28 August 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. On SEBI chairperson’s conflicts of interests
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Important aspects of governance – Transparency and accountability, GS4 – Ethics – Ethics in civil services & public administration: |
| Context |
|
Conflict of Interest for SEBI Chief:
- Investment in Offshore Fund: Madhabi Buch and Dhaval Buch invested over ₹5.6 crore in Bermuda-based Global Dynamic Opportunities Fund in 2015, managed by Anil Ahuja, an Adani Enterprises director at the time. Buch redeemed this investment in 2018 while serving as a SEBI member.
- Undisclosed Holdings: Madhabi Buch owned 99% of Agora Advisory Private Limited, which remained active and profitable during her SEBI tenure, violating SEBI’s conflict of interest code.
- Promotion of REITs: Buch’s husband works for Blackstone, benefiting from SEBI’s favourable decisions on Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs), raising concerns about preferential treatment.
Issues:
- Potential lack of transparency and regulatory integrity.
- Questions on SEBI’s role in the Adani group investigation.
- Violation of SEBI’s conflict of interest rules by the chairperson.
| Conflict Of Interest In Governance: |
|
Definition: Conflict of interest in governance occurs when an individual’s personal interests or relationships could improperly influence their official duties, leading to biassed decisions or actions. Importance for Civil Servants to Avoid:
Ways to Avoid Conflict of Interest in Civil Service:
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of conflicts of interest in governance for civil servants. How can such conflicts be effectively managed to maintain integrity and public trust in the civil service? (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. The invisible lives of sanitation workers who clean Mumbai’s drains
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice- Vulnerable Sections |
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 2)
| Context |
|
Issues faced by sanitation workers:
- Hazardous Conditions: Sanitation workers are often required to clean stormwater drains and sewers manually, exposing them to toxic substances and unsafe conditions, including direct contact with sewage.
- Lack of Recognition: Manual scavenging in stormwater drains is not officially recognized, which prevents workers from receiving proper protections and benefits under laws prohibiting manual scavenging.
- Regulatory Gaps: Inadequate separation of sewers from stormwater drains results in the discharge of sewage into drains, increasing the risk and difficulty of sanitation work.
- Temporary Employment: Workers are often seasonal migrants, with unstable income and limited job security, exacerbating their vulnerability and lack of access to social protections.
- Inadequate Safety Measures: Despite regulations mandating safety gear, workers frequently work without proper protection, as enforcement of safety standards is insufficient.
- Generational Poverty: The sanitation work is often inherited across generations, trapping families in a cycle of poverty and limiting opportunities for upward mobility.
- Child Labour: Children from these communities are often involved in hazardous work, impacting their education and future prospects.
- Lack of Accountability: There is a lack of proper tracking and record-keeping, which hinders efforts to ensure fair treatment and rehabilitation of workers.
Way Forward:
- Enforce Safety Regulations: Strictly implement and monitor adherence to safety standards and provide necessary protective gear for workers.
- Acknowledge Manual Scavenging: Officially recognize manual scavenging in stormwater drains to ensure workers receive appropriate benefits and protections.
- Improve Infrastructure: Upgrade drainage systems to separate sewage from stormwater, reducing the risk and difficulty of cleaning tasks.
- Support Stable Employment: Provide stable and secure employment opportunities to migrant workers to reduce their economic vulnerability.
- Enhance Child Protection: Implement measures to prevent child labour and ensure access to education and support for affected children.
- Strengthen Record-Keeping: Establish comprehensive tracking systems for workers to ensure fair treatment and facilitate rehabilitation efforts.
| Practice Question: Discuss the challenges faced by sanitation workers in urban India, particularly concerning their safety, recognition, and employment conditions. How can policy interventions address these issues effectively? (250 Words /15 marks) |
3. Government Bans 156 Fixed-Dose Combination Drugs, Targeting Irrational and Ineffective Medications
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained;)
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Health GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
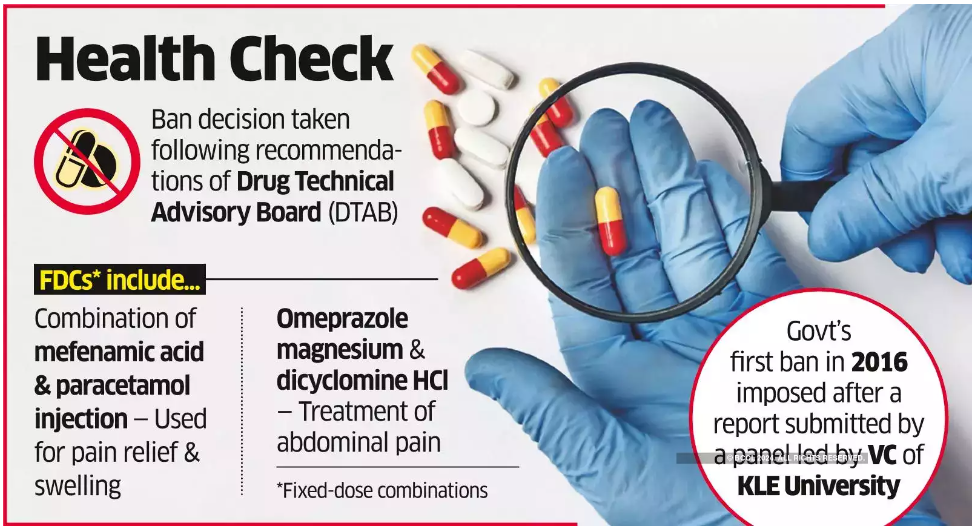
Understanding Fixed-Dose Combinations (FDCs)
- Definition: FDCs are medications that contain more than one active ingredient in a single dosage form, such as a pill, capsule, or injection.
- Purpose: These combinations are designed to help patients, especially those with chronic conditions like tuberculosis and diabetes, by reducing the number of pills they need to take daily, thereby improving treatment adherence.
- Issue: The use of FDCs can sometimes result in patients taking drugs they don’t need, leading to unnecessary consumption of medications.
Specific FDCs Banned
The banned FDCs include:
- Gastrointestinal Treatments: Various enzyme combinations.
- Anti-Allergic Combinations: Including levocetirizine with nasal decongestants, and syrups for mucus breakdown.
- Skin Condition Treatments: Combinations involving menthol, aloe vera, vitamin E, and antiseptics.
- Migraine Treatments: FDCs combining migraine relief with anti-nausea drugs.
- Menstrual Cramp Relief: Mefenamic acid combined with tranexamic acid.
- Erectile Dysfunction: Sildenafil combined with muscle relaxants.
Availability and Immediate Impact
- Market Availability: Manufacturers are required to stop production, stocking, and sale of these drugs immediately. However, these medications may still be available in the market due to legal challenges allowing the sale of existing stock.
- Health Impact: For consumers, taking one of these banned FDCs now is unlikely to cause harm, but the ban was necessary to prevent irrational drug use.
Reasons Behind the Ban
- Irrational Combinations: The banned FDCs often contain ingredients that either do not work well together or are unnecessary when combined.
- Antibiotic Resistance: A significant concern is the overuse of antibiotics, which can lead to increased antibiotic resistance. Banning irrational combinations helps reduce unnecessary antibiotic consumption.
- Price Control Evasion: Some companies create FDCs to avoid government-imposed price controls on essential medicines.
Timing and Context of the Ban
- Regulatory Reforms: The ban aligns with the government’s efforts to eliminate irrational drug combinations that were previously approved by state authorities without proper trials. The 2019 regulations classify FDCs as new drugs, requiring central approval.
- Historical Background: The issue of irrational drug combinations was first highlighted by a parliamentary panel in 2012. A 2014 committee reviewed 3,450 FDCs and identified 963 as irrational, leading to the progressive banning of such drugs.
| What is the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO)? |
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the rationale behind the Indian government’s recent ban on 156 Fixed-Dose Combination (FDC) drugs. What are the potential impacts of this ban on public health and the pharmaceutical industry? (250 words/15 m) |
4. Government Aims to Open Over 3 Crore New Jan Dhan Accounts in 2024-25 as Scheme Marks 10 Years
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Economy; Page: 13)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government Policies |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
What is Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana?
- PMJDY creates a platform for universal access to banking facilities with at least one basic banking account for every household, financial literacy, and access to credit, insurance, and pension facilities.
Features of PMJDY:
- It aims to expand banking services through branches and Banking Correspondents (BCs).
- It covers both urban and rural areas and those who open an account would get indigenous Debit Card (RuPay card).
- There is no requirement to maintain any minimum balance in PMJDY accounts.
- Accident Insurance Cover of Rs.1 lakh (enhanced to Rs. 2 lakh to new PMJDY accounts opened after 28.8.2018) is available with RuPay card issued to the PMJDY account holders.
- It provides an overdraft facility of Rs. 10,000 to every eligible adult.
- PMJDY accounts are eligible for Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT), Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY), Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY) and Atal Pension Yojana (APY).
Achievements Over the Decade
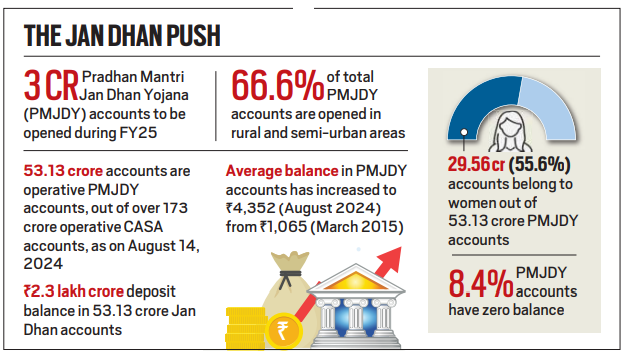
- Since its launch on August 28, 2014, by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, the number of PMJDY accounts has grown nearly fourfold, reaching 53.13 crore by August 16, 2024, compared to 14.72 crore in March 2015.
- Total deposits under the scheme have surged to over Rs 2.31 lakh crore, up from Rs 15,670 crore in March 2015.
Focus on Reaching the Unbanked
- Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman highlighted that most adults in the country now have bank accounts, with a focus on covering the remaining unbanked adults and new adults (neo-adults).
- The average balance in PMJDY accounts has increased significantly, with 80% of accounts being active.
Impact of PMJDY
- The PMJDY has been foundational for people-centric economic initiatives, enabling direct benefit transfers, COVID-19 financial assistance, and schemes like PM-KISAN.
- The JAM Trinity (Jan Dhan, Aadhaar, Mobile) has expanded the Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) program, particularly in rural and semi-urban areas, where 66.6% of PMJDY accounts are held. Additionally, 55.6% of accounts belong to women.
Accessibility and Features
- As of now, 99.95% of inhabited villages have access to banking facilities within a 5-km radius.
- PMJDY accounts offer various benefits, including no charges for opening, maintaining, or minimum balances, a free RuPay debit card with Rs 2 lakh accident insurance, and an overdraft facility of up to Rs 10,000.
| Significance |
|
|
PYQ: ‘Pradhan Mantri Jan-Dhan Yojana’ has been launched for (2015) (a) providing housing loan to poor people at cheaper interest rates Ans: (c) |
| Practice Question: Examine the role of the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) in promoting financial inclusion in India over the last decade. Discuss the challenges and opportunities associated with the expansion of the scheme in the coming years. (250 words/15 m) |
5. Machine learning helps predict crustal movements in Tibetan Plateau
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2049046 )
| Topic: GS1 – Geography, GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
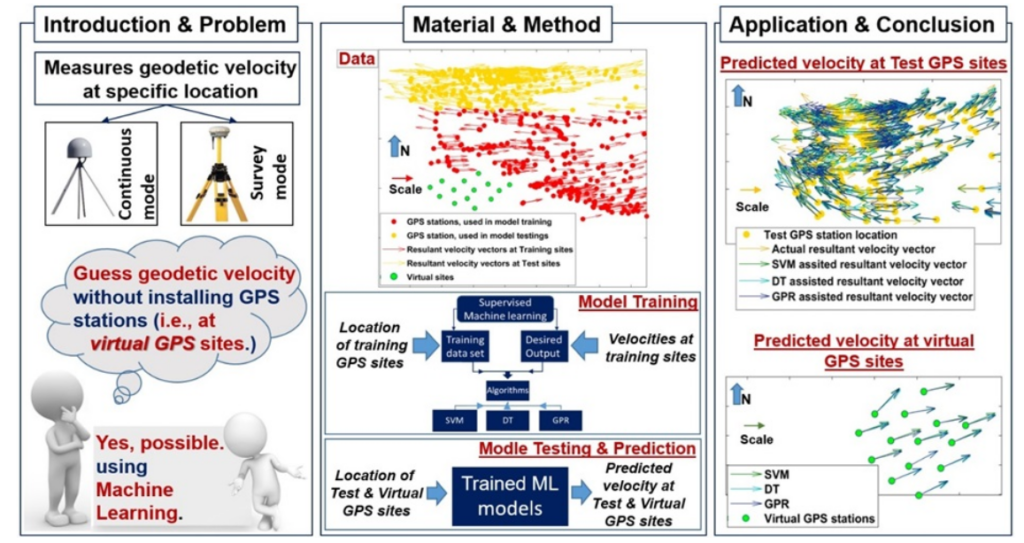
Key Insights Of The Research:
- Objective: To improve the understanding of crustal dynamics and tectonic movements in this geologically active Tibetan region.
- Scientists utilised a dense network of GPS and geodetic sensors to measure crustal strain and movement across the plateau.
- Key Findings:
- The Tibetan Plateau experiences significant tectonic stress due to its position between the Indian and Eurasian plates.
- Crustal deformation was observed, indicating continuous uplift and horizontal stretching of the region.
- Applications:
- Findings contribute to earthquake risk assessments and predictions in surrounding regions, especially in China and India.
- Enhanced understanding of plate tectonics in one of the Earth’s most complex collision zones.
- Impact: The mission has improved the accuracy of geophysical models for predicting seismic activity in the region.
| Geology of Tibetan Plateau |
|
| PYQ: Bring out the causes for more frequent landslides in the Himalayas than in Western Ghats. (100 words/5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2013) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the role of tectonic activity in shaping the geology of the Tibetan Plateau and its impact on regional climate and seismic activity. (150 Words /10 marks) |
6. New smart sensor for adjusting drug dosage to manage Parkinson’s Disease
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2049045 )
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
Parkinson’s Disease:
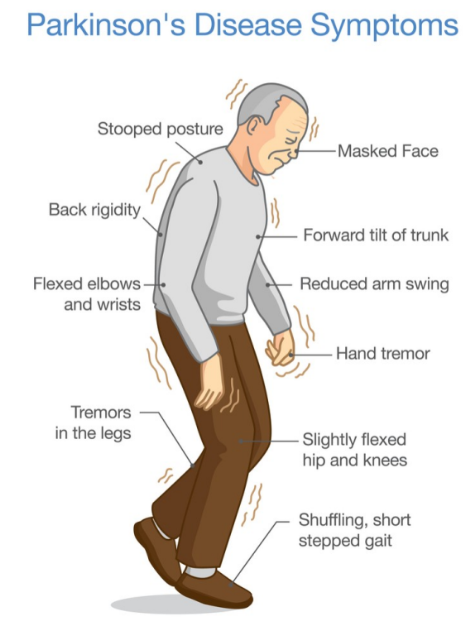
- Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterised by the gradual loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain.
- This deficiency leads to motor symptoms such as tremors, rigidity, slowness of movement, and postural instability.
- Non-motor symptoms, including cognitive decline, mood disorders, and sleep disturbances, also commonly occur.
- The exact cause is unknown, though genetic and environmental factors are believed to play roles.
- Treatment primarily focuses on managing symptoms through medications like L-dopa, which is converted to dopamine in the brain, and various therapies.
- While there is no cure, advancements in research aim to improve symptom management and quality of life for affected individuals.
7. ANUBHAV AWARDS 2024 will be conferred by Union Minister in Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2049061 )
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context |
| Dr. Jitendra Singh, Minister of State for Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions, will confer the Anubhav Awards 2024 and launch the Integrated Pensioners’ Portal on 28th August, 2024. |
Anubhav Awards:
- The Anubhav Awards, instituted by the Department of Pension & Pensioners’ Welfare (DOPPW) in 2016, recognize retiring and retired Central Government employees for documenting their notable work experiences and contributions during their service.
- These awards promote the sharing of professional knowledge to benefit the workforce and governance.
- The awards are conferred annually, celebrating excellence and encouraging the dissemination of best practices across various government sectors.
- A significant portion of the awardees are women, reflecting their growing contributions to governance.
Prelims Facts
1. Himachal Assembly passes Bill raising marriage age for women to 21 from 18
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 5)
| Context |
| Himachal Pradesh has raised the minimum marriage age for women from 18 to 21 through the Prohibition of Child Marriage (Amendment) Bill, 2024, aiming to promote gender equality and higher education. |
Analysis of the news:
- Himachal Pradesh Assembly passed a Bill raising the minimum age of marriage for women from 18 to 21 years.
- The Prohibition of Child Marriage (Himachal Pradesh Amendment) Bill, 2024 was introduced to amend the Prohibition of Child Marriage Act, 2006.
- The Bill was passed by voice vote.
- Early marriages are seen as a hindrance to women’s career progress and physical development.
- By increasing the marriage age, the Bill intends to provide women with better opportunities for personal growth and education.
- Himachal Pradesh became the first state in India to raise the minimum age for marriage for women to 21 years.
2. Northern bald ibis returns from near extinction
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- The northern bald ibis, notable for its black-and-iridescent green plumage, bald red head, and long curved beak, was hunted to near extinction by the 17th century.
- IUCN Status: Endangered (Downlisted from Critically Endangered to Endangered in 2018)

- Historically found in North Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, and Europe, the species was also considered a delicacy and vanished from Europe.
- Breeding and rewilding efforts have revived the species over the past two decades, moving its status from “critically endangered” to “endangered.”
- The reintroduction project began in 2002 by biologist Johannes Fritz and the Waldrappteam in Austria.
- The birds lack instinctive migratory knowledge, requiring human intervention for successful migration.
- Chicks are raised by foster parents and are being trained to follow a microlight aircraft during migration.
- The project has led to nearly 300 northern bald ibises in Central Europe, with hopes to exceed 350 birds by 2028 and establish a self-sustaining population.
3. OPEC+ output cut may push Indian refiners to source oil from Americas
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 12)
| Context |
|
Key Differences Between OPEC and OPEC+:
- Formation: OPEC was formed in 1960 by Iraq, Iran, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela. OPEC+ was established in 2016, including 10 non-OPEC oil producers such as Russia.
- Members: OPEC has 13 member countries. OPEC+ extends beyond OPEC to include additional countries like Russia, expanding its influence.
- Objectives: OPEC’s primary goal is to coordinate petroleum policies among member countries. OPEC+ aims to include both OPEC and non-OPEC producers in managing oil production and prices.
- Production Control: OPEC sets production targets solely for its members. OPEC+ coordinates production targets among both OPEC and non-OPEC countries, including major producers like Russia.
- Market Influence: OPEC+ controls a larger share of global oil production (about 59% in 2022) compared to OPEC alone, enhancing its impact on global oil prices.
4. IIL, Australian varsity develop needle-free COVID-19 vaccine
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- Indian Immunologicals Ltd (IIL) and Griffith University have developed a needle-free intranasal booster vaccine against SARS-CoV-2.
- The vaccine utilises “codon de-optimisation” technology for virus attenuation, which is faster and safer than conventional methods.
| “Codon De-Optimisation” Technology |
|
- The vaccine aims to address ongoing concerns about COVID-19 variants and boost immunity.
5. Indian Army Places Order for 73,000 Additional SIG716 Rifles from US Firm SIG Sauer
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 10)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
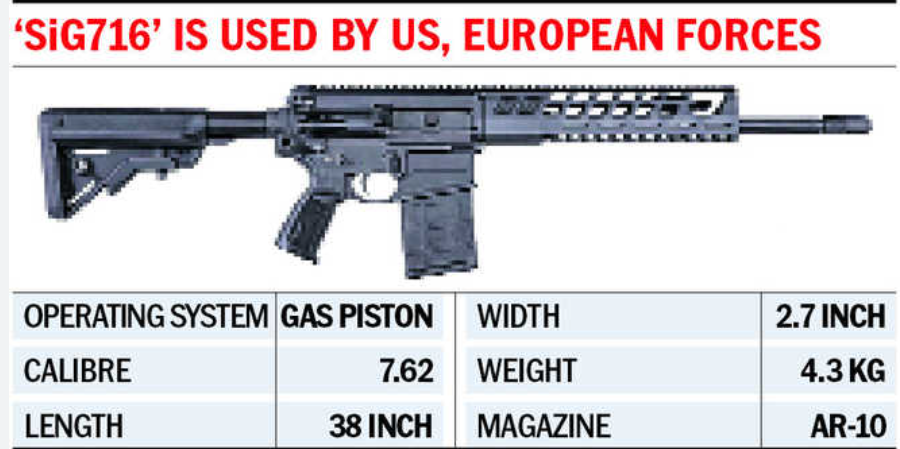
Background and Initial Procurement
- The Ministry of Defence initially awarded a contract to SIG Sauer in 2019 for 72,400 SIG716 rifles.
- These rifles are currently in use by the Armed Forces of the US and several European countries.
- The procurement was done under the fast-track procurement procedure to quickly modernize the Indian Army’s arsenal.
Replacement of Existing Rifles
- The SIG716 rifles are intended to replace the Indian Army’s existing 5.56×45mm INSAS rifles with the more powerful 7.62×51mm modern assault rifles.
- The Indian Armed Forces have traditionally used Russian-origin AK-47s and the 5.56×45mm INSAS rifles.
- Additionally, India and Russia are jointly producing AK203 rifles at a factory in Amethi, Uttar Pradesh.
6. Assam Introduces New Bill for Compulsory Registration of Muslim Marriages and Divorces
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 10)
| Context: |
| The Assam legislative Assembly introduced the Assam Compulsory Registration of Muslim Marriages and Divorces Bill, 2024, aiming to replace the 1935 Act that previously governed these matters. |
Analysis of News:
Objectives of the Bill
- The primary objectives of the new Bill include preventing child marriages, ensuring marriages are based on the free consent of both parties, and checking polygamy.
- The Bill also aims to protect women’s rights to matrimonial homes, maintenance, inheritance, and to deter men from deserting women after marriage. It emphasizes strengthening the institution of marriage.
Changes from the 1935 Act
- Under the 1935 Act, Muslim registrars were licensed by the state to register marriages and divorces.
- The new Bill eliminates the position of Muslim registrars and instead assigns the responsibility of registration to the Marriage and Divorce Registrar of the concerned district.
Key Provisions for Registration
- The Bill mandates that women must be at least 18 years old and men 21 years old at the time of marriage. Marriages must be based on the free consent of both parties.
- It also includes provisions to report underage marriages to Child Marriage Prohibition Officers and requires a 30-day notice period for marriage registration, during which objections can be raised.
Appeal Process
- If a Registrar refuses to solemnize a marriage, the Bill allows for two levels of appeal: first to the District Registrar and then to the Registrar General of Marriages.



