26 July 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Supreme Court Affirms States’ Authority to Tax Mining Activities, Distinguishing Royalties from Taxes
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 17)
| Topic: GS2 – Polity
GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Case Background
- The case, Mineral Area Development Authority v. M/s Steel Authority of India, pending for over 25 years, was decided by an 8-1 split, with Chief Justice DY Chandrachud authoring the majority opinion.
Understanding Royalties and Taxes
- Royalties are fees paid for the right to use a product, distinct from taxes.
- Section 9 of the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957 (MMDRA) requires leaseholders to pay royalties to those leasing the land.
Legal Questions and Historical Decisions
- The Supreme Court’s 1989 India Cement Ltd v. State of Tamil Nadu decision initially deemed royalties as taxes, a position challenged and revisited over the years.
- In 2004, State of West Bengal v. Kesoram Industries Ltd clarified that royalties are not taxes, correcting a typographical error from the India Cement decision.
- The Mineral Area Development Authority case sought to resolve conflicts arising from these interpretations.
Majority Decision: Royalties Are Not Taxes
- The majority ruled that royalties are payments based on specific contracts between leaseholders and lessors, not taxes.
- Taxes serve public purposes, while royalties compensate lessors for exclusive mineral rights.
States’ Power to Tax Mineral Development
- The court held that states can tax mineral development activities, independent of the MMDRA, under Entry 50 of the State List, which grants exclusive state powers over mineral rights taxes.
- Entry 54 of the Union List grants the Centre regulatory power over mines and mineral development but not taxing power.
Dissenting Opinion by Justice Nagarathna
- Justice Nagarathna argued that royalties should be considered taxes to maintain uniform mineral development.
- She believed the MMDRA’s purpose would be undermined by allowing states to impose additional levies.
- She also contended that the MMDRA denuded states’ taxing powers post-enactment and that Entry 49 of the State List does not permit taxing mineral-bearing land.
Implications
- This ruling allows states to generate additional revenue through taxes on mining activities and land used for mining, providing clarity on the distinction between royalties and taxes and reinforcing states’ fiscal autonomy in mineral development.
| Practice Question: Examine the implications of the recent Supreme Court ruling on the distinction between royalties and taxes in the context of mining activities. How does this decision affect the revenue-generating capacities of states and the regulatory framework of mineral development in India? Discuss the potential challenges and benefits arising from this judgment? (250 words/15 m) |
2. Paris 2024 Aims to be the Greenest Olympics Yet, Balancing Ambitious Climate Goals with Real-World Challenges
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 17)
| Topic: GS3 – Environment |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
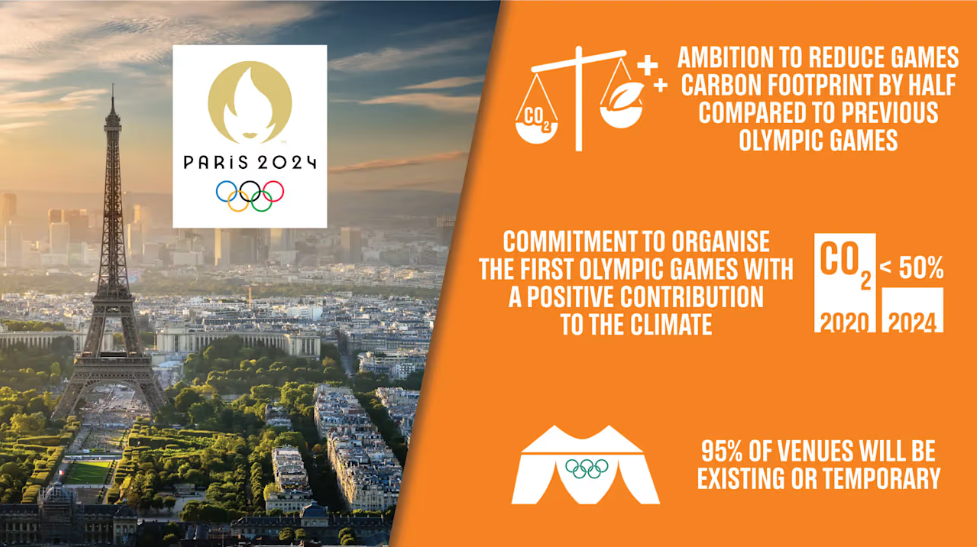
Climate Crisis Context
- Mega sporting events, with their large carbon footprints, might seem wasteful amid a climate emergency.
- However, they can also promote sustainable practices and justify public investments by reducing their environmental impact.
Renewable Energy and Climate-Friendly Initiatives
Paris 2024 will rely on renewable energy sources like geothermal and solar power. Several climate-friendly measures are being implemented:
- Food: Promotion of plant-based, local, and sustainable food, with food-related infrastructure to be reused post-Games.
- Transport: Enhanced public transport accessibility and development of 1,000 km of dedicated cycle lanes.
- Construction: 95% of events will be held in existing or temporary structures. The new Aquatics Centre will be solar-powered and built with recycled, natural materials.
- Living Arrangements: Athletes’ accommodations will use recycled materials, and new apartments in the Olympic Village will become homes post-Games.
Challenges and Realities
- Despite efforts, the Games will generate significant GHG emissions due to the influx of athletes, volunteers, media, and tourists.
- Paris 2024 has a program to offset these emissions, but some experts criticize offsetting as ineffective, advocating for real reductions instead.
Long-Term Impact and Legacy
- Paris 2024 will be the most climate-friendly Olympics to date, providing a blueprint for future sporting events and long-term benefits for Paris through improved public transit and infrastructure.
| Practice Question: Evaluate the environmental strategies of Paris 2024 in its bid to be the greenest Olympics in history. How effective are these strategies in addressing the climate impact of mega-events, and what are the potential challenges and limitations of their implementation? (250 words/15 m) |
3. Google’s Emissions Soar 13% in 2023: AI’s Energy Demand Under Scrutiny
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 17)
| Topic: GS3 – Environment
GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Google’s 2023 Environmental Report: Key Highlights and Analysis
- Increased Emissions: Google’s emissions footprint rose by 13% in 2023, primarily due to increased electricity consumption in data centers and supply chains. This increase is linked to the growing use of artificial intelligence (AI) tools, which require significant energy.
- Energy Consumption by AI: AI tools, including those used in Google’s data centers, consume considerably more energy than traditional searches. AI models, like ChatGPT, can use 10 to 33 times more energy per query compared to a standard Google search. Image-based AI applications require even more energy.
- Impact on Data Centers: The high energy demand of AI increases the workload on data centers, which not only process more data but also need more cooling to handle the generated heat. This contributes to a larger carbon footprint.
- Global Electricity Demand: Data centers currently account for 1% to 1.3% of global electricity demand, a figure expected to rise to between 1.5% and 3% by 2026. Comparatively, electric vehicles consume about 0.5% of global electricity.
- Country-Specific Data: In Ireland, data centers use 18% of national electricity; in the U.S., they account for 1.3% to 4.5%. India’s data is not specified, but growth in AI and data centers is expected.
- Water Usage: Data centers also have significant water demands for cooling. For example, a center in Iowa serving OpenAI’s GPT-4 consumed 6% of the district’s water supply in July 2022.
- Future Implications: The increasing deployment of AI in India will likely lead to higher environmental costs. It’s crucial for companies to enhance efficiency and minimize emissions.
- Alternative Perspectives: While AI increases energy use, it also holds potential for reducing global emissions by 5-10% by 2030 through optimized industrial and corporate practices. This could generate substantial economic value.
Conclusion:
- The rise in emissions due to AI and data centers poses significant environmental challenges, but strategic implementation and efficiency measures could mitigate these impacts while leveraging AI’s benefits for global emission reductions.
| How AI Can Help in Addressing Climate Change? |
Designing materials with reduced resource usage, and improved battery storage, and enhanced carbon capture capabilities contributes to sustainability efforts.
For example, Google has created artificial intelligence that’s able to save the amount of electricity it uses to power its data centres. Using machine learning developed by the firm’s AI research company, DeepMind, it was possible to reduce the energy used for cooling the centres by a staggering 40%.
|
| PYQ: PYQ: With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
1) Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units 2) Create meaningful short stories and songs 3) Disease diagnosis 4) Text-to-Speech Conversion 5) Wireless transmission of electrical energy Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only (b) 1, 3 and 4 only (c) 2, 4 and 5 only (d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 Ans: (b) |
| Practice Question: How is the increasing deployment of artificial intelligence (AI) tools impacting the energy consumption and environmental footprint of data centers, and what measures can be implemented to mitigate these effects while leveraging AI’s potential benefits? (250 words/15 m) |
4. India’s illegal coal mining problem
(Source – The Hindu, Text & context- Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Incidents of worker fatalities in illegal coal mines:
- Apart from this case, there are ample f examples of how illegal coal mining has led to worker fatalities in India, for Instance:
- On June 2023, three people, including a 10-year-old child, died in a mine collapse at Dhanbad, Jharkhand.
- In October 2023, at least three people were killed in a mine collapse at Paschim Bardhaman, West Bengal.
Responsibility for dealing with illegal Mining:
- Illegal mining constitutes a law and order problem, which is a State list subject. Hence, the onus of dealing with it falls on State governments rather than the Union government.
- State governments are responsible for dealing with illegal mining, rather than the Union government.
Legal Framework:
- The Coal Mines (Nationalisation) Act of 1973 is the central legislation that determines eligibility for coal mining in India.
- Coal in India was nationalized in two phases: first with the coking coal (used for the production of coke in the steel industry) in 1971-72, and then with the non-coking coal mines in 1973.
Various factors contribute to illegal coal mining in India.
- The high demand for coal often outstrips the legal supply, prompting illegal supply.
- Many areas that are rich in coal are also situated close to homes for populations struggling with poverty and unemployment, which contributes to illegal mining in these areas.
- Weak mining regulations and inadequate monitoring in remote areas further led to weaker enforcement and resulted in the rise of coal mafias.
- Illegal coal mining also receives support from political leaders in areas where it is prevalent.
Characteristics of Illegal Coal Mining
- Illegal mining is often carried out using rudimentary techniques like surface mining and rat-hole mining despite a blanket ban on such mining by the NGT in 2014.
- Minimal operational costs also lead to significant profits, making illegal mining lucrative.
Reasons for Worker Fatalities in Illegal Coal Mines
- The primary reason for the deaths is a lack of safety equipment and protocols.
- Increased respiratory risks faced by miners due to inhaling coal dust.
- Illegal mines lack proper structural support to extract coal, making working conditions hazardous and vulnerable to cave-ins, landslides, and explosions.
- Workers are exposed to high levels of toxic substances like lead and mercury, causing acute poisoning or long-term chronic medical conditions.
- The lack of proper training, quick response facilities, and knowledge in case of emergencies are also some of the reasons.
Challenges in Curbing Illegal Coal Mining
- The Union government often shifts the blame to State authorities since it is a law and order issue.
- The high demand for coal as a fuel makes illegal mining rampant and challenging to control.
- Bureaucratic hurdles and inefficiency in governance also led to illegal mining to exist.
- There is a lack of effective governance and regulation, and also there is a need for a comprehensive approach to address the issues.
PYQ:
2. What are the consequences of illegal mining? Discuss the ministry of environment and forests’ concept of “GO AND NO GO” zones for coal mining. (200 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2013) |
5. PM to visit kargil on the occasion of the 25th Kargil Vijay Diwas
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2036644 )
| Topic: GS3 – Defence |
| Context |
| ● PM to visit kargil on 26th july to pay homage and to carry out first blast of the strategic shinkun la tunnel project |
Analysis of the news:
- On the occasion of the 25th Kargil Vijay Diwas on 26th July 2024, PM Modi will visit the Kargil War Memorial to pay homage to the bravehearts who made the supreme sacrifice in the line of duty.
- After that PM will also carry out the first blast of the Shinkun La Tunnel Project, virtually
- Once completed, it will be the highest tunnel in the world.
About Shinkun La Tunnel Project:
- The 1-kilometre-long twin-tube tunnel will be constructed at an altitude of approximately 15,800 feet on the Nimu-Padum-Darcha road.
- It aims to provide all-weather connectivity between Himachal Pradesh and the Union Territory of Ladakh.
- The tunnel will be a vital link that connects the Zanskar Valley in Ladakh with the Lahaul Valley in Himachal Pradesh.
- The tunnel is equipped with firefighting, mechanical ventilation, communication, and supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems.
- The Shinkun La tunnel will not only ensure swift and efficient movement of the armed forces and equipment but also foster economic and social development in Ladakh.
6. India’s Installed Nuclear Power Capacity to Triple by 2031-32
(Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2037046)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Nuclear Power Capacity
- As India aims to achieve Net Zero target by 2070, the country’s installed nuclear power capacity is projected to nearly triple by 2031-32.
- The country’s nuclear power capacity has increased by more than 70% in the last 10 years, which has increased from 4,780 MW in 2013-14 to 8,180 MW at present across 24 nuclear power reactors.
Electricity Generation
- The annual electricity generation from nuclear power plants has also increased from 34,228 million units in 2013-14 to 47,971 million units in 2023-24.
Future Projects
- At present, 21 reactors with a total capacity of 15,300 MW are at various stages of implementation by the Nuclear Power Corporation India Ltd (NPCIL).
7. Discovery of Lithium Resources in Mandya and Yadgiri districts Karnataka
(Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2037050)
| Topic: GS3 – Economy |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Lithium Exploration and Resources
- AMD has established 1,600 tonnes (G3 stage) of Lithium resources in the Marlagalla area, Mandya district,
- Ongoing Exploration: Preliminary surveys and limited subsurface exploration have been carried out in the Yadgiri district to know about the deposits.
- Potential Exploration: AMD is also investigating potential lithium deposits in the Korba District of Chhattisgarh.
- Other Geological Domains: Other potential geological domains for lithium exploration include major mica belts in Rajasthan, Bihar, and Andhra Pradesh, as well as pegmatite belts in Odisha, Chhattisgarh, and Karnataka.
Uranium Exploration
- Also, the preliminary survey carried out recently by AMD in Himachal Pradesh has led to the identification of surface uranium occurrence in Masanbal, Hamirpur district.
International Cooperation
- Government of India and Government of Russian Federation have expressed interest to expand the cooperation in the field of the use of nuclear energy for peaceful purposes including cooperation in the field of Small Modular Reactor.
PRELIMS FACTS
1. Listeriosis Outbreaks in US and Canada: Multiple Cases and Fatalities Linked to Contaminated Foods
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 17)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
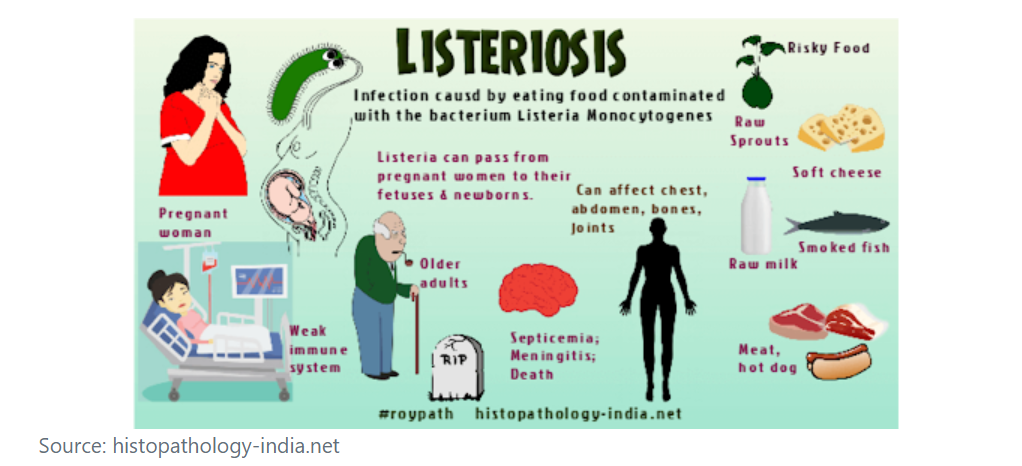
Outbreak Details:
- Two separate listeriosis outbreaks have been reported, affecting the US and Canada.
- In the US, 28 people across 12 states have been hospitalized, with two fatalities. In Canada, 12 cases have been reported in three provinces, with two deaths.
Listeria and Listeriosis:
- Listeria monocytogenes, the bacteria causing listeriosis, is found in soil, vegetation, water, sewage, and animal and human feces.
- It commonly contaminates certain foods like milk, raw sprouts, soft cheeses, and deli meat.
Risk Factors and Symptoms:
- While many who ingest contaminated food remain asymptomatic, vulnerable populations (e.g., the elderly, immunocompromised individuals, pregnant women) are at higher risk.
- Symptoms include vomiting, nausea, cramps, severe headache, constipation, and fever.
Treatment:
- Intestinal listeriosis can be treated with antibiotics. Invasive listeriosis, where the infection spreads beyond the intestines, may require urgent hospitalization.
- Approximately 1 in 6 non-pregnant individuals with invasive listeriosis die from the infection.
Recent Outbreak Sources:
- The US outbreak is linked to raw or undercooked meat from delis.
- In Canada, the outbreak is associated with plant-based refrigerated beverages, including products from Danone’s Silk brand, which have been recalled.
Preventive Measures:
- The CDC advises high-risk groups to avoid unheated deli meats, cheeses, and salads, and instead choose packaged items.
- It is crucial to heat deli meats to an internal temperature of 165°F and to thoroughly sanitize surfaces and equipment that have been in contact with these foods.
- Medical attention should be sought if symptoms arise.
2. Government Revamps Skill Loan Scheme, Raises Loan Limit to Rs 7.5 Lakh to Boost Access to Skill Development
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt & Politics; Page: 07)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
About Skill Loan Scheme:
- It was introduced in July, 2015, to offer institutional credit to individuals pursuing skill development courses aligned with National Occupations Standards and Qualification Packs.
- These courses are conducted by training institutes following the National Skill Qualification Framework (NSQF) and lead to certifications, diplomas, or degrees.
- The Scheme applies to all member banks of the Indian Banks’ Association (IBA) and other banks and financial institutions as advised by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
Revamped Model Skill Loan Scheme: Key Highlights and Analysis
- Increased Loan Limit: The Indian government has relaunched the ‘model skill loan scheme’ with an increased maximum loan limit of Rs 7.5 lakh, up from the previous Rs 1.5 lakh, aiming to make skill development courses more accessible.
- Broader Lending Framework: The scheme now includes non-banking financial companies (NBFCs), NBFC-Microfinance Institutions (MFIs), and small finance banks as eligible lenders, expanding beyond traditional banks.
- Expanded Course Eligibility: The scheme covers more skill development courses, including those not aligned with the National Skill Qualification Framework (NSQF), provided they are listed on the Skill India Digital Hub platform.
- Rationale for Changes: The previous version of the scheme had low uptake, with Rs 115.75 crore in loans extended to 10,077 borrowers by March 31. The limited loan amount and rising course fees were barriers.
- Government’s Vision: The scheme’s revamp aligns with a broader vision for strategic skill development, anticipating future technological advancements and job market changes by 2047.
- Expected Impact: The government expects the revamped scheme to benefit 25,000 students annually, better preparing them for a dynamic job market.
3. White Category Industries to Be Exempt from Pollution Control Permits Under New Draft Notifications
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt & Politics; Page: 07)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Changes to Pollution Control Permits for ‘White Category’ Industries: Key Points
- Exemption from Permissions: Industries categorized as ‘white’ by the Central Pollution Control Board, deemed non-polluting, will no longer need prior state pollution control board permissions— ‘consent to establish’ (CTE) and ‘consent to operate’ (CTO)—under the Air Act, 1981, and Water Act, 1974.
- Draft Notifications: The Environment Ministry has issued two draft notifications proposing the elimination of CTE permits for projects requiring prior environmental clearance (EC). The CTE conditions may be integrated into the environmental clearance process.
- Current Requirements: Under existing regulations, CTE and CTO are required before construction and operation of units.
- Self-Declaration: Exempt industries must inform state pollution control boards of their operations through self-declarations rather than seeking formal permissions.
- Public Feedback: The draft notifications are open for public comments and objections for 60 days.
4. Rashtrapati Bhavan Halls Renamed to Reflect Indian Cultural Values and Republic Ideals
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt & Politics; Page: 07)
| Context: |
|
 Rashtrapati Bhavan’s Ashok Hall
Rashtrapati Bhavan’s Ashok Hall
 Rashtrapati Bhavan’s Durbar Hall
Rashtrapati Bhavan’s Durbar Hall
Analysis of the Renaming of Rashtrapati Bhavan Halls
Cultural and Symbolic Justification:
- Ganatantra Mandap: The term ‘Durbar’ is associated with colonial-era courts and assemblies, while ‘Ganatantra’ (republic) aligns with India’s current status and historical roots in republic values.
- Ashok Mandap: ‘Ashok’ refers to Emperor Ashoka, symbolizing peace and unity. Renaming aims to remove colonial influences and emphasize cultural significance.
Historical Context:
- Amrit Udyan: Previously known as the Mughal Gardens, the gardens were renamed in January 2023 as part of the 75th Independence Day celebrations to reflect India’s heritage.
- Rajpath to Kartavya Path: In 2022, the pathway was renamed to symbolize a shift from colonial to Indian values.
Government Perspective:
- The renaming efforts are framed as part of a broader initiative to remove colonial remnants from Indian public spaces, aligning with the Prime Minister’s vision for a post-colonial India.
5. High-Level Committee Approves ₹3,945 Crore for Disaster Mitigation and Capacity Building Projects Across India
(Source: Indian Express; Section: The Second Page; Page: 02)
| Context: |
|
Approval of Disaster Mitigation Projects by High-Level Committee
- Urban Flooding Projects: Rs 2,514.36 crore approved for urban flood management in Mumbai, Kolkata, Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad, and Pune.
- Fire Services Expansion: Rs 810.64 crore allocated for modernizing fire services in Assam, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu under the Yuva Aapda Mitra Scheme.
- Glacial Lake Outburst Flood Risk: Rs 150 crore approved for mitigating glacial lake outburst flood risks in Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh.
- Disaster Training Program: Rs 470.50 crore approved for the Yuva Aapda Mitra Scheme to train 2.37 lakh volunteers in disaster preparedness and response across 315 disaster-prone districts.
| About Apada Mitra Scheme |
Aim:
Objectives:
|
6. ‘Focus is on raising the employment intensity of growth’
(Source – The Hindu, Business- Page No. – 12)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- The Union Budget 2024-25 also focuses on giving direct thrust for job creation, especially for first-time job seekers and breaking the “no experience, no jobs” barrier in the labour market.
- The government announced an employment-linked scheme of incentives; with this scheme, the government is,
- Using scalable incentives to nudge companies towards hiring more people
- Incentivizing companies to hire first-time job seekers and,
- Aiming to increase the rate of employment growth for a given level of GDP growth
- The objective of the Scheme is
- To help first-time job seekers break into the employment market
- To overcome the entry barrier for those without experience
- To widen the pool of people selected for jobs



