25 February 2025 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Scientists propose tabletop test to check quantumness of gravity
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
Conflict Between General Relativity and Quantum Mechanics
- General relativity explains gravity, while quantum mechanics explains the other three fundamental forces.
- Scientists do not yet know how gravity fits into quantum mechanics.
- There is a need for experiments to test whether gravity behaves according to quantum rules.
Concepts of Quantum Mechanics
- Quantum mechanics includes principles like superposition and entanglement, which defy classical physics.
- A quantum system collapses into a definite state when measured, unlike classical systems.
- If gravity follows quantum rules, measuring it should collapse its state.
| Quantum Nature of Gravity |
|
Proposed Experiment to Test Quantum Gravity
- Scientists suggest an experiment using a test mass in superposition of two paths.
- A probe mass will interact with it gravitationally, forcing it into one path.
- If gravity causes this collapse, it may indicate that gravity is quantum in nature.
Testing Weak Gravity
- Previous studies focused on strong gravity near black holes.
- This experiment aims to test weak gravity effects, making it more feasible.
- If successful, quantum gravity effects could be observed in tabletop experiments.
Challenges and Future Prospects
- The experiment requires placing a nanocrystal, one-trillionth of a gram, in superposition.
- The set-up must be in a near-perfect vacuum to prevent interference.
- Despite challenges, scientists believe testing quantum gravity is now possible within a decade.
2. Surveillance capitalism: the power to control personal data
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 11)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context |
|

Understanding Surveillance Capitalism
- Surveillance capitalism is an economic system where companies collect, analyze, and sell personal data to predict and influence human behavior.
- Social media platforms and tech companies track online activities and use the data for targeted advertisements and content recommendations.
- This system has reshaped capitalism by making human experience a source of profit.
How It Works
- Unlike traditional capitalism, which focuses on goods and services, surveillance capitalism extracts behavioral data to drive profit.
- Companies use this data to create detailed user profiles and sell them to advertisers, political campaigns, and businesses.
- Search engines, social media, and e-commerce platforms track every click, purchase, and even offline movements to refine predictive models.
Instrumentarian Power and Behavior Control
- Surveillance capitalism does not rely on force but uses predictive analytics and recommendation algorithms to influence behavior.
- Personalized advertisements, news feeds, and video suggestions guide users toward certain actions, often without them realizing it.
- This level of control makes people more predictable economic actors, benefiting corporations at the cost of individual autonomy.
Comparison with Industrial Capitalism
- Industrial capitalism focused on material goods and labor, while surveillance capitalism profits from human experience and online activity.
- In industrial capitalism, efficiency and productivity were key, but surveillance capitalism aims to control user engagement for maximum profit.
- Algorithms are designed to keep users online longer, increasing data collection and advertising revenue.
Involvement of Governments
- Governments collaborate with tech companies to access personal data for security and intelligence purposes.
- Instead of creating independent surveillance networks, authorities obtain data from private companies through legal and extra-legal means.
- This partnership raises concerns about privacy, as corporate and state interests align, reducing public accountability.
Threats to Personal Freedom
- Surveillance capitalism weakens personal autonomy by conditioning people’s preferences and choices through algorithmic manipulation.
- Constant monitoring and data collection influence decision-making in subtle ways, often prioritizing corporate interests over individual freedom.
- The 2014 misuse of social media data for political advertising revealed how personal data can be exploited to shape democratic outcomes.
Regulatory Challenges
- Laws like the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA) aim to enhance data privacy.
- However, these regulations do not stop the core practice of turning personal information into a commodity.
- Tech companies and political leaders often resist stronger regulations, as surveillance capitalism benefits them financially and politically.
Need for Awareness and Policy Changes
- As technology becomes more integrated into daily life, the risks of surveillance capitalism must be addressed.
- Stronger laws and better oversight are needed to protect privacy and prevent excessive corporate control.
| Practice Question: Discuss the concept of surveillance capitalism and its implications for privacy, democracy, and individual autonomy. Suggest measures to regulate this evolving economic model. (250 Words /15 marks) |
3. Reducing Fertiliser Dependence: India’s Shift Towards Balanced and Efficient Alternatives
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained- Page No. – 12)
| Topic: GS3 – Agriculture |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Strategic Need for Reducing Fertiliser Consumption
- India’s reliance on imported fertilisers like urea, di-ammonium phosphate (DAP), and muriate of potash (MOP) has made capping their usage a strategic priority.
- MOP is entirely imported due to the absence of domestic potash reserves.
- Although 85% of urea demand is met domestically, it depends heavily on imported liquefied natural gas.
- DAP’s complex import requirements further increase India’s vulnerability to global market fluctuations and foreign exchange pressures.
Challenges of High-Analysis Fertilisers
- Urea, DAP, and MOP are high-analysis fertilisers with concentrated nutrient content.
- However, most crops do not require such high levels of individual nutrients.
- Excessive use leads to nutrient imbalance in soils, affecting crop yields. Additionally, overdependence on imported fertilisers escalates costs, especially with rupee depreciation.
- Balanced fertilisation, involving secondary and micronutrients, is essential for sustainable agriculture and efficient use of foreign exchange.
Ammonium Phosphate Sulphate (APS): An Effective DAP Alternative
- APS has emerged as a viable substitute for DAP.
- It offers balanced nutrients, including sulphur, crucial for crops like oilseeds, pulses, and maize.
- Unlike DAP, APS requires significantly less expensive phosphoric acid, making it a cost-effective solution.
- Its rising consumption, surpassing single super phosphate (SSP), highlights its growing acceptance across India due to its water-soluble phosphorus and balanced nutrient composition.
Economic and Market Dynamics Driving APS Adoption
- Government policies and market economics are pivotal in promoting APS.
- The rising cost of DAP imports, coupled with limited subsidies, has made DAP less viable. In contrast, APS offers profitability to manufacturers while being marginally cheaper for farmers.
- The increasing adoption of APS is reflected in its sales surge, positioning it as India’s third-largest consumed fertiliser after urea and DAP.
Way Forward: Diversification and Efficiency in Fertiliser Use
- India must further diversify fertiliser use by promoting other balanced complexes .
- The goal should be reducing high-analysis fertiliser consumption, encouraging nutrient-efficient practices, and optimising foreign exchange use.
- A robust marketing push, supported by government incentives, can facilitate this transition, ensuring sustainable agricultural growth and reduced import dependency.
| PYQ: With reference to chemical fertilizers in India, consider the following statements: (2020) At present, the retail price of chemical fertilizers is market-driven and not administered by the Government.Ammonia, which is an input of urea, is produced from natural gas.Sulphur, which is a raw material for phosphoric acid fertilizer, is a by-product of oil refineries. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 2 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (b) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the challenges associated with India’s dependence on imported fertilisers like urea, DAP, and MOP. How can alternatives such as ammonium phosphate sulphate (APS) contribute to sustainable agriculture and reduce import reliance? (150 Words /10 marks) |
4. Revitalizing India’s Textile Industry: Overcoming Competitiveness and Sustainability Challenges
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Economy- Page No. – 13)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news
Overview of India’s Textile Industry
- India’s textile industry is the second-largest globally, spanning from cotton farming to apparel manufacturing.
- Despite this, it trails China, Vietnam, and Bangladesh in exports due to fragmented supply chains, high production costs, and complex regulations.
Fibre to Fabric: Strengths and Gaps
- India leads in cotton production and man-made fibres (MMF).
- However, per capita fibre consumption remains low compared to global averages.
- MSME clusters dominate the value chain but lack integration, impacting cost efficiency and scalability.
Growth and Export Performance
- The industry contributes 13% to industrial production and 12% to exports but has seen contraction post-Covid.
- In FY24, textile and apparel exports were $34.1 billion, with significant dependence on US and EU markets.
- The garment sector witnessed a decline, highlighting competitiveness issues.
Challenges Hindering Export Competitiveness
India faces stiff competition due to:
- Fragmented supply chains increasing logistical costs.
- High MMF costs, with domestic fibres priced significantly higher than imports.
- Complex export procedures and lack of favourable FTAs.
Competitor countries benefit from vertical integration and streamlined regulations.
Sustainability: The Emerging Challenge
- With global markets adopting strict sustainability norms, Indian firms face rising costs for compliance.
- The EU’s new legislation poses hurdles, especially for small enterprises.
- However, India’s textile recycling market, projected to reach $400 million, offers growth opportunities.
Way Forward
To enhance competitiveness, India must:
- Promote vertical integration in textile clusters.
- Simplify regulatory processes and negotiate strategic FTAs.
- Invest in sustainable practices and textile recycling infrastructure.
- Reduce MMF production costs through policy support.
| What are the Government Initiatives to boost the Textile Sector? |
|
1. PM MITRA Parks Scheme– It aims to develop world-class textile infrastructure through Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) with the Budget allocation of ₹4445 crore for a period up to 2027-28. 2. Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme– It focuses on boosting production of MMF (man-made fibers) and technical textiles. It offers financial incentives for meeting investment and turnover thresholds. 3. Amended Technology Upgradation Fund Scheme (ATUFS)– It Provides capital investment subsidies to modernize textile infrastructure. 4. National Technical Textile Mission (NTTM)– It Promotes research, market development, export promotion, and skill development in technical textiles. 5. Samarth (Scheme for Capacity Building in Textile Sector)– It aims to provide skill training aligned with industry needs. 6. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): 100% FDI (automatic route) is allowed in textile and apparel sector in India. 7. Branding Initiatives– “Kasturi Cotton India” launched to promote premium Indian cotton globally. |
| Practice Question: Discuss the challenges faced by India’s textile industry in competing with global players like China, Vietnam, and Bangladesh. Suggest measures to enhance the export competitiveness of India’s textile sector, considering sustainability and supply chain integration. (150 Words /10 marks) |
5. Innovative Biotech Solutions for Farming, Livestock, and Aquaculture
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2105824 )
| Topic: GS3 – Agriculture |
| Context |
|
Power of Biotechnology in Agriculture, Aquaculture, and Animal Sciences
- Biotechnology is transforming agriculture, aquaculture, and animal sciences by improving crops, managing diseases, and promoting sustainable farming.
- Advancements in genome editing, molecular breeding, and biocontrol solutions are increasing productivity and resilience.
Agricultural Biotechnology: Innovations for Sustainable Farming
- Climate-Smart Crops
- A new drought-tolerant and high-yielding chickpea variety, SAATVIK (NC 9), has been approved for cultivation.
- This variety enhances yield under drought stress, improving food security in dry regions.
- Genome-Edited Crops
- Loss-of-function mutations have been introduced in rice genes to boost productivity.
- Genome-edited rice variety MTU-1010 shows higher yield and larger spikes with increased grain numbers.
- Genotyping Arrays
- The 90K Pan-genome SNP genotyping array IndRA for rice and IndCA for chickpea have been commercialized.
- These tools help in DNA fingerprinting, variety identification, and genetic purity testing for better crop development.
- Amaranth Genetic Resources
- A genomic resource database and SNP chip have been developed for amaranth.
- Screening techniques help identify amaranth varieties that combat obesity, aiding in nutritional improvements.
- Fungal Biocontrol
- A nano-formulation from Myrothecium verrucaria has been created to control powdery mildew in tomato and grape.
- This eco-friendly solution reduces the need for chemical pesticides.
- Kisan-Kavach: Safety for Farmers
- A protective suit has been designed to safeguard farmers from pesticide exposure.
- This innovation enhances health safety in agricultural settings.
Animal Biotechnology: Enhancing Livestock Health and Productivity
- India has the largest livestock population in the world, supporting rural livelihoods.
- Innovations in veterinary medicine and livestock management are improving disease resistance and productivity.
Aquaculture and Marine Biotechnology: Boosting Fisheries and Marine Resources
- Improved Shrimp Diet
- Fish meal is a key ingredient in shrimp feeds but has cost and sustainability issues.
- Research has shown that yeast-fermented soybean meal can replace fish meal, improving shrimp growth by 8.5%.
- CIFA-Brood-Vac Vaccine
- A new vaccine has been developed to prevent fish spawn mortality, ensuring healthy aquaculture stocks.
- Cost-Effective Fish Feed Formulation
- Interactive Fish Feed Designer (IFFD) version 2 helps create affordable fish feed using non-conventional ingredients.
Conclusion
- Biotechnology is revolutionizing agriculture, aquaculture, and animal sciences by enhancing crop resilience, livestock health, and marine productivity.
- These innovations contribute to food security, disease management, and sustainable farming.
- As research progresses, biotechnology will continue to strengthen global food systems and environmental sustainability.
| Practice Question: Discuss the role of biotechnology in transforming India’s agriculture and aquaculture sectors. How can these innovations contribute to sustainable food production and environmental conservation? (150 Words /10 marks) |
Prelims Facts
1. How does space travel affect the health of an astronaut?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|

Challenges of Space Travel
- The human body is not designed for space travel, where microgravity and radiation exposure cause various health issues.
- Astronauts face physical and psychological challenges, especially on long-duration missions.
- More research is needed to develop protective measures and personalized health strategies.
Radiation Exposure Risks
- Earth’s atmosphere and magnetic field shield humans from space radiation, but astronauts lack this protection in space.
- High-energy radiation exposure can damage DNA, increase cancer risk, and affect the immune system.
- Neurodegenerative effects may occur due to prolonged exposure.
- Low-Earth orbit missions provide some protection, but deep-space missions, like those to the moon, involve higher radiation doses.
Effects of Microgravity
- Gravity regulates many body functions, and its absence causes fluid shifts, leading to increased intracranial pressure and vision problems.
- Muscles weaken, bones lose density, and the cardiovascular system struggles to regulate blood pressure.
- The inner ear loses its ability to sense movement, causing balance and coordination issues.
Psychological Effects
- Living in confined spaces with limited social interaction can lead to stress, sleep problems, and mood disorders.
Post-Spaceflight Recovery
- Short missions see 95% biological recovery, but longer missions require extended rehabilitation.
- Some health issues, such as vision impairment, may persist after returning to Earth.
2. Our aim is to reach defence exports worth ₹50,000 crore by 2029, says Rajnath Singh
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|
Achievement in Defence Production and Exports
- India has achieved 88% self-sufficiency in ammunition production.
- Defence exports have reached ₹23,000 crore in 2023-24.
- The government aims to increase defence exports to ₹50,000 crore by 2029.
Strengthening the Defence Industry
- The government is focused on building a strong defence industry to ensure national security and economic growth.
- Students, especially from technical institutions, are encouraged to contribute to defence innovation and self-reliance.
Importance of Innovation and Entrepreneurship
- Innovation and knowledge creation are key to India’s technological leadership.
- The government promotes advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and digital technologies.
- Students should adopt the principles of “initiate, improve, and transform (IIT)” to drive change and progress.
India’s Growing Startup Ecosystem
- India has a thriving startup ecosystem, with more than 1.25 lakh startups and 110 unicorns.
- The country is emerging as the third-largest startup hub globally.
- The technological sector in India is expected to grow to $300-350 billion in the next five years.
Growth of India’s Digital Economy
- India has the second-largest telecom sector in the world.
- The success of UPI (Unified Payments Interface) has made India a global leader in digital transactions.
- A digital revolution is underway, and students are encouraged to contribute to India’s digital ecosystem for long-term growth.
3. Internet shutdowns highest in 2024 globally, India tops in government-ordered curbs
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|
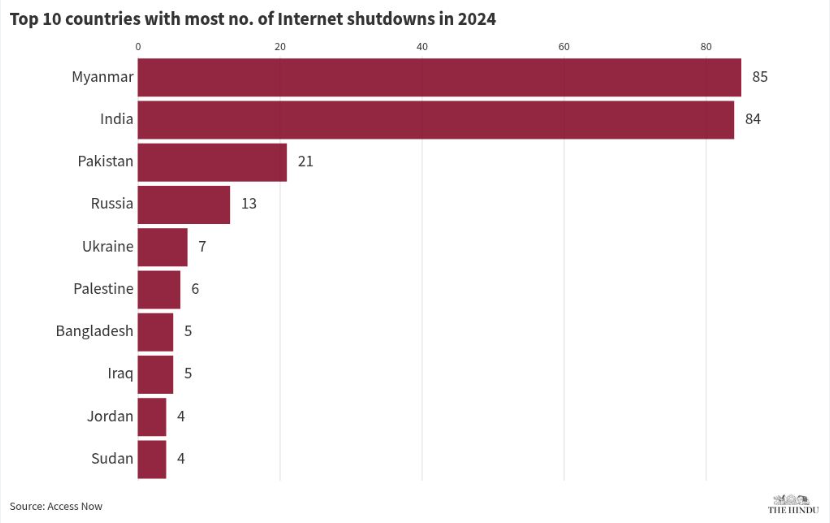

India-Specific Shutdowns
- India imposed 84 internet shutdowns, accounting for 28% of global cases.
- Myanmar experienced the most shutdowns (85), with some imposed by external countries and armed groups.
Shutdowns in Indian States
- Internet shutdowns affected 16 states and union territories in India.
- The highest number of shutdowns occurred in Manipur (21), Haryana (12), and Jammu & Kashmir (12).
- Out of 84 shutdowns, 41 were linked to protests, and 23 to communal violence.
4. The Ancient Tea Horse Road: A Historic Trade Link Between China and India
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained- Page No. – 14)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:

A Historical Analysis
- The Tea Horse Road, an ancient trade network connecting China to India via Tibet, played a significant role in fostering economic and cultural exchanges between the regions.
- Despite being overshadowed by the more famous Silk Road, this route contributed immensely to trade, diplomacy, and cultural interactions over centuries.
Origin and Historical Significance
- The origins of the Tea Horse Road trace back to the Tang dynasty (618–907 CE).
- Historical accounts, including those by the Buddhist monk Yijing, highlight the movement of goods such as sugar, textiles, and rice noodles from China to Tibet and India, while horses, leather, and medicinal herbs were transported to China.
- Over time, the trade became heavily focused on tea and horses, essential commodities due to Tibet’s harsh climate and China’s military needs.
Geographical Scope and Challenges

- Unlike a single defined path, the Tea Horse Road was a complex network of routes originating in southwest China, passing through cities like Dali and Lijiang in Yunnan, reaching Lhasa in Tibet, and branching into present-day India, Nepal, and Bangladesh.
- The journey was arduous, traversing treacherous terrain and elevations as high as 10,000 feet, making it one of the most challenging trade routes in the world.
Economic and Cultural Impact
- Tea Trade: Tea became a staple among Tibetan nomads due to its nutritional value and ability to provide warmth in cold climates. The demand led to the creation of “tea bricks,” which were used as currency in medieval Tibet.
- Horse Trade: Horses were critical for China’s military campaigns and transportation needs. The lack of local horse breeds in China’s central plains made Tibet and Yunnan essential suppliers, giving rise to the complementary tea-for-horses trade system.
Role in Modern History
- During the early 20th century, domestic unrest and foreign interventions in China reinvigorated trade along the route.
- The Tea Horse Road also played a crucial logistical role during World War II, helping transport supplies inland when Japanese forces dominated China’s coastal regions.
- However, after the establishment of the People’s Republic of China in 1949 and subsequent land reforms, the route gradually declined in economic significance.
Contemporary Relevance and Tourism
- In recent decades, China has revived interest in the Tea Horse Road, primarily through tourism.
- Cities like Lijiang have gained recognition as UNESCO World Heritage Sites, highlighting their historical role in regional trade.
- The route now serves as a cultural and historical attraction, reflecting the shared heritage between China, Tibet, and India.
5. Jhumur Dance
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Govt & Politics- Page No. – 07)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:

The Tea Garden Community in Assam
- The tea tribe community in Assam comprises descendants of workers brought from Central India, primarily Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, and West Bengal, during the 19th century under British rule.
- Often subjected to harsh working conditions and exploitation, these migrants faced significant hardships, including high mortality rates due to diseases and brutal punishments for attempting to escape.
- Today, they are concentrated in Upper Assam districts like Tinsukia, Dibrugarh, and Sivasagar, as well as the Barak Valley.
- Although classified under the Other Backward Classes (OBC) category in Assam, they continue to demand Scheduled Tribe (ST) status, highlighting their ongoing socio-economic marginalization despite their crucial role in Assam’s tea economy.
Understanding the Jhumur Dance
- Jhumur is a vibrant folk dance that reflects the cultural identity of Assam’s tea garden community, particularly the Sadan ethnolinguistic group from the Chotanagpur region.
- Central to tea garden festivals like Tushu Puja and Karam Puja, it symbolizes both celebration and resilience.
- Women predominantly perform the dance, adorned in red and white sarees, while men accompany them with instruments such as the madal, dhol, and shehnai.
- The dancers form shoulder-to-shoulder lines, performing synchronized steps to upbeat tunes.
Cultural Significance and Socio-Historical Narratives
- While Jhumur’s melodies are lively, the lyrics often narrate the grim realities of migration, exploitation, and socio-economic challenges faced by the tea workers.
- These songs serve as an oral history of their struggles and a form of social cohesion.
- Jhumur thus plays a dual role: preserving cultural heritage and articulating the collective memory of a marginalized community.
- It has evolved linguistically in Assam, blending Nagpuri, Khortha, and Kurmali languages with Assamese influences.
check more – 24 February 2025 : Daily Current Affairs


