23 August 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. India, Poland formulate action plan, upgrade ties to strategic partnership
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations – Bilateral Relations |
| Context |
|
Advancements in India-Poland Relations
- Strategic Partnership: India and Poland upgraded their ties to a strategic partnership, focusing on enhanced bilateral cooperation.
- Five-Year Action Plan (2024-2028): A comprehensive plan was agreed upon to guide collaboration across diverse sectors including political dialogue, security, trade, and investment.
- Economic Cooperation:
- Food Processing: Invitation to Polish companies to invest in India’s mega food parks.
- Urbanisation: Opportunities in water treatment, solid waste management, and urban infrastructure are to be explored.
- Technology and Innovation:
- Clean Energy: Emphasis on clean coal technology, green hydrogen, and renewable energy.
- Artificial Intelligence: Identified as a common priority.
- Youth Exchange Program: Introduction of the Jam Saheb of Nawanagar youth exchange program for 20 Polish youths annually.
- Space Exploration: Agreement to promote safe, sustainable space use and commercial space ecosystems, including human and robotic exploration.
- Social Security Agreement: Agreement to enhance mobility and welfare of skilled workers.
- International Cooperation: Poland acknowledged India’s ambition to join the International Energy Agency.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the recent strategic partnership between India and Poland. How do the agreed-upon areas of cooperation, including trade, technology, and space exploration, align with India’s foreign policy objectives and contribute to bilateral relations? (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. Opposition members raise an array of objections to Waqf Amendment Bill
| Topic: GS2 – Indian Polity |
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 5)
| Context |
|

Objections Raised by Opposition Parties
- Excessive Government Interference:
- Opposition parties criticised provisions that they believe grant excessive control to the government over Waqf properties.
- Inclusion of Non-Muslim Members:
- There is strong opposition to the inclusion of non-Muslim members in Waqf Boards, arguing it undermines the primary purpose of these boards, which is to manage Waqf properties for the benefit of the Muslim community.
- Deed Records Requirement:
- The requirement to submit “deed records” for Waqf properties has been objected to, with concerns raised about the burden it places on managing and recording these properties.
- Authority Designation:
- Opposition parties are united in their objection to the clause designating the District Collector as the primary authority in determining whether a property is Waqf or government land. They argue this could lead to misclassification and misuse.
- Consultation Process:
- There are complaints about the lack of proper consultation with stakeholders before drafting the Bill, with the argument that the government did not fully consider the Sachar Committee’s recommendations.
- Broad-Basing Membership:
- The broad-basing of Waqf Board membership is contested, as it is seen as misinterpreting recommendations intended to include more community members rather than altering the core composition of the boards.
- Divisive Sub-sects Representation:
- Objections have been raised against provisions allowing representation of specific sub-sects in Waqf Boards, which are viewed as potentially divisive and counterproductive to unified board management.
| Joint Parliamentary Committee (JPC) |
|
| Practice Question: Q.1 Analyse the key objections raised against the Waqf (Amendment) Bill 2024. How do these objections reflect broader concerns about governance and minority rights in the context of legislative reforms? (150 Words /10 marks) Q.2 Discuss the significance of Joint Parliamentary Committees (JPCs) in the Indian political system. How do they contribute to effective governance and legislative oversight?(250 Words /15 marks) |
3. When sweltering heat turns public hospitals into potential ‘death traps’
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Health |
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
Infrastructure Drawbacks in Indian Healthcare:
- Overcrowding: Public hospitals face extreme overcrowding, with patients often waiting for hours or even days in inadequate conditions.
- Poor Ventilation: Many facilities, especially in rural areas, lack proper ventilation, exacerbating issues during heatwaves.
- Inadequate Cooling: The absence of air conditioning in many hospitals leads to stifling, humid environments that affect patient health.
- Overheated Wards: Hospital wards, particularly in poorly ventilated areas, can become excessively hot, worsening the condition of patients, especially those with fever or other ailments.
- Limited Respite: Patients do not have access to cooling devices or shaded waiting areas, leading to heat-related illnesses.
- Underreporting of Heat-Related Illnesses: Heat-related deaths may be underreported due to inadequate diagnostic capabilities and lack of awareness among healthcare professionals.
Future Directions:
- Enhanced Infrastructure: Invest in improving hospital infrastructure, including better ventilation systems, air conditioning, and shaded waiting areas.
- Heat Management Protocols: Develop and implement protocols for managing heat-related illnesses, including regular temperature monitoring and appropriate hydration measures.
- Cooling Measures: Install automated weather and water level monitoring systems to anticipate and manage extreme weather conditions affecting hospital environments.
- Awareness and Training: Train healthcare staff to recognize and manage heat-related illnesses and incorporate heat management into patient care protocols.
- Public Health Strategy: Develop comprehensive strategies to deal with heatwaves, including improving public awareness and implementing preventive measures across healthcare facilities.
- Systematic Changes: Ensure systematic improvements such as reducing patient wait times, providing access to drinking water, and improving overall hospital environment conditions to mitigate the impact of heat on patients.
| Practice Question: Discuss the impact of inadequate infrastructure in public hospitals on patient health. What measures should be taken to improve hospital conditions and prevent heat-related illnesses? (150 Words /10 marks) |
4. A look at ongoing Indian space missions
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Context |
|
Aditya L1:

- Launched on September 2, 2023, Aditya L1 is India’s solar science mission aimed at studying the Sun from the Earth-Sun Lagrange point (L1).
- After launch aboard ISRO’s Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), it reached L1 on January 6, 2024.
- It observed a solar storm in May 2024 and began its first L1 orbit on July 2, 2024.
- The mission focuses on understanding solar activities and their impact on space weather.
Gaganyaan:

- On October 21, 2023, ISRO conducted its first abort mission for the Gaganyaan human spaceflight program using a modified L-40 Vikas engine.
- This test demonstrated the Crew Escape System’s ability to safely detach and descend, ensuring astronaut safety.
- The crew module was successfully recovered by the INS Shakthi.
XPoSat:
- Launched on January 1, 2024, XPoSat is India’s X-ray Polarimeter Satellite.
- It aims to study the polarisation of X-ray radiation from celestial objects.
- The satellite, equipped with XSPECT and POLIX instruments, began operations on January 5 and 10, respectively, to enhance our understanding of cosmic phenomena.
INSAT-3DS:
- Launched on February 17, 2024, INSAT-3DS is a meteorological satellite carried by a Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV).
- It is critical for validating the GSLV’s performance before the NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) mission.
- INSAT-3DS aims to enhance weather forecasting and climate monitoring.
The Reusable Launch Vehicle-Technology Demonstrator (RLV-TD):
- The Reusable Launch Vehicle-Technology Demonstrator (RLV-TD) conducted landing experiments LEX-02 and LEX-03 on March 22 and June 7, 2024.
- These tests, simulating space re-entry, used the Pushpak vehicle to evaluate landing dynamics. Success in these tests supports ISRO’s plans for a reusable space vehicle.
Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV):
- On August 16, 2023, ISRO launched its third Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) flight, placing EOS-08 and SR-0 Demosat satellites into orbit.
- This successful mission confirmed the SSLV’s readiness for commercial use, marking a key development in ISRO’s small satellite launch capabilities.
NewSpace India Ltd. (NSIL) Missions:
- NewSpace India Ltd. (NSIL) handles commercial satellite launches and activities.
- Notable recent missions include a SpaceX launch for GSAT-20/GSAT-N2 and a partnership with Australian private space companies for SSLV launches.
- NSIL also transferred remote sensing satellite data activities from ISRO and is involved in public-private partnerships.
5. Chandrayaan-3 Confirms Lunar Magma Ocean Hypothesis with Groundbreaking Findings Near Moon’s South Pole
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 10)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context: |
| Chandrayaan-3’s findings provide new insights into the composition and formation of the Moon’s southern latitudes, supporting the lunar magma ocean hypothesis. |
Analysis of News:
What is the Chandrayaan 3 Mission?
- The Chandrayaan 3 Mission was launched using the LVM3 rocket system. LVM3 is the new launch vehicle of ISRO with the capability to place the modules into the GTO (Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit) in a cost-effective manner.
- It is a three-stage launch vehicle with two solid strap stages and one core liquid stage.
- The Launcher, LVM3 M4, placed the integrated Modules in an Elliptic Parking Orbit of size approx. 170 x 36500 km (a GTO).
Objectives of Chandrayaan 3 Mission
One of the many goals of the Mission is to look for water ice that could support future human life on the Moon and also for supplying propellants for spacecraft in future interplanetary missions. The objectives of the Chandrayaan-3 mission are:
- Safe and Soft Landing on the Lunar Surface by the Lander
- Roving on the Moon by the Rover
- In-situ scientific experiments by the Rover

Analysis of Chandrayaan-3’s Findings on Lunar Topsoil
Key Findings:
- Uniform Terrain: The area around Chandrayaan-3’s landing site is relatively uniform.
- Lunar Magma Ocean (LMO) Hypothesis: The findings support a layered formation of the Moon’s crust, reinforcing the LMO hypothesis.
- Mineral Distribution: The topsoil near the lunar south pole contains more minerals from deeper layers than expected.
Significance:
- First Polar Study: Chandrayaan-3 conducted the first detailed analysis of lunar soil near the Moon’s south pole.
- Support for LMO: The data aligns with models suggesting a stratified crust formed from a once-molten surface.
- New Discoveries: Evidence of mixing in the lunar crust, likely due to asteroid impacts, was observed.
Future Implications:
- Calibration Point: The uniform surface could serve as a reference for remote sensing in future missions.
- Further Research: Findings may aid in understanding the Moon’s evolution and guide future lunar explorations.
| Significance of the Chandrayaan 3 Mission |
|
India’s Chandrayaan-3 mission aims to continue the nation’s lunar exploration efforts and build on the achievements of previous missions like Chandrayaan-1 and 2. The undertaking holds significance for multiple reasons: Future lunar exploration:
Advancing space education:
Lunar Surface Exploration:
Scientific Discoveries:
Boosting private investment:
Job creation:
Nurturing startups:
Strengthening international reputation:
Strategic Positioning:
|
| Practice Question: How do Chandrayaan-3’s analyses of the Moon’s southern topsoil composition support the Lunar Magma Ocean hypothesis and inform our understanding of the Moon’s formation? (250 words/15 m) |
6. India and the United States discusses advancements in Energy Collaboration
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations – Bilateral Relations |
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2047766 )
| Context |
|
Key Areas of Collaboration:
- Grid and Transmission Modernization: Exploration of technical exchanges and policy consultations to upgrade grid transmission systems for future load growth, including potential financial support.
- Enhancing Manufacturing Capacity: Focus on increasing India’s production capabilities for critical components such as large transformers, aiming to reduce import dependency and boost domestic manufacturing.
- Energy Storage Systems: Discussion on state-to-state partnerships for long-duration energy storage studies and collaboration on grid-scale battery storage solutions to enhance energy storage capabilities.
- High-Efficiency Cooling Systems: Emphasis on stimulating projects and policies to expand India’s capacity to manufacture, deploy, and export high-efficiency air conditioning systems and fans.
| PYQ: The question of India’s Energy Security constitutes the most important part of India’s economic progress. Analyse India’s energy policy cooperation with West Asian Countries. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2017) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of advancing energy infrastructure in India for sustainable economic growth and energy security. What are the key challenges and potential solutions? (250 Words /15 marks) |
PRELIMS FACTS
1. Assam Identifies 47,928 Foreigners Between 1971-2014, 43% are Hindus: CM Sarma
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt & Politics; Page: 07)
| Context: |
| The Assam government reported that nearly 48,000 people were declared foreigners between 1971 and 2014, with a significant portion being Hindus. |
Analysis of News:
Analysis of Assam Government’s Report on Detected Foreigners (1971-2014)
Key Statistics:
- Total Detected Foreigners: 47,928 people declared as foreigners in Assam from 1971 to 2014.
- Religious Breakdown: 27,309 were Muslims (57%), 20,613 were Hindus (43%), and 6 belonged to other religions.
Regional Impact:
- Cachar District: Highest number of foreigners detected, with 10,152 declared, including 8,139 Hindus.
Assam Accord Context:
- According to the Assam Accord, all foreigners arriving on or after March 25, 1971, are to be detected and deported.
Demographic Note:
- Bengali-Speaking Population: 90.24 lakh Bengali-speaking people in Assam, comprising 28.92% of the state’s population.
| Assam Accord |
|
2. IIA finds a novel way to explore the sun’s secrets by studying solar magnetic fields
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 3)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- Astronomers at the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) have developed a new technique to study the Sun’s magnetic fields.
- The research is based on data from IIA’s Kodaikanal Tower Tunnel Telescope.
- The solar atmosphere’s magnetic fields connect its various layers, transferring energy and mass, addressing the coronal heating problem and driving solar wind.
- Understanding magnetic fields at different heights of the solar atmosphere is crucial to understanding these processes.
- The Tunnel Telescope’s 3-mirror system tracks the Sun and adjusts the light beam for observations at the Kodaikanal Solar Observatory.
| Why is it important to study the Sun’s magnetic field? |
|
3. NDMA to monitor 189 high-risk glacial lakes to prevent disasters
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Context |
|
More information about Glacier Lakes:
- Glacial lakes are formed from melting glaciers, creating depressions that fill with water.
- These lakes are commonly found in mountainous regions where glaciers exist or have existed.
- Geologically, glacial lakes are significant as they can provide insights into past climatic conditions and glacial activity.
- They are often characterised by clear, cold waters and can vary in size from small ponds to large lakes.
- Due to their origins, they are prone to sudden changes, such as outburst floods, if the natural barriers (moraines or ice) holding the water fail.
- The stability of these lakes is crucial, as their overflow can lead to devastating floods in downstream areas.
4. What is vaccine-derived polio?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
Vaccine-Derived Polio Overview
- Definition: Vaccine-derived polio occurs when the weakened poliovirus in the oral polio vaccine (OPV) mutates and causes paralysis, rather than immunity.
Mechanism of OPV
- Vaccine Composition: OPV contains live, attenuated poliovirus which stimulates immune response and is excreted in the stool.
- Mutation and Spread: In rare cases, the virus can mutate and regain virulence, spreading in areas with low immunisation, poor sanitation, or among immunocompromised individuals.
Types of Poliovirus
- Wild Poliovirus: Includes WPV1, WPV2 (eradicated in 2015), and WPV3 (eradicated in 2012).
- Vaccine-Derived Poliovirus (VDPV): Includes types derived from OPV, primarily type 2, which has seen increased outbreaks.
Vaccine Types
- Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV): Safer, containing inactivated virus, does not risk causing vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis (VAPP).
- Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV): Easier to administer but carries a risk of Vaccine-Associated Paralytic Poliomyelitis(VAPP).
Recent Developments
- Modified Vaccine: A genetically modified type 2 OPV, introduced in 2021, has reduced risks of reversion and Vaccine-Derived Poliovirus(VDPV).
5. President of India presents Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar –2024
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2047748 )
| Context |
|
Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar/National Science Awards:
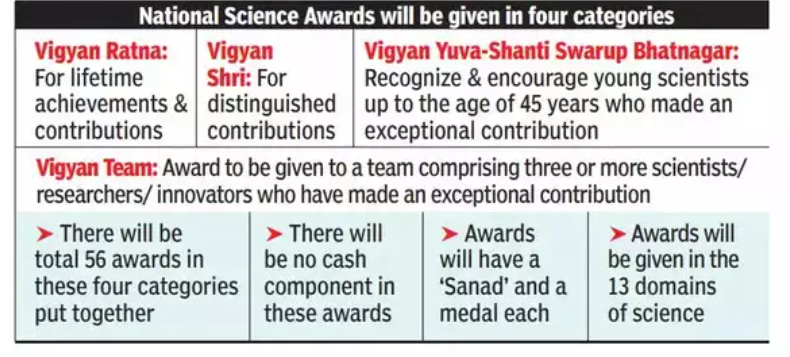
National Science Awards are prestigious awards conferred by the Government of India to recognize outstanding contributions in the field of science and technology. They are awarded by the Department of Science and Technology.
The purpose of these awards is to:
- Encourage excellence in science and technology.
- Inspire young scientists.
- Promote scientific research.
- Motivate the scientific community of the country.
The award includes:
- A medal
- A certificate
- Cash prize
Eligibility:
- Must be an Indian citizen.
- Should have made significant contributions in the field of science and technology.
Selection process:
- Candidates are selected by a selection committee.
- The selection committee comprises experts from various fields.
National Science Awards are one of the most prestigious awards in the field of science and technology in India.



