24 March 2025 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Time to float more Indian ships
- 1. Time to float more Indian ships
- 2. Railway Connectivity in Meghalaya: Development Stalled Amid Local Opposition
- 3. US Seeks Greater Market Access in India for Soyabean, Corn, and Cotton Amid Trade Barriers
- 4. PRESIDENT OF INDIA’S MESSAGE ON THE EVE OF WORLD TUBERCULOSIS DAY
- 5. Prime Minister pays tributes to Dr Ram Manohar Lohia on his birth anniversary
- Prelims Facts
- 1. Why do people get tattoos? Study of twins says it’s nurture, not nature
- 2. Lapis lazuli: earth’s best blues
- 3. Indonesia’s Lewotobi Laki-laki volcano erupted on March20
- 4. The complex struggle for ‘Kurdistan’
- 5. Top 10 Toll Plazas Contribute Over ₹13,988 Crore to India’s Toll Revenue in Five Years
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 13)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context |
|
Urgency for India to Strengthen Its Shipping Industry
- The ongoing Red Sea crisis and the US decision to impose tariffs on Chinese ships highlight the need for India to build a strong domestic shipping fleet.
- A self-sufficient fleet will reduce dependence on foreign shipping companies and help India manage global maritime crises more effectively.
- The government’s plan to launch Bharat Container Line (BCL) is a step in this direction.
Impact of the Red Sea Crisis and US Tariffs
- The Israel-Palestine conflict and attacks by Yemen’s Houthi rebels in the Red Sea have forced ships to take a longer and more expensive route via the Cape of Good Hope.
- These disruptions have increased delays and costs in global trade.
- The US plans to charge Chinese-owned and China-built cargo ships over $1 million per port call, further straining global shipping costs.
India’s Heavy Dependence on Foreign Ships
- India relies on foreign ships for transporting its cargo, including trade with the US.
- Nearly 30% of the world’s major shipping fleets are Chinese-owned.
- Maritime transport handles 95% of India’s trade volume, but India has only about 1,500 ships, with fewer than 50 container vessels mainly operating along the coast.
High Shipping Costs for India
- India’s shipping expenses amount to $90 billion annually, making it the second-largest import cost after crude oil.
- The country also depends on leased containers, particularly from China.
Challenges for Bharat Container Line (BCL)
- Even with 100 vessels, BCL will remain a small player in global shipping.
- The competition in the Asia-Pacific region is intense, and market consolidation through mergers and acquisitions is expected.
- The initiative is seen as India’s attempt to create an alternative to China’s Belt and Road Initiative.
| Ship Building Industry in India |
|
Importance of Building a Domestic Shipping Industry
Challenges in Shipbuilding and Proposed Reforms
|
Steps to Boost India’s Shipbuilding Industry
- The government has announced a ₹25,000 crore maritime development fund and an ₹18,090 crore shipbuilding financial assistance policy.
- Removing the Goods and Services Tax (GST) on shipping operations can encourage investment in vessels.
- Shipbuilding can generate employment since it has a high direct-to-indirect job creation ratio of 1:5.
Conclusion
- Strengthening India’s shipping industry is crucial for economic security and reducing dependency on foreign fleets.
- Government policies and investments in shipbuilding can improve competitiveness and lower costs.
- Addressing structural issues in the shipbuilding sector will be key to making India a major player in global shipping.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of India developing a strong domestic shipping fleet in the context of global trade disruptions and maritime security. What challenges does India face in this endeavor? (250 Words /15 marks) |
2. Railway Connectivity in Meghalaya: Development Stalled Amid Local Opposition
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained, Page – 12)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
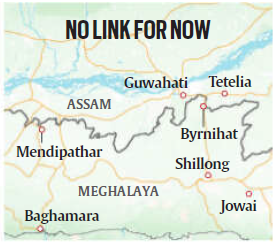
Status of Rail Connectivity in Meghalaya
- Meghalaya currently has only one operational railway station at Mendipathar in North Garo Hills, which became functional in 2014.
- Apart from this, three railway projects were planned, but due to strong opposition, they have either stalled or are facing uncertainty.
Key Railway Projects and Their Status
- Tetelia-Byrnihat Line: A 21.5 km railway line sanctioned in 2010 to connect Assam’s Tetelia with Byrnihat in Meghalaya’s Ri Bhoi district. Work on the Assam side is complete, but opposition in Meghalaya has halted progress. The Indian Railways is now considering terminating the project at the Assam border.
- Byrnihat-Shillong Line: Sanctioned in 2011, this 108.76 km project with 10 stations aimed to connect Meghalaya’s capital. However, resistance from the Khasi Students’ Union (KSU) has kept it in limbo. Funds allocated for land acquisition remain unused, and the state has been asked to return them.
- Chandranathpur-Jowai Line: Approved in 2023 to connect Assam’s Chandranathpur with Jowai in Meghalaya’s Jaintia Hills, this project is still at the survey stage but already faces opposition from local groups.
Reasons for Opposition
- Fear of Influx: Khasi and Jaintia pressure groups worry that rail connectivity will lead to large-scale migration, threatening the indigenous population.
- Demand for Inner Line Permit (ILP): Protesters argue that without an ILP regime, regulating migration will be difficult, leading to demographic and cultural shifts.
- Security of Land & Identity: Groups fear that the economic and social fabric of the region could be altered without protective mechanisms.
Diverging Opinions on Railway Connectivity
- Supporters’ View: Many argue that railway connectivity would reduce transportation costs, boost local businesses, and make essential goods more affordable in Meghalaya, where road transport makes commodities expensive.
- Garo Hills’ Push for Expansion: Unlike the Khasi and Jaintia Hills, representatives from the Garo Hills are advocating for railway expansion, emphasizing economic benefits and improved logistics.
Government’s Stand
- While Meghalaya’s Chief Minister has assured that railway projects will move forward only with consensus, he has also highlighted their economic necessity.
- The future of rail connectivity in the state remains uncertain, with public sentiment divided between protecting indigenous identity and fostering economic growth.
Conclusion
- Balancing infrastructure development with local concerns is crucial for Meghalaya’s progress.
- While railway connectivity can boost the economy, addressing indigenous communities’ fears through safeguards like the Inner Line Permit (ILP) is essential for consensus-driven development.
| Practice Question: Railway connectivity in Meghalaya faces strong local opposition due to concerns over migration and demographic changes. Discuss the challenges in balancing infrastructure development with indigenous rights and suggest measures for consensus-driven progress. (250 Words /15 marks) |
3. US Seeks Greater Market Access in India for Soyabean, Corn, and Cotton Amid Trade Barriers
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained, Page – 12)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
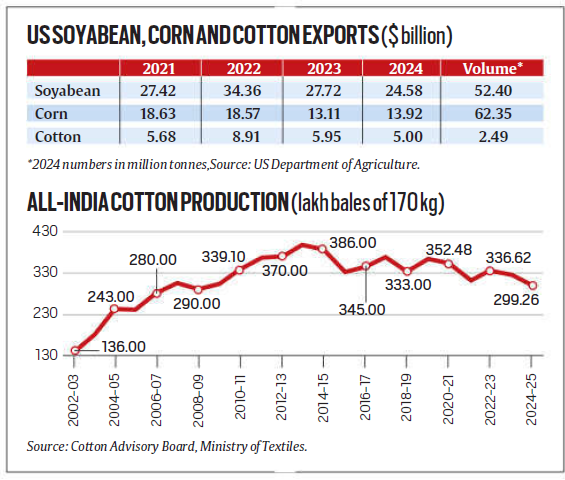
US Agricultural Exports and Market Focus
- The US is a major exporter of soyabean, corn, and cotton.
- With declining demand from China, the US seeks to expand its market in India.
- However, India maintains high import tariffs and strict regulations on genetically modified (GM) crops, creating barriers to US exports.
India’s Growing Feed Demand
- A USDA report predicts rising Indian demand for feed due to increasing consumption of milk, eggs, fish, and meat.
- Domestic corn and soyabean meal consumption is projected to rise sharply by 2040 and 2050, making India a potential major importer.
- However, current imports remain minimal due to high tariffs and regulatory constraints.
Challenges in US-India Trade
- Tariff Barriers: India imposes a 45% duty on soybean and 50% on corn, limiting US exports.
- GM Crop Restrictions: India bans GM imports, further restricting US access to the market.
- Uncertain Consumption Growth: While India’s feed demand is growing, it may not match USDA projections, as past imports of feed ingredients have been limited.
Cotton: From Exporter to Importer
- India was a leading cotton producer and exporter but is now becoming an importer due to stagnant GM crop approvals and pest resistance.
- The US sees this as an opportunity to increase its cotton exports, especially if India removes the 11% duty on imports.
Conclusion
- While India holds potential as a major market for US corn, soyabean, and cotton, regulatory and tariff barriers remain significant.
- Any trade policy changes, particularly under the Trump administration’s stance on reciprocal tariffs, could impact future agricultural trade dynamics between the two countries.
| Practice Question: Discuss the challenges and opportunities for India in opening its agricultural market to US exports of soybean, corn, and cotton. How can India balance trade liberalization with domestic agricultural interests and food security? (250 Words /15 marks) |
4. PRESIDENT OF INDIA’S MESSAGE ON THE EVE OF WORLD TUBERCULOSIS DAY
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2114205 )
| Context |
|
What is Tuberculosis (TB)?
- TB is a contagious bacterial infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, primarily affecting the lungs but can impact other organs.
- World Tuberculosis Day is observed every year on March 24 to raise awareness about TB and efforts to eliminate it globally.
Prevalence in India:
- India accounts for the highest TB burden globally, contributing to nearly 27% of global TB cases (WHO Global TB Report 2023).
Government Initiatives:
- National TB Elimination Programme (NTEP) aims to eliminate TB by 2025, five years ahead of the global 2030 target.
- Ni-kshay Mitra Initiative encourages community participation to support TB patients.
Challenges:
- Drug-resistant TB (MDR-TB, XDR-TB) is rising.
- Malnutrition, poverty, and lack of awareness hinder control efforts.
Recent Progress:
- TB incidence in India has declined by 13% from 2015 to 2022.
- Free diagnosis and treatment provided under Ayushman Bharat and PM TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan.
| Practice Question: Discuss the challenges in eliminating tuberculosis in India and evaluate the effectiveness of the National TB Elimination Programme in achieving the 2025 target. (150 Words /10 marks) |
5. Prime Minister pays tributes to Dr Ram Manohar Lohia on his birth anniversary
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2114112 )
| Context |
|
Freedom Struggle:
- Played a key role in the Quit India Movement (1942) and was imprisoned multiple times by the British.
- Worked with Subhas Chandra Bose’s Azad Hind Fauj and spread anti-British propaganda through underground radio.
Social Justice and Socialist Ideology:
- A prominent socialist leader who advocated for economic equality and upliftment of marginalized communities.
- Championed reservations for backward classes in government jobs and education.
Political Contributions:
- One of the prominent leaders of the Praja Socialist Party (1952) and later strengthened the Samyukta Socialist Party.
- Opposed Congress hegemony, promoting an alternative socialist political structure.
Women’s Rights & Governance:
- Advocated gender equality and representation of women in politics.
- Promoted decentralized governance and empowerment of local bodies.
Legacy:
- His ideas influenced the Mandal Commission (1990s) and India’s social justice policies.
- Inspired leaders like Jayaprakash Narayan and Lalu Prasad Yadav in socialist movements.
Prelims Facts
1. Why do people get tattoos? Study of twins says it’s nurture, not nature
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
Difference Between Nature and Nurture:
| Aspect | Nature | Nurture |
| Definition | Refers to genetic inheritance and biological factors influencing behavior and traits. | Refers to environmental influences such as upbringing, culture, and experiences shaping behavior. |
| Key Influences | DNA, genes, hereditary traits, biological predisposition. | Family, education, culture, social interactions, personal experiences. |
| Examples | Eye color, height, genetic disorders, natural intelligence, temperament. | Language spoken, beliefs, values, personality shaped by upbringing, career choices. |
| Scientific Basis | Based on genetics, heredity, and biological evolution. | Based on psychology, sociology, and environmental studies. |
| Research Methods | Twin studies, genetic mapping, heritability estimates. | Observational studies, social experiments, case studies. |
| Key Theorists | Charles Darwin (Evolution), Francis Galton (Heredity). | John B. Watson (Behaviorism), Albert Bandura (Social Learning). |
| Real-World Application | Studies on inherited diseases, intelligence quotient (IQ) research. | Impact of childhood trauma, influence of peer groups on behavior. |
| Debate in Psychology | Supports the idea that traits and behaviors are pre-determined by genes. | Argues that behavior is shaped by life experiences and external factors. |
Both nature and nurture interact in shaping human behavior, with modern research emphasizing the importance of both rather than a strict division.
2. Lapis lazuli: earth’s best blues
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
Lapis Lazuli:
- Composition & Color: Lapis lazuli is a deep blue metamorphic rock composed of 25-40% lazurite, which gives it its vivid blue color.
- Mineral Content: It also contains calcite (which can reduce its blueness), pyrites (adding a golden sparkle), diopside, and sodalite in smaller amounts.
- Geographical Sources: Found in Afghanistan, Chile, Russia, and the U.S., with Afghanistan’s Badakhshan province producing the highest quality lapis lazuli.
- Historical Trade & Use: India imported it from Badakhshan around 1000 BC; it was found in Indus Valley Civilization sites like Mohenjo-daro and Harappa.
- Ancient Applications: Egyptians used it for jewelry and eye shadow; in the Renaissance, European artists ground it into ultramarine pigment for paintings.
- Cultural & Artistic Significance: Used for royal ornaments, sculptures, and decorative items throughout history.
3. Indonesia’s Lewotobi Laki-laki volcano erupted on March20
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
Indonesia’s Lewotobi Laki-laki volcano:
- Lewotobi Laki-laki is an active stratovolcano located in East Nusa Tenggara province, Indonesia.
- It is part of the Lewotobi volcanic complex, which consists of twin volcanoes—Lewotobi Laki-laki (Male Lewotobi) and Lewotobi Perempuan (Female Lewotobi).
- The volcano has a history of frequent eruptions, with the latest major eruption occurring on March 20, 2025.
- During this eruption, it spewed ash clouds over 8 km high, prompting authorities to raise the alert status to the highest level.

- Since March 13, the volcano had experienced dozens of smaller eruptions before the major event.
- Authorities are closely monitoring the situation to ensure public safety and disaster preparedness.
4. The complex struggle for ‘Kurdistan’
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Context |
|
Kurdistan:
- Geographical Region: Encompasses parts of Turkey, Iraq, Iran, and Syria, though it is not an independent state.
- Historical Context: The idea of Kurdistan emerged after World War I, with the Treaty of Sèvres (1920) proposing Kurdish autonomy. However, it was nullified by the Treaty of Lausanne (1923).
- Iraqi Kurdistan: Recognized as an autonomous region under Iraq’s 2005 Constitution; held an independence referendum in 2017.
- Syrian Kurdistan (Rojava): Declared autonomy during the Syrian civil war, with governance by the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF).
- Political Challenges: Kurdish independence efforts face resistance from Turkey, Iran, Iraq, and Syria.
- Strategic Importance: Kurdistan has significant oil reserves and a unique cultural-linguistic identity, influencing regional geopolitics.
Kurdish People:
- Ethnicity: Kurds are an Indo-Iranian ethnic group, mainly speaking Kurdish, a language with several dialects.
- Population: Estimated at 30–40 million, spread across Turkey, Iraq, Iran, Syria, and Armenia.
- Religious Diversity: Predominantly Sunni Muslims, with minorities of Shia Muslims, Alevis, Yazidis, and Christians.
- Statelessness: Despite having a distinct identity, Kurds lack a nation-state, leading to ongoing struggles for autonomy.
- Major Uprisings: Kurdish rebellions in Turkey (1925, 1930, 1984–present), Iraq (1961, 1991, 2017), and Syria (2012–present).
- Political Representation: Key Kurdish parties include PKK (Turkey), KDP & PUK (Iraq), PYD (Syria), and PJAK (Iran).
- Persecution: Faced historical oppression, including Saddam Hussein’s Anfal genocide (1988) against Iraqi Kurds.
5. Top 10 Toll Plazas Contribute Over ₹13,988 Crore to India’s Toll Revenue in Five Years
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Economy, Page – 11)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:

Highest Toll Collection Plazas
- The data from the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) highlights the top toll plazas with the highest revenue collection over the past five years.
- The Bharthana toll plaza in Gujarat leads the list with a toll collection of ₹2,043.81 crore from 2019-20 to 2023-24. Other key toll plazas include Shahjahanpur (Rajasthan), Jaladhulagori (West Bengal), and Barajore (Uttar Pradesh), indicating that highways connecting major economic hubs generate the most revenue.
Regional Distribution and Highway Importance
- The top-10 toll plazas are strategically located on major highways like NH-48 (Delhi-Mumbai), NH-16 (East Coast), NH-19 (Grand Trunk Road), and NH-44 (Srinagar-Kanyakumari).
- These highways are part of the Golden Quadrilateral and other critical road networks that facilitate high traffic movement, thereby ensuring significant toll revenue.
Total Toll Collection and Growth Trend
- The combined toll revenue of the top-10 plazas stood at ₹13,988.51 crore, contributing 7% of the national total of ₹1.93 lakh crore between 2019-20 and 2023-24.
- The increase in toll revenue, with the highest collection of ₹55,882 crore in 2023-24, reflects a growing dependence on toll-based infrastructure financing.
Infrastructure Expansion and Future Prospects
- With 457 new toll plazas added in the last five years, the government’s focus on road expansion is evident.
- As the number of vehicles increases and expressways are developed, toll revenues are expected to rise further, supporting India’s infrastructure growth.
- However, concerns about high toll charges and their impact on logistics costs remain significant.
Challenges and Policy Considerations
- Cost Burden on Commuters: Rising toll charges can increase transportation costs, affecting both commercial and personal vehicle users.
- Traffic Congestion at Toll Plazas: Despite FASTag implementation, congestion remains a challenge at high-traffic toll plazas.
- Alternatives to Toll-Based Funding: Exploring alternative funding models like fuel cess or public-private partnerships could help balance revenue generation and commuter convenience.
check more – 22 March 2025 : Daily Current Affairs

