29 August 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. India and Russia sign a working plan to handle emergencies
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations – Bilateral Relations |
| Context |
|
India-Russia Emergency Management Cooperation
Working Plan Agreement
- India and Russia signed a working plan for the Joint Russian-Indian Commission on Cooperation in Emergency Management for 2025-26.
- The agreement was signed by Union Minister of State for Home Nityanand Rai and Russian Minister for Civil Defence, Emergencies, and Elimination of Consequences of Natural Disasters.
Historical Context
- The agreement follows previous collaborations, including the Inter-Governmental Agreement (IGA) from December 2010 and the establishment of the Indo-Russian Joint Commission for Cooperation in 2013.
- The first meeting of this commission took place in New Delhi in 2016.
Areas of Cooperation
- Space Monitoring Technologies: Implementation of space-based technologies for risk forecasting and emergency response.
- Disaster Response Experiences: Exchange of experiences in managing large-scale disasters.
- Training: Cooperation in training fire and rescue specialists.
Future Plans And Objectives
- The working plan aims to enhance bilateral efforts, improve early warning systems, and boost capacity building in emergency preparedness, prevention, response, and planning.
- The agreement is intended to upgrade existing frameworks and support mutual assistance in enhancing emergency management capabilities in both countries.
| Practice Question: Discuss the impact of the 2025-26 working plan between India and Russia on their cooperation in emergency management and disaster response. (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. Wanted: a strategy to turn climate research into disaster management
| Topic: GS3 – Disaster and disaster management. |
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
Awareness and Challenges
- India faces a range of location-specific natural hazards, including heatwaves, wildfires, heavy rains, landslides, droughts, and cyclones.
- The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) is recognized for its effective disaster response and efforts to reduce mortality and damage.
- Despite its achievements, NDMA contends with knowledge gaps and barriers in improving its operations to enhance weather readiness and climate resilience.
Weather Extremes and Climate Change
- Indian regions experience weather extremes in all seasons, with phenomena such as heatwaves, wildfires, and rainfall extremes occurring outside the traditional monsoon period.
- Climate change impacts include cooler trends in northern-central India and warmer trends in peninsular India.
- Additionally, increased wildfires and landslides are being observed recently.
Vulnerability Factors
- Vulnerability is exacerbated by population and economic growth, with people moving to unsafe regions and informal housing in unstable or flood-prone areas.
- Increased tourism and infrastructure development in these regions contribute to the problem, as does the replacement of forest cover with cash crops.
Ineffective Translation of Climate Research
- India invests heavily in climate research and services to support various sectors, but uptake remains low due to insufficient location- or sector-specific information and inadequate skills for using it.
- Efforts to downscale global forecasts to hyperlocal scales are ongoing, but operationalizing these forecasts remains a major hurdle.
Case Studies of Implementation Issues
- Irrigation Advisories:
- Weather forecasts are used to provide farm-scale irrigation advice, which can save up to 30% of water without affecting crop yield.
- Large-scale implementation requires local government, NGOs, and farmer organisations for effective use and feedback collection. Current lack of extension agencies and funding structures hampers progress.
- Urban Flood Predictions:
- Effective urban flood management requires downscaled rainfall forecasts and coordination of drainage pumps, traffic control, and other city functions.
- Municipalities use sensors and weather data, but comprehensive flood management is constrained by inadequate research-to-operation systems and lack of trained personnel.
From Research to Operations
- Climate research needs to transition from academic goals to practical applications for effective disaster management and climate resilience.
- There is a need for sector-specific extension agents to bridge the gap between research and operational needs, ensuring that solutions are tailored to local contexts.
- Sustained financing and capacity-building are essential for developing effective research-to-operations systems at local and sectoral levels.
Conclusion
- To ensure India’s development is sustainable and safe, there must be a focus on improving weather readiness and climate resilience through better integration of research with practical applications.
- Training and deploying sector-specific extension agents who can communicate in local languages and manage cultural factors is crucial for effective disaster management and risk mitigation.
| PYQ: Vulnerability is an essential element for defining disaster impacts and its threat to people. How and in what ways can vulnerability to disasters be characterised? Discuss different types of vulnerability with reference to disasters. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2019) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the challenges and solutions in improving disaster management and climate resilience in India, focusing on translating climate research into practical applications. (250 Words /15 marks) |
3. High amount of microplastics in Indian personal care products
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Health |
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
Where Micro Plastic Found
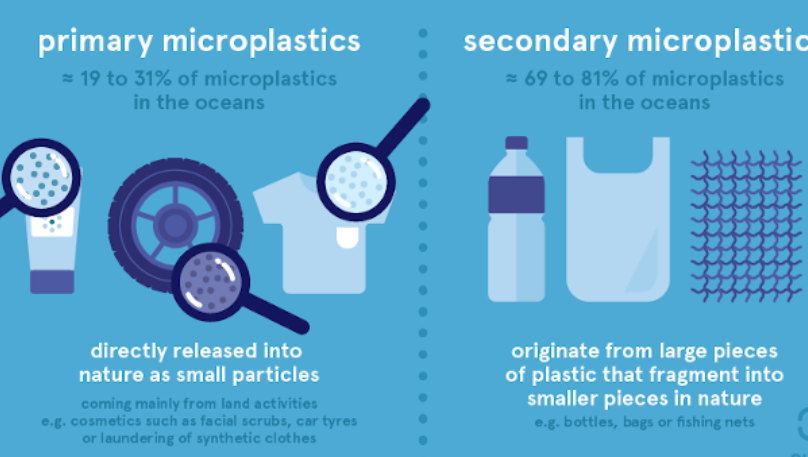
Definition of Microplastics
- Microplastics are small plastic particles under 5 millimetres in size. They include microbeads, which have a diameter under 5 millimetres, and are often used in personal care products like face washes and scrubs.
Increasing Uses of Microplastics
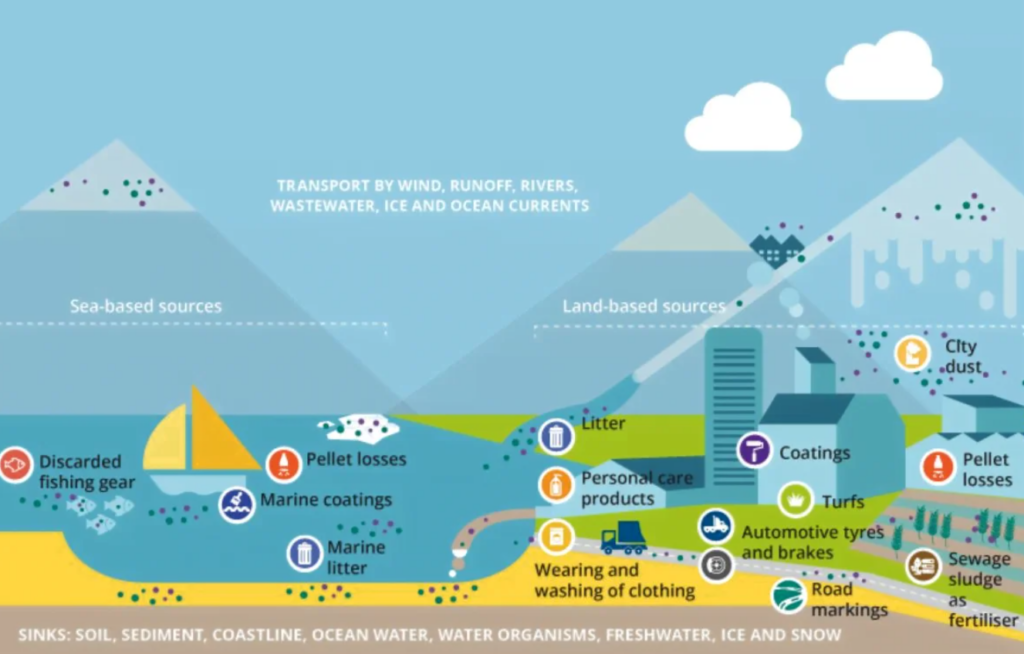
- Personal Care Products: Microplastics, such as polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene, are commonly used in face washes, scrubs, and shower gels as exfoliating agents and to enhance ingredient delivery.
- Pharmaceuticals: Bioplastics like polycaprolactone are utilised as drug carriers due to their anti-ageing and antibacterial properties.
- Consumer Goods: Microplastics are found in various products including cleaning agents and cosmetics, often under labels like “natural” or “eco-friendly,” which can be misleading.
Adverse Impacts of Microplastics
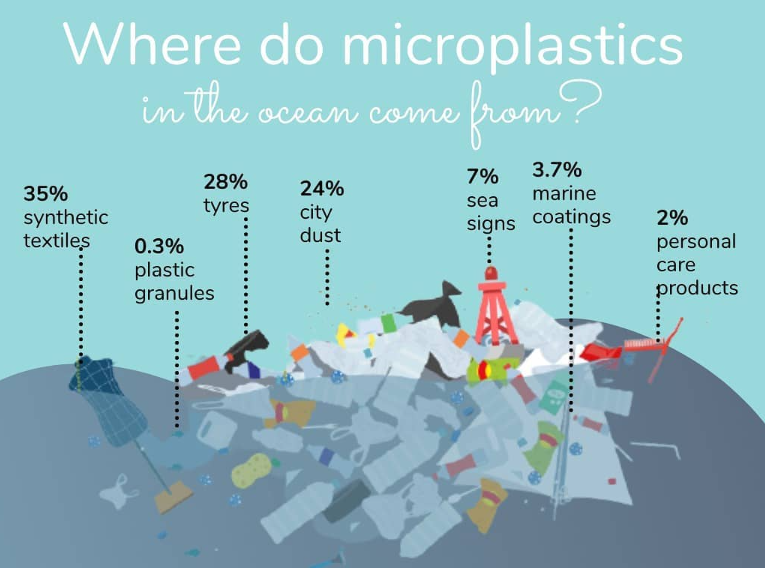
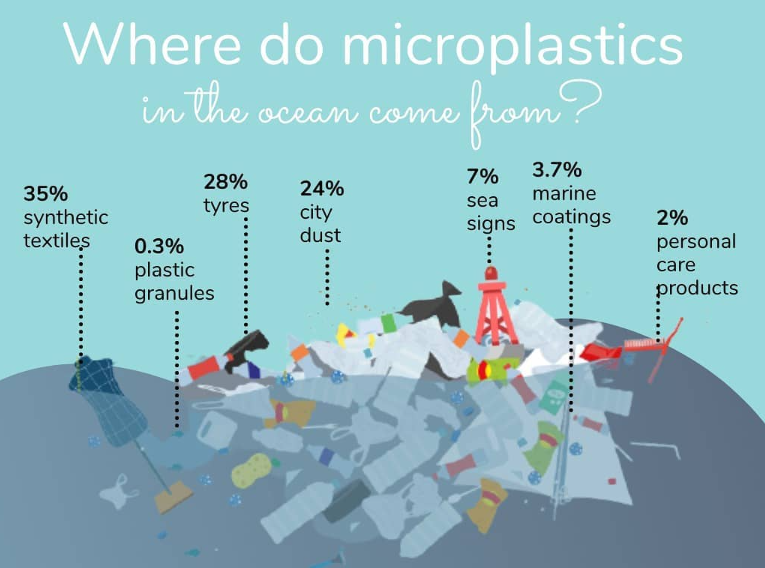
- Environmental Pollution: Microplastics contaminate water bodies and soil, adversely affecting both aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems.
- Impact on Wildlife: Marine organisms ingest microplastics, leading to disruptions in food chains and harm to wildlife.
- Health Risks: Microplastics are found in human tissues, such as the brain, blood, lungs, and digestive system, raising concerns about potential health impacts.
- Bioaccumulation: Microplastics can accumulate in human and animal bodies, leading to unknown long-term health effects.
- Greenwashing: Products labelled as “organic” or “eco-friendly” may still contain microplastics, misleading consumers about their environmental impact.
- Complicated Efforts: Greenwashing undermines efforts to reduce plastic pollution and complicates the pursuit of product transparency and environmental responsibility.
| Practice Question: Discuss the environmental and health impacts of microplastics in personal care products. How can policies be improved to address microplastic pollution effectively in India? (250 Words /15 marks) |
4. Supreme Court Reaffirms: ‘Bail is the Rule, Jail the Exception’ Even Under PMLA
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Cover Page; Page: 01)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context: |
| The Supreme Court reaffirmed that the legal principle “bail is the rule and jail is the exception” applies even in cases registered under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) 2002. |
Analysis of News:
What is PMLA, 2002?
- The Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA) is an Act of the Parliament of India enacted to prevent money laundering and provide for the confiscation of property derived from money laundering.
- It aims to combat money laundering related to illegal activities such as drug trafficking, smuggling, and terrorism financing.
- Objectives of PMLA:
- Prevention: To prevent money laundering by implementing stringent measures and monitoring financial transactions.
- Detection: To detect and investigate instances of money laundering through proper enforcement and regulatory mechanisms.
- Confiscation: To confiscate properties derived from money laundering activities to deter offenders and disrupt illicit financial flows.
- International Cooperation: To facilitate international cooperation in combating money laundering and terrorist financing activities.
Reference to Previous Rulings
- In granting bail to Prem Prakash, the bench referred to the July 27, 2022, ruling in Vijay Madanlal Choudhary and Ors. vs. Union of India and Ors., which upheld the constitutional validity of PMLA and the powers of the Enforcement Directorate (ED).
- The Court highlighted that Section 45 of PMLA does not impose an absolute restraint on granting bail.
Significance of Article 21
- The bench emphasized that the principle of “bail is the rule and jail is the exception” aligns with Article 21 of the Constitution, which guarantees that no person shall be deprived of their life or personal liberty except by lawful procedures.
Application of Section 45 of PMLA
- While Section 45 of PMLA imposes twin conditions for bail, these conditions do not override the constitutional principle.
- The Court noted that prolonged pre-trial incarceration should not be used as a punishment, and the conditions for bail can be relaxed in cases where the accused has been in custody for a long time.
Role of the Public Prosecutor
- The judgment underlined that when opposing bail, the Public Prosecutor must present a cogent case showing how the foundational facts required by the Vijay Madanlal Choudhary ruling are established.
- Only after this can the presumption under Section 24 arise, shifting the burden onto the accused.
Inadmissibility of Statements under Section 50 PMLA
- The bench also held that any statement made under Section 50 of PMLA by a person in custody to the same Investigating Agency is inadmissible, as the individual cannot be considered to be operating with a free mind.
| What Factors Necessitated the Adoption of PMLA, 2002? |
|
Flourishing Drug Trade at Global Level:
Formation of Financial Action Task Force:
Adoption by Indian Parliament:
Recommendations of the Narasimham Committee:
Adhering to Provisions of Erstwhile Legislations:
|
| PYQ: Discuss how emerging technologies and globalisation contribute to money laundering. Elaborate measures to tackle the problem of money laundering both at national and international levels. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2021) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of the Supreme Court’s reaffirmation that “bail is the rule and jail is the exception” in the context of the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA). How does this principle align with Article 21 of the Constitution? (250 words/15 m) |
5. Union Cabinet Approves Railway Projects Worth Rs 6,456 Crore
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt & Politics; Page: 05)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy – Infrastructure |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
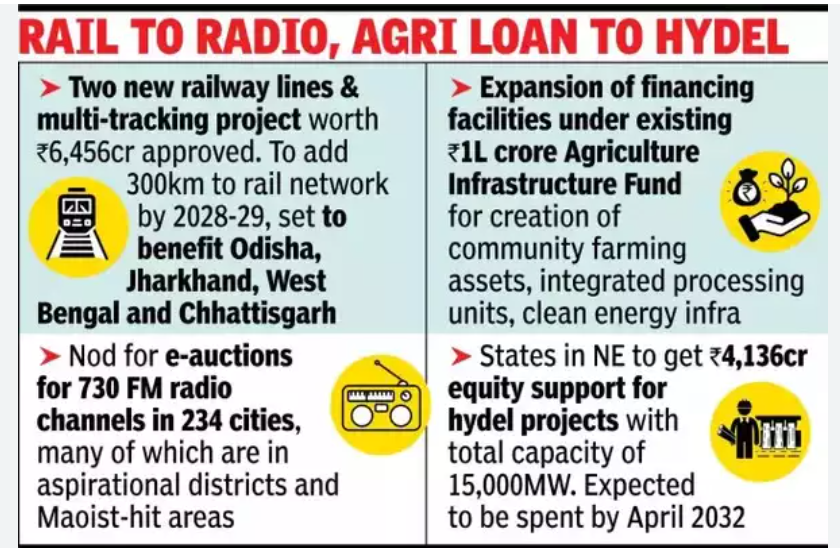
Key Projects and Corridors
- Jamshedpur-Purulia-Asansol (121 km): A third line connecting Jharkhand and West Bengal, linking the Delhi-Howrah and Mumbai-Howrah corridors. Cost: Rs 2,170 crore.
- Sardega-Bhalumuda (37 km): A new double line between Odisha and Chhattisgarh.
- Bargarh-Nawapara Road (138 km): A new line in Odisha, enhancing connectivity for agricultural goods and promoting local textile products. Cost: Rs 2,926 crore.
Economic and Environmental Impact
- The projects aim to boost transportation efficiency, particularly for industrial goods, and reduce CO2 emissions by shifting cargo transport from road to rail.
- The Jamshedpur-Purulia-Asansol corridor alone is expected to save 72 crore kg of CO2 emissions.
Infrastructure Development
- These projects will include the construction of 14 new stations and provide connectivity to approximately 1,300 villages, benefiting about 11 lakh people.
- The routes will support the transportation of essential commodities, aligning with the PM-Gati Shakti National Master Plan.
| About PM Gati Shakti |
Integrated Approach: It intends to bring together 16 infrastructure related Ministries.
|
| PYQ: Investment in infrastructure is essential for a more rapid and inclusive economic growth. Discuss in the light of India’s experience. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2021) |
| Practice Question: Examine the significance of the recent Union Cabinet-approved railway projects in enhancing regional connectivity and economic development in eastern India. How do these projects align with the goals of the PM-Gati Shakti National Master Plan? (250 words/15 m) |
6. Cabinet accords approval for progressive expansion of Central Sector Scheme of ‘Agriculture Infrastructure Fund’
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2049318 )
| Topic: GS3 – Agriculture – Storage, transport and marketing of agricultural produce |
| Context |
|
Agricultural Infrastructure Fund (AIF)

Aim of the Fund:
- To enhance and strengthen agricultural infrastructure in India.
- To support the development of farming communities and improve productivity.
- To foster a sustainable agricultural ecosystem by investing in infrastructure projects.
- To promote convergence with other government schemes for integrated benefits.
- To drive private sector investments and create rural employment opportunities.
Features of the Fund:
- Expansion of Scope: Includes viable community farming assets as eligible projects for funding.
- Integrated Processing Projects: Allows funding for primary and secondary processing projects; standalone secondary projects are covered under MoFPI schemes.
- Convergence with PM KUSUM: Facilitates alignment of Component-A of PM-KUSUM with AIF, supporting clean energy solutions for farmers, FPOs, and cooperatives.
- Extended Credit Guarantee: Expands credit guarantee coverage for FPOs, enhancing financial security.
- Achievement Metrics: Since its launch in 2020, AIF has funded 74,508 projects, creating 500 LMT of additional storage capacity and generating over 8.19 lakh rural jobs.
- Investment Mobilisation: Total sanctioned amount of Rs 47,575 Crore has mobilised Rs 78,596 Crore in investments, with significant contributions from private entities.
| PYQ: Investment in infrastructure is essential for a more rapid and inclusive economic growth. Discuss in the light of India’s experience. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2021) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the objectives and key features of the Agricultural Infrastructure Fund (AIF) introduced by the Government of India. How has the fund contributed to enhancing agricultural infrastructure since its inception? (250 Words /15 marks) |
7. Cabinet approves 12 Industrial nodes/cities under National Industrial Corridor Development Programme
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy – Infrastructure |
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2049314 )
| Context |
| The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs has approved 12 new industrial smart city projects under the National Industrial Corridor Development Programme (NICDP), with a total investment of Rs. 28,602 crore. |

Analysis of the news:
- These projects span across 10 states, including Uttarakhand, Punjab, Maharashtra, Kerala, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and Rajasthan, and are aligned along six major corridors.
- The industrial cities will be developed as greenfield smart cities, incorporating ‘plug-n-play’ and ‘walk-to-work’ concepts to ensure advanced and efficient infrastructure.
- The NICDP aims to boost India’s manufacturing capabilities, contributing towards the $2 trillion export target by 2030, and enhance the country’s position in Global Value Chains.
- The projects are expected to create up to 1 million direct and 3 million indirect jobs, promoting regional economic growth and socio-economic development.
- Emphasis on sustainability includes ICT-enabled utilities and green technologies to minimise environmental impact, aligning with the vision of ‘Viksit Bharat’ or a developed India.
8. Piezoelectric polymer nanocomposite developed can be used for energy harvesting
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2049436 )
| Context |
|
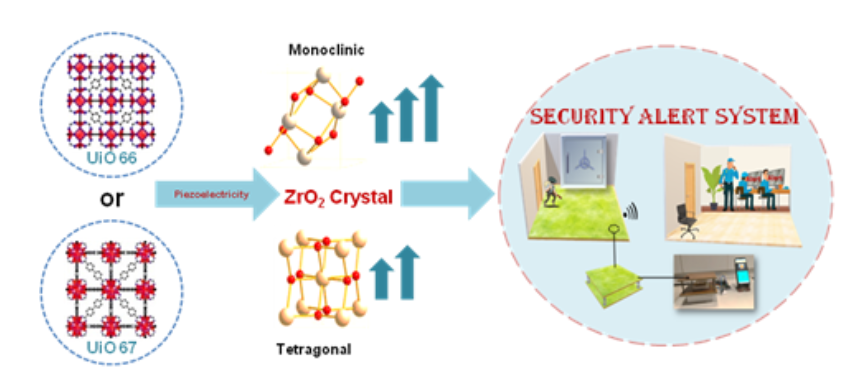
Potential Applications:
- Pressure Sensing: The nanocomposite can be used in flexible, wearable sensors for monitoring pressure changes in various environments.
- Energy Harvesting: It can convert mechanical energy from sources like footsteps into electrical energy, suitable for powering small devices or contributing to energy-efficient systems.
- Security Systems: The material is employed in piezoelectric pavement prototypes that activate security alerts when pressure is detected, with wireless communication through Bluetooth.
- Wearable Electronics: The composite’s flexibility and efficiency make it ideal for integration into wearable technology, offering both energy generation and pressure sensing.
- Sustainable Technologies: The material supports the development of eco-friendly and sustainable energy solutions by harnessing mechanical energy.
| What Is Piezoelectric Performance? |
|
Prelims Facts
1. India signs repeat order for 73,000 SIG 716 rifles; deliveries by 2025-end
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|
SIG 716 Rifles:
- The SIG 716 is a modular, gas-operated, semi-automatic rifle manufactured by Sig Sauer.
- Weighing 3.82 kg, it features a 16-inch barrel and an effective range of 600 metres.
- Designed for reliability and versatility, it is equipped with a free-floating handguard, adjustable stock, and Picatinny rail for accessories.
- The rifle utilises a short-stroke piston system, enhancing its durability and performance under various conditions.
- Compared to the INSAS rifles, the SIG 716 offers improved accuracy, reliability, and modern features, making it suitable for both standard and counter-insurgency operations.
- It has been adopted by several military forces globally for its robust performance.
2. Orcas Ramp Up Attacks on Sailboats: Researchers Investigate Mysterious Behavior in Iberian Waters
(Source: Indian Express; Section: The World)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Key facts related to Orcas:
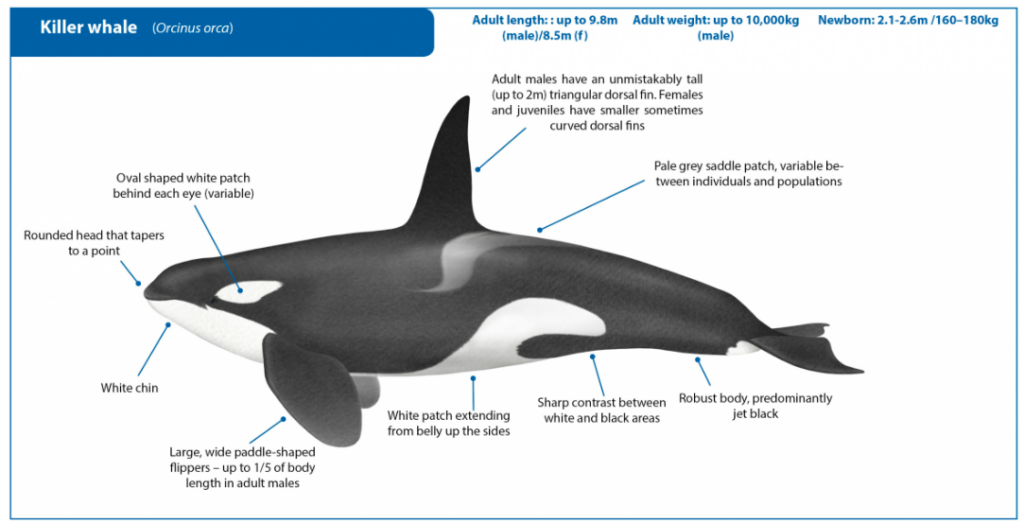
- Common name – Killer whale
- Family – They are largest of the Dolphin family.
- Biology & Size – Adults, Killer Whale males are considerably larger than the females. They are about 9.5 m long and weigh up to 8 tons, whilst females are 7 to 8.5 m long and weigh 4 tons or more. Calves at birth, 2-2.4 m long.
- Along with pilot whales and sperm whales, this is the only mammal species other than humans, where females are known to have an extended post-reproductive period (menopause)
Theories Behind the Behavior
- Researchers are uncertain about the motivations behind these attacks. Some suggest that orcas might be using boats as practice targets for hunting techniques, while others believe the behavior could stem from past traumatic encounters or simple playfulness.
- The Bottlenose Dolphin Research Institute in Spain has proposed a new theory, suggesting that orcas may be practicing hunting techniques on sailboats, which resemble their prey, Atlantic bluefin tuna.
Impact on Sailors and Ongoing Research
- These incidents have caused alarm among sailors in the region, who have tried various deterrents, such as painting hulls or playing loud music, to avoid orca attacks.
- While researchers continue to study the behavior, it appears that young orcas are primarily involved, possibly under the guidance of adults. The orcas seem to have learned that sailboat rudders are vulnerable targets, making these vessels a convenient tool for training.
Overall, this phenomenon poses a growing challenge for sailors navigating these heavily trafficked waters, and further research is needed to understand and mitigate the risks.
3. Uttar Pradesh Introduces Digital Media Policy 2024: Influencers to be Paid Up to Rs 8 Lakh per Month for Promoting State Schemes
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Cover Page; Page: 01)
| Context: |
| The Uttar Pradesh Digital Media Policy 2024 allows the state government to pay up to Rs 8 lakh per month to influencers for promoting government schemes, with content payments based on views and strict guidelines on acceptable content. |
Analysis of News:

Uttar Pradesh Digital Media Policy 2024: Key Highlights
- The Uttar Pradesh government has introduced the Digital Media Policy 2024, enabling it to pay influencers up to Rs 8 lakh per month to promote state schemes.
- Influencers are categorized based on their followers, with payments tied to content views.
- The policy also grants the Information Director authority to halt payments and take action if content is deemed anti-national, anti-social, indecent, or misleading.
Controversy and Clarifications
- Opposition parties have criticized the policy as a means to control social media content.
- In response, the Information Director clarified that the policy only allows for legal action under existing laws against problematic content, such as lodging FIRs or discontinuing advertisements.
- The policy also includes guidelines for influencer empanelment, requiring a minimum of two years of activity and no criminal records.
Payment Structure
- The policy outlines payment structures across various digital platforms like Facebook, Instagram, YouTube, and X (formerly Twitter), with categories based on the number of followers or subscribers.
- Payments range from Rs 10,000 per post to Rs 8 lakh per month, depending on the platform and content type.
4. Favorable Weather Boosts India’s Life Expectancy by One Year Amid Decline in PM2.5 Pollution
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 11)
| Context: |
| A study by the Energy Policy Institute at the University of Chicago (EPIC) found that favorable meteorological conditions led to a decline in PM2.5 particulate pollution in India between 2021 and 2022, contributing to an increase in life expectancy by one year. |
Analysis of News:
What is PM 2.5?
- PM 2.5 is an atmospheric particulate matter of diameter of fewer than 2.5 micrometres, which is around 3% the diameter of a human hair.
- PM 2.5 particles are small enough to penetrate deep into the lungs and even enter the bloodstream, and long-term exposure to PM 2.5 can lead to lung cancer, heart disease, stroke, and other chronic health conditions.
Role of Meteorology and Emissions
- The study highlighted that the decline in PM2.5 levels was not solely due to reduced emissions but was amplified by favorable weather conditions, which had a significant impact on reducing pollution across South Asia.
Regional Variations and Life Expectancy Gains
- Despite the overall decline, 42.6% of India’s population still lived in areas exceeding the national air quality standard of 40 µg/m³.
- The most significant reductions were seen in Purulia and Bankura districts in West Bengal and Dhanbad district in Jharkhand, where pollution levels decreased by over 20 µg/m³.
- Sustained reductions in these areas could lead to life expectancy gains of up to 2.3 years.
Global Context and Health Impacts
- The EPIC report emphasized that air pollution remains the greatest external threat to human life expectancy globally, surpassing other factors such as child and maternal malnutrition, tobacco use, and unsafe water and sanitation.
- Despite slight global declines in pollution, particulate pollution still significantly reduces life expectancy, especially in India, where it takes 3.6 years off the average resident’s life.



