23 November 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. A lake ecosystem gasping for breath
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 9)
| Context |
|
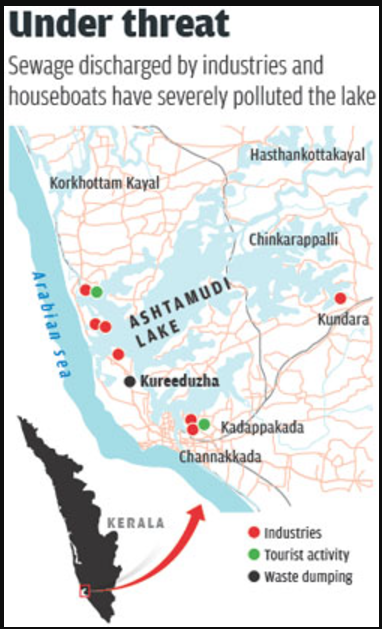
Deterioration of Ashtamudi Lake Ecosystem:
Water Pollution
- The lake suffers from untreated sewage discharge, with many households directing septic waste and toilet pits into the water.
- Plastic waste, poultry refuse, and abattoir by-products are frequently dumped into the lake, contributing to its pollution.
- Microplastic pollution is a significant concern, with high levels detected in fish, shellfish, sediment, and water samples. Polymers like nylon and polypropylene, along with heavy metals such as barium and iron, pose risks to aquatic life and public health.

Algal Blooms and Fish Mortality
- Excessive nutrient inflow from pollutants has led to frequent algal blooms, depleting dissolved oxygen levels in the water.
- Algal blooms suffocate aquatic organisms, resulting in mass fish mortality.
- Streptococci and E. coli bacteria, indicators of sewage contamination, have also been found in the lake water.
Habitat Degradation
- Sediment buildup in canals and channels impedes water flow, disrupting the estuarine ecosystem.
- Invasive species like water hyacinth have spread rapidly, restricting fishing activities and damaging equipment.
Impact of Anthropogenic Activities
- Illegal encroachments along the lake’s banks disrupt natural water flow and exacerbate waste accumulation.
- Unsustainable tourism practices and unregulated aquaculture activities contribute significantly to the lake’s deterioration.
Threats to Biodiversity and Livelihoods
- Habitat degradation has led to the extinction of several fish species and reduced yields for fishers.
- Contamination of fish tissues with harmful substances, including heavy metals, threatens public health and aquatic biodiversity.
- Fishers and cage farmers face declining livelihoods due to pollution, sediment buildup, and invasive plant growth.
| Ashtamudi Lake |
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the ecological challenges faced by Ramsar wetlands in India, with specific reference to the causes and consequences of pollution in Ashtamudi Lake. Suggest measures for sustainable wetland management. (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. India-China Relations: Navigating Trust Deficit Amid Efforts to Normalize Ties Post-Border Standoff
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 17)
| Context: |
| The article discusses the cautious efforts by India and China to rebuild trust and normalize bilateral ties amid the ongoing border standoff and lingering mistrust following the 2020 Galwan clashes |
Analysis of News:
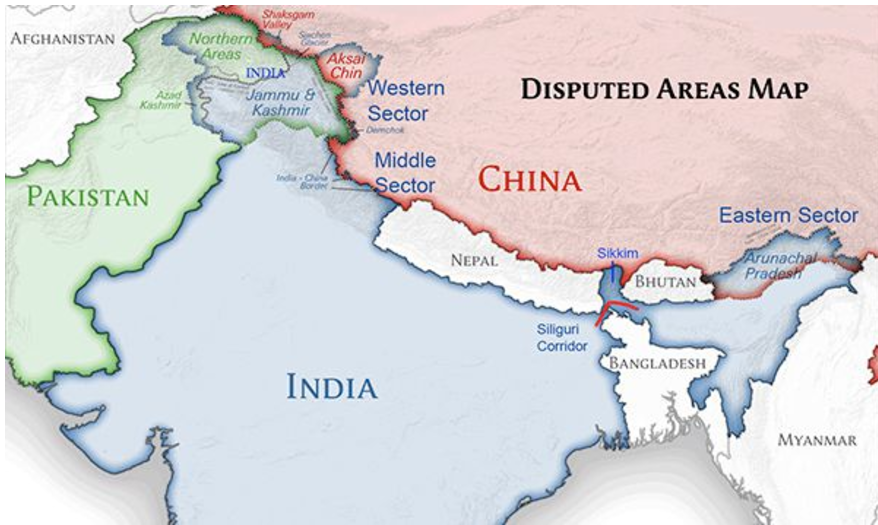
Background: Trust Deficit and Border Standoff
- The ongoing India-China border standoff in Ladakh since 2020 has significantly strained bilateral relations.
- The Galwan Valley clash in June 2020, which resulted in fatalities on both sides, marked the most severe conflict along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) since 1967.
- Trust between the nations remains fragile, with India emphasizing border stability as a prerequisite for normalizing ties.
Efforts to Rebuild Bilateral Relations
- Chinese officials, during interactions with an Indian media delegation, expressed willingness to restore ties to pre-standoff levels.
- They highlighted the “chemistry” between Prime Minister Modi and President Xi Jinping and proposed steps like resuming direct flights, easing visa restrictions, and encouraging media and cultural exchanges.
- India remains cautious, emphasizing border de-escalation and disengagement as essential.
- Recent breakthroughs, including agreements on patrolling arrangements and dialogue mechanisms, signal tentative progress.
Convergences and Divergences in Priorities
- Both nations agree on practical steps like direct flights, journalist exchanges, and visa facilitation. However, divergence persists:
- India’s Focus: Kailash Mansarovar Yatra, river data-sharing, and conditional normalization based on border stability.
- China’s Focus: Celebrating the 75th anniversary of diplomatic ties and emphasizing broader exchanges.
- India’s cautious approach reflects domestic concerns and public sentiment, whereas China frames the situation as a “restart and re-launch.”
Next Steps: De-escalation and Confidence-Building
- The ongoing troop presence along the LAC underscores the need for significant de-escalation.
- Recent meetings, such as those between Defence Ministers, underscore the mutual desire to prioritize cooperation over conflict.
- India views de-escalation as the next critical step to building trust and advancing diplomatic and economic ties.
Conclusion: Fragile Optimism Amid Persistent Caution
- While both nations have signaled a willingness to engage, the path forward hinges on resolving the border issue.
- India’s guarded stance reflects its focus on sovereignty and security, while China seeks broader normalization.
- Meaningful progress will depend on sustained dialogue, trust-building, and visible de-escalation measures.
| Significance of India-China Relations |
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the key challenges in rebuilding trust and normalizing relations between India and China in the aftermath of the 2020 Galwan Valley clashes. Suggest measures to address the trust deficit and ensure long-term stability in bilateral ties. (250 words/15 m) |
3. CULMINATION OF PAN-INDIA COASTAL DEFENCE EXERCISE – ‘SEA VIGIL 24’
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2076147®=3&lang=1 )
| Topic: GS3 – Internal Security |
| Context |
|
:
Exercise Sea Vigil – Key Highlights
- Fourth Edition: Sea Vigil 24 concluded on 21 November 2024, emphasizing India’s commitment to maritime security and coastal defence.
- Duration and Scope: Conducted over 36 hours, it spanned India’s 11,098 km coastline and a 2.4 million sq. km Exclusive Economic Zone.
- Multi-Agency Participation: Over 21 agencies from six ministries, including the Navy, Army, Air Force, Coast Guard, Marine Police, BSF, and Customs, participated.
- Security Focus: Prioritized securing oil rigs, ports, nuclear installations, and merchant ships. Simulated scenarios included hijacking and vessel re-routing.
- Community Outreach: Engaged fishing communities, NCC cadets, Scouts, and coastal youth to enhance grassroots maritime security awareness.
- Inter-Agency Coordination: Evaluated cooperation and readiness among agencies to address maritime threats.
- Legacy and Vision: Established in 2018, Sea Vigil strengthens India’s Coastal Defence Architecture through real-time scenario simulations.
Prelims Facts
1. Young Balinese girls preserve traditional Rejang Dewa festival
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 13)
| Context |
|
Rejang Dewa Festival Information
- Purpose: The Rejang Dewa is part of the Ngusaba Goreng festival, a two-week-long thanksgiving celebration for a rich harvest in Bali.
- Meaning of Ngusaba: “Ngusaba” refers to a gathering of gods and goddesses, central to the festival.
- Sacred Dance: Rejang Dewa is a sacred Balinese dance performed by young girls who have not yet reached puberty, signifying purity.
- Ritual Significance: It is performed as an offering to the gods, emphasising the connection between the people, their heritage, and the divine.
- Rejang Forms: Various forms of Rejang are performed, with Rejang Dewa and Rejang Pucuk reserved for young girls.
- Concerns for Tradition: There is a growing concern that younger generations may move to cities, risking the fading of these traditions.

2. Argentina’s Reconsideration of Paris Agreement Raises Global Climate Concerns
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 17)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Overview of the Paris Agreement
- Adopted in 2015, the Paris Agreement seeks to limit global warming to below 2°C, with an aspirational target of 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels.
- Participating countries must submit increasingly ambitious nationally determined contributions (NDCs) every five years to combat climate change.
- Withdrawal from the treaty is allowed under Article 28, requiring a formal notification and a one-year waiting period before taking effect.
Reasons Behind Argentina’s Reconsideration
- Argentina’s government, led by Milei, has expressed dissatisfaction with the Paris Agreement, citing ideological differences and economic priorities.
- Climate Change Denial: President Milei has previously dismissed climate change as a “socialist lie” and favors a natural cycles argument for global warming.
- Economic Factors: Argentina’s significant fossil fuel resources and exports, including shale gas and oil, may conflict with the emission reduction goals of the Paris Agreement.
- Political Stance: Argentina’s government has indicated the need to reassess its climate strategy without making definitive decisions yet.
Potential Impacts of Withdrawal
- Global Climate Goals: Argentina’s exit, as the 24th-largest GHG emitter, could weaken international climate efforts and embolden other nations to reconsider their commitments, threatening the 1.5°C target.
- Economic Isolation: Withdrawal may harm Argentina’s trade relations, particularly with regions like the EU that impose tariffs on carbon-intensive imports.
- Domestic Challenges: Given Argentina’s constitutional status for ratified treaties, Milei’s proposal would face significant hurdles in parliament, where domestic opposition to withdrawal is strong.



