22 June 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. India’s Business Activity Surges in June with Fastest Job Creation in 18 Years: HSBC Survey
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Economy; Page: 19)
|
Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
|
Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Increased Business Activity and Job Creation:
- The HSBC survey highlights a notable increase in business activity in June, reflected by the final Manufacturing, Services, and Composite Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) figure rising to 60.9 from 60.5 in May.
- This uptick in the composite output index was supported by an increase in new orders, prompting firms to hire more in both manufacturing and services sectors.
- The pace of job creation reached its highest in over 18 years, underscoring robust demand conditions.
Sector-Specific Performance:
- While both manufacturing and services sectors experienced growth, the manufacturing sector saw a more significant boost.
- The composite flash PMI indicated a rise in both sectors, with manufacturing recording a faster pace of growth.
- New orders, primarily domestic, surged, with manufacturers witnessing a quicker pace of increase compared to service providers.
- International demand, although slowed in June, remained above historical averages, with service-related firms performing better than manufacturers in this aspect.
Input Costs and Margins:
- June saw a moderation in input cost inflation, which fell below the long-term average, benefiting both manufacturing and service sectors.
- However, overall price levels stayed elevated due to higher labor and material costs, especially for food, steel, and electronics.
- Output prices showed divergence: manufacturing firms experienced a rise, while service firms saw moderation.
- Consequently, corporate margins improved, particularly for manufacturing firms that managed to pass on part of their input costs to customers.
Future Outlook and Caution:
- Despite the positive trends, the survey advises caution as the future output index dropped sharply, reflecting a weakened degree of optimism to a three-month low.
- However, the overall sentiment remained above the series average, with private sector firms believing that sustained demand momentum could be achieved through enhanced marketing efforts.
Conclusion:
- The HSBC survey paints a promising picture of India’s business activity, driven by gains in manufacturing and services sectors, leading to significant job creation and improved corporate margins.
- Nevertheless, the need for cautious optimism is emphasized, given the dip in future output expectations, necessitating strategic efforts to maintain and build on the current growth momentum.
|
Practice Question: Discuss the recent trends in India’s business activity as indicated by the HSBC survey, particularly focusing on the gains in the manufacturing and services sectors. What are the challenges and potential risks that could affect the sustainability of this growth? Suggest policy measures to address these challenges. (250 words/15 m) |
2. High Court Stays Bail for Delhi CM Arvind Kejriwal in PMLA Case; Legal Battle Over Twin Test Continues
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 15)
|
Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government policies – Interventions for development in various sectors |
|
Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
The Twin Test and PMLA Bail Controversy:
Section 45 and Twin Test:
- Section 45 of the PMLA states that no court can grant bail for offenses under this law, with few exceptions. The provision mandates that the public prosecutor must be heard in all bail applications, and when the prosecutor opposes bail, the court must apply a twin test.
- This test includes two conditions: there must be reasonable grounds for believing the accused is not guilty of the offense, and the accused is not likely to commit any offense while on bail.
Legal Challenges to Twin Test:
- The twin test’s constitutional validity faced a major challenge in 2017 with the Nikesh Tarachand Shah v Union of India case. A two-judge Bench struck down the bail provision as unconstitutional, citing unreasonable classification.
- However, Parliament reinstated these provisions through the Finance Act, 2018. This reinsertion was subsequently challenged, leading to the 2022 Supreme Court ruling in Vijay Madanlal Choudhary v Union of India, which upheld the twin test’s application.
Legal and Practical Implications:
Comparison with Other Stringent Laws:
- The twin test is similar to provisions in laws dealing with serious offenses like The Drugs and Cosmetics Act, The Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, and The Unlawful Activities Prevention Act.
- However, legal experts question the logic of equating money laundering with anti-terror and narcotics laws, considering the maximum sentence for money laundering is generally seven years, except in cases involving narcotics.
Government’s Defense:
- The government defends the stringent bail conditions, arguing that those involved in money laundering are influential and resourceful, using advanced technology to conceal transactions.
- This makes it difficult for investigative agencies to detect and trace evidence.
Current Legal Position:
Pending Challenges and Reviews:
- Despite the Supreme Court’s agreement to review its ruling in Vijay Madanlal Choudhary, the twin test remains valid law, and all courts must rigorously apply it.
- However, a challenge to the amendments being passed through the Money Bill route remains pending.
- A larger Bench will address whether laws like the Aadhaar Act and service conditions of Tribunal members can be passed as Money Bills.
Section 436A of the CrPC:
- An accused can benefit from Section 436A of the Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC), which entitles them to bail after serving half of the maximum sentence as an undertrial.
- In most money laundering cases, if the ED cannot finish the trial within three and a half years, the accused is entitled to bail, irrespective of the twin test.
Conclusion:
- The bail controversy under PMLA highlights the ongoing legal complexities and the stringent requirements placed on bail applications.
- As the High Court stays the trial court’s bail order for Delhi CM Kejriwal, the application of the twin test continues to be a critical and contentious issue in the Indian legal landscape.
|
What is PMLA? |
|
· The Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA) was enacted to prevent cases of money laundering and provide for the confiscation of property derived from money laundering. · It aims to combat money laundering related to illegal activities such as drug trafficking, smuggling, and terrorism financing.
|
|
PYQ: Money laundering poses a serious threat to country’s economic sovereignty. What is its significance for India and what steps are required to be taken to control this menace? (200 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2013) |
|
Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the ‘twin test’ in bail applications under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA). Evaluate the constitutional validity and legal challenges associated with this test, citing recent judicial developments. Suggest reforms or amendments that could address the concerns raised by critics regarding the application of the twin test in PMLA cases. (250 words/15 m) |
3. Surge in Cereal Production in India: Shifting Consumption Patterns and Rising Surplus
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 15)
|
Topic: GS3 – Agriculture |
|
Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Declining Per Capita Consumption:
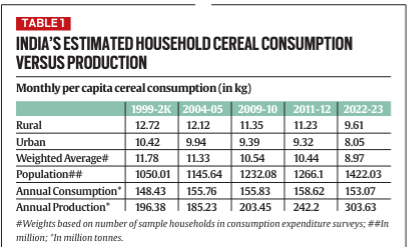
- Despite the growth in cereal production, the per capita consumption of cereals in India has declined.
- Data from the Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) by the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) shows a marked decrease in the quantity of cereals consumed per person per month.
- In rural India, this figure dropped from 12.72 kg in 1999-2000 to 9.61 kg in 2022-23. In urban areas, the decline was from 10.42 kg to 8.05 kg.
- Overall, the per capita consumption decreased from 11.78 kg to 8.97 kg during this period. This decline suggests a shift in dietary patterns and the consumption of other food items over cereals.
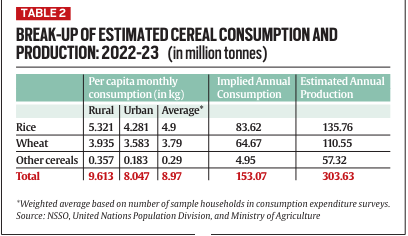
Shift Towards Processed and Industrial Use:
- A significant portion of the increased cereal production is not consumed directly by households but is diverted towards processed foods and industrial uses.
- The processed form includes products like bread, biscuits, noodles, and various baked goods. Additionally, cereals are increasingly used for making animal feed, industrial starch, potable liquor, and ethanol fuel.
- The expansion in these sectors has created a new demand for cereals beyond direct consumption, changing the traditional utilization patterns of these grains.
Export of Cereals:
- India has also become a notable exporter of cereals. In 2021-22, the country exported a record 32.3 mt of cereals, which included 21.2 mt of rice, 7.2 mt of wheat, and 3.9 mt of other grains.
- The following year, cereal exports totaled 30.7 mt. While these exports contribute to bridging the gap between production and domestic consumption, they only account for a fraction of the excess production.
Government Procurement and Surplus:
- The surplus production of cereals is also managed through government procurement.
- The Food Corporation of India (FCI) and other agencies have been mopping up the excess grains, resulting in substantial stockpiles.
- In the 2022-23 crop year, around 56.9 mt of rice and 26.2 mt of wheat were procured, exceeding the annual requirement for the public distribution system (PDS).
- This accumulation of grains in government warehouses helps stabilize market prices and ensures food security under the National Food Security Act, which provides cereals to over 813.5 million people at subsidized rates.
Unexplained Surplus and Production Estimates:
- Despite the substantial increases in production and various avenues of cereal utilization, there remains an unexplained surplus of grains.
- Even after accounting for exports, processed food consumption, and industrial use, there is a discrepancy between the estimated production and the actual usage.
- This raises questions about the accuracy of official production estimates and their implications for market dynamics.
- Recent trends in cereal inflation and declining government stockpiles suggest that the actual availability of cereals might be lower than reported, highlighting the need for more precise data and better resource management.
|
Practice Question: Analyze the implications of India’s increased cereal grain production over the past two decades on domestic consumption patterns, export trends, and government stockpiling. Discuss the challenges posed by the disparity between production estimates and actual utilization, and suggest policy measures to address these issues. (250 words/15 m) |
4. Act punishing organised cheating comes into effect
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 3)
|
Topic: GS2 – Governance |
|
Context |
|
● The Union government has enacted the Public Examinations (Prevention of Unfair Means) Act, 2024, effective June 21, to combat cheating in government recruitment exams. ● The Act prescribes severe penalties, including imprisonment and hefty fines, to ensure the integrity of public examinations. |
Analysis of the news:
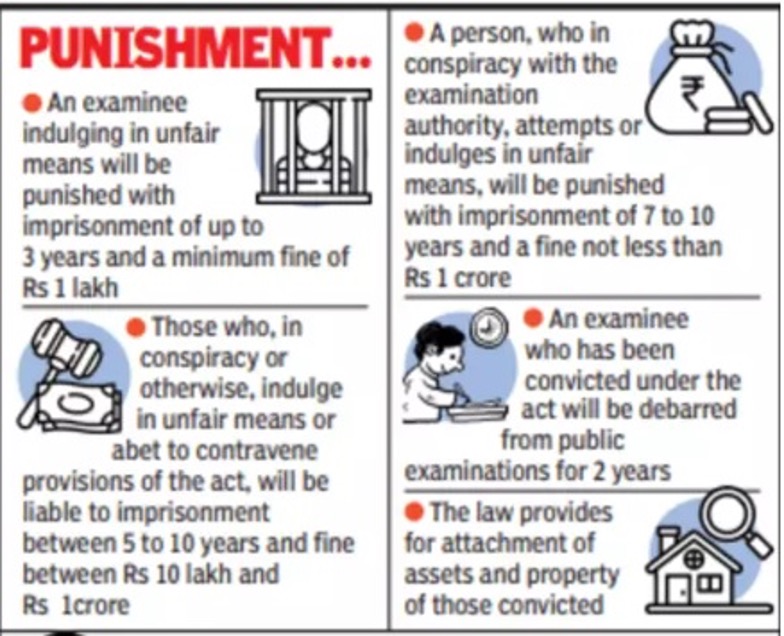
- Introduction:
- The Public Examinations (Prevention of Unfair Means) Act, 2024 was enacted to prevent malpractices and organised cheating in government recruitment exams.
- The Act was passed by Parliament on February 6, 2024, and came into effect on June 21, 2024.
- Penalties:
- Imprisonment: Offenders face imprisonment for a term not less than three years, extendable up to five years.
- Fine: A fine of up to ₹10 lakh for individuals involved in malpractices.
- Service providers can be fined up to ₹1 crore and have to bear the proportionate cost of the compromised examination.
- Service providers will be barred from public examination responsibilities for four years.
- Offences Covered:
- Leakage of question papers or answer keys.
- Unauthorised assistance to candidates.
- Tampering with computer networks, resources, or systems.
- Creation of fake websites for cheating or monetary gain.
- Conducting fake examinations, issuing fake admit cards, or offer letters for monetary gain.
- Manipulation in seating arrangements, allocation of dates, and shifts to facilitate cheating.
- Exclusions:
- The UGC-NET 2024 exam, cancelled on June 19, 2024, for being compromised, is not covered under this Act.
- Authority:
- The Act was notified by the Department of Personnel and Training (DoPT).
- Purpose:
- To uphold the integrity and fairness of public examinations and deter fraudulent activities and organised cheating.
- Scope:
- Applies to individuals, groups, institutions, and service providers engaged in the conduct of public examinations.
|
Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the Public Examinations (Prevention of Unfair Means) Act, 2024 in ensuring the integrity of government recruitment exams. Evaluate the potential challenges in its implementation. (250 Words /15 marks) |
5. ‘Growth sacrifice’ view grows in MPC
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 11)
|
Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy – Issues relating to Planning |
|
Context |
|
● Ashima Goyal and Jayanth R. Varma, external members of the RBI’s MPC, called for a 0.25% rate cut, warning that maintaining a tight monetary policy could hinder growth. ● They argued that current high real repo rates, amid stable inflation, risk reducing economic growth in upcoming years. |
Analysis of the news:
- Ashima Goyal and Jayanth R. Varma, external MPC members, voted for a 0.25% rate cut at the latest MPC meeting.
- They warned against the risks of maintaining a tight monetary policy, leading to ‘status quo sim’ and ‘growth sacrifice.’
- Goyal highlighted that headline inflation has been around 5% since January and core inflation below 4% since December 2023.
- She noted the projected headline inflation of 4.5% for 2024-25 implies a real repo rate of 2%, which would stay above neutral for too long if unchanged.
- Goyal warned that high real repo rates would reduce real growth rates, with expected growth for 2024-25 at 7%, down from 8% in 2023-24.
- She emphasised avoiding past mistakes, such as 2015’s insufficient rate cuts despite falling global crude oil prices.
- Jayanth Varma expressed concerns about restrictive monetary policy inducing growth sacrifices in 2024-25 and potentially in 2025-26.
- RBI Deputy Governor Michael Debabrata Patra argued for maintaining focus on aligning inflation to target to avoid undermining medium-term growth.
|
The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC): |
|
● Purpose: The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) in India is constituted to maintain price stability while keeping in mind the objective of growth. ● Composition: It consists of six members: three from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)—the Governor, Deputy Governor, and an officer nominated by the RBI—and three external members appointed by the Government of India. ● Functions: The MPC determines the policy interest rate (Repo Rate) required to achieve the inflation target set by the government. It meets at least four times a year to review economic indicators and decide on monetary policy actions. ● Decision Making: Decisions are taken through voting, with each member having one vote. The Governor has a casting vote in case of a tie. ● Transparency: The MPC’s decisions and rationale are communicated through policy statements, which include inflation forecasts and risks considered. ● Impact: Its decisions influence interest rates across the economy, affecting borrowing costs, investments, and overall economic activity. |
|
PYQ: Q. If the RBI decides to adopt an expansionist monetary policy, which of the following would it not do? (UPSC civil services prelims 2020) 1. Cut and optimise the Statutory Liquidity Ratio 2. Increase the Marginal Standing Facility Rate 3. Cut the Bank Rate and Repo Rate Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 and 2 only Ans: Option B |
|
Practice Question: Discuss the role and significance of the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) in India’s economic framework. How does the MPC contribute to achieving the dual objectives of price stability and economic growth? (250 Words /15 marks) |
6. IBBI to strengthen creditors’ rights on personal guarantors
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 11)
|
Topic: GS2 – Governance |
|
Context |
|
● The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI) proposes amendments clarifying that resolution plans under the IBC do not automatically release personal guarantors from liabilities. ● This follows the Supreme Court’s decision affirming the continued obligations of guarantors despite corporate debtor resolutions. |
Analysis of the news:
- The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI) proposes amendments to clarify that approving a resolution plan under the IBC does not release guarantors from their debt obligations.
- The IBBI’s move follows the Supreme Court’s stance in Lalit Kumar Jain vs Union of India, affirming that resolution plan approval does not absolve personal guarantors from liability.
- Experts like Sushmita Gandhi and Misha express support but note concerns about potential conflicts with creditor agreements.
- Hari Hara Mishra of the Association of ARCs in India sees the proposal as beneficial for creditors, enhancing recovery efforts.
- Sumit Khanna highlights the amendment’s role in strengthening creditor positions and improving recovery rates, crucial amid current recovery challenges.
|
The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI): |
|
● Establishment: The IBBI was established on October 1, 2016, under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 (IBC). ● Regulatory Authority: It serves as the regulatory body overseeing insolvency resolution and bankruptcy processes in India. ● Key Functions: ○ Regulates insolvency professionals (IPs), insolvency professional agencies (IPAs), and information utilities (IUs). ○ Develops and enforces the Code’s rules and regulations to ensure fair and efficient resolution processes. ○ Facilitates corporate and individual insolvency resolution through its framework and guidelines. ● Role in Resolution Process: ○ Monitors and supervises corporate insolvency resolution processes (CIRP) and liquidation proceedings. ○ Adjudicates on issues arising from the insolvency resolution process. ○ Provides clarity and guidance through circulars and notifications to stakeholders. ● Impact: ○ Has significantly influenced the corporate and financial landscape by providing a structured framework for distressed asset resolution. ○ Aims to enhance creditor confidence and promote a faster resolution of insolvency cases in India. This framework aims to promote transparency, efficiency, and accountability in insolvency proceedings, crucial for economic stability and creditor rights protection. |
|
PYQ: Q. Which of the following statements best describes the term ‘Scheme for Sustainable Structuring of Stressed Assets (S4A)’, recently seen in the news? (UPSC civil services prelims 2017) (a) It is a procedure for considering ecological costs of developmental schemes formulated by the Government. Ans: Option B |
|
Practice Question: Discuss the role of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI) in the resolution and regulation of insolvency processes in India. How has it impacted the corporate and financial sectors? (250 Words /15 marks) |
Prelims Facts
1. Anthropic Unveils Claude 3.5 Sonnet: A Game-Changer in AI with Superior Speed and Vision Capabilities
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 15)
|
Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Overview of Claude 3.5 Sonnet:
- Claude 3.5 Sonnet is a large language model (LLM) developed by Anthropic, part of the generative pre-trained transformer family. These models are pre-trained to predict the next word in large amounts of text.
- Claude 3.5 Sonnet succeeds Claude 3 Sonnet, introduced in March this year. It is likely the middle model in the upcoming series, with the smallest and largest models yet to be released.
- Claude 3.5 Sonnet reportedly outperforms Claude 3 Opus by a significant margin and is twice as fast.
Performance Capabilities:
- Anthropic claims that Claude 3.5 Sonnet sets new industry benchmarks in coding proficiency (HumanEval), graduate-level reasoning (GPQA), and undergraduate-level knowledge (MMLU). The new model shows significant improvement in understanding nuance, humor, and complex instructions.
- It excels in writing high-quality content with a natural and relatable tone. According to benchmark scores shared by Anthropic, Claude 3.5 Sonnet outperforms GPT-4o, Gemini 1.5 Pro, and Meta’s Llama 3400B in seven out of eight overall benchmarks.
- However, it is essential to note that benchmark scores can be selectively highlighted to present the model in a favorable light.
Vision Capabilities
- Claude 3.5 Sonnet is touted as Anthropic’s strongest vision model. A vision model in AI can interpret and analyze visual data such as images and videos.
- The improvements in Claude 3.5 Sonnet are most noticeable in tasks requiring visual reasoning, such as decoding charts and graphs. The model is also capable of accurately transcribing text from imperfect images.
- For example, when tested with a random picture from Claude’s iOS app, the model immediately identified the location by reading a poster and text on a distant wall.
- This ability makes Claude 3.5 Sonnet particularly beneficial for industries such as retail, logistics, and financial services, where AI relies more on insights from images, graphics, or illustrations than from text.
2. Global headwinds may dampen India’s exports of steel
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 11)
|
Context |
|
● In June, India’s steel exports are encountering sluggish demand in key markets like the EU, West Asia, and Southeast Asia. ● Competitive pricing from Chinese suppliers and economic challenges in Europe are contributing factors, while domestic concerns include rising imports and monsoon-induced reduced demand |
Analysis of the news:
- India’s steel exports face sluggish demand in June across key markets like the EU, West Asia, and Southeast Asia.
- Hot rolled coil (HRC) offers to Southeast Asia and West Asia are hindered by competitive Chinese pricing resistance, with offers to West Asia around $600 per tonne, higher than expected.
- European demand remains subdued due to economic challenges, though Hot rolled coil (HRC) prices saw a slight increase to $560-610 per tonne due to extended safeguard measures restricting imports.
- Cold rolled coil offers to Europe decreased by 6-7% to $700 per tonne, impacting India’s export prospects.
- Indian steel mills have kept HRC export prices to Europe steady amidst domestic market focus and expectations of market sluggishness post-monsoon.
- Monsoon onset in India is expected to dampen domestic steel demand, coupled with increasing import competition, leading to downward price pressure and pessimistic market sentiment.
9. Armenia becomes the latest nation to recognise Palestine
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 12)
|
Context |
|
● Armenia’s recent recognition of the State of Palestine amid the Israel-Hamas conflict underscores its stance against civilian violence. ● This move, which prompted Israel to summon Armenia’s ambassador, aligns with global calls for peace in the Middle East, despite ongoing regional tensions and past conflicts involving Armenia. |
Analysis of the news:
- Armenia announced recognition of the State of Palestine amid Gaza conflict, citing opposition to violence against civilians.
- This move drew strong condemnation from Israel, leading to the summoning of Armenia’s ambassador for reprimand.
- Yerevan emphasised commitment to international law, equality, sovereignty, and peaceful coexistence in its decision.
- Armenia criticised both Israel’s military actions in Gaza and Hamas for holding civilian captives, aligning with international calls for their release.
- Earlier, Spain, Ireland, and Norway also recognized Palestine, viewed as a step towards regional peace, although Israel criticised these actions as endorsing terrorism.
10. ICC unveils arrest warrant for top Sahel jihadist leader
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 12)
|
Context |
|
● The International Criminal Court (ICC) has issued an arrest warrant for Iyad Ag Ghaly, leader of the jihadist group JNIM, for alleged atrocities committed in Timbuktu, Mali, between 2012 and 2013. JNIM, linked to al-Qaeda, is accused of attacks on national forces and civilian atrocities. |
Analysis of the news:
- The ICC is a permanent international tribunal established to prosecute individuals for genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes, and aggression.
- It was founded in 2002 and is based in The Hague, Netherlands.
- The Court’s jurisdiction covers crimes committed after July 1, 2002, by individuals from state parties to the Rome Statute or referred to by the UN Security Council.
- Currently, 124 countries are parties to the Rome Statute, which established the ICC.
- The Court operates independently of the United Nations, but it can cooperate with it.
- The Court has faced criticism for selectivity in its cases and challenges in executing arrests.
- Notable cases include investigations in Sudan, Uganda, Libya, and the Central African Republic.
- The ICC plays a crucial role in addressing impunity for serious international crimes and promoting global justice and accountability.



