27 December 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. A global polio resurgence and the need to reevaluate the basics
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
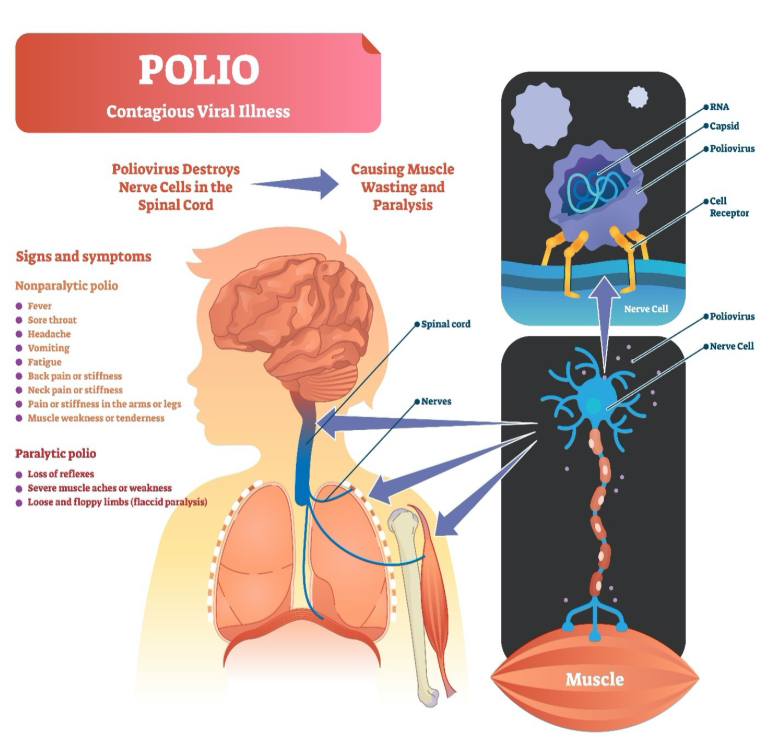
Detection of Polio Cases and Environmental Samples
- The World Health Organization (WHO) detected poliovirus in wastewater systems across five countries in the WHO European Region: Finland, Germany, Poland, Spain, and the UK. These detections occurred from September 2024.
- Despite the detection of the virus in environmental samples, no confirmed cases of polio have been reported in these countries to date.
- WHO emphasized the importance of ongoing vaccination and surveillance to mitigate any potential risks, as the presence of the virus still poses a global threat.
Polio Cases and Virus Detection Worldwide
- In Pakistan, four cases of wild poliovirus type 1 (WPV1) and eight WPV1-positive environmental samples have been reported.
- Other countries, including Cameroon, Côte d’Ivoire, Chad, and Nigeria, have reported circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus type 2 (cVDPV2) cases.
- Environmental samples containing cVDPV2 were detected in various cities, including Barcelona (Spain), Warsaw (Poland), and Munich (Germany). This indicates the widespread nature of the virus.
Vaccination and Immunity Levels
- Countries like Finland, Germany, Poland, Spain, and the UK maintain high immunization rates, ranging from 85% to 95%, with three doses of the inactivated polio vaccine (IPV).
- This provides substantial protection from paralysis caused by the virus.
- Subnational areas with lower vaccination coverage may have immunity gaps, which WHO is investigating to address potential risks.
Resurgence of Vaccine-Derived Polio and Debates on Transmission Routes
- There has been a growing debate regarding the primary transmission route of poliovirus. While the faecal-oral route was traditionally assumed, recent studies suggest respiratory transmission may also play a significant role.
- A study published in the Infectious Diseases journal argues that poliovirus shedding in the throat is critical for transmission, indicating that respiratory transmission could be more prevalent than previously believed.
Switching from OPV to IPV
- Experts recommend switching from the oral polio vaccine (OPV) to IPV globally to prevent further cases of vaccine-derived polio and accelerate the eradication of the virus.
| Practice Question: Discuss the challenges to global polio eradication efforts, focusing on the resurgence of vaccine-derived polio and the implications of shifting from oral polio vaccine (OPV) to inactivated polio vaccine (IPV). (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. Should assisted dying be legalised?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Context |
|

Recent Legal Developments in the UK
- On November 29, 2024, the U.K. House of Commons voted to legalize assisted dying for terminally ill adults in England and Wales.
- The Bill aims to allow terminally ill, mentally competent adults with less than six months to live the option to end their life.
- The proposal has generated significant debate, with 75% of the public supporting it, according to a U.K. National Centre for Social Research survey.
- Advocates argue that assisted dying offers a humane solution for those enduring painful and debilitating conditions.
- Opponents, including the Church of England, fear it could lead to vulnerable individuals being pressured into ending their lives.
Current and Proposed Laws in the UK
- The 1961 Assistive Suicide Act makes suicide not a criminal offense but criminalizes assisting suicide, with a 14-year prison sentence for helping.
- The new Bill would allow assisted death but requires approval from two doctors and a High Court judge for any request.
Legal Precedents
- U.K. courts have repeatedly stated that the issue of assisted dying should be addressed by Parliament, not the judiciary.
- Previous petitions for assisted dying based on human rights violations were rejected, but in 2014, the Supreme Court suggested that Parliament could amend the law.
- The European Court of Human Rights also upheld the stance that Parliament must address the issue.
| Assisted Dying in India: |
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the ethical and legal implications of the legalization of assisted dying in the U.K. and compare it with India’s position on euthanasia and the right to die with dignity. (150 Words /10 marks) |
3. Why is strengthening fisheries extension services crucial?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context |
|
India’s Fisheries and Aquaculture Sector
- India’s fisheries resources provide livelihood to around three crore fishers and fish farmers.
- The country saw an 83% increase in fish production since 2013-14, reaching 175 lakh tons in 2022-23.
- Inland fisheries contribute 75% of this total, making India the second-largest global producer of fish and aquaculture.
Importance of Strengthening Extension Services
- Experts stress the need for strengthening last-mile fisheries and aquaculture extension services.
- These services should offer request-based support on improved species, water quality, disease management, rearing technologies, and training on sustainable practices.
- Addressing challenges faced by seed growers and hatcheries is essential to foster viable business models in the sector.
Role of Matsya Seva Kendras (MSKs)

- The Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana supports the establishment of MSKs, which provide a range of services by trained aquaculture professionals.
- Government assistance for setting up MSKs is available up to 60%, specifically for women and weaker sections.
- State governments and Union Territories have been provided funds to operationalize 102 MSKs, such as those in Thrissur, Kerala, and Nasik and Sangli, Maharashtra.
- MSKs are focused on capacity building, disease testing, and promoting best practices, including regenerative and conservation management practices in both inland and marine fisheries.
Role of Sagar Mitras
- Sagar Mitras are deployed in coastal States and U.T.s to serve as an interface between the government and sea-borne fishers.
- They collect data on marine catches, price fluctuations, and marketing needs, while also disseminating crucial information on regulations, weather forecasts, and hygienic practices.
Improving Extension Services
- Extension services can be improved by institutional convergence with over 700 Krishi Vigyan Kendras and State government services.
- Promoting digital outreach is crucial, and platforms like AquaBazaar are helping fishers with virtual learning on breeding and seed production.
- A World Bank-assisted project aims to create digital identities for fishers, enhancing extension services and capacity building.
| PYQ: What are the forces that influence ocean currents? Describe their role in the fishing industry of the world.(150 Words /10 marks) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2022) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the importance of strengthening extension services in India’s fisheries and aquaculture sector. How do initiatives like Matsya Seva Kendras and Sagar Mitras contribute to sustainable development in this sector? (150 Words /10 marks) |
4. India’s Rural Connectivity Revolution
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2088194®=3&lang=1 )
| Context |
|
Role of Mobile and Internet Connectivity in Empowering Women and Driving Self-Independence
- Mobile and internet connectivity plays a crucial role in fostering self-independence (Aatma Nirbharta) and empowering women, particularly in rural areas, by providing access to opportunities that bridge gaps and transform lives.
- The Government e-Marketplace (GeM) has enabled rural entrepreneurs to expand their markets and increase their income by promoting products to a broader audience.
- This digital empowerment has enhanced their confidence and allowed them to compete in larger markets.
Government Initiatives to Improve Connectivity in Rural Areas
- The Indian government has made significant strides in extending mobile and internet coverage to rural and remote areas, ensuring digital inclusion and socio-economic development.
- As of September 2024, 6,22,804 out of 6,44,131 villages have mobile coverage, with over 6,14,564 villages having 4G connectivity.
- Under the Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM JANMAN) Mission, 1,136 out of 4,543 Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) habitations have been provided mobile coverage.
- By October 2024, 1,018 mobile towers have been sanctioned to enhance 4G coverage in PVTG habitations, with an estimated cost of Rs 1,014 Crore.
Key Government Programs for Digital Inclusion
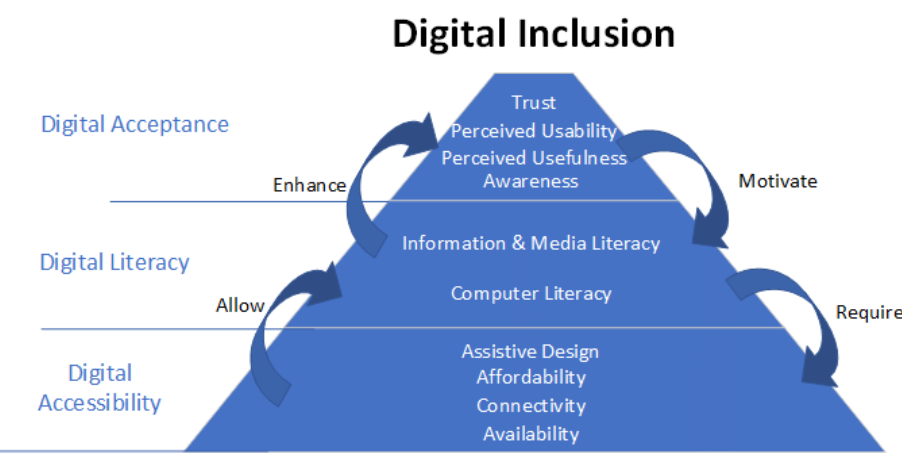
- Digital Bharat Nidhi (DBN): Previously known as the Universal Service Obligation Fund, DBN has funded the installation of mobile towers to provide communication services to underserved areas. As of December 27, 2024, 8,730 towers have been installed, covering 1.99 lakh villages.
- BharatNet Project: This initiative aims to provide affordable, high-speed internet to every Gram Panchayat in India. As of December 27, 2024, over 2.14 lakh gram panchayats are connected through BharatNet.
- PM-WANI: The Wi-Fi Access Network Interface aims to create a network of public Wi-Fi hotspots across India. As of December 27, 2024, 247,076 Wi-Fi hotspots have been established.
Protecting Telecom Users
- The government has implemented measures to protect telecom users, including the “Know Your Mobile Connections” facility and regulations to block unsolicited calls through the “Do Not Disturb” (DND) service.
- The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) uses Artificial Intelligence to detect unregistered telemarketers and imposes penalties on telecom service providers for non-compliance.
Impact of Connectivity on Socio-Economic Landscape
- The extension of mobile and internet coverage in rural areas has transformed India’s socio-economic landscape.
- Initiatives like DBN, BharatNet, and PM-WANI have laid the foundation for a digitally inclusive India.
| PYQ: Has digital illiteracy, particularly in rural areas, coupled with lack of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) accessibility hindered socio-economic development? Examine with justification. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2021) |
| Practice Question: Evaluate the effectiveness of government initiatives like GeM, BharatNet, and PM-WANI in bridging the digital divide and fostering socio-economic growth. (150 Words /10 marks) |
5. Impact of Smart Cities Mission: Boost in School Enrolment and Enhanced Urban Safety
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 17)
|
Topic: GS2 – Governance |
|
Context: |
|
● The article evaluates the positive impacts of the Smart Cities Mission on education and urban safety while highlighting challenges in data collection, infrastructure maintenance, and project completion. |
Analysis of News:
What is the Smart Cities Mission (SCM)?
- It is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme, launched in June 2015 to transform 100 cities to provide the necessary core infrastructure and clean and sustainable environment to enable a decent quality of life to their citizens through the application of “Smart Solutions”.
- It aimed to improve the quality of life for citizens through sustainable and inclusive development.
Objectives:
- Provide core infrastructure and decent quality of life
- Clean and sustainable environment
- Application of ‘Smart’ Solutions
- Sustainable and inclusive development
- Compact areas
- Replicable model
Impact of Smart Classrooms on Education
- The IIM-Bangalore study reveals that the implementation of smart classrooms under the Smart Cities Mission has significantly boosted school enrolment by 22% in 19 cities.
- Over 9,433 classrooms were developed across 2,398 government schools at a cost of ₹1,071.7 crore.
- Students, especially those in smaller cities like Ajmer, appreciated the enhanced learning experience provided by smart classrooms.
- However, challenges persist, including data gaps that hinder progress assessment and evaluation of gender parity. Maintaining the digital infrastructure post-mission is crucial for sustained benefits.
Challenges in Data Collection and Reporting
- The study highlights the absence of reliable data on key indicators like enrolment and gender ratios, which restricts the ability to measure long-term outcomes.
- Many cities failed to provide complete data, underscoring the need for better data collection mechanisms.
- Without comprehensive data, assessing the broader impact of smart classroom initiatives remains difficult.
Impact of Surveillance and Safety Measures
- Another IIM-B study examined the role of Integrated Command and Control Centres (ICCCs) and surveillance systems in enhancing urban safety.
- Across 93 Smart Cities, 59,802 CCTV cameras were installed, while 78 cities implemented 13.95 lakh streetlights.
- In Nagpur, Chennai, and Tumakuru, the use of CCTV footage significantly improved crime-solving rates and fostered a greater sense of security among residents.
- For instance, in Nagpur, camera footage assisted in resolving 36% of police requests, with the evidence also aiding judicial trials.
Public Perception and Law Enforcement
- The adoption of advanced surveillance technologies has strengthened law enforcement and increased public confidence in urban safety.
- Real-time monitoring systems have enabled faster crime resolution and better enforcement of law and order, particularly in cities like Nagpur.
- Residents of these cities report heightened feelings of safety, reflecting the effectiveness of the initiatives.
Delayed Completion of the Smart Cities Mission
- Launched in 2015, the Smart Cities Mission has faced repeated extensions, with only 9% of projects yet to be completed. Initially planned for completion by 2023, the mission has been extended to March 2025.
- This delay underscores the importance of timely execution and sustained funding to ensure the long-term success of initiatives like smart classrooms and ICCCs.
Conclusion
- The studies underscore the tangible benefits of the Smart Cities Mission in education and urban safety while highlighting persistent challenges in data collection, infrastructure maintenance, and project completion.
- Sustained efforts and funding will be critical to ensure the mission’s continued impact on urban development and quality of life.
|
What are the Steps Needed to Strengthen the Smart City Mission? |
|
The Standing Committee on Housing and Urban Affairs gives the following overarching recommendations. ● Governance and Implementation: ● Dedicated CEO should be appointed with fixed tenure, ensuring the representation of experts and stakeholders, and utilising existing expertise. ● Members of Parliament (MPs) need to be included in State-Level Advisory Forums, and should be consulted for project identification, selection, and implementation, as they have grassroots-level expertise. ● Project Focus and Priorities: ● The emphasising should be more on pan-city projects for comprehensive and holistic development, optimising resource allocation and reducing wastage. ● Digital infrastructure protection mechanisms are needed to safeguard against cyber threats and maintain data privacy. ● Capacity Building and Funding: ● A plan to strengthen Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) capabilities in small cities and central government assistance for organisational restructuring and capacity building in states requiring support should be taken up. ● Project Completion: ● The focus should be on timely completion of project. The ministry’s role should not be confined to fund transfer but extend to ensuring execution and completion by intervening with inputs and expertise. |
|
PYQ: With a brief background of quality of urban life in India, introduce the objectives and strategy of the ‘Smart City Programme’ (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2016) |
|
Practice Question: Evaluate the impact of the Smart Cities Mission on education and urban safety in India. What challenges persist in its implementation, and how can they be addressed to ensure sustainable outcomes? (250 words/15 m) |
Prelims Facts
1. Nation mourns former PM Manmohan Singh, economist-ruler credited with liberalization
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Context |
|

As an Economist and Administrator
- Chief Economic Adviser (1972–76): Played a crucial role in shaping India’s economic policies during a challenging period.
- Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (1982–85): Strengthened India’s monetary and financial systems.
- Deputy Chairman, Planning Commission (1985–87): Helped frame India’s development strategies.
Contributions as Finance Minister (1991–1996)
- Economic Liberalization (1991): Spearheaded historic reforms under Prime Minister P.V. Narasimha Rao, introducing liberalization, privatization, and globalization (LPG).
- Dismantling License Raj: Abolished complex licensing systems, paving the way for ease of doing business.
- Boosting Foreign Investment: Opened multiple sectors to foreign direct investment (FDI), fostering global partnerships and inflows.
- Fiscal Consolidation: Implemented policies to reduce fiscal deficits, stabilizing the economy.
- Exchange Rate Reforms: Transitioned to a market-determined exchange rate, boosting export competitiveness.
- Banking and Financial Reforms: Strengthened banking systems, introduced reforms in the capital markets, and established SEBI as a regulator.
- Export Promotion: Introduced policies to diversify and boost India’s export base.
Contributions as Prime Minister (2004–2014)
- Sustained Economic Growth: Oversaw years of high GDP growth, elevating India to the status of a global economic powerhouse.
- Mahatma Gandhi NREGA: Launched flagship rural employment schemes to reduce poverty and promote social welfare.
- Nuclear Deal with the U.S.: Finalized the Indo-U.S. Civil Nuclear Agreement, cementing India’s global standing.
- Social and Economic Inclusion: Expanded healthcare, education, and infrastructure programs, focusing on inclusive growth.
- Technology and Innovation: Promoted digital technology, laying groundwork for initiatives like Digital India.
- Foreign Policy Leadership: Strengthened India’s global partnerships, especially with the U.S., Russia, and Southeast Asia.
- Legislative Milestones: Oversaw the passage of key laws like the Right to Information Act, and Food Security Act.
Dr. Singh’s contributions as a reformist economist and statesman defined modern India’s economic and political trajectory
For more such UPSC-related Current Affairs, Check Out-26 December 2024: Daily Current Affairs
2. China to build world’s largest hydropower dam in Tibet
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt & Politics; Page: 09)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
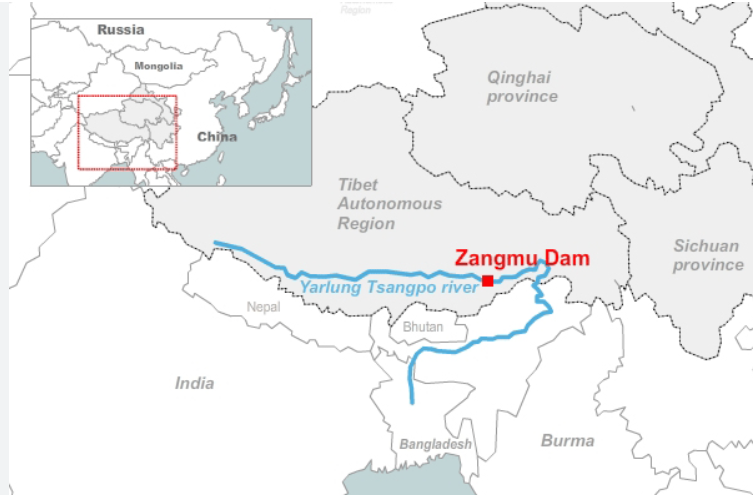
Overview of the Hydropower Project
- China has approved the construction of the world’s largest hydropower dam on the lower reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River on the eastern Tibetan plateau.
- With an estimated annual electricity production of 300 billion kilowatt-hours, the project will significantly surpass the capacity of the Three Gorges Dam.
- This ambitious undertaking aligns with China’s carbon neutrality goals, aims to boost engineering and related industries, and is expected to create jobs in Tibet.
Economic and Engineering Challenges
- The dam will require extensive investment, with costs likely to exceed the $34.83 billion spent on the Three Gorges Dam, including engineering and resettlement expenses.
- Unique engineering challenges arise from the dramatic 2,000-meter descent of the river within a 50-kilometer span, offering vast hydropower potential.
- However, specifics regarding displacement and ecological impact remain undisclosed.
Ecological and Regional Concerns
- The dam’s construction raises significant concerns about its impact on the local ecosystem, one of the richest and most diverse on the Tibetan plateau.
- India and Bangladesh, located downstream, worry about potential changes to the flow and course of the river.
- Such alterations could affect water availability, agriculture, and biodiversity in the Brahmaputra basin, which is crucial for millions of people in these regions.
Geopolitical Implications
- The Yarlung Zangbo transitions into the Brahmaputra River as it flows through India and Bangladesh.
- Any modifications to the river’s natural course could strain transboundary water-sharing agreements and escalate tensions between China, India, and Bangladesh.
- These countries have expressed concerns over China’s unilateral decision-making in such ecologically and geopolitically sensitive projects.



