24 October 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Spraying Diamond Dust: A Bold Proposal to Combat Global Warming Through Geoengineering
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 12)
|
Topic: GS3 – Science & Technology |
|
Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Spraying Diamond Dust: A Potential Climate Solution
- A new study suggests spraying millions of tonnes of diamond dust in the upper atmosphere could effectively reduce global warming.
- The concept involves reflecting solar radiation back into space to cool the Earth, an approach previously considered using materials like sulfur and calcium compounds.
- This method, termed solar radiation management (SRM), falls under broader geoengineering efforts aimed at altering Earth’s climate system.
The Urgency of Cooling Measures
- Global warming has continued unabated, with temperatures already 1.2°C higher than pre-industrial levels. Current measures to curb greenhouse gas emissions have proven insufficient.
- Despite global pledges, emissions reductions are minimal, making it almost impossible to meet the Paris Agreement’s target of limiting the rise to 1.5°C.
- Scientists are exploring drastic technological solutions like geoengineering to temporarily cool the planet while emissions reduction strategies lag behind.
Geoengineering and SRM
- Geoengineering refers to large-scale interventions in the Earth’s climate, with SRM aiming to prevent sunlight from reaching the Earth.
- Diamonds, the focus of the recent study, were found to be more effective than other materials previously tested.
- Achieving a temperature reduction of 1.6°C could require spraying 5 million tonnes of diamond dust annually. However, SRM is still theoretical, and no practical implementation has occurred so far.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
- Besides SRM, geoengineering also includes carbon dioxide removal (CDR) methods, such as carbon capture and storage (CCS), where carbon emissions are trapped and stored underground.
- While CCS has been tested, its scalability and high costs remain significant barriers.
- Some innovative techniques, like direct air capture, are also under experimentation but face similar hurdles.
Challenges and Risks of SRM
- Although SRM offers promising results, it presents substantial technological, economic, and environmental challenges.
- Manipulating natural processes on a large scale could lead to unintended consequences like altering weather patterns, disrupting agriculture, and affecting biodiversity.
- The feasibility of deploying such technologies remains uncertain, with concerns over their effectiveness, costs, and long-term sustainability.
Conclusion: Geoengineering’s Role in Climate Solutions
- While geoengineering, especially SRM, offers potential quick fixes to mitigate global warming, it remains untested and fraught with risks.
- Both SRM and CCS technologies are seen as necessary, but practical and scalable solutions are yet to be realized.
- As global temperatures rise, these interventions could become critical, albeit contentious, tools in the fight against climate change.
|
Practice Question: What are the potential benefits and challenges of using geoengineering methods like solar radiation management (SRM) to combat global warming, and how feasible are these solutions in addressing climate change? (250 words/15 m) |
2. SC Upholds States’ Power to Tax Industrial Alcohol in Landmark 8:1 Ruling
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 12)
|
Topic: GS2 – Governance |
|
Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
What is Industrial Alcohol?
- Industrial alcohol, unlike alcoholic beverages, is not meant for human consumption (denatured).
- It finds applications in various sectors, including manufacturing pharmaceuticals, disinfectants, chemicals, and even biofuels.
Key Decision
- The Supreme Court, in an 8:1 majority ruling, held that states can tax not only alcoholic beverages but also industrial alcohol.
- This ruling bolsters states’ revenue from alcohol, which is a significant income source for most.
- The court’s primary question was whether “intoxicating liquor” includes industrial alcohol.
- The majority, including CJI Chandrachud, ruled in favor of states, while Justice Nagarathna dissented, advocating for central control over industrial alcohol.
Overlapping Entries in the Constitution
- The issue stems from overlapping entries in the Seventh Schedule of the Constitution, which divides legislative powers between the Centre and the states.
- Entry 8 of the State List grants states control over intoxicating liquors, while Entry 52 of the Union List allows the Centre to regulate industries.
- The Centre argued that it controls industrial alcohol under the 1961 Industries Act, while states contended that regulation is necessary to prevent misuse in the production of illegal liquor.
Impact of the Ruling
- This ruling significantly impacts states’ ability to raise revenue from alcohol, clarifying their control over both potable and industrial alcohol.
- It also reaffirms the states’ authority to legislate on State List subjects, even when the Centre has broad powers over industries.
- The judgment overruled a 1990 decision that excluded industrial alcohol from states’ taxing powers.
Defining ‘Intoxicating Liquor’
- CJI Chandrachud argued that the term “intoxicating liquor” should be interpreted broadly, encompassing both drinkable and industrial alcohol due to its potential for intoxication or poisoning.
- This wide interpretation was aimed at covering all stages of alcohol production under state regulation.
- Justice Nagarathna, however, held that industrial alcohol should be regulated based on its intended use, distinguishing it from intoxicating liquor.
Maintaining Federal Balance
- The majority emphasized preserving federal balance, choosing an interpretation that allows states to regulate intoxicating liquor, including industrial alcohol.
- They concluded that giving the Centre control would undermine states’ powers.
- Justice Nagarathna dissented, believing that the Centre retains control over alcohol-related industries under the 1961 Act, restricting states’ regulatory power.
|
What are the Other Similar Cases? |
|
Synthetics & Chemicals Ltd v. State of Uttar Pradesh Case, 1989:
Ch Tika Ramji v State of UP Case, 1956:
|
|
Practice Question: Discuss the implications of the Supreme Court’s recent ruling on states’ power to tax industrial alcohol in the context of Centre-State relations and the federal structure as outlined in the Indian Constitution. (250 words/15 m) |
PRELIMS FACTS
1. E. Coli Outbreak Linked to McDonald’s Burgers in the US
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 12)
| Context: |
| One person has died, and 10 others have been hospitalized in the US due to an E. coli infection, suspected to be linked to McDonald’s quarter pound patties and slivered onions. McDonald’s has stopped serving these ingredients in several states as a precaution. |
Analysis of News:
About E. coli:
- Escherichia coli, commonly known as E. coli, is a type of bacteria that can be found in the intestines of humans and animals.
- E. coli is a rod-shaped bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family.
- While most strains of E. coli are harmless and even beneficial, some strains can cause illness and infections.
- Some kinds of E. coli can cause diarrhea, while others cause urinary tract infections, respiratory illness and pneumonia, and other illnesses.
- Transmission: Pathogenic E. coli can be transmitted to humans through contaminated food, water, or contact with fecal matter from infected individuals or animals.
Prevalence of E. Coli Infections
- E. coli is a prevalent pathogen, particularly in gastrointestinal and urinary tract infections.
- In 2023, over 500 diarrhoeal outbreaks were reported in India, with E. coli being the most common bacteria isolated in patient samples, according to ICMR’s Antimicrobial Surveillance Network.
- The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is working to enhance food safety testing across the country.
How does E. coli make you sick?
- The most familiar strains of E. coli that make you sick do so by producing a toxin called Shiga.
- This toxin damages the lining of your small intestine and causes diarrhea.
- These strains of E. coli are also called Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC).
- The STEC that is most well-known and most often referred to is E. coli O157:H7, or just E. coli O157.
Symptoms:
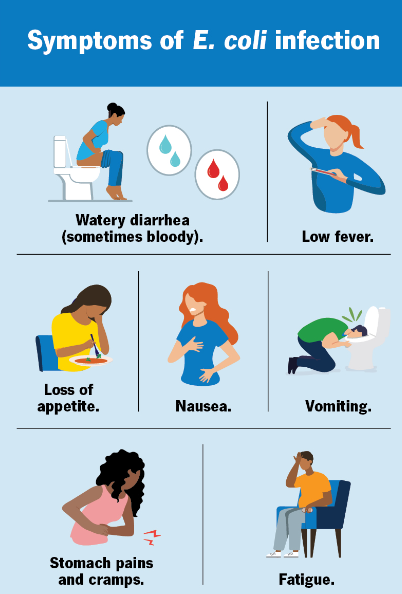
- Symptoms of an E. coli infection can vary depending on the specific strain and severity of the infection.
- Common symptoms include diarrhea (which may be bloody), abdominal pain and cramping, nausea, and sometimes fever.
- In severe cases, E. coli infections can lead to hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS), a condition that can cause kidney failure and other complications, especially in young children and the elderly.
Treatment:
- Most E. coli infections are self-limiting and resolve on their own without treatment. However, it’s essential to stay hydrated during the course of the illness.
- In severe cases or when complications arise, medical attention may be required.
2. Cyclone Dana Poised to Strike Odisha: 4 Lakh Evacuated, Heavy Rainfall and Wind Speeds Up to 120 km/h Expected
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 09)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
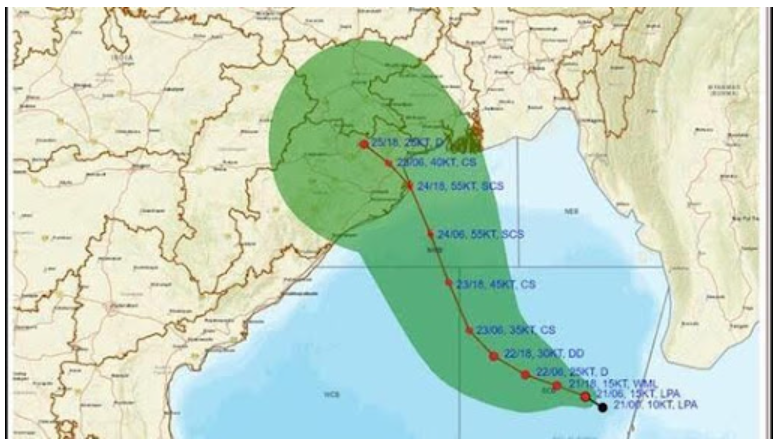
Impact Zones and Storm Surge Risk
- Jagatsinghpur, Kendrapara, Bhadrak, Balasore (Odisha), and East Medinipur (West Bengal) are expected to bear the brunt of the cyclone.
- IMD predicts storm surges in low-lying areas, posing risks of inundation in Kendrapara, Bhadrak, and Balasore.
Expected Damage
- The cyclone is likely to cause damage to thatched houses, disrupt power and communication lines, uproot trees, and affect standing crops.
- The state is on high alert, with preparations for rescue operations underway.
About Cyclones:
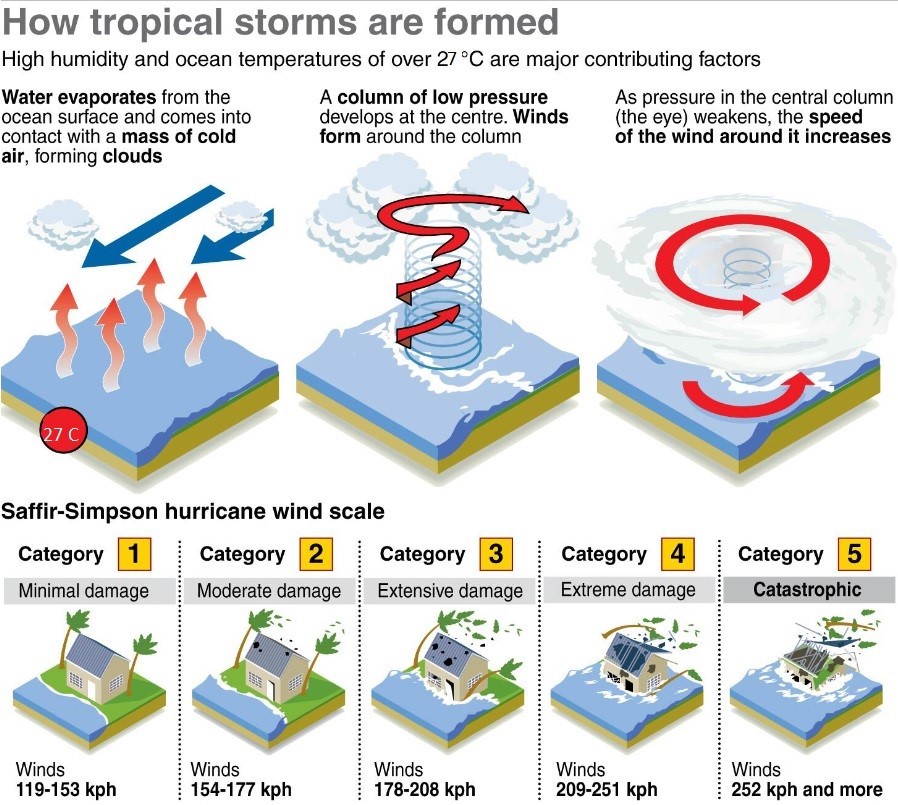
- Cyclones are centres of low pressure surrounded by closed isobars and having increasing pressure outwards.
- As air enters an area of low pressure from all directions, the Coriolis Effect bends the direction of the wind to the right of its path.
- This creates a counter clockwise rotation around the low and convergence near the centre of the system. As the air collides near the centre it is forced aloft where divergence takes air away from the centre of the system.
- A Cyclone is a system of low level convergence and high level divergence with a rising column of air in the centre of the rotating air mass. If the upper air is not diverging then there cannot be a cyclone present.
Types of Cyclones
Cyclones, hurricanes, and typhoons are all the same weather phenomenon. The difference lies in their location.
- Hurricanes occur in the North Atlantic and Northeast Pacific.
- Typhoons form in the Northwest Pacific Ocean.
- Cyclones are found in the South Pacific and Indian Oceans.
Cyclone Naming Process:
- Since 2004, the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) has managed cyclone naming in the North Indian Ocean.
- Member countries include Bangladesh, Iran, Maldives, Myanmar, Oman, Pakistan, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Sri Lanka, Thailand, UAE, and Yemen.
- Each country suggests four names. When a cyclone forms, it is named sequentially from the list. Once a name is used, it is retired and not repeated.
3. INDIAN ARMY TO HOST THE SECOND EDITION OF CHANAKYA DEFENCE DIALOGUE: A GLOBAL PLATFORM FOR STRATEGIC INSIGHTS
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2067374®=3&lang=1 )
| Context |
|
Chanakya Defence Dialogue Overview
- The Chanakya Defence Dialogue is a prominent international seminar organised by the Indian Army.
- Purpose: It aims to discuss the integration of security dynamics into national and international policymaking, focusing on strategies for sustainable development.
- Theme: The second edition, set for October 24-25, 2024, is themed “Drivers in Nation Building: Fuelling Growth Through Comprehensive Security.”
- Sessions: The dialogue comprises six expert-led sessions addressing critical topics such as:
- Geopolitical dynamics and strategic partnerships.
- The intersection of economic development and national security.
- Balancing economic growth with environmental sustainability.
- The role of social cohesion in strengthening internal security.
- The integration of emerging technologies into national security frameworks.
- Innovations and future trends in land warfare.
- Objectives: The dialogue aims to develop visionary strategies that emphasise comprehensive security as a cornerstone of national development.
- Significance: It serves as a crucial platform for collaboration among military leaders, security specialists, and policymakers, influencing India’s strategic direction for future national security and development initiatives.
4. Stubble burning violates right to clean environment: court
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Context |
|

Supreme Court’s View on Stubble Burning and Pollution:
- Violation of Article 21: The Supreme Court emphasised that the citizens’ right to live in a pollution-free environment, guaranteed under Article 21 of the Constitution, was being violated by ineffective handling of stubble burning.
- The court criticised the Punjab and Haryana governments for selectively penalising a few offenders while allowing many violators to go unpunished by paying nominal fines.
- The court noted the failure of authorities in effectively implementing environmental laws, impacting citizens’ dignity and right to clean air.
- Lack of Proper Enforcement Mechanism: Justice Oka highlighted the absence of a well-structured system for collecting fines under Section 15 of the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
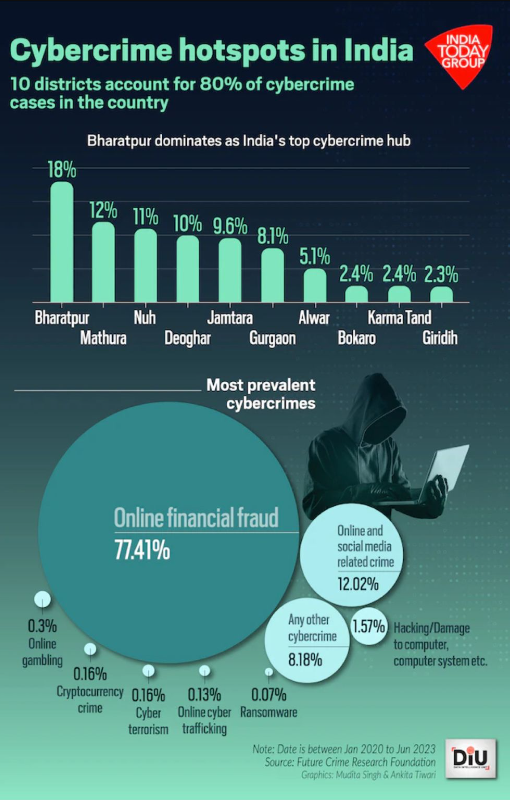
5. Cyberfraud losses could amount to 0.7% of GDP, projects Ministry’s study
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|
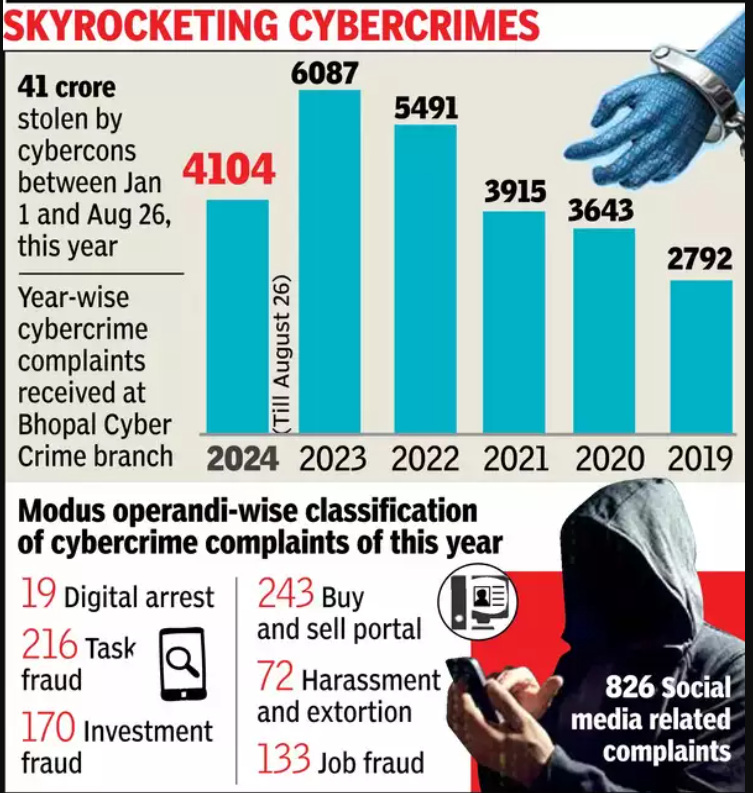
Analysis of the news:
- Online financial scams, driven significantly by mule bank accounts, could potentially siphon off 0.7% of India’s GDP.
- A large portion of the defrauded money is sent overseas, with many scams originating from China or entities linked to China.
- Domestically run scams also contribute, with funds withdrawn from ATMs after passing through several accounts.
- I4C identifies approximately 4,000 mule bank accounts daily.
| Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) |
|
- The government is working to curb scams involving “scam compounds” in South East Asia and is collaborating with banks to monitor suspicious transactions.
6. ‘Germany has given India special status for military purchase’
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Context |
| Germany has granted India special status to expedite military procurement approvals and enhance defence collaboration. |
Special Status Granted by Germany to India
- Purpose: Germany has accorded special status to India to accelerate approvals for military purchases.
- Focus Paper: The German Cabinet has issued a focus paper favouring swift approval for military deals with India.
- Streamlined Process: The special status aims to reduce bureaucratic delays, enhancing the speed of defence procurement processes.
Potential Benefits
- Enhanced Military Cooperation: Strengthened defence ties could lead to improved collaboration in military technology and innovation.
- P-75I Submarine Deal: It will help in multi-billion dollar P-75I submarine deal, involving six advanced conventional submarines for the Indian Navy.
- Technology Transfer: Special status may facilitate technology transfer agreements, enhancing India’s indigenous defence manufacturing capabilities.
- Strategic Partnerships: Increased military engagement can foster stronger geopolitical alliances, crucial in the context of regional security dynamics.
- Timely Acquisition: Accelerated approvals ensure that India can quickly acquire necessary military equipment, enhancing its defence readiness.
7. Ancient meteorite was ‘giant fertiliser bomb’ for life on earth
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
Impact of the Meteorite
- A massive meteorite, approximately 37-58 km in diameter, struck Earth about 3.26 billion years ago, significantly larger than the asteroid that caused the dinosaurs’ extinction.
- The meteorite was a carbonaceous chondrite rich in carbon, phosphorus, and iron, essential nutrients for early life forms.
Devastation from the Impact
- The impact was so powerful that it vaporised both the meteorite and the surface materials it struck, creating a vast cloud of dust and debris that enveloped the planet.
- This cloud turned the sky dark for hours, resulting in a drastic rise in atmospheric temperatures and potentially boiling the upper layers of the oceans.
Nutrient Enrichment and Evolution
- Despite the initial devastation, the nutrients released by the impact acted as a “giant fertiliser bomb,” enriching the environment for single-celled organisms such as bacteria and archaea.
- Researchers found evidence in ancient rocks from the Barberton Greenstone Belt in South Africa, indicating that life rebounded quickly after the impact.
- The influx of phosphorus facilitated crucial biochemical processes, while iron mixed into shallower waters provided energy sources for thriving microbial communities, contributing to the early evolution of life on Earth.

8. Green Energy Goal: Wind players fret over land issues
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 12)
| Context |
| The Union Ministry of New and Renewable Energy expresses confidence in exceeding India’s renewable energy targets by 2030, particularly in wind energy.However, challenges related to land acquisition pose significant hurdles to achieving the ambitious installation goals for wind projects. |
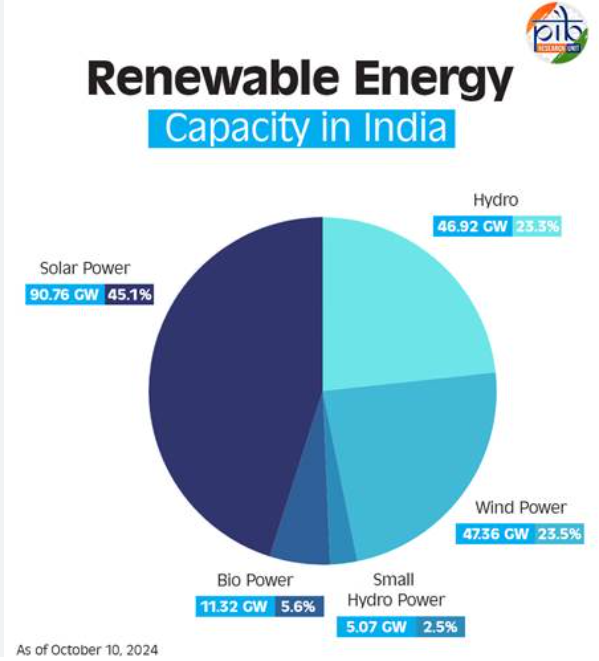
Overview of Renewable Energy Targets
- The Union Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) is optimistic about exceeding India’s target of 500 GW in renewable energy capacity by 2030, which includes 100 GW from wind energy.
Current Renewable Energy Status
- India has surpassed 200 GW of renewable energy capacity, currently standing at 210 GW.
- There is a significant installation pipeline of nearly 160 GW, with an additional 100 GW under tendering.
Wind Energy Capacity
- India ranks as the fourth largest globally in installed wind energy capacity.
- The country installed 2.8 GW of wind energy last year and is projected to add 4.5-5 GW this year.
- To meet future goals, India needs to scale up installations to around 10 GW annually.
Challenges in Development
- Challenges such as land acquisition and infrastructure development have been hindering the development of wind energy.
- There is a need for better coordination between the Centre and States to identify suitable land for wind projects.



