27 August 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Two-Year-Old in Meghalaya Tests Positive for Vaccine-Derived Polio: India’s Polio-Free Status Remains Intact
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 09)
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Health GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context: |
| A two-year-old in Meghalaya tested positive for vaccine-derived polio, raising concerns but not affecting India’s polio-free status. |
Analysis of News:

Vaccine-Derived Polio in Meghalaya
- A two-year-old child in Meghalaya’s West Garo Hills district tested positive for vaccine-derived polio, a rare occurrence related to the oral polio vaccine (OPV).
- While India remains polio-free, vaccine-derived cases can occur in children with weakened immune systems.
- In such cases, the weakened virus in the vaccine can circulate, regain virulence, and cause infection.
- Despite this, India’s polio-free status is not jeopardized by such incidents, as they are not caused by the wild poliovirus.
Causes and Prevention of Vaccine-Derived Polio
- Vaccine-derived polio occurs when the weakened virus in OPV either circulates and mutates or causes chronic infection in immunocompromised children.
- Although the OPV has been instrumental in eradicating polio, its rare side effect of triggering the disease has led some experts to recommend switching to the injectable polio vaccine (IPV).
- However, the IPV has its limitations, such as requiring trained personnel for administration and not preventing the spread of the virus between individuals.
India’s Polio Immunization Strategy
- India uses both OPV and IPV to maintain high levels of immunization and prevent polio outbreaks.
- While OPV is crucial for community-level immunity, IPV is included in routine immunizations to protect individual children without the risk of vaccine-derived polio.
- This dual approach aims to balance the need for widespread immunity with the safety concerns associated with OPV.
| What Initiatives have been taken to Eradicate Polio? |
|
Global: Global Polio Eradication Initiative:
World Polio Day:
Indian: Pulse Polio Programme:
Universal Immunization Programme (UIP):
|
|
PYQ: ‘Mission Indradhanush’ launched by the Government of India pertains to (2016)
Ans: (a) |
| Practice Question: Examine the challenges associated with vaccine-derived poliovirus in the context of India’s polio eradication efforts. How can the balance between oral polio vaccine (OPV) and injectable polio vaccine (IPV) be optimized to prevent future outbreaks? (250 words/15 m) |
2. India and US Bolster Defense Ties with New Security Agreements and Strategic Military Cooperation
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 09)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations – Bilateral Relations |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Security of Supply Arrangement (SOSA)
- Under SOSA, both countries will provide reciprocal priority support for goods and services related to national defense.
- This arrangement aims to address supply chain disruptions and strengthen interoperability.
- While SOSA is non-binding, it sets the stage for a binding Reciprocal Defence Procurement (RDP) Agreement that promotes standardization and interoperability of defense equipment.
Memorandum of Agreement on Liaison Officers
- The Memorandum of Agreement regarding the Assignment of Liaison Officers will increase information-sharing between India and the US. India will deploy its first Liaison Officer to the US Special Operations Command headquarters in Florida, marking a significant step in strategic military cooperation.
Cooperation Milestones
- 2023 Roadmap: This plan includes priority co-production projects, such as jet engines and unmanned platforms, and envisions India’s integration into global defense supply chains.
- iCET: The US-India Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technology (iCET), discussed in January 2023, aims to expand strategic technology partnerships.
- INDUS-X: Launched in June 2023, INDUS-X is a defense innovation bridge under the iCET initiative, strengthening defense ties further.
Foundational Agreements and Defense Sales
- India and the US have signed several foundational agreements over the years, including LEMOA (2016), COMCASA (2018), and BECA (2020), which facilitate logistical support, secure communication, and the sharing of military information.
- India, designated as a Major Defence Partner by the US in 2016, has also made significant military procurements, such as MH-60R Seahawk helicopters and M777 howitzers, with ongoing negotiations for manufacturing jet engines and procuring UAVs.
| Challenges |
|
| PYQ: “What introduces friction into the ties between India and the United States is that Washington is still unable to find for India a position in its global strategy, which would satisfy India’s National self- esteem and ambitions” Explain with suitable examples. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2019) |
| Practice Question: Examine the significance of recent defense agreements between India and the United States, such as the Security of Supply Arrangement (SOSA) and the Memorandum of Agreement on Liaison Officers, in the context of enhancing bilateral military cooperation. How do these agreements contribute to India’s strategic autonomy and regional security? (250 words/15 m) |
3. India to Launch ₹10,000 Crore Mission to Revamp Weather Forecasting and Enhance Extreme Weather Predictions
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 06)
| Topic: GS3 – Disaster management |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Mission Details
- Budget and Scope: The new mission is expected to be substantially larger than the Monsoon Mission launched in 2012. It will involve advanced research and development to enhance weather prediction accuracy, particularly for extreme weather events.
- Focus Areas: The mission will prioritize developing better computer simulation models, deploying more sophisticated instruments like Doppler radars, and integrating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) for hyperlocal forecasts.
Current Challenges
- Accuracy Issues: Despite improvements over the past decade, the IMD has struggled with local-level predictions. For instance, forecasts for Mumbai’s rainfall were inaccurate on approximately 40% of the days in July.
- Extreme Weather: Extreme weather events have become more frequent and intense due to climate change, making accurate prediction even more challenging. Recent extreme rainfall events have caused significant disasters, highlighting the need for better forecasting.
Planned Enhancements
- Infrastructure: The new mission will strengthen the weather monitoring network, including deploying additional weather satellites to improve data resolution. India’s current satellites, INSAT-3D, INSAT-3DR, and INSAT-3DS, will be complemented by next-generation satellites under development.
- AI/ML Integration: The mission will leverage AI and ML to enhance predictive models. Research teams, such as those from IIT-Bombay, have demonstrated that AI-driven models can provide more accurate hyperlocal forecasts.
Expected Outcomes
- Improved Forecasts: The mission aims to provide more precise forecasts and early warnings for extreme weather, enabling better preparedness and response at the local level.
- Enhanced Data: By incorporating advanced technology and expanding the network of monitoring tools, the mission will improve the quality and reliability of weather predictions across India.
| Practice Question: Discuss the objectives and expected outcomes of India’s upcoming ₹10,000 crore mission to enhance weather forecasting capabilities. How will this initiative address current challenges in predicting extreme weather events and improve disaster management in the country? (250 words/15 m) |
4. Railways eyes nuclear energy
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 13)
| Topic: GS3 – Infrastructure – Railways |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:

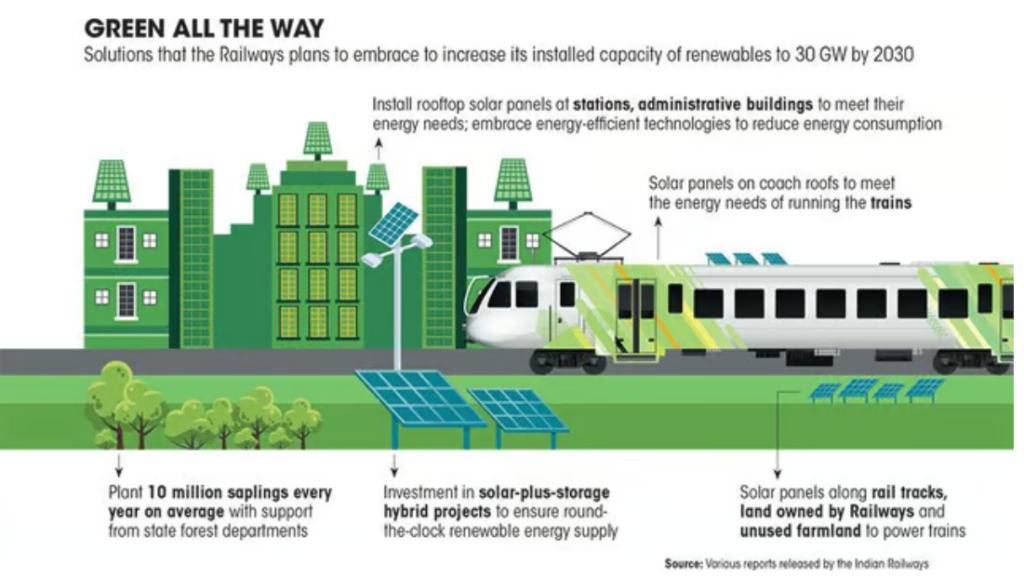
- Indian Railways aims to achieve Net Zero carbon emissions by 2030 and plans to install 30,000 MW of renewable energy capacity by 2029-30.
- The Railways is exploring the use of captive nuclear power alongside solar, wind, and hydel energy to reduce fossil fuel dependence.
- The Railways plans to establish its own captive power generating units, including small reactors, to lower operating costs.
- It spends approximately ₹20,000 crore annually on electricity for trains and its facilities.
- In 2023, the Railways commissioned 147 MW of solar power and 103 MW of wind power, with an additional 2,150 MW of renewable capacity secured.
| Potential for renewable energy in Indian Railways |
|
Prospects:
Challenges:
|
| PYQ: The setting up of a Rail Tariff Authority to regulate fares will subject the cash strapped Indian Railways to demand subsidy for obligation to operate non-profitable routes and services. Taking into account the experience in the power sector, discuss if the proposed reform is expected to benefit the consumers, the Indian Railways or the private container operators. (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2014) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the potential role of nuclear energy in achieving the Indian Railways’ goal of Net Zero carbon emissions by 2030. Evaluate the benefits and challenges associated with integrating nuclear power into the Railways’ energy mix. (250 Words /15 marks) |
5. New Bioeconomy policy rolled out by the central government is set to place India as a global leader
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2048873)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context |
|


Introduction
- The BioE3 (Biotechnology for Economy, Employment, and Environment) Policy, recently launched by the central government, aims to transform India into a global biotech powerhouse.
- By focusing on sustainable bio-manufacturing, innovation, and employment generation, this policy positions India to lead in the bioeconomy and 4th Industrial Revolution.
Growth of India’s Bioeconomy
- Remarkable Surge: India’s bioeconomy has grown from $10 billion in 2014 to $130 billion in 2024, with a projected value of $300 billion by 2030.
- Economic Impact: The BioE3 policy will reignite growth and position India at the forefront of the 4th Industrial Revolution, contributing significantly to the ‘Make in India’ initiative.
Key Focus Areas
- Transition to Bio-Based Economy:
- Shift from traditional chemical-based industries to sustainable bio-based models.
- Circular Bioeconomy:
- Promotes recycling and waste reduction through biomass utilisation, reducing carbon footprints.
- Climate Action:
- Aims for net-zero carbon emissions through innovative waste management, such as biomass, landfills, and greenhouse gases.
- Ethical Biosafety:
- Emphasises global regulatory harmonisation and aligning with international standards for safety.
Innovation and Infrastructure
- Bio Manufacturing Hubs:
- Establishes hubs for large-scale production and commercialization of bio-based products, such as mRNA vaccines.
- Bio-AI Hubs:
- Integrates artificial intelligence to analyse biological data, fostering innovation in gene therapies and food processing.
Employment Generation
- Focus on Tier-II and Tier-III Cities:
- Bio manufacturing hubs will be established in smaller cities, creating jobs and boosting local economies by utilising local biomass resources.
Conclusion
- The BioE3 policy is a game changer, fostering sustainable economic growth and environmental stewardship.
- With its focus on bio-based industries, innovation, and job creation, it not only contributes to India’s ‘Make in India’ initiative but also drives the nation’s vision of becoming a developed and sustainable global leader.
| PYQ: How can biotechnology improve the living standards of farmers? (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2019) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of India’s BioE3 Policy in fostering economic growth, innovation, and sustainability within the biotechnology sector. (250 Words /15 marks) |
Prelims Facts
1. Education Ministry defines ‘literacy’, ‘full literacy’ in push for adult literacy
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Context |
|
New Definition of Literacy
- The government defines literacy as the ability to read, write, and compute with comprehension, including critical life skills like digital and financial literacy.
- Full literacy is achieved when a State or Union Territory reaches 95% literacy.
- Individuals are considered literate under the NILP if they pass the Foundational Literacy and Numeracy Assessment Test (FLNAT).
| Foundational Literacy and Numeracy Assessment Test (FLNAT): |
|
Statistical Data on Literacy in India
- 2011 Census: India had 25.76 crore non-literate individuals aged 15 and above, with 9.08 crore males and 16.68 crore females.
- Saakshar Bharat: Certified 7.64 crore individuals as literate between 2009-10 and 2017-18.
- 2023 FLNAT: 39,94,563 adult learners appeared, with 36,17,303 certified as literate.
- 2024 FLNAT: 34,62,289 learners appeared, and 29,52,385 (85.27%) were certified, down from 89.64% to 91.27% in 2023.
2. SpaceX to test new tech in risky private spacewalk
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
More information about SpaceX Mission:

- SpaceX’s Polaris Dawn mission introduces innovative spacewalk technology.
- It features new slim spacesuits and a modified Crew Dragon vehicle capable of opening its hatch door directly into space, eliminating the need for an airlock.
- This mission, launching a billionaire, a retired fighter pilot, and two SpaceX engineers, aims to reach 700 km altitude, well beyond the ISS.
- Crew Dragon and spacesuits will be tested against high-radiation environments in the Van Allen belt.
| Van Allen belt: |
|
- The mission will involve a 20-minute spacewalk, with preparation including a “pre-breathe” process to ensure safety in the vacuum of space.
3. The working behind some simple medical tools one sees in a doctor’s office
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 11)
| Context |
| This article explains how common medical instruments like thermometers, stethoscopes, weighing scales, and sphygmomanometers function scientifically, detailing their mechanisms in healthcare for accurate measurements. |
Thermometer:
- A thermometer measures temperature through various mechanisms. Mercury thermometers use the expansion of mercury in a glass capillary; as temperature rises, mercury expands and rises through the capillary, indicating temperature on a scale.
- Modern digital thermometers use thermistors or infrared sensors. Thermistors are semiconductors whose resistance changes with temperature, allowing precise measurements.
- Infrared thermometers detect thermal radiation emitted by objects and convert it to temperature readings via changes in voltage or resistance in a circuit.
Stethoscope:
- A stethoscope amplifies internal body sounds using a diaphragm and earpiece.
- The diaphragm, when placed on the body, vibrates in response to sound waves from the heart or lungs, creating pressure waves that travel through the connecting tube to the earpiece.
- Electronic stethoscopes use microphones to convert sound waves into electrical signals, which are amplified and transmitted to the earpieces or recorded for analysis.
Weighing Scale:
- Weighing scales measure force due to gravity. Spring scales use Hooke’s Law, where the amount of spring deformation (compression or stretching) correlates with the applied force (weight).
- Electronic scales often use load cells or strain gauges. Load cells convert force into an electrical signal by measuring the change in electrical resistance of a strain gauge under load, while strain gauges measure resistance changes directly related to deformation.
Sphygmomanometer:
- A sphygmomanometer measures blood pressure using an inflatable cuff and a manometer.
- The cuff inflates to occlude the brachial artery, and as the pressure is released, blood flow resumes.
- The point where blood flow begins is the systolic pressure, and where it becomes unobstructed is the diastolic pressure.
- Mechanical versions use mercury to measure these pressures, while electronic models detect oscillations in cuff pressure correlated with arterial pressure changes, converting them into digital readings.
4. Media groups call on EU to suspend treaty with Israel
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 15)
| Context |
| Sixty media and rights organisations have urged the EU to suspend its cooperation accord with Israel and impose sanctions due to alleged violations of press freedom, including the killing of over 130 journalists in Gaza since October 7. |
About the Treaty:
- The EU-Israel Association Agreement is a treaty that governs the bilateral relationship between the European Union and Israel.
- It covers various aspects including trade, political cooperation, and economic collaboration.
- Key provisions emphasise respect for human rights and democratic principles, outlined in Article 2 of the agreement.
- The treaty aims to enhance cooperation in areas such as trade, technology, and research.
- It also provides a framework for dialogue and collaboration on issues of mutual interest.
- The agreement is a part of the EU’s broader strategy to foster closer ties with non-member countries while upholding fundamental values.
5. RBI to Launch Unified Lending Interface (ULI) Nationwide, Aiming to Revolutionize Credit Delivery
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 19)
| Context: |
| The RBI is preparing to launch the Unified Lending Interface (ULI) nationwide, which is expected to streamline the lending process and enhance India’s digital financial infrastructure. |
Analysis of News:
Introduction of the Unified Lending Interface (ULI)
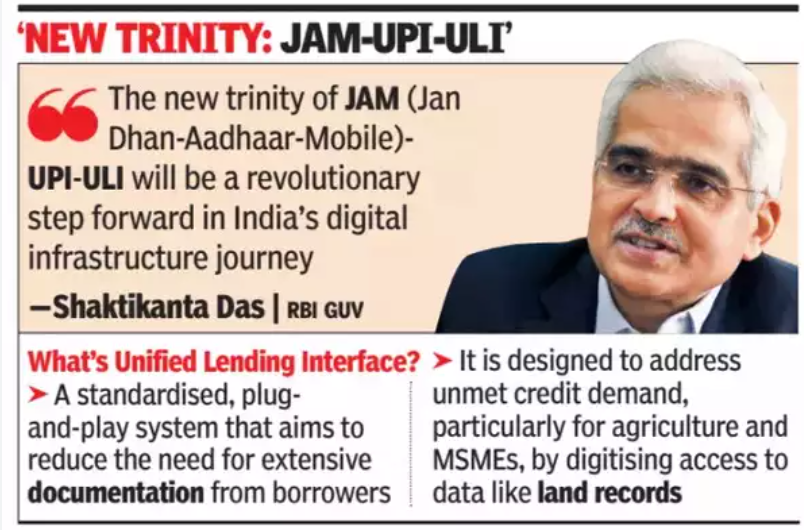
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is set to launch the Unified Lending Interface (ULI) nationwide, a platform poised to revolutionize the lending landscape in India similarly to how the Unified Payment Interface (UPI) transformed the retail payments ecosystem.
- Currently in the pilot stage, ULI aims to streamline the lending process by reducing costs, accelerating disbursement, and enhancing scalability.
Functionality of ULI
- ULI will facilitate a seamless and consent-based flow of digital information, such as land records, from various data providers to lenders.
- By integrating financial and non-financial data that are currently siloed across different entities, ULI will simplify credit appraisal and expedite credit delivery, especially benefiting smaller and rural borrowers who often face delays due to extensive documentation requirements.
Significance of ULI in India’s Digital Infrastructure
- ULI represents a significant advancement in India’s digital public infrastructure, complementing existing initiatives like JAM (Jan Dhan, Aadhaar, and Mobile) and UPI.
- By standardizing APIs for digital access to diverse data sources, ULI will address the large unmet demand for credit, particularly in sectors like agriculture and MSMEs.
- The “new trinity” of JAM, UPI, and ULI is expected to drive innovation in payments, credit, and other financial services, marking a milestone in India’s digital infrastructure journey.
6. Zelenskyy Unveils New Long-Range Missile-Drone Hybrid “Palianytsia” Capable of Striking Deep into Russia
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 09)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Born Out of Necessity
- The Palianytsia was developed out of necessity, with its development beginning around 18 months ago.
- While Ukraine receives long-range weapons from Western allies like the United States, these are restricted from being used deep within Russian territory to avoid escalation.
- The Institute for the Study of War noted that Russia is using deep rear areas for military infrastructure, with around 250 significant targets in Russia within range of ATACMS missiles, but restrictions limit Ukraine to striking only 20 of them.
About Army Tactical Missile Systems (ATACMS):
- ATACMS is a conventional surface-to-surface artillery weapon system capable of striking targets well beyond the range of existing Army cannons, rockets, and other missiles.
- It is manufactured by the US defense company Lockheed Martin.
- It is also designated M39 by the US Army, and its Department of Defence (DoD)designation is MGM-140.
- The missile first saw use during the 1991 Persian Gulf War.
- This weapon’s known operators other than the US are Bahrain, Greece, South Korea, Taiwan, and the United Arab Emirates.
- Features:
- ATACMS are 24/7, all-weather, surface-to-surface, inertially guided ballistic missiles.
- It has a range of about 190 miles (305 km).
- Propulsion: Single-stage, solid propellant.
- ATACMS missiles are fired from the High Mobility Artillery Rocket System (HIMARS) and the M270 Multiple Launch Rocket System (MLRS) platforms. The MLRS can fire 12 surface-to-surface missiles in less than a minute.
- It has the ability to carry cluster munitions, which destroy a targeted area by releasing hundreds of bomblets instead of a single warhead.
- Targets include air defense artillery sites, surface-to-surface missile units, logistics sites, command and control complexes, and helicopter forward operating bases.
Possible Game-Changer
- The Palianytsia missile, with a 700-km range similar to ATACMS, allows Ukraine to bypass these Western restrictions.
- Ukraine’s technology minister, Mykhailo Fedorov, described it as a potential “game changer,” enabling strikes deep behind enemy lines.
- The missile uses a solid-fuel booster and a jet engine, with each missile costing under $1 million.
- Ukraine is also working with the private sector to reduce production costs further.
7. Ladakh to Gain Five New Districts as Part of Government Push for Better Governance and Development
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt & Politics; Page: 05)
| Context: |
| The Indian government announced the creation of five new districts in Ladakh to enhance governance and bring services closer to its remote populations. |
Analysis of News:
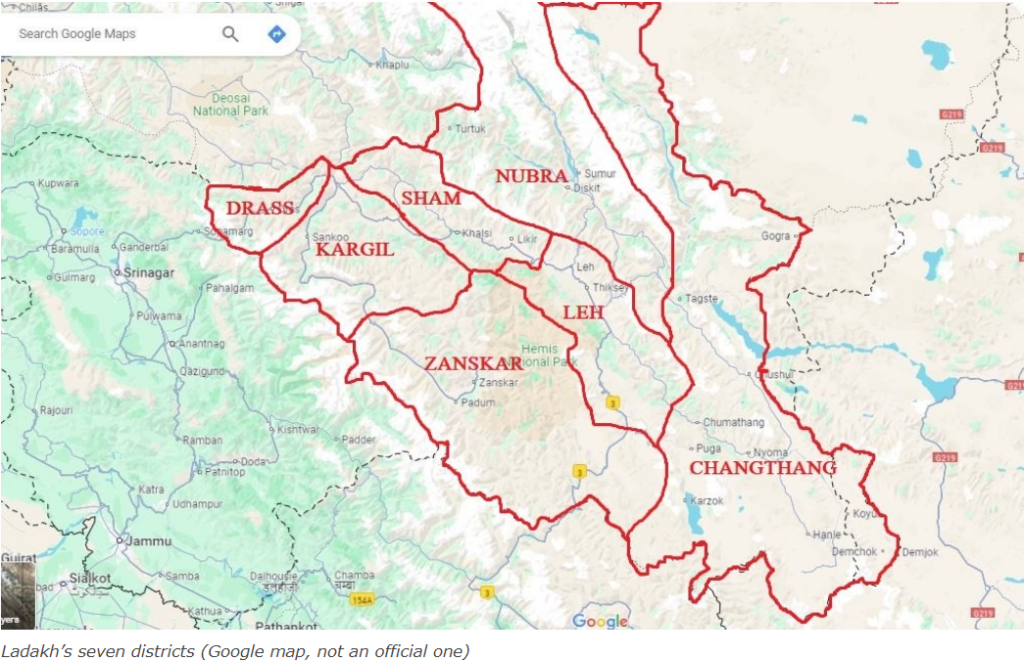
Creation of Five New Districts in Ladakh
- Union Home Minister Amit Shah announced the formation of five new districts in Ladakh: Zanskar, Drass, Sham, Nubra, and Changthang.
- This decision aims to bring governance and public services closer to the people of this remote Union Territory.
Focus on Better Governance
- The creation of these districts is part of Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s vision to develop Ladakh.
- The new districts are expected to improve governance by making administration more accessible and efficient in the region.
Administrative Process
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has instructed the Ladakh administration to form a committee to assess various aspects of the new districts, including boundaries, headquarters, and administrative posts.
- The committee’s report is expected within three months, after which a final proposal will be submitted to the MHA for approval.
Rationale for the New Districts
- Ladakh, currently consisting of Leh and Kargil districts, is a vast and sparsely populated region with challenging terrain.
- The creation of additional districts is intended to overcome difficulties in administration and ensure that government welfare schemes reach the grassroots level.
Census Boundary Implications
- Despite the Registrar General of India (RGI) typically freezing administrative boundaries before the Census, the government has proceeded with the creation of new districts.
- This decision, though unusual, is permissible as both the RGI and Ladakh Administration fall under the MHA, and post facto permission can be obtained.
8. ISRO Finalizes Design of Humanoid Skull for Gaganyaan Mission to Test Human Spaceflight Safety
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 07)
| Context: |
| ISRO has designed a humanoid skull for testing spaceflight conditions and safety ahead of India’s first human space mission, Gaganyaan, scheduled for 2025. |
Analysis of News:

Design and Specifications
- Humanoid Skull: ISRO has finalized the design of an 800-gram, 200 mm x 220 mm humanoid skull, made from high-strength aluminum alloy. It is intended to withstand space pressures and vibrations.
- Prosthetic Material: The skull is covered with a prosthetic material that mimics human skin and houses the facial actuation mechanisms to simulate human expressions and functions.
Role of Vyommitra
- Vyommitra: The skull will be part of Vyommitra, a half-humanoid robot designed to replicate the upper torso of a human. Vyommitra will be used in uncrewed missions to test human-like functions and the effects of space travel on the human body.
- Functions: The humanoid will perform tasks related to crew operations and measure the impact of space conditions on humans.
Mission Preparations
- Gaganyaan Mission: Scheduled for 2025, this will be India’s first human spaceflight, aiming to send three astronauts to around 400 km from Earth for three days.
Preparatory Missions: Before the main flight, ISRO will conduct two uncrewed missions:
- Gaganyaan-1 (G1): To test the safe re-entry and orientation of the spacecraft.
- Gaganyaan-2 (G2): To carry Vyommitra in a human-rated module to record data on the effects of spaceflight on human physiology.
Significance and Future Plans
- Human Spaceflight: If successful, India will join Russia, the US, and China in the list of countries that have sent humans into space.
- Data Collection: The humanoid will gather critical data on the impacts of space travel, aiding in the design of safer and more comfortable space capsules.
- Robotic Assistance: Robotic systems will also play a role in future missions to assist astronauts with repetitive or hazardous tasks.



