26 November 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. ISRO to Launch ESA’s Proba-3 Mission for Groundbreaking Study of the Sun’s Corona
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 18)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:

What is Proba-3?
- Proba-3, costing €200 million, comprises two satellites flying in a highly elliptical orbit of 600 x 60,530 km with a 19.7-hour period.
- The satellites will separate post-launch and work in tandem to form a solar coronagraph, blocking sunlight to observe the solar corona.
- The mission aims to provide six hours of uninterrupted corona observation, equivalent to 50 solar eclipses annually, over its two-year lifespan.
Scientific Objectives
Proba-3 will study the Sun’s corona and space weather phenomena like solar storms and winds, which impact satellite operations and Earth’s communication systems. The mission will deploy three instruments:
- ASPIICS (Coronagraph): Focuses on the Sun’s outer and inner corona using an occulting disk for detailed imaging.
- DARA: Measures the Sun’s total energy output (solar irradiance).
- 3DEES: Analyzes electron fluxes in Earth’s radiation belts for space weather data.
Uniqueness of Proba-3
The mission mimics a solar eclipse using precision formation flying:
- The Occulter Spacecraft casts a shadow 150 meters away onto the Coronagraph Spacecraft.
- This configuration blocks the Sun’s light, enabling detailed corona observations.
- Precise autonomous positioning will be maintained within millimetres for extended periods.
- This setup allows unprecedented study durations, far exceeding natural solar eclipse events.
India’s Strategic Gains
- ISRO’s involvement underscores its cost-effective and reliable launch capabilities, strengthening its reputation in global space missions.
- Indian scientists may gain exclusive data access, facilitating collaborative research with ESA and leveraging insights from Aditya L1, India’s first solar mission.
- This collaboration fosters advancements in solar physics and reinforces India’s position in space science.
Conclusion
- Proba-3 marks a significant step in solar research, combining technological innovation and international collaboration.
- With ISRO’s launch prowess and Indian scientists’ potential contributions, this mission could unlock new insights into the Sun’s corona and space weather, benefitting both India and global scientific communities.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the Proba-3 mission in advancing solar research and the role of international collaboration in enhancing India’s space capabilities and scientific contributions. (250 words/15 m) |
2. India’s Trade Deficit: A Reflection of Strength in Services and Investment Attractiveness
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 18)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Capital Inflows and Current Account Deficit: Interlinked Realities
Capital inflows and current account deficits are intrinsically connected. When India attracts foreign investment, it supplements domestic savings, enabling higher investment and growth. However, this inflow must balance with either a current account deficit or reserve accumulation.
- Reserve Accumulation: While reserves act as a buffer against economic shocks, excessive accumulation is costly.
- Sensible Deficit Policy: India maintains a stable current account deficit (~2% of GDP) alongside capital inflows, demonstrating prudent economic management.
India’s Goods Deficit and Services Strength
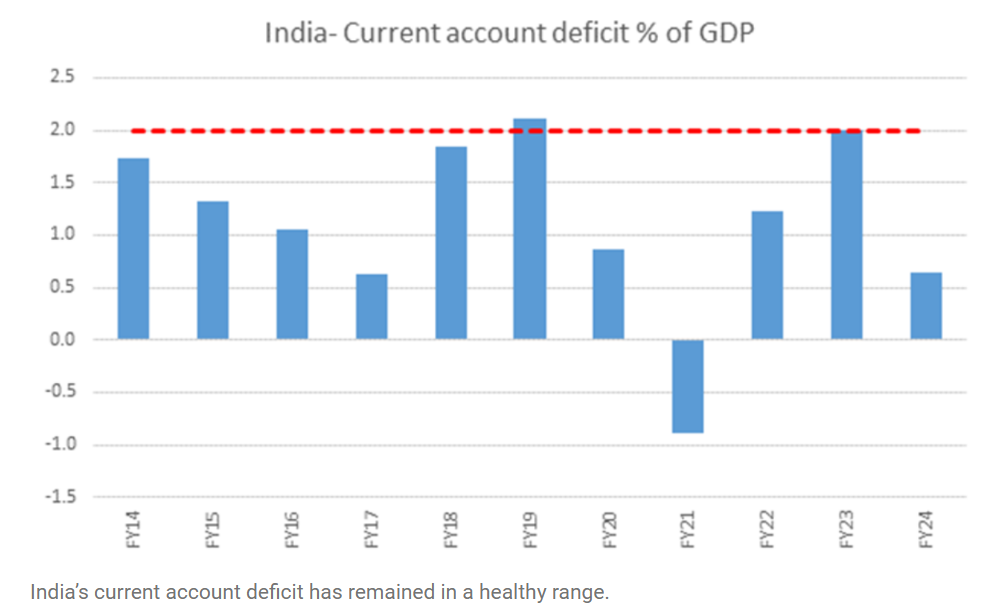
India’s comparative advantage in services drives its net export of services and its goods trade deficit. This deficit does not signal weak manufacturing but reflects India’s focus on its strengths:
- Export Strengths: Pharmaceuticals, automobiles, and auto components dominate India’s goods exports.
- Comparative Advantage: India’s smaller manufacturing exports compared to Vietnam or Bangladesh highlight its greater productivity in services, not an absolute lack of manufacturing efficiency.
The Role of Domestic Demand in Manufacturing Growth
- For manufacturing to grow faster, domestic demand must play a central role. Stronger local demand, combined with a stable current account deficit, would directly drive greater production.
- This approach aligns with India’s economic realities, where manufacturing is adequately competitive but outpaced by services in comparative advantage.
Conclusion: Rethinking the Trade Deficit
- India’s trade deficit reflects its economic structure, where services dominate due to comparative advantage and foreign investment inflows support growth.
- The path to boosting manufacturing lies in harnessing domestic demand while maintaining a balanced current account deficit.
| What Measures can be taken to Control the Trade Deficit? |
|
Trade Agreements: Negotiating and implementing FTAs with key partners can reduce tariffs and other barriers to Indian exports, making them more competitive in foreign markets. Improving Export Infrastructure: Investing in infrastructure development, such as modernising ports, roads, and logistics networks can streamline the export process and reduce transportation costs. Import Substitution: The government shall encourage the use of domestic substitutes for imported products through public procurement policies and campaigns promoting locally made goods. Rationalise Imports: Analysing import data can help identify non-essential or luxury goods that could be substituted with domestically produced alternatives. Skilling the Workforce: Investing in skill development programs can create a workforce with the expertise needed for modern industries, enhancing domestic production capabilities and reducing reliance on imports. Managing Currency and Debt Levels Effectively: The RBI should manage the rupee’s exchange rate effectively, aiming for a balance that promotes exports without causing excessive depreciation. The government should focus on fiscal consolidation to reduce its debt burden, creating a more stable economic environment for domestic industries to flourish. |
| Practice Question: India’s trade deficit is often misunderstood as a weakness in manufacturing, whereas it reflects the country’s comparative advantage in services and foreign investment appeal. Critically analyze this statement and discuss the role of domestic demand in boosting manufacturing growth. (250 words/15 m) |
3. On stubble burning and satellite data
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Context |
|
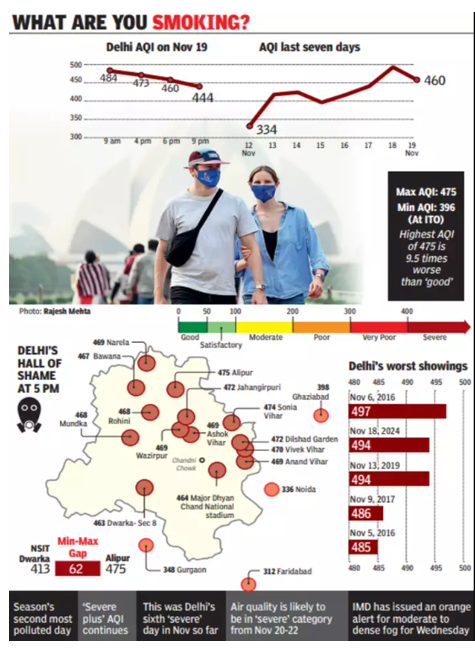
Air Quality Crisis in Delhi Post-Deepavali
- Despite GRAP Stage IV measures, Supreme Court interventions, and actions by the Delhi government, Delhi’s air quality remains poor after Deepavali.
- Farm fires in Punjab and Haryana, where paddy stubble is burned for wheat sowing, are significant contributors to the pollution.
- Although not solely responsible, these fires are under scrutiny due to their severe impact on air quality.

Tracking Farm Fires Using Satellites
- Paddy Stubble Burning: Farmers burn stubble post-rice harvest to prepare for wheat sowing due to time and cost constraints.
- NASA Satellites: India uses data from Aqua and Suomi-NPP satellites to track farm fires.
- Aqua, launched in 2002, uses the MODIS instrument to monitor atmospheric changes.
- Suomi-NPP, launched in 2011, employs the VIIRS instrument for fire and smoke detection and the Ozone Mapping Profiler Suite for aerosol tracking.
- Both satellites pass over locations at 1:30 PM and 1:30 AM local time, capturing visible and infrared images.
Emerging Controversy Over Satellite Data
- A senior NASA scientist noted fewer fires in 2024 but highlighted the possibility of burning after satellite overpass times.
- Comparisons with South Korea’s GEO-KOMPSAT 2A satellite showed smoke increasing after Aqua and Suomi-NPP’s daily passes.
- Aerosol levels in the atmosphere remain consistent with previous years, contradicting reduced fire claims.
| Discrepancy in Reporting and Data |
|
Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM):
Goodhart’s Law:
|
Government’s Response and Challenges
- Supreme Court Criticism: CAQM has been criticized for its inefficacy in reducing stubble burning and air pollution.
- CAQM Claims: Asserted a 71% reduction in Punjab and 44% in Haryana between 2020 and 2024.
- Efforts to develop accurate satellite protocols are underway, with collaboration with NRSC and ISRO.
Indian Satellites and Limitations
- INSAT-3DR: Provides coarse-resolution data unsuitable for precise fire detection.
- RESOURCESAT Satellites: Offer better spatial resolutions with instruments like LISS and AWiFS but still face limitations.
- GISAT-1: Could have contributed but failed during its launch in 2021.
Conclusion
- The controversy around farm fires highlights the urgent need for accurate measurement systems and actionable solutions to mitigate Delhi’s recurring air quality crisis.
- Enhanced technology and inter-agency coordination are critical.
| PYQ: Mumbai, Delhi and Kolkata are the three megacities of the country but the air pollution is a much more serious problem in Delhi as compared to the other two. Why is this so? (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2015) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the challenges in managing air pollution in Delhi caused by farm fires in neighbouring states. Highlight the role of technology in monitoring and the importance of inter-state collaboration to address this recurring issue. (250 Words /15 marks) |
4. MACE in Ladakh opens its one-of-a-kind eye to cosmic gamma rays
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 9)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
Significance of Gamma Rays
- Gamma rays, the highest-energy light in the electromagnetic spectrum, are produced by cosmic events like pulsars, black holes, and supernovae.
- These rays are blocked by Earth’s atmosphere, making indirect ground-based detection crucial.
- When gamma rays interact with the atmosphere, they produce Cherenkov radiation, a faint blue light that MACE detects.
| Overview of MACE Telescope |
|
Location and Altitude: Situated in Hanle, Ladakh, at an altitude of 4.3 km, making it the world’s highest imaging Cherenkov telescope. Size and Features: Features a 21-meter-wide dish, the largest in Asia and second-largest globally. Technology and Components: Equipped with 356 honeycomb-structured mirror panels and a high-resolution camera with 1,088 photomultiplier tubes. Construction and Collaboration: Built by BARC, TIFR, ECIL, and the Indian Institute of Astrophysics, showcasing indigenous capabilities. Scientific Goal: Studies gamma rays with over 20 billion eV energy and explores cosmic phenomena like black holes, pulsars, and dark matter. Advanced Mechanics: Has a 180-tonne moving weight and operates on a 27-meter-wide curved track for precise sky observations. Significance: Marks a significant step in India’s gamma-ray astronomy and high-energy astrophysics research. |
Scientific Goals
- MACE studies gamma rays with energy exceeding 20 billion eV, focusing on phenomena like black holes, pulsars, and gamma-ray bursts.
- It aims to search for dark matter particles like WIMPs, potentially produced in galactic centers and clusters.
India’s Milestone
- The MACE telescope advances India’s five-decade-long journey in gamma-ray astronomy.
- Its indigenous design and capabilities position India as a leader in high-energy astrophysics and particle physics research.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the MACE telescope and its potential in understanding cosmic phenomena like dark matter and gamma rays (150 Words /10 marks) |
5. ‘Secular, socialist’ are an inalienable part of the Constitution, to stay in Preamble, orders SC
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Context |
|
Challenge to Inclusion in the Preamble
- A batch of petitions challenged the inclusion of the words ‘socialist’ and ‘secular’ in the Preamble through the 42nd Constitution Amendment of 1976.
- Petitioners argued that these terms, inserted retrospectively from the adoption of the Constitution in 1949, were unconstitutional and that the inclusion of ‘socialist’ limited economic policy choices.
Supreme Court’s Decision
- The Supreme Court ruled that the inclusion of ‘socialist’ and ‘secular’ was valid and part of the Constitution.
- The court dismissed the petitioners’ arguments as flawed and questioned their motives, noting the delay of nearly 44 years in filing the case.
Preamble and Constitutional Amendment
- The Preamble is an integral part of the Constitution, and Parliament has the power to amend it under Article 368.
- The retrospective amendment was upheld, affirming that the Constitution is a living document adaptable to changing needs.
| Interpretation of Words ‘Secular’ and ‘Socialist’ |
|
Supreme Court’s Interpretation of ‘Secular’ The Supreme Court explained that secularism in India means the State neither supports nor discriminates against any religion. It ensures equal respect for all faiths and guarantees citizens’ rights to freely practice their religion. This interpretation is grounded in Articles 14, 15, and 16 of the Constitution, which prohibit discrimination on the basis of religion. These provisions ensure equal protection under the law and guarantee equal opportunities in public employment, reinforcing the secular ethos of the Constitution. Supreme Court’s Interpretation of ‘Socialist’ The Supreme Court clarified that ‘socialist’ in India’s context signifies the state’s commitment to being a welfare state, ensuring equality of opportunity and socio-economic justice. It does not dictate a specific economic policy, whether left or right. The term reflects the Constitution’s goal of promoting social welfare and addressing inequality. India adopts a mixed economy model, where both the private sector and the government play crucial roles in fostering economic development. |
| PYQ: How is the Indian concept of secularism different from the western model of secularism? Discuss. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2018) |
| Practice Question: Analyze the significance of the terms ‘secular’ and ‘socialist’ in the Indian Constitution, highlighting their implications for governance, socio-economic policies and economic development. (250 Words /15 marks) |
6. Increase in Tiger Population
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2076921®=3&lang=1 )
| Context |
|
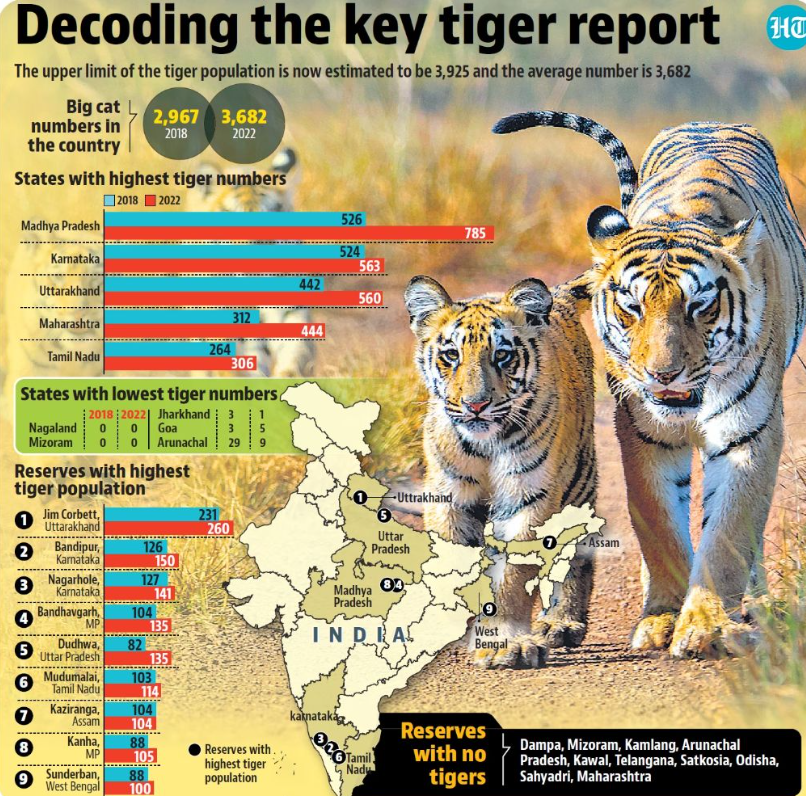
Tiger Population in India: Growth and Estimation
- The All India Tiger Estimation 2022 reported a significant increase in the tiger population, estimated at 3,682 (range: 3,167–3,925), compared to 2,967 in 2018 and 2,226 in 2014.
- The tiger population in India is growing at an annual rate of 6% in consistently sampled areas.
Three-Pronged Strategy for Managing Human-Wildlife Interactions
1. Material and Logistical Support
- The Centrally Sponsored Scheme of Project Tiger provides funding for tiger reserves to enhance capacity through infrastructure and material acquisition.
- Activities include:
- Ex-gratia payments and compensation for conflict cases.
- Awareness campaigns to educate the public on man-animal conflict.
- Procurement of immobilization equipment and training for forest staff.
2. Restricting Habitat Interventions
- Habitat interventions are aligned with the carrying capacity of tiger reserves to minimize wildlife spillover and conflict.
- Buffer zones have restricted interventions to facilitate dispersal to other rich habitats.
3. Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
- The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) has issued SOPs to address:
- Straying of tigers into human areas.
- Tiger depredation on livestock.
- Rehabilitation of tigers in low-density areas.
Tiger Population Across Landscapes (2006–2022)
- Shivalik-Gangetic Plains: Increased from 297 in 2006 to 819 in 2022.
- Central India and Eastern Ghats: Grew from 601 in 2006 to 1,439 in 2022.
- Western Ghats: Rose from 412 in 2006 to 1,087 in 2022.
- North-Eastern Hills and Brahmaputra Floodplains: Increased from 100 in 2006 to 236 in 2022.
Tiger Population in 2022: States with Maximum Population
| State | Tiger Population (2022) |
| Madhya Pradesh | 785 |
| Karnataka | 563 |
| Uttarakhand | 560 |
| Maharashtra | 444 |
| Tamil Nadu | 306 |
| Practice Question: Discuss the role of the All India Tiger Estimation and the National Tiger Conservation Authority in conserving India’s tiger population. What can be the strategy to address human-wildlife conflicts? (250 Words /15 marks) |
PRELIMS FACTS
1. Centre Launches ₹2,481 Crore National Mission on Natural Farming to Promote Sustainable Agriculture
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt & Politics; Page: 12)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:

Objective and Rationale
- The mission seeks to foster an ecosystem for sustainable and chemical-free farming to improve soil quality and human health.
- Highlighting the growing need for eco-friendly agriculture, Information and Broadcasting Minister Ashwini Vaishnav called the decision “path-breaking,” emphasizing its role in promoting health-conscious and environmentally sustainable farming practices.
Implementation and Scope
- Natural farming will be promoted on a mission mode following successful pilot experiments conducted between 2019-20 and 2022-23.
- Currently, 10 lakh hectares of agricultural land in India are under natural farming.
- The mission intends to scale this up significantly, targeting 1 crore farmers across the country to transition toward natural farming methods.
Budget and Coverage
- The scheme has been allocated ₹2,481 crore, reflecting the government’s commitment to advancing sustainable agriculture.
- The coverage will include extensive training, awareness campaigns, and the provision of resources to encourage farmers to adopt chemical-free farming techniques.
Significance
- The NMNF is a strategic move to address pressing agricultural challenges such as declining soil fertility, over-reliance on chemical fertilizers, and the environmental impact of conventional farming methods.
- By emphasizing natural farming, the initiative aims to ensure food security, environmental sustainability, and better public health outcomes.
2. Union Cabinet Approves ₹1,435 Crore PAN 2.0 Project to Modernize Taxpayer Services and Introduce QR Code-Enabled PAN Cards
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Cover Page; Page: 01)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:

Key Features of PAN 2.0
- QR Code Integration: New PAN cards will feature a QR code for enhanced functionality and security. Existing cardholders can upgrade their cards free of cost.
- Common Business Identifier: PAN will serve as a unified identifier across specified government digital systems, streamlining processes for businesses.
- Digital Backbone Overhaul: The system will undergo a complete upgrade, replacing software that is 15-20 years old, ensuring modern, agile, and secure infrastructure.
- Focus on E-Governance: The project emphasizes paperless, online processes and a robust grievance redressal system for improved taxpayer services.
Benefits for Stakeholders
- Individuals: Improved ease of access with upgraded digital systems.
- Businesses: Elimination of multiple identifiers, simplifying compliance.
- Government Agencies: Consistent and unified data for enhanced governance.
Scale and Impact
- Approximately 78 crore PAN cards have been issued, with 98% belonging to individuals.
- The transformation will align the PAN system with contemporary technology, making it a “single source of truth” for taxpayer identification while bolstering data security and consistency.
3. Cephalopod-Inspired Ingestible Capsules Offer Breakthrough in Oral Drug Delivery, Eliminating Need for Injections
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 18)
| Context: |
| Researchers from MIT, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Novo Nordisk have developed ingestible capsules capable of delivering drugs like insulin directly into the digestive system. Inspired by the jet propulsion of cephalopods, these capsules offer a potential alternative to traditional drug injections. |
Analysis of News:
Significance of the Innovation
- Alternative to Injections: These capsules address the challenges of administering large-molecule drugs, which are usually degraded by digestive enzymes or the liver when taken orally.
- Patient Comfort: Unlike injections, capsules eliminate risks like infection, skin irritation, and discomfort, making drug administration simpler and less invasive.
- High Efficiency: The technology significantly improves drug bioavailability, ensuring more effective absorption in animal models, according to experts like Omid Veiseh of Rice University.
Design and Mechanism
- Cephalopod Inspiration: The jet propulsion mechanism of squids and octopi inspired the capsule’s design, mimicking their ability to eject substances with precision.
- Propulsion System: Capsules use compressed carbon dioxide or coiled springs to release a jet of liquid drugs. A carbohydrate-based trigger dissolves upon contact with stomach humidity or acidity, activating the propulsion system.
- Targeted Delivery: The jets ensure drugs are absorbed directly into gastrointestinal tissue before breakdown by the body.
Potential Impact
- This breakthrough could revolutionize the oral delivery of macromolecule drugs like insulin, vaccines, and antibodies.
- By eliminating the need for injections and enhancing bioavailability, the capsules promise better patient compliance and a more efficient drug delivery system.
4. Cabinet approves next phase of Atal Mission
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
| The Union Cabinet approved the continuation of the Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) with an enhanced allocation of ₹2,750 crore until March 2028.AIM 2.0 aims to strengthen India’s global competitiveness and drive job creation, innovation, and high-impact services across sectors. |
Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) Overview:
- Launched by NITI Aayog in 2016, AIM is India’s flagship initiative to foster innovation and entrepreneurship.
- Aimed at creating a culture of problem-solving and innovative mindsets in schools and an entrepreneurial ecosystem in universities, research institutions, and the private sector.
- Holistic approach includes establishing Atal Tinkering Labs (ATLs) in schools, incubation centres in universities, and community innovation centres in underserved regions.
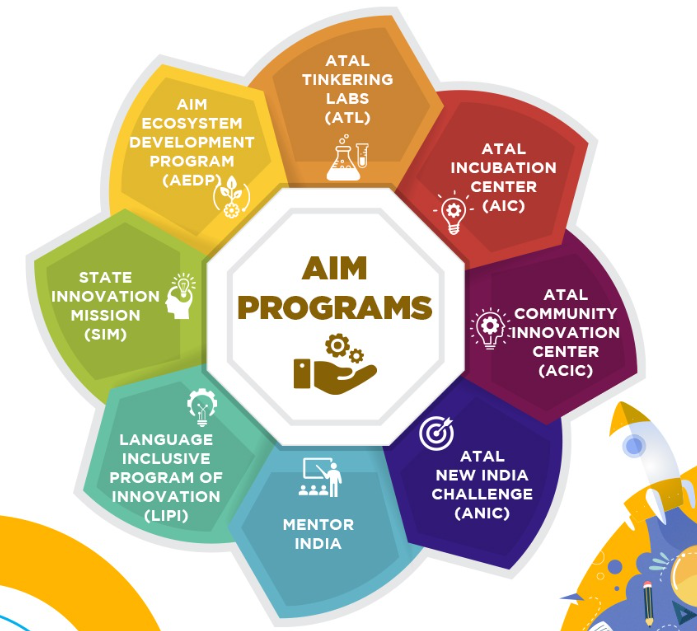
Key Initiatives:
- Atal Tinkering Labs (ATL):
- Established in 10,000 schools across India for grades 6-12, aiming to foster curiosity and innovation using technologies like IoT, 3D printing, robotics, and miniaturized electronics.
- Atal Incubation Centres (AICs):
- 72 centres supporting 3500+ startups, providing mentorship, funding, and technical facilities to foster innovation and entrepreneurship.
- Focus on startups in sectors like HealthTech, EdTech, FinTech, SpaceTech, and more.
- Atal Community Innovation Centres (ACICs):
- Targeting under-served regions to promote innovation and entrepreneurship.
AIM Impact:
- Creating jobs, promoting entrepreneurship, and enhancing India’s global competitiveness in innovation.
5. YOUTH UNEMPLOYMENT RATES IN INDIA – Lower Than Global Levels
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2076956®=3&lang=1 )
| Context |
|
India’s employment scenario shows improvement, with youth unemployment decreasing to 10.2% in 2023-24, compared to global levels. Worker Population Ratio has increased, and formalisation of jobs is evident through significant EPFO enrolments. Government schemes prioritize employment generation and skill development. |
Youth Unemployment: Global vs. India
- The India Employment Report, 2024, by the Institute for Human Development (IHD) and International Labour Organisation (ILO), highlights improved youth employment in India compared to global levels.
- Globally, youth unemployment rates were 15.6% in 2021 and 13.3% in 2023, as per ILO reports.
- In India, the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) 2023-24 reported a youth unemployment rate (ages 15–29) of 10.2%, significantly lower than global averages.
Key Labour Force Indicators
- Worker Population Ratio (WPR): Increased from 31.4% in 2017-18 to 41.7% in 2023-24, reflecting higher youth employment.
- EPFO Payroll Data: Over 1.3 crore net subscribers joined EPFO in 2023-24, with 7.03 crore net subscribers added between September 2017 and August 2024, indicating growing formal employment.
Government Initiatives for Employment Generation
- Employment generation and enhancing employability are priorities for the government.
- Key schemes include:
- Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP).
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS).
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY).
- Deen Dayal Antodaya Yojana (DAY-GKY and DAY-NULM).
- These schemes are implemented by ministries such as MSME, Rural Development, Housing and Urban Affairs, and Finance.
| PYQ: Besides the welfare schemes, India needs dem management of inflation and unemployment to serve the poor and the underprivileged sections of the society. Discuss.(250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2022) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the role of government initiatives and formal sector reforms in addressing unemployment and improving the employment scenario in India. Cite recent data and indicators to substantiate your answer. (150 Words /10 marks) |
6. CONTRIBUTION OF TOURISM IN GDP
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2076960®=3&lang=1 )
| Context |
|
The tourism sector’s contribution to India’s GDP recovered to 5.00% in 2022-23 after a pandemic-induced decline. Government initiatives such as Swadesh Darshan 2.0, PRASHAD, and e-visa reforms aim to boost sustainable tourism, improve connectivity, and create employment. |
Tourism’s Contribution to GDP
- The tourism sector’s share in India’s GDP fluctuated between 5.01% in 2018-19 and 5.18% in 2019-20, dropping sharply to 1.50% in 2020-21 due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- It showed recovery in 2022-23, contributing 5.00% to GDP, with 2.60% direct and 2.40% indirect shares.
Government Initiatives for Tourism Development
- Infrastructure Development:
- Schemes like Swadesh Darshan, PRASHAD, and Assistance to Central Agencies for Tourism Infrastructure Development provide financial support to states/UTs for developing tourist facilities.
- The revamped Swadesh Darshan 2.0 promotes sustainable, tourist-centric destinations.

- Domestic and Thematic Tourism Promotion:
- Programs such as Dekho Apna Desh encourage domestic travel.
- Focus on niche tourism themes like wellness, rural, and eco-tourism broadens the sector’s scope.
- Visa Reforms and Connectivity:
- Liberalized e-visa facilities are extended to 167 countries, including seven subcategories.
- Collaboration with the Ministry of Civil Aviation under RCS-UDAN operationalized 53 tourism routes.
- Capacity Building and Employment:
- The Incredible India Tourist Facilitator Certification Program develops skilled local guides.
- Initiatives like Paryatan Mitra and Paryatan Didi train individuals for responsible tourism.
| Practice Question: Discuss the contribution of the tourism sector to India’s GDP and evaluate the effectiveness of government initiatives in promoting sustainable and responsible tourism. (150 Words /10 marks) |


