22 February 2025 : Daily Current Affairs
1. India, China worked hard to save G-20: Jaishankar
- 1. India, China worked hard to save G-20: Jaishankar
- 2. Concept of sexual equality must be part of syllabus: SC
- 3. Understanding the Importance and Quality of Government Spending in India
- 4. India-Qatar LNG Trade: Powering a Strategic Energy Partnership for 2030
- 5. How Biotechnology is Transforming North East India
- Prelims Facts
- 1. A record 6.5 lakh Olive Ridley turtles reach Odisha beach for mass nesting
- 2.Ex-Gratia Payments
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Context |
|
Discussions on Bilateral Relations
- The meeting addressed regional and global issues, including the situation along the Line of Actual Control (LAC).
- Previous discussions on border peace were reviewed, building on past diplomatic engagements between the two countries.
- Maintaining peace and stability along the border was highlighted as a key objective for future talks.
Key Areas of Cooperation
- Talks included topics such as resuming the Kailash Mansarovar pilgrimage, trans-border river management, flight connectivity, and easing travel restrictions.
- Strengthening economic and infrastructure collaboration was also discussed.
Global Concerns and Multilateralism
- The importance of protecting multilateral organizations from global divisions was highlighted.
- It was emphasized that international cooperation should be more transparent and inclusive rather than serving the interests of a few.
- The need for “plurilateralism” was stressed to address global issues effectively.
Engagements with Other Nations
- Discussions were also held with leaders from other BRICS countries and key international partners.
- The importance of collaboration in the Indo-Pacific region was reaffirmed in trilateral talks with strategic partners.
| Practice Question: Beyond bilateral concerns, how do India-China engagements in multilateral forums like the G-20, BRICS, and SCO shape global governance? Analyze. (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. Concept of sexual equality must be part of syllabus: SC
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|
Supreme Court Emphasizes Gender Equality Education in Schools
- The court stressed that early moral training is essential to change societal attitudes.
- A judge noted that many schools either do not have moral education classes or cancel them for other subjects.
Gender Equality Must Start at Home
- The court highlighted that discrimination begins within families.
- Parents often focus on restraining their daughters rather than educating their sons about respectful behavior.
- The concept of gender discrimination must be eliminated from society to ensure equality.
Lack of Basic Education on Gender Equality
- A petitioner argued that the increase in crimes against women is due to the lack of gender equality education at an early stage.
- The petitioner emphasized that 50% of the population, consisting of women, live in constant insecurity due to increasing crimes.
- The court agreed that education is the key to changing attitudes towards women in society.
Women’s Independence and Social Awareness
- The court observed that many communities still believe that a woman neither belongs to her parents’ home nor her in-laws’ home after marriage.
- It stressed the need to recognize that a woman is an independent individual who deserves equal respect and rights.
- Awareness about women’s autonomy and their equal role in society must be taught from an early age.
Legal Awareness and the Role of Media
- The petitioner suggested that awareness about stringent laws against crimes like rape must be promoted in media and public spaces.
- It was argued that people often realize the seriousness of these laws only after facing severe punishments.
- Public awareness campaigns in cinema halls and media platforms can help spread knowledge about strict legal consequences for crimes against women.
Need for Systematic Educational Reform
- The court noted that environmental science was introduced in schools following a Supreme Court order and suggested a similar approach for moral education.
- The government has been asked to submit a report on steps taken to include gender equality in the school syllabus.
- The petition emphasized that reactive measures, such as increasing punishments after a crime, are not enough.
- Instead, proactive education and awareness are necessary to change the male mindset and instill respect for women.
Bridging the Gap Between Law and Society
- The petition highlighted the gap between legal provisions and societal attitudes.
- Identifying the root cause of gender-based crimes is crucial for effective solutions.
- The goal is to educate young minds, instill fear of law among potential offenders, and promote long-term gender equality.

| Gender Equality In India: |
|
Need for Gender Equality Education in Schools
Challenges in Implementing Gender Equality Education Lack of Priority:
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the role of education in promoting gender equality and preventing crimes against women. How can school curricula be reformed to inculcate moral and ethical values from an early age? (150 Words /10 marks) |
3. Understanding the Importance and Quality of Government Spending in India
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained – Page No. – 15)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Why Government Spending Matters
-
- Government expenditure is fundamentally the people’s money, sourced through taxes and borrowings.
- According to Margaret Thatcher, government spending ultimately burdens citizens, either through direct taxation or borrowing from their savings.
- Therefore, how and where the government spends significantly impacts economic growth, social development, and the financial well-being of citizens.
- Efficient public spending ensures optimal use of resources, leading to better infrastructure, education, healthcare, and overall economic progress.
Key Trends in India’s Public Expenditure
Over the past two decades, India’s public spending has been shaped by two major trends:
- Fiscal Discipline:
Instituted through the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act in 2003, fiscal discipline aims to limit government borrowing. The Act mandates that the fiscal deficit should not exceed 3% of GDP and the revenue deficit should be zero. This ensures borrowing is channeled toward capital expenditure, which enhances economic capacity rather than funding daily operational costs.
- Focus on Capital Expenditure:
Capital expenditure (Capex) is critical as it boosts the economy’s productive capacity. Investments in infrastructure like roads, railways, and ports stimulate long-term growth. In contrast, revenue expenditure, such as salaries and subsidies, offers limited long-term benefits. India’s increasing emphasis on Capex reflects a strategic shift toward sustainable economic development.
Challenges in Maintaining Spending Quality
Despite consensus on fiscal prudence and Capex emphasis, India faces challenges that affect the quality of public expenditure:
- Crisis-Driven Spending: Events like the 2008 Global Financial Crisis and the 2020 Covid-19 pandemic forced governments to increase revenue expenditure through stimulus packages, eroding spending quality.
- Political Populism: Policies like loan waivers and subsidies, though politically popular, divert funds from productive investments, impacting long-term growth potential.
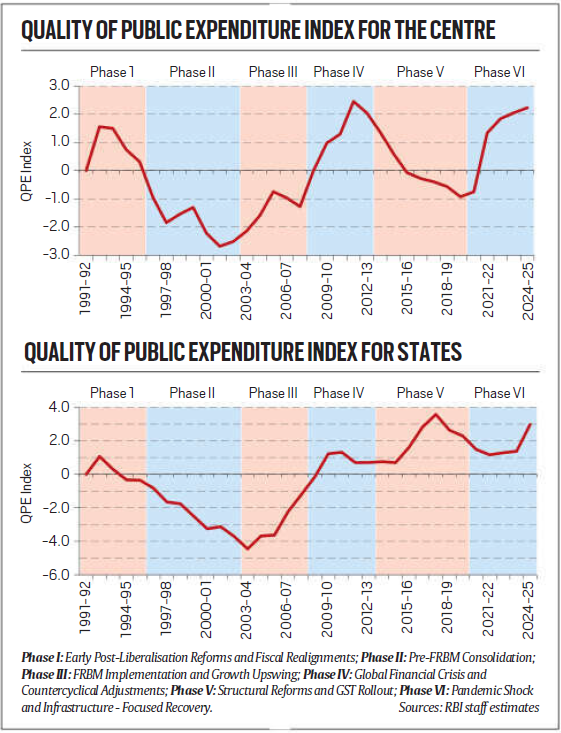
RBI’s Quality of Public Expenditure (QPE) Index
To holistically measure spending quality, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) developed the QPE Index using five key indicators:
- Capital Outlay to GDP Ratio: Higher ratios indicate better spending quality due to infrastructure investments.
- Revenue Expenditure to Capital Outlay Ratio: Lower ratios suggest more productive spending.
- Development Expenditure to GDP Ratio: Higher ratios reflect greater investments in growth-stimulating sectors like education, healthcare, and R&D.
- Development Expenditure to Total Expenditure: A higher proportion indicates prioritization of growth-centric spending.
- Interest Payments to Total Expenditure Ratio: Lower values indicate fiscal health, showing reduced reliance on debt.
India’s Performance Across Six Phases

The RBI’s analysis (1991-present) divides India’s spending trends into six phases:
- Phase 1 (Early Reforms):
Marginal improvements at the Centre, with states experiencing a slight decline due to fiscal pressures and reduced public investments. - Phase 2 (Pay Commission Impact):
Both Centre and states saw sharp declines in spending quality due to higher interest payments and revenue expenditures following the Fifth Pay Commission. - Phase 3 (Growth and Fiscal Discipline):
The introduction of the FRBM Act and robust economic growth improved the QPE index significantly. States also benefited from higher fiscal devolution. - Phase 4 (Global Financial Crisis):
The 2008 crisis led to increased countercyclical spending, raising deficits and slowing improvements in expenditure quality. - Phase 5 (GST and State Gains):
States improved their QPE through development-focused spending, aided by GST revenue-sharing reforms, while the Centre faced fiscal challenges. - Phase 6 (Covid Recovery and Capex Focus):
Post-Covid recovery efforts, marked by substantial capital expenditure, have pushed India’s public spending quality to near-record highs.
Conclusion
- India’s journey toward improving public expenditure quality reflects a balance between fiscal discipline and growth-oriented investments.
- Despite crises and political pressures, the emphasis on capital expenditure and prudent fiscal management has led to significant improvements.
- The RBI’s QPE index now indicates that India’s public spending quality is at one of its best levels since 1991, signaling a promising trajectory for sustained economic growth.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of government expenditure patterns in India with reference to the Reserve Bank of India’s Quality of Public Expenditure (QPE) index. How do fiscal discipline and capital expenditure influence economic growth and development? (150 Words /10 marks) |
4. India-Qatar LNG Trade: Powering a Strategic Energy Partnership for 2030
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained – Page No. – 15)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Strategic Energy Partnership
- India and Qatar share a robust energy partnership, with liquefied natural gas (LNG) at its core.
- Qatar is India’s largest LNG supplier, accounting for nearly 39% of India’s total LNG imports.
- The two nations now aim to double bilateral trade to $28 billion annually by 2030, driven significantly by LNG imports.
Growing LNG Demand in India
- India’s natural gas consumption is projected to rise by 60% by 2030, with LNG imports expected to double to 65 billion cubic metres annually.
- This surge is fueled by India’s goal to increase the share of natural gas in its primary energy mix from 6% to 15% by 2030, making LNG a critical component of India’s energy strategy.
Qatar’s Expanding Export Capacity
- Qatar plans to nearly double its LNG export capacity from 77 million tonnes per annum (mtpa) to 142 mtpa by 2027.
- This expansion aligns perfectly with India’s rising LNG demand, likely strengthening Qatar’s position as India’s primary LNG supplier for the foreseeable future.
US: An Emerging Competitor
- The US, India’s second-largest LNG supplier, poses significant competition to Qatar.
- Recent policy shifts in the US, including lifting export bans on LNG projects, could boost its LNG exports to India.
- Indian companies are actively exploring long-term LNG contracts in the US, potentially altering future trade dynamics.
Conclusion
- The India-Qatar LNG trade relationship remains pivotal as both nations aim to deepen economic ties.
- With India’s LNG demand surging and Qatar’s export capacity expanding, LNG will continue to drive this strategic partnership.
- However, the growing US presence in the LNG market could reshape India’s import landscape in the coming years.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of liquefied natural gas (LNG) in shaping the India-Qatar trade relationship. How can this partnership contribute to India’s energy security and economic growth? (150 Words /10 marks) |
5. How Biotechnology is Transforming North East India
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2105241 )
| Context |
|
Introduction
- India’s North East Region (NER) is rich in biodiversity, culture, and natural resources.
- Biotechnology is playing a key role in preserving this heritage while promoting growth and sustainability.
- The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) has been supporting various initiatives to harness bioresources, improve education, and create job opportunities.
Funding and Major Initiatives
- Since 2010, DBT has allocated 10% of its annual budget to specialized programs in NER.
- These programs focus on research, education, and employment in biotechnology.
Key Programs Under the North Eastern Programme

Twinning R&D Programme for NER
- Launched in 2010-11 to build biotechnology capacity in NER.
- Collaborations between 65+ institutions have supported nearly 650 R&D projects.
- Benefitted around 450 researchers and 2,000 students.
Biotech Hubs
- Since 2011, 126 Biotech Hubs have been established in universities, colleges, and institutions.
- These hubs provide infrastructure and training to support biotechnology education and research.
Biotechnology Labs in Senior Secondary Schools (BLiSS)
- Initiated in 2014 to provide students with well-equipped biology laboratories.
- Aims to create awareness and interest in biological sciences at the school level.
Visiting Research Professorship (VRP) Programme
- Started in 2015 to bring expert scientists to institutions in NER.
- Focuses on advancements in biotechnology and life sciences.
Specialized Training for NE Researchers
- Chemical Ecology Programme (2015): Trained young scientists from NER in chemical ecology through collaboration with Bangalore institutions.
- Genomics-Driven Research (2016): Focused on training scientists, researchers, and clinicians in biomedical research and molecular genetics.
Human Resource Development (HRD) in NER
- Programs emphasize services for farmers and academics.
- DBT-North East Centre for Agricultural Biotechnology (DBT-NECAB): Phase III focuses on agricultural advancements.
- Citrus Research Facilities: Established in Assam to develop disease-free citrus varieties.
Support for Farmers and Entrepreneurs
- 64.1 acres dedicated to cultivating medicinal crops like Curcuma caesia and lemongrass.
- 649 farmers and entrepreneurs have received training and awareness.
- An essential oil distillation unit set up in Arunachal Pradesh to help farmers generate income.
- Docynia indica (Assam apple) Value Addition: Farmers and tribal communities trained to make products like pickles, jam, and juice.
Major Achievements
Development of Bacterial Blight-Resistant Rice
- A new rice variety named “Patkai” was developed in Assam.
- It is resistant to bacterial blight and has been approved by the Central Variety Release Committee (CVRC).
Rapid Disease Detection for Livestock
- A lateral flow assay was developed for detecting brucellosis in livestock.
- The test provides quick and accurate results based on serum samples.
Mobile Application for Pig Disease Diagnosis
- Pig Disease Diagnosis Expert System (PDDES) was developed to assist in diagnosing pig diseases.
- The app is available on the Google Play Store and helps veterinarians and farmers manage livestock health.
Conclusion
- Biotechnology initiatives in NER are helping preserve biodiversity, boost education, and promote entrepreneurship.
- By integrating science with traditional knowledge, the region is advancing toward sustainable economic growth.
| Practice Question: How has biotechnology contributed to sustainable development in India’s North East Region (NER), and what are the key initiatives driving this transformation? (150 Words /10 marks) |
Prelims Facts
1. A record 6.5 lakh Olive Ridley turtles reach Odisha beach for mass nesting
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 5)
| Context |
|
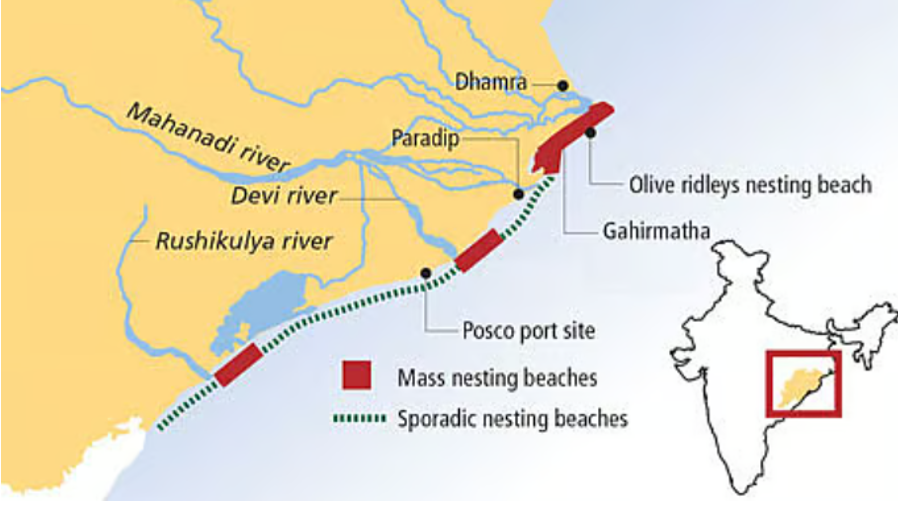
Analysis of the news:
- In the previous two years (2023-24 and 2024-25), only sporadic nesting was observed at the site, with the last major nesting event recorded in 2022-23.
- This is the highest number of turtles ever recorded at Rushikulya beach.
- Mass nesting at Gahirmatha in Odisha’s Kendrapara district is expected to begin soon, following the usual pattern.
- The Indian Coast Guard is patrolling the area to prevent human interference through seaward poaching or leisure activities.
- ‘Operation Olivia’, conducted from November 1 to May 31, is helping protect Olive Ridley turtles, showing positive results.
| Olive Ridley Turtles |
|
Conservation Status: Listed as Vulnerable under the IUCN Red List. Legal Protection: Protected under Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972. Habitat: Found in warm tropical waters of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans. Mass Nesting (Arribada): Known for synchronous mass nesting at sites like Rushikulya, Gahirmatha, and Devi River (Odisha). Threats: Poaching, fishing net entanglement, habitat destruction, and climate change. Reproductive Cycle: Females lay 100-150 eggs per clutch, with hatching occurring in 45-60 days. International Protection: Covered under CITES Appendix I and CMS (Convention on Migratory Species).
|
2.Ex-Gratia Payments
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained- Page No. – 15)
|
Context |
|
● The Ministry of Railways disbursed ex-gratia payments in cash to the next of kin of victims of the New Delhi railway station stampede, raising concerns over the mode of payment. |
Analysis of the news:
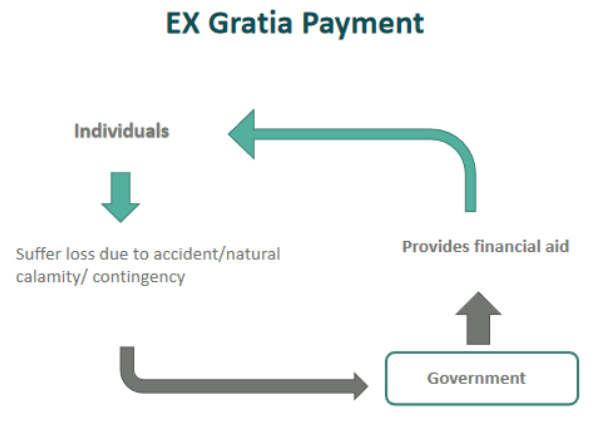
Ex-Gratia Payments: Meaning and Difference from Compensation
- Ex-gratia payments are goodwill payments made out of moral obligation, without any legal liability.
- In contrast, compensation is a legally mandated payment aimed at reimbursing losses such as life, property, or livelihood.
- The recent disbursal of ex-gratia payments by the Ministry of Railways after the New Delhi railway station stampede falls under the former category, intended to provide immediate relief rather than admitting responsibility.
Mode of Ex-Gratia Payments: Cash vs. Bank Transfers
- Typically, ex-gratia payments are disbursed through bank transfers for better accountability and transparency.
- However, in exceptional cases, such as the recent railway stampede, entire payments were made in cash after Aadhaar verification.
- Although cash disbursals are rare, authorities justified them by citing exigencies like victims lacking immediate access to bank details.
- However, legal experts argue that bank transfers provide concrete proof and are preferable for maintaining transparency.
Government Guidelines and Past Practices
- The 2023 Railway Board communication allows a cash disbursal of up to ₹50,000 for initial expenses, with the balance recommended via bank transfers.
- However, the entire ₹10 lakh ex-gratia amount was paid in cash during this incident, raising questions about adherence to these guidelines.
- Comparatively, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the Delhi government mandated Aadhaar-linked Direct Benefit Transfers for ex-gratia payments, ensuring traceability and minimizing risks of mismanagement.
Government’s Justification and Challenges
- Railway officials defended the cash disbursal by pointing out that similar practices were followed during the Balasore train accident.
- They argued that cash payments were necessary due to the lack of bank accounts or readily available bank details among some recipients.
- While immediate cash relief addresses urgent needs, it also raises concerns over transparency, accountability, and potential misuse, highlighting the need for standardized protocols across all government departments.
check more – 21 February 2025 : Daily Current Affairs





