25 September 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. India Approves First Mission to Venus, Launch Set for 2028 with Focus on Exploring the Planet’s Atmosphere and Surface
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 11)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
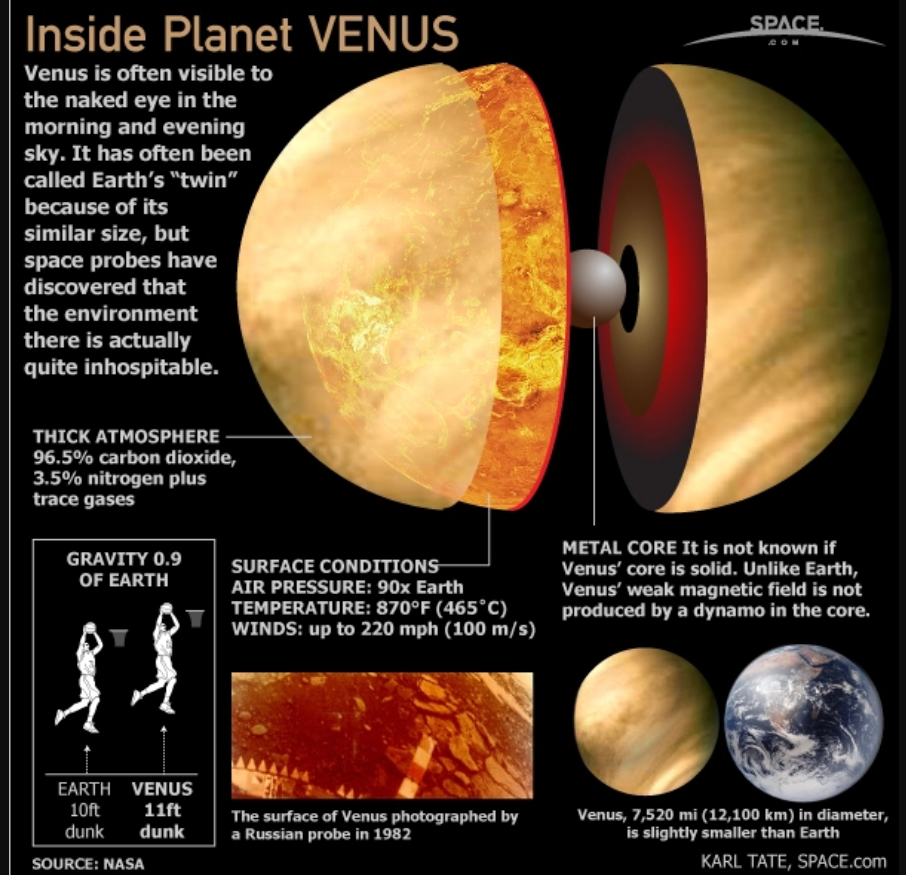
Importance of Studying Venus
- Venus is often referred to as Earth’s “twin” due to similarities in mass, density, and size, and it was once thought to have had liquid water.
- Understanding the differences between Venus and Earth, such as Venus’ extreme surface temperature (462°C), its dense carbon dioxide atmosphere, and its runaway greenhouse gas effect, helps scientists better comprehend planetary evolution and why Earth became habitable.
ISRO’s Venus Mission Details
- The mission will launch in March 2028 when Earth and Venus are closest, taking 140 days to reach the planet.
- It will carry scientific payloads weighing around 100 kg, including instruments to image Venus’ surface, study interplanetary dust, and analyze the planet’s atmosphere and ionosphere.
- The spacecraft will follow a trajectory similar to previous ISRO missions, gaining speed in Earth’s orbit before heading towards Venus.
Aero-Breaking Technology: A First for ISRO
- A key difference in this mission will be aero-breaking technology, where the spacecraft will be initially placed in a highly elliptical orbit around Venus.
- To conduct scientific experiments, it will gradually descend to a lower orbit by skimming through Venus’ atmosphere to create drag.
- This manoeuvre will take six months and help reduce the spacecraft’s orbit without using excessive fuel.
Other Global Venus Missions
- Countries like the United States, Japan, and Europe have previously sent missions to Venus.
- Upcoming missions include the DaVinci (2029) and Veritas (2031) missions by the U.S. and the EnVision (2030) mission by the European Space Agency.
| Scientific Payloads for the Venus Mission |
|
The upcoming Venus mission will carry a range of scientific payloads, aimed at enhancing our understanding of the planet. Proposals for at least 17 Indian experiments and seven international ones were selected by 2019, as reported in a parliamentary response. Key Indian payloads include:
|
|
PYQ: Consider the following statements: (2016) The Mangalyaan launched by ISRO
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (c) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the scientific and technological significance of India’s first mission to Venus, highlighting the challenges and innovations involved. How will this mission contribute to our understanding of planetary evolution and space exploration? (150 words/10 m) |
2. Indian Railways to overhaul ageing signalling systems for better safety
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy – Infrastructure – Railways |
| Context |
|
Ageing Signalling System in Indian Railways:
- Ageing Infrastructure: Several signalling systems in the Indian Railways have outlived their recommended codal life, leading to increased failures and safety risks.
- Impact on Operations: Ageing signals have caused disruptions, such as delays in train operations, posing potential risks of accidents.
- Recent Accidents: Notable accidents, including the Balasore triple train collision (June 2023), which killed 291 people, have been linked to signalling failures. Other rear-end collisions in Waltair and Katihar divisions also highlight this concern.
Future Steps Taken by Indian Government:
- Replacement of Outdated Signal Assets: The Indian Railways has initiated the replacement of signalling systems that have outlived their codal life to enhance operational safety.
- PRIME Initiative: A “Plan for Reliability Improvement and Maintenance Effectiveness (PRIME)” was rolled out to improve the reliability and maintainability of signalling systems.
- Staff Training: Special focus on training staff across departments on the new systems and safety protocols to ensure operational efficiency.
- Cable Cut Prevention: Addressing frequent cable cuts along tracks to minimise signalling failures, a key cause of disruptions.
- Safety Emphasis: Railway Ministry prioritises the independent execution of these replacements without affecting ongoing infrastructure projects, ensuring swift modernization.
- Accident Prevention: The overarching goal is to minimise accidents through upgraded signalling technology and improved operational protocols.
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of outdated signalling systems on railway safety in India. What measures can be taken to enhance the reliability and effectiveness of signalling infrastructure in the Indian Railways? (150 Words /10 marks) |
3. Why the ‘fact-checking’ unit was invalidated
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS2 – Indian Polity – Judiciary |
| Context |
|
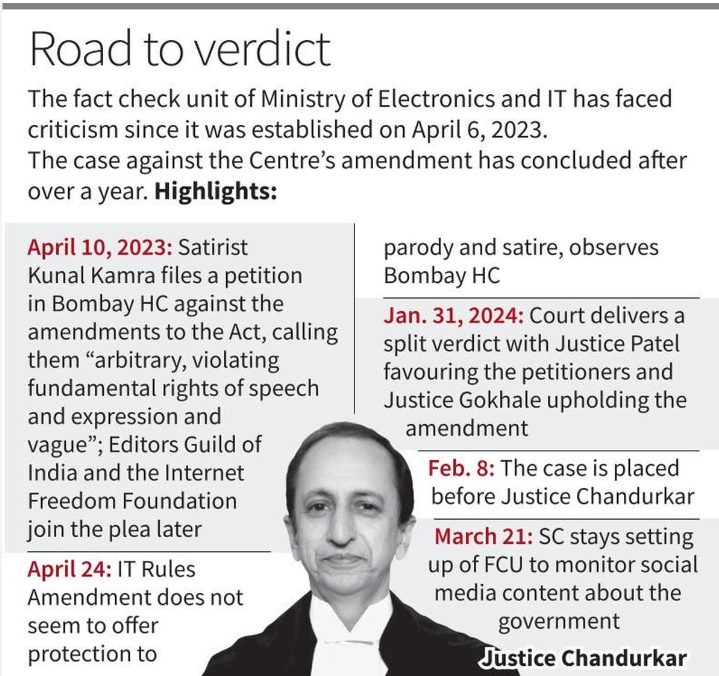
Fact-Checking Unit (FCU)
- The Fact-Checking Unit (FCU) was established under the amended Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Amendment Rules, 2023.
- It empowered the Union government to designate any information regarding its operations as “fake, false, or misleading.”
- Social media intermediaries were mandated to take “reasonable efforts” to prevent users from uploading flagged content and required to remove such content within 36 hours to maintain safe harbour protection against liability for third-party content.
Court’s Invalidation Rationale
- On September 20, 2024, the Bombay High Court ruled the FCU and amended rules as unconstitutional and vague.
- Justice Atul Sharachchandra Chandurkar articulated that the rules exhibited manifest arbitrariness, infringing upon the fundamental right to freedom of speech and expression protected under Article 19(2) of the Constitution.
- The terms “fake, false, or misleading” were criticised for being overbroad and vague, allowing for subjective interpretation and potential misuse by the government.
- The absence of procedural safeguards meant the government could act as a “judge in its own cause,” undermining impartiality.
- The court emphasised that the rules could create a “chilling effect” on intermediaries, jeopardising their legal protections.
Way Forward for the Government
- The Union government is likely to appeal the ruling in the Supreme Court to uphold the FCU and the amended IT Rules.
- It may be necessary for the government to revise the rules to include clearer definitions, procedural safeguards, and mechanisms that ensure transparency and accountability.
- The implications for similar fact-checking units in states like Tamil Nadu and Karnataka need careful consideration to ensure compliance with the ruling.
- Engaging with stakeholders, including media organisations and civil society, may help in formulating guidelines that balance misinformation control with the protection of freedom of speech.
| PYQ: What do you understand about the concept “freedom of speech and expression”? Does it cover hate speech also? Why do the films in India stand on a slightly different plane from other forms of expression? Discuss. (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2014) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of the Bombay High Court’s ruling against the Fact-Checking Unit on freedom of speech and expression in India. What steps should the government take moving forward? (150 Words /10 marks) |
4. What are retractions and why do they matter?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
What is Retraction?
- Retraction is a formal withdrawal of a published scientific paper from academic literature due to significant errors, misconduct, or fraudulent data.
- It serves as a mechanism for correcting the scientific record, maintaining accountability, and preserving the integrity of research.
- Retractions are issued when the findings are deemed unreliable, ensuring that the academic community recognizes the flaws and preventing the dissemination of misleading or inaccurate information.
What is the Retraction Index?
- The retraction index measures the frequency of retractions within a specific time frame relative to the total number of published articles.
- It is calculated by multiplying the number of retractions by 1,000 and dividing by the total articles published, with higher-impact journals exhibiting a greater likelihood of retractions.
Why Do Scientists Prefer Retraction?
- Researchers may opt for retraction when errors are identified to maintain scientific integrity and accountability.
- Retractions allow for corrections in the scientific record, serving as a mechanism for self-regulation within the academic community.
Impact of Retraction
- Retractions can severely damage reputations, funding opportunities, and institutional credibility.
- They create mistrust among scientists and in the scientific literature, affecting the broader perception of research reliability.
- The increasing rate of retractions indicates a growing concern about the quality and ethics of scientific research.
How Can We Control This?
- To mitigate retractions, there is a need for better oversight and rigorous peer-review processes in academic publishing.
- Implementing training on research ethics and integrity for researchers can help reduce instances of misconduct.
- Journals could leverage technology, such as AI, to detect potential issues in submitted papers before publication.
- A shift in academic culture from “publish or perish” to valuing quality over quantity in research outputs may also curb the prevalence of retractions.
| Practice Question: What is retraction in scientific literature? Discuss the impact of these retractions on research credibility. Also, suggest measures that can be taken to prevent retractions and enhance research integrity. (150 Words /10 marks) |
5. Expanding Horizons in Space Sector: From Lunar Exploration to a National Space Station
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2058137 )
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
Introduction
- India is embarking on an ambitious journey in space exploration, as evidenced by a series of visionary missions and projects approved by the Union Cabinet.
- Spearheaded by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), these initiatives highlight the nation’s dedication to becoming a leader in space technology and research.
Chandrayaan-4 Mission

- The Chandrayaan-4 mission is designed to develop and demonstrate essential technologies for returning to Earth after a successful lunar landing.
- The mission will focus on collecting lunar samples for analysis on Earth, crucial for establishing India’s capabilities for future human missions to the Moon, projected for 2040.
- Key technologies for docking, undocking, landing, and safe return to Earth will be showcased during this mission, alongside lunar sample collection.
- The mission will be managed by ISRO and is expected to be completed within 36 months post-approval, with strong participation from industry and academia.
- All critical technologies will be developed domestically, generating high employment potential and technological spin-offs for various sectors.
- The total funding requirement is ₹2,104.06 crore, which encompasses spacecraft development, two launch vehicle missions of LVM3, and additional support for deep space network operations.
Venus Orbiter Mission

- The Venus Orbiter Mission (VOM) marks a significant advancement in India’s planetary exploration beyond the Moon and Mars.
- As the planet closest to Earth, Venus offers a unique opportunity to study planetary environments that evolve under varying conditions.
- The mission aims to place a scientific spacecraft in orbit around Venus, enhancing understanding of its surface, subsurface, and atmospheric processes.
- Investigating the causes behind Venus’s transformation from a potentially habitable planet will provide crucial insights into both Venus and Earth’s evolutionary paths.
- Scheduled for launch in March 2028, the mission is backed by an approved budget of ₹1,236 crore, which includes ₹824 crore for spacecraft development.
- The collaboration with Indian industries will not only bolster employment but also yield technological benefits across sectors.
Bharatiya Antariksh Station
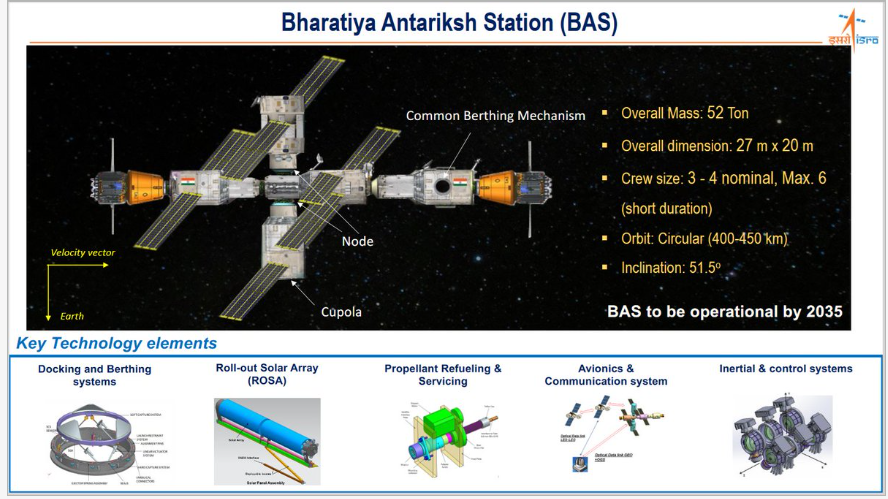
- The construction of the first module of the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS-1) marks a critical expansion of the Gaganyaan program.
- The expanded scope of Gaganyaan includes missions aimed at validating technologies necessary for building and operating the Indian space station.
- The program’s vision now encompasses establishing an operational space station by 2035 and launching an Indian crewed mission to the Moon by 2040.
- ISRO will lead the Gaganyaan program, collaborating closely with industry, academia, and national agencies.

Funding and Economic Impact
- The revised Gaganyaan program has a total funding allocation of ₹20,193 crore, including ₹11,170 crore in newly approved funding.
- The program is designed to inspire youth towards careers in science and technology, yielding technological advancements that benefit society.
Union Budget 2024-25
- The Union Budget 2024-25 has introduced a ₹1,000 crore Venture Capital Fund for space startups, designed to stimulate growth in India’s burgeoning space sector.
Conclusion
- India’s space program is entering an exhilarating phase marked by groundbreaking missions and technological advancements.
- The approval of Chandrayaan-4, the Venus Orbiter Mission, and the Bharatiya Antariksh Station illustrates the government’s commitment to enhancing India’s space exploration capabilities.
- These initiatives not only elevate India’s standing in the global space arena but also catalyse technological innovation and employment opportunities.
- As India progresses with its space ambitions, these missions will secure its position at the forefront of scientific discovery and space research for years to come.
| PYQ: What is India’s plan to have its own space staSon and how will it benefit our space programme? (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2019) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of India’s recent initiatives in space exploration, particularly the Chandrayaan-4 mission and the Venus Orbiter Mission. What challenges do you foresee in implementing these projects? (250 Words /15 marks) |
PRELIMS FACTS
1. New Study Challenges Link Between Horseback Riding and Skeletal Changes, Casting Doubt on Kurgan Hypothesis
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 11)
| Context: |
| A recent study published in Science Advances on September 20, titled “Tracing horseback riding and transport in the human skeleton,” examines whether horseback riding can alter the shape of the human skeleton. |
Analysis of News:

Impact of Horseback Riding on Human Skeleton
- Subtle Changes: Horseback riding can leave subtle marks on human skeletons, but these changes cannot conclusively confirm if a person has ridden horses.
- Similar Effects from Other Activities: Other activities, like prolonged sitting or riding in carts, can result in similar skeletal alterations, making it difficult to attribute these changes solely to horseback riding.
The Kurgan Hypothesis
- Origin and Theory: The Kurgan hypothesis, proposed in the early 20th century, suggests that horse domestication began around 3500 BC by the Yamnaya people near the Black Sea. This domestication played a role in spreading Indo-European languages across Eurasia.
- Previous Evidence: A 2023 study found wear and tear in the skeletons of Yamnaya people, which was believed to be from horse riding, supporting the Kurgan hypothesis.
Findings of the New Study
- Skepticism Introduced: The new study, led by Lauren Hosek, reexamined medical data and ancient remains, revealing that skeletal changes attributed to horseback riding could result from other forms of transportation like riding in carts or chariots.
2. India’s Official Entry for 97th Academy Awards
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 11)
| Context: |
| Kiran Rao’s directorial Laapataa Ladies has been chosen as India’s official entry for the Best International Feature Film category at the 2024 Academy Awards. |
Analysis of News:
Film Federation of India (FFI) and Selection Process
- About FFI: The FFI promotes and safeguards the interests of the Indian film industry, representing producers, distributors, and exhibitors. It selects the film to represent India at the Academy Awards.
- Jury: A 13-member jury, consisting of senior creative professionals, is responsible for evaluating the entries. This year, the jury was led by Assamese director Jahnu Barua.
Best International Feature Film Category at the Oscars
- Process: Countries submit their best films, and a preliminary committee shortlists 15 films. A nominating committee selects the final five, and Academy members vote for the winner.
- Indian Nominations: Only three Indian films have previously made it to the final nominations — Mother India (1957), Salaam Bombay! (1988), and Lagaan (2001).
3. Army to receive Apache choppers in December; deploy LCH in Ladakh next year
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|
Apache Helicopter (AH-64E):
- Origin: Developed by Boeing, USA.
- Type: Attack helicopter designed for multi-role combat.
- Specifications: Twin-engine, four-blade rotor; max speed of 279 km/h.
- Advanced Systems: Equipped with modern avionics, target acquisition systems, and night-vision capabilities.
- Role: Used for close air support, anti-armor operations, and armed reconnaissance.
- Deployment in India: India signed a deal with Boeing for six Apaches, for the Army, at a cost of around $800 million in February 2020.

Indigenous Light Combat Helicopter (LCH):
- Origin: Designed and developed by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), India.
- Type: Multi-role light attack helicopter.
- Specifications: Twin-engine, max speed of 268 km/h, 5.8-ton weight.
- Armament: Equipped Mistral air-to-air missiles, 20mm turret gun, and rockets.
- Role: Specifically built for high-altitude warfare, ideal for operations in places like Ladakh and Siachen.
- Unique Capability: Can perform in extreme cold and high-altitude areas (up to 16,000 feet).

4. Beads on the moon suggest it had volcanoes more recently than thought
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|

Analysis of the news:
- Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences analysed lunar glass beads collected by the Chang’e-5 mission, focusing on their formation from volcanic eruptions and impacts.
- The study identified specific glass beads indicative of volcanic origins through their chemical composition and unique isotopic signatures.
- Three volcanic samples were accurately dated using uranium-lead radiometric dating, revealing ages between 116 and 135 million years.
- The presence of minerals like potassium and rare earth elements in the beads indicates they contributed to the volcanic heat necessary for eruptions.
- The findings open new avenues for research, particularly regarding how volcanic activity persisted despite the moon’s cooling interior.
- Future Indian Chandrayaan missions may further explore the moon’s volcanic history and search for preserved lunar ice that may contain gases from past eruptions.
5. Why is it colder at higher altitudes?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
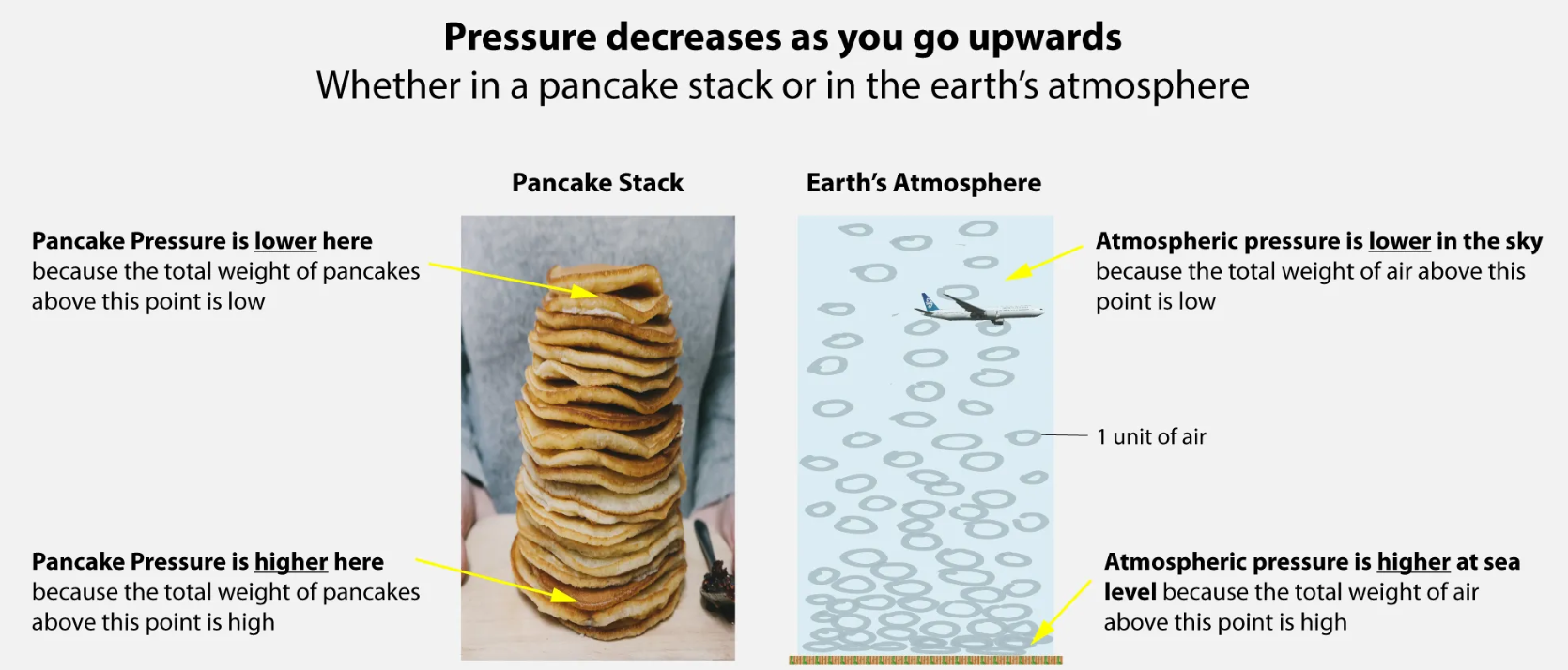
Why is it colder at higher altitudes?
- As altitude increases, the air pressure decreases, leading to fewer air molecules to absorb heat, resulting in cooler temperatures.
- The Earth’s surface absorbs solar radiation and warms the air directly above it, causing temperatures to be higher near the ground.
- Heat is transferred upwards by convection, where warm air rises and cool air sinks, creating a cooler atmosphere at higher altitudes.
- In the troposphere, this cooling trend continues because the air expands as it rises, which cools it down due to lower pressure.
- Although there are temperature variations in different atmospheric layers (like the stratosphere and mesosphere), the overall trend is that temperature decreases with altitude in the troposphere.
- Dynamic processes, such as air movement and radiation, affect temperature, but the general pattern of cooler temperatures at higher altitudes remains consistent.
6. Tuvalu fights to keep maritime boundaries amid alarming rise in sea levels
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 15)
| Context |
|
About Tuvalu:
- Tuvalu is a small island nation in the Pacific Ocean, consisting of nine atolls.
- With a population of around 11,000, it is one of the world’s least populous countries.
- The economy relies on fishing, agriculture, and remittances, while its culture is deeply rooted in Polynesian traditions.
Crisis For Tuvalu:
- Tuvalu is threatened by rising sea levels, with projections indicating that half of the main atoll, Funafuti, could be submerged by 2050.
- Groundwater contamination from saltwater has devastated local agriculture, forcing reliance on rainwater tanks and limited gardening.
- A treaty with Australia will allow 280 Tuvaluans to migrate annually, highlighting the difficult choice of leaving behind their culture and family.
- Tuvalu is constructing seawalls and creating artificial land to delay displacement, aiming for sustainability until 2100.
- The Tuvalu government is advocating for legal recognition of its maritime boundaries to ensure sovereignty and economic viability amidst climate change challenges.
7. How BMI is becoming an inadequate measure for health
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 11)
| Context |
|
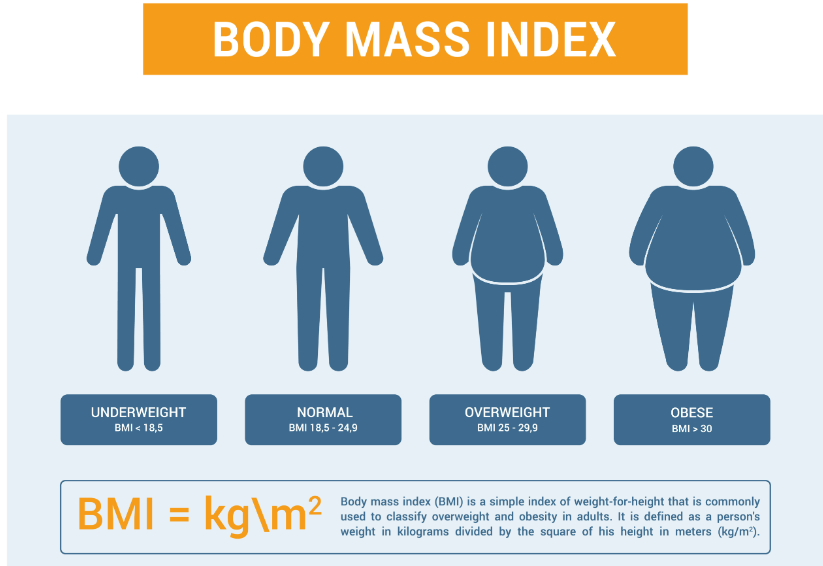
More About BMI:
- BMI Definition: Body Mass Index (BMI) is calculated by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by their height in metres squared, used to categorise individuals into weight categories (underweight, normal, overweight, and obese).
- Limitations of BMI:
- Fails to differentiate between fat, muscle, and water content, making it inaccurate for assessing body composition.
- Does not account for fat distribution; abdominal fat poses a greater health risk than fat in other areas.
- Originated from 19th-century European data, making it less applicable to diverse ethnic groups, such as Asians, who may have higher body fat percentages at lower BMI levels.
- Health Risks: High BMI does not always indicate health risks; individuals with normal weight can still have metabolic issues, while those with a high BMI might be healthy athletes.
Alternatives to BMI:
- Body Roundness Index (BRI): Measures body roundness using height and waist circumference, correlating better with body fat levels and health risks.
- Waist-to-Height Ratio: Indicates health risks based on the proportion of waist circumference to height, with a ratio less than 0.5 suggesting a healthier body composition.
- A-body Shape Index (ABSI): Assesses body shape and fat distribution, providing insights into metabolic risks.
- Waist Circumference: Directly measures abdominal fat, a key indicator of health risks associated with obesity.


