27 July 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Supreme Court Extends Stay on UP Police Notice Requiring Shops on Kanwar Yatra Route to Display Owners’ Names
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 18)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government policies – Issues arising out of their design & implementation. |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Background of the Police Notice
- The police issued the notice on July 17, claiming that past “law-and-order situations” had arisen due to the names of shops causing “confusion” among Kanwariyas, who follow a strictly vegetarian diet.
- Despite stating that no “religious discrimination” was intended, the notice was challenged by various parties, including TMC MP Mahua Moitra and the Association for Protection of Civil Rights, who argued that it targeted Muslim-owned businesses by forcing individuals to reveal their religious identity.
Court’s Observations
Absence of Government Order
- The Supreme Court Bench, comprising Justices Hrishikesh Roy and S V N Bhatti, noted the lack of a government order empowering the police to issue such directions.
- The Bench observed that such directives could be issued under the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006, or the Street Vendors Act, 2014, to ensure “shudh shakahari” (strictly vegetarian) food is served to the Kanwar Yatris.
Limits to Police Action
- The Bench emphasized that even if actions were to be taken under these Acts, the police could not usurp the powers of the competent authority without a legal foundation.
- The court took note of the petitioners’ submissions that penal actions had been initiated against food business operators despite the police’s claim that the display of names was “voluntary.”
Question of Discrimination
- The court did not delve into the constitutional arguments presented by the petitioners, who claimed that the directions discriminated against individuals on the grounds of religion, violating Article 15(1) and supporting economic boycotts akin to untouchability, banned under Article 17.
- Senior advocate A M Singhvi argued that the directions targeted Muslim-owned businesses, causing an economic boycott.
Legal Basis for Directions
- The police did not cite any specific law in their directions. However, the state of UP, in its reply referred to Regulation 2.1.1(5) of the Food Safety and Standards (Licensing & Registration of Food Businesses) Regulations, 2011.
- This regulation requires petty food manufacturers to display their registration certificate and photo identity card prominently.
- The state also cited Section 92 of the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006, which empowers the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) to create regulations.
Allegations of Discrimination
- Article 15(1) prohibits discrimination on various grounds, including religion. The court will need to determine whether requiring individuals to reveal their names—and potentially their religious and caste identities—constitutes discrimination against shop owners and employees, particularly targeting Muslim-owned businesses.
- Justice Roy questioned whether Kanwariyas had expectations of being served food only by people from “a certain community.”
Right to Privacy Concerns
- The court will also consider if forcing businesses to disclose the names of owners and employees violates their right to privacy under Article 21.
- The Supreme Court’s Right to Privacy judgment in 2017 established that individuals have a fundamental right to privacy, including the freedom to express or not express their religious faith.
Three-Fold Test for Privacy Restrictions
Justice D Y Chandrachud’s majority decision outlined a “three-fold” test to determine when the government can restrict the right to privacy:
- The existence of a law providing for such restrictions.
- A “legitimate state aim” in restricting the right to privacy.
- A “rational nexus” between the restriction and the objective, ensuring the restriction is not disproportionate to the objective of the government.
The court’s future deliberations will hinge on these principles to decide the legality and fairness of the police notice.
| Practice Question: Discuss the legal and constitutional implications of the Uttar Pradesh police notice requiring shops along the Kanwar Yatra route to display the names of their owners and employees. How does this directive intersect with issues of religious discrimination, right to privacy, and the state’s power to regulate? (250 words/15 m) |
2. Customs Duty Exemptions on Targeted Cancer Drugs Announced in India’s Budget 2024-25
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 18)
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Health GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
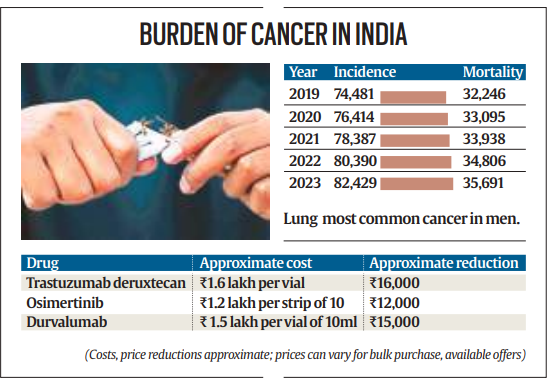
Understanding Targeted Cancer Drugs
- Targeted cancer drugs specifically attack cancer cells, sparing normal cells.
- They target genetic changes in cancer cells that aid their growth, division, and spread, resulting in better outcomes and fewer side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy.
How These Drugs Work
- Trastuzumab Deruxtecan: An antibody-drug conjugate targeting the HER-2 receptor, used for certain breast and gastrointestinal cancers. Marketed as Enhertu, it costs around Rs 1.6 lakh per vial.
- Osimertinib: Commonly used in India for lung cancers with epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR). Marketed as Tagrisso, it costs around Rs 1.5 lakh per strip of ten pills.
- Durvalumab: An immunotherapy drug for lung, biliary tract, bladder, and liver cancers. Marketed as Imfinzi, it costs around Rs 1.5 lakh for every 10 ml vial.
Impact of Customs Duty Exemptions
- The exemptions are expected to reduce the financial burden on cancer patients and their families, making these expensive but effective therapies more affordable.
- Even a small decrease in cost can significantly impact the ability of patients to afford additional necessities like nutrition supplements and medical tests.
Cancer Profile in India
- Cancer cases are on the rise in India, with an estimated 14.6 lakh new cases in 2022. Lung and breast cancers are among the most common types, with breast cancer prevalent among women and lung cancer among men.
- The exemption of customs duty on these drugs is particularly significant given their effectiveness in treating these common cancers.
| What are the Government Initiatives Related to Cancer Treatment? |
|
| Practice Question: The Indian government’s recent decision to exempt customs duties on three targeted cancer drugs has been hailed as a significant move for public health. Evaluate the potential impact of this policy on cancer treatment accessibility and patient outcomes in India. Discuss the broader implications of such fiscal measures on healthcare in the country. (250 words/15 m) |
3. Finance Ministry to Launch Digital Footprint-Based Home Loan Model Following MSME Success
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Cover Page; Page: 01)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context: |
| The Finance Ministry is developing a new model for home loans based on digital footprints, following the success of a similar approach for MSME credit assessment announced in the Budget 2024-25. |
MSME Credit Assessment Model
- Objective: Enable banks to assess creditworthiness of MSMEs using digital footprints rather than traditional financial documents.
- Challenge: Many MSMEs lack proper balance sheets, making it difficult to access loans.
- Solution: Utilize digital data such as salary payments and EPF contributions to evaluate creditworthiness.
- Impact: Easier loan access for smaller businesses without detailed financial documentation.
Home Loan Model
- Objective: Develop a similar digital footprint-based model for home loans.
- Current Limitation: Home loans are primarily available to salaried individuals or those who file tax returns.
- Proposed Change: Assess individuals’ spending and consumption patterns to determine creditworthiness.
- Implementation: Expected within a quarter, allowing banks to offer loans to a broader demographic.
Benefits
- For MSMEs: Streamlines the loan process for small businesses, facilitating growth and financial inclusion.
- For Individuals: Provides loan access to those without traditional financial documentation, based on digital behavior.
Examples
- MSME Case: A small shop can demonstrate creditworthiness through bank transactions or utility bills, enabling access to loans.
- Individual Case: Non-salaried individuals can secure home loans by showcasing digital spending habits.
Conclusion
- This initiative aims to broaden access to credit for both MSMEs and individuals by leveraging digital footprints, thus enhancing financial inclusion and supporting economic growth.
4. ASEAN cornerstone of India’s Act East Policy: Jaishankar
(Source – The Hindu, News- Page No. – 4)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations |
| Context |
|
About ASEAN:
- The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) is a regional intergovernmental organisation comprising ten Southeast Asian countries.
- Founded on August 8, 1967, in Bangkok, Thailand, its members include Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Brunei, Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar (Burma), and Cambodia.
- ASEAN aims to promote regional peace, stability, economic growth, and socio-cultural development through cooperation and dialogue.
- Its key principles include mutual respect, non-interference in internal affairs, peaceful dispute resolution, and cooperation for mutual benefit.
- The ASEAN Summit is the organization’s highest decision-making body, where member states discuss and coordinate regional policies and initiatives.
- The organization addresses various regional challenges, including territorial disputes, transnational crime, terrorism, natural disasters, and environmental issues.
- ASEAN promotes intra-regional trade and economic cooperation through initiatives such as the ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA) and regional economic integration efforts.
About India’s ‘Act East’ policy:
- The ‘Act East Policy’ is a diplomatic initiative to promote economic, strategic and cultural relations with the vast Asia-Pacific region at different levels.
- It expands on the earlier ‘Look East’ policy with aim to strengthen ties with Asia-Pacific countries, particularly Southeast Asia.
- Emphasizes strategic partnerships, including defense and security cooperation.
- Promotes connectivity through infrastructure projects and enhances cultural and people-to-people exchanges.
- Positions India as a bridge between Asia-Pacific and major global powers.
| Importance of ASEAN countries for India’s Act East policy: |
|
5. Inclusion of Maidams as the UNESCO World Heritage Site is a Great Moment of Pride & Glory for the People of Assam: Shri Sarbananda Sonowal
(Source https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2037734 )
| Topic: GS1 – Art and culture |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:

The centuries old royal burial site of Ahom Dynaty in Assam, Charaideo district.
About Charaideo Moidams:
- The 600-year-old mound-burial system of the Ahom dynasty is known as the Moidams.
- The Moidams is situated on the foothills of the Patkai Ranges in eastern Assam, the burial mounds are considered sacred by the Tai-Ahom and reflect their unique funerary practices.
- The Tai-Ahom people arrived in Assam in the 13th century, establishing Charaideo as their first capital and the site of the royal necropolis.
- For 600 years, from 1228 till Assam’s annexation to the British through the Treaty of Yandabo in 1826, the the Tai-Ahoms constructed moidams, using natural elements like forests, hills, and water to create a sacred geography.
- Maidams are elevated, often double-storied, and entered through an arched passage.
- Atop the hemispherical mud-mound layers of bricks and earth is laid, where the base of the mound is reinforced by a polygonal toe-wall and an arched gateway on the west.
- Eventually, the mound would be covered by a different layer of vegetation reminiscent of a group of hillocks, transforming the area into an undulating landscape.
- Believing their monarchs to be divine, the Tai-Ahom developed a distinct funerary tradition of constructing moidams for royal burials.
| About UNESCO World Heritage Sites |
|
PRELIMS FACTS
1. PUBERTY BLOCKERS
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 18)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Puberty Blockers: Definition and Purpose
- Puberty blockers are medications that delay the physical changes of puberty in transgender and gender-diverse teens.
- These drugs, also known as gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analogues, work by stopping the body from producing sex hormones.
- This can help reduce the anxiety and distress associated with gender dysphoria, a condition where there is a conflict between an individual’s assigned gender at birth and their gender identity.
How Puberty Blockers Work
- For individuals assigned male at birth, puberty blockers slow the growth of facial and body hair, prevent voice deepening, and limit the growth of genitalia.
- For those assigned female at birth, they limit or stop breast development and menstruation.
- Puberty blockers are also used in cases of precocious puberty, where children begin puberty unusually early.
Usage and Administration
- In India, puberty blockers are commonly prescribed for precocious puberty and, less frequently, for those seeking gender reassignment surgery, which is typically not conducted before age 18.
- The medication can be administered through monthly, tri-monthly, or semi-annual injections, or via an implant under the skin, which needs to be replaced annually.
Side Effects
- Potential side effects of puberty blockers include insomnia, weight gain, muscle aches, fatigue, mood shifts, changes in breast tissue, and irregular periods or spotting in women.
- There may also be risks of depression or self-harm tendencies.
2. Indian Government to Centralize Employment Data, Launches Employment-Linked Incentive Schemes and Internship Program
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Economy; Page: 17)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Integration of Employment Data
- Union Minister for Labour and Employment Mansukh Mandaviya emphasized the need to consolidate various employment data sources across government departments to develop a comprehensive understanding of employment generation in India.
- He highlighted the lack of a centralized employment database, despite numerous schemes and projects generating significant employment.
Focus on Youth and Skills Development
- Mandaviya also stressed the importance of equipping youth with the necessary skills and qualifications to meet industry demands.
- He urged industry bodies to provide internship opportunities to young people, facilitating their entry into the job market and supporting the government’s employment initiatives.
Budget and Employment Schemes
- The Budget 2024-25, described as “youth and employment-centric,” allocated Rs 2 lakh crore over the coming years to the Prime Minister’s Package for Employment and Skilling.
- For the current financial year, Rs 12,000 crore has been allocated, with Rs 10,000 crore designated for the Ministry of Labour and Employment’s three ELI schemes and Rs 2,000 crore for an internship program under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
Employment Data Sources
- Currently, employment data are dispersed across various ministries, with the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) conducting the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) and payroll data provided by the Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO).
- The ELI schemes will utilize EPFO enrolment data to recognize first-time employees, workers in manufacturing, and additional job creation.
3. Gaza Conflict: UNESCO Inscribes Palestinian Monastery of Saint Hilarion on World Heritage List and List of World Heritage in Danger
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt & Politics; Page: 09)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Reasons for Inscription
- The WHC recognized the site’s cultural significance and the urgent need to protect it from threats posed by the conflict in Gaza.
- The Monastery of Saint Hilarion, dating back to the 4th century, is one of the earliest monastic sites in the Middle East.
Significance of the Site
- The Monastery of Saint Hilarion/Tell Umm Amer holds significant historical and cultural value, representing early monastic life in the Middle East.
- Its inclusion in the World Heritage List underscores the global importance of protecting such sites, especially in conflict zones.
| UNESCO World Heritage Committee (WHC) |
|
4. India and US Sign Cultural Property Agreement to Facilitate Repatriation of Stolen Antiquities
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt & Politics; Page: 09)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of the News:
Details of the Agreement
- Signed by US Ambassador to India Eric Garcetti and India’s Culture Secretary Govind Mohan, the agreement was finalized on the sidelines of the UNESCO World Heritage Committee meeting in New Delhi.
- It marks the culmination of nearly two years of collaborative efforts between experts from both countries and aligns with commitments made by President Joe Biden and Prime Minister Narendra Modi to enhance cultural heritage cooperation.
Context and Significance
- India joins 29 other countries, including Afghanistan, China, and Egypt, in having a bilateral cultural property agreement with the US.
- This agreement is part of India’s broader efforts to recover its cultural heritage, with over 400 antiquities repatriated since 2014.
- The agreement underscores India’s commitment to cultural preservation and international cooperation in protecting cultural heritage.




