property Cards
- The primary advantage of the property cards is that they provide rural families with a recognized legal document for their property, which they can use to access financial services like loans.
- This has enabled many villagers to start small businesses, securing economic growth.
- Additionally, these cards assist in property tax determination, enhancing financial flows to Gram Panchayats and improving land market liquidity.
- The cards also support rural land record creation, helping in planning, addressing land disputes, and eliminating encroachments.
Implementation Process
- The SVAMITVA scheme is implemented through a multi-stage process that begins with an agreement between the Survey of India (SoI) and state governments.
- Drones and satellite images are employed for accurate mapping of rural properties.
- After the collection of data, a ground verification process ensures the accuracy of the maps.
- The final property cards are issued digitally or physically to property owners.
- The whole process includes community awareness programs, conflict resolution, and detailed mapping of abadi areas (inhabited land).
Progress and Coverage of the Scheme
- The scheme, initially rolled out as a pilot in 2020, has made significant progress.
- As of now, drone surveys have been completed in over 3.17 lakh villages, covering 92% of the targeted villages.
- States such as Haryana, Goa, and Uttarakhand have achieved full saturation.
- The scheme’s reach extends over 67,000 sq.km of rural land, valued at an estimated Rs. 132 lakh crore.
- With the target to cover all 6.62 lakh villages by the end of FY 2023-24, the scheme is steadily advancing towards its goal.
For more such UPSC related Current Affairs, Check Out- 18 January 2025 : Daily Current Affairs




