29 June 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. South African Researchers Inject Radioactive Material into Rhino Horns to Combat Poaching
(Source: Indian Express; Section: The World)
| Topic: GS3 – Environment – Conservation |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:

Methodology:
- The process involves tranquilizing the rhinos, drilling a hole into their horns, and inserting the radioactive isotopes.
- This procedure, conducted by experts from the University of the Witwatersrand, is intended to serve as a deterrent by making the horns detectable at borders, leveraging the global network of radiation monitors.
Rationale and Goals:
- Experts leading the project, explains that the initiative seeks to utilize technology designed for nuclear security to combat wildlife trafficking.
- By making rhino horns detectable through radiation, authorities hope to curb the illegal trade that has significantly reduced rhino populations.
Current Rhino Population and Poaching Trends:
- The global rhino population has plummeted from about 500,000 in the early 20th century to around 27,000 today.
- South Africa, home to the largest rhino population, faces severe poaching issues, with over 500 rhinos killed annually.
- While poaching declined during the COVID-19 pandemic, numbers have risen again as restrictions eased.
Challenges and Criticism:
- Despite its innovative approach, the project faces criticism regarding its efficacy and ethical implications.
- Critics argue that poachers may circumvent traditional border crossings, rendering the strategy less effective.
- Ethical concerns about the impact of radiation on the animals have also been raised, though researchers assure that extensive testing has been conducted.
Conclusion
- As rhino poaching continues to threaten populations, this new approach represents a novel effort to combat the crisis.
- While the project faces skepticism and challenges, it highlights the need for innovative solutions in wildlife conservation.
| What are the Conservation Efforts by India ? |
|
|
PYQ: Consider the following statements: (2019) 1) Asiatic lion is naturally found in India only. 2) Double-humped camel is naturally found in India only. 3) One-horned rhinoceros is naturally found in India only. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (a) |
| Practice Question: Evaluate the effectiveness and ethical implications of using radioactive material in rhino horns as a deterrent against poaching. Consider the potential impacts on wildlife conservation and international trafficking prevention.. (250 words/15 m) |
2. Maharashtra announces own ‘Ladli Bahin’ scheme, sops for OBCs, EWS
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt and Politics; Page: 08)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government policies– Interventions for development in various sectors |
| Context: |
| Ahead of the upcoming Assembly elections, the Maharashtra Government has introduced a series of populist measures in its budget, focusing on social welfare and financial support for various groups. |
Analysis of News:

Key Initiatives:
- The budget includes initiatives such as the ‘Mukhya Mantri Majhi Ladki Bahin Yojana’, providing a monthly allowance of Rs 1,500 to eligible women aged 21 to 60.
- Additionally, the ‘Mukhya Mantri Annapurna Yojana’ offers three free LPG cylinders annually to over 52 lakh families, reflecting the government’s focus on women and household welfare.
Educational and Youth Support
- The government announced full tuition and examination fee reimbursement for girls from OBC and EWS households, covering professional degree and diploma courses.
- This initiative aims to benefit about 2.05 lakh girls, starting in the 2024-25 academic year. For unemployed youth, the ‘Mukhya Mantri Yuva Karyaprashikshan Yojana’ will provide skill training and a monthly stipend, with a substantial allocation of Rs 10,000 crore.
Support for Farmers and Fuel Price Reductions
- The budget includes provisions to cover electricity bills for over 44.06 lakh farmers and free power for agriculture pumps up to 7.5 horsepower.
- Additionally, fuel prices in Mumbai, Thane, and Navi Mumbai have been reduced, offering relief to residents in these metropolitan areas.
Political Context
- These measures come after the ruling alliance’s significant reduction in seats in the recent Lok Sabha elections.
- The government’s ambitious schemes are seen as a response to bolster support ahead of the state elections, though they face criticism from the opposition, who view them as election-centric announcements.
Conclusion
- The Maharashtra Government’s budget reflects a strategy to appeal to a broad section of society through financial support and welfare initiatives.
- The effectiveness and implementation of these measures remain to be seen, as a high-level committee is set to evaluate and rationalize the schemes.
| PYQ: Performance of welfare schemes that are implemented for vulnerable sections is not so effective due to absence of their awareness and active involvement at all stages of policy process – Discuss. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2019) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of populist measures in state budgets on fiscal health and electoral outcomes, using the recent Maharashtra budget as a case study. Analyze the balance between social welfare and economic sustainability. (250 words/15 m) |
3. India Achieves High Compliance with FATF Standards, But Further Measures Needed in Non-Financial Sectors
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Economy; Page: 11)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations – Important International institutions, agencies and fora – their structure, mandate. |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News
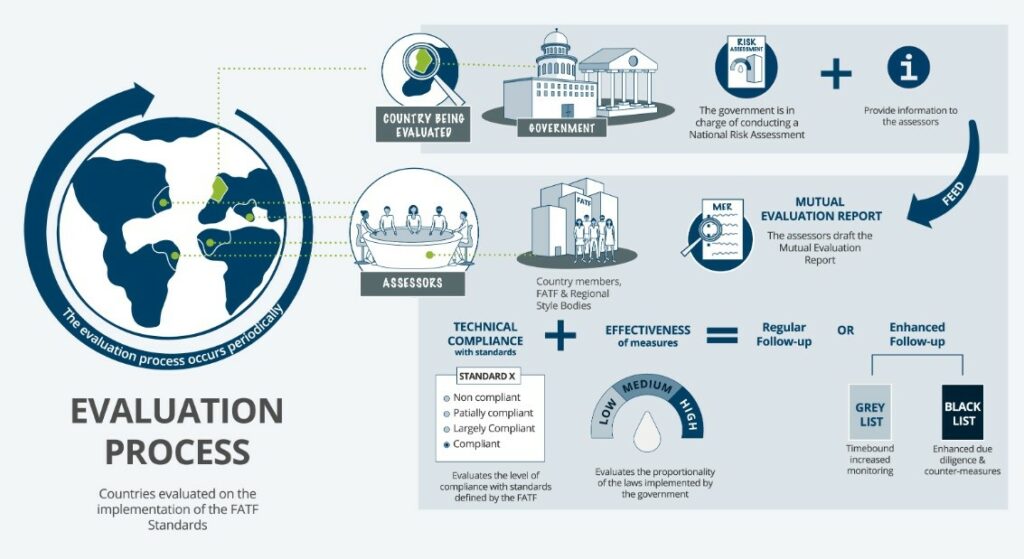
What is the FATF?
- FATF is the global money laundering and terrorist financing watchdog set up in 1989 out of a G-7 meeting of developed nations in Paris.
Objective:
- Initially, its objective was to examine and develop measures to combat money laundering.
- After the 9/11 attacks on the US, the FATF in 2001 expanded its mandate to incorporate efforts to combat terrorist financing.
- In April 2012, it added efforts to counter the financing of proliferation of Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMD).
Areas for Improvement:
- Despite the high compliance rating, the FATF noted that India must address certain delays in concluding money laundering (ML) and terrorist financing (TF) prosecutions.
- Additionally, the watchdog emphasized the need for enhanced supervision and implementation of preventive measures in specific non-financial sectors, such as real estate agents, dealers in precious metals and stones, professional accountants, and virtual asset service providers (VASPs).
- The FATF also called for measures to prevent the non-profit sector from being exploited for terrorist financing, aligned with a risk-based approach.
Mutual Evaluation Report and Technical Compliance:
- The FATF adopted the joint Financial Action Task Force mutual evaluation report of India, which assessed the effectiveness of India’s measures to combat ML, TF, and proliferation financing, as well as their compliance with FATF recommendations.
- The report concluded that India has reached a high level of technical compliance, with significant achievements in understanding ML and TF risks, international cooperation, access to basic and beneficial ownership information, financial intelligence usage, and counter-proliferation financing measures.
FATF’s Global Monitoring and Other Countries:
- In the same plenary session, the FATF added Monaco and Venezuela to the list of jurisdictions under increased monitoring.
- The watchdog also urged Kuwait to focus on preventing the misuse of legal persons and protecting the non-profit sector from TF abuse.
- Additionally, it acknowledged significant progress made by Jamaica and Türkiye in addressing strategic AML and CFT deficiencies.
Concerns Over Russia and North Korea:
- The FATF maintained its suspension on the Russian Federation, initially imposed in March 2022, and called for vigilance against measures circumventing sanctions.
- The watchdog also reiterated concerns over North Korea’s continued failure to address significant deficiencies in its AML and CTF regimes and the serious threats posed by the country’s illicit activities related to the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction and their financing.
| What are the Issues Associated with FATF? |
|
The challenges associated with the adoption and implementation of FATF codes in member states include:
The challenges associated with the implementation of new technologies for AML/CFT include:
The other factors that encourage ML/TF include:
|
| Practice Question: Examine the recent evaluation by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) on India’s anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorist financing (CFT) regime, highlighting the areas where India has shown compliance and the sectors where improvements are needed. Discuss the potential impact of these findings on India’s financial and non-financial sectors. (250 words/15 m) |
4. Botanical institute sets out to revive rare flowers used in Jagannath Temple
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 2)
| Topic: GS3 – Environment – Conservations |
| Context |
| The National Botanical Research Institute (NBRI) in Lucknow is collaborating with the Shree Jagannath Temple in Puri to revive and supply endangered flower species for temple rituals, preserving both biodiversity and ancient traditions. |
Analysis of the news:
- Lucknow-based National Botanical Research Institute (NBRI), under CSIR, is reviving endangered flower species for the 12th-century Shree Jagannath Temple in Puri, Odisha.
- In collaboration with the Shree Jagannath Temple Administration (SJTA), NBRI has supplied Maurya and Davana (Dayana) flowers a year after signing an MoU.
- The NBRI Director highlighted that the temple’s rich traditions involve using specific flowers and leaves for rituals, many of which are now rare.
- NBRI aims to ensure the availability of these sacred flowers and revive endangered species, preserving temple traditions and plant biodiversity.
- Quality planting materials of marigold, tuberose, tulsi, jasmine, and davana were supplied and introduced in the temple’s Matitota garden for worship purposes.
- Gardeners are trained periodically in agro-practices for these plants, and a poly-house was established for year-round cultivation.
- The Namoh 108 variety of lotus, released by CSIR-NBRI, was introduced in the Koili Baikuntha garden, meeting the temple’s demand for aromatic plants used in daily rituals.
| National Botanical Research Institute (NBRI): |
|
| Practice Question: Evaluate the contributions of the National Botanical Research Institute (NBRI) in the field of plant sciences and biodiversity conservation in India. How does its research impact sustainable development? (150 Words /10 marks) |
5. Make world governance more effective and balanced: Xi
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 12)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations |
| Context |
| Chinese President Xi Jinping called for Global South’s active participation in global governance reform, emphasising peaceful development and criticism of colonialism and hegemony, marking the 70th anniversary of the “Five Principles of Peaceful Coexistence”. |
Analysis of the news:
- Chinese President Xi Jinping emphasised the Global South’s role in reforming global governance for balance and effectiveness.
- He reaffirmed China’s commitment to peaceful development and criticised colonialism and hegemony.
- Xi commemorated the 70th anniversary of the “Five Principles of Peaceful Coexistence,” emphasising their global significance.
- The principles include mutual respect, non-aggression, non-interference, equality, and peaceful coexistence.
- Xi called on the Global South to lead in promoting peace, settling disputes peacefully, and advancing open development.
- He advocated for upholding the UN Charter principles, opposing interference, bloc confrontation, and advocating true multilateralism for global governance.
| World Governance: |
|
| PYQ: Discuss the impediments India is facing in its pursuit of a permanent seat in UN Security Council. (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2016) |
| Practice Question: How can global governance be enhanced to ensure effective and balanced decision-making on international issues? Discuss in brief. (250 Words /15 marks) |
PRELIMS FACTS
1. Modi to Skip SCO Summit; Jaishankar to Lead Indian Delegation in Kazakhstan
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt and Politics; Page: 08)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:

What is Shanghai Cooperation Organization?
- SCO is a permanent intergovernmental international organization.
- It’s a political, economic and military organization aiming to maintain peace, security and stability in the region.
- It was created in 2001.
- The SCO Charter was signed in 2002 and entered into force in 2003.
Objectives:
- Strengthening mutual trust and neighborliness among the member states.
- Promoting effective cooperation in -politics, trade & economy, research & technology and culture.
- Enhancing ties in education, energy, transport, tourism, environmental protection, etc.
- Maintain and ensure peace, security and stability in the region.
- Establishment of a democratic, fair and rational new international political & economic order.
Structure:
- Heads of State Council: The supreme SCO body which decides its internal functioning and its interaction with other States & international organisations, and considers international issues.
- Heads of Government Council: Approves the budget, considers and decides upon issues related to economic spheres of interaction within SCO.
- Council of Ministers of Foreign Affairs: Considers issues related to day-to-day activities.
- Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS): Established to combat terrorism, separatism and extremism.
SCO Secretariat:
- Based in Beijing to provide informational, analytical & organizational support.
Official language:
- The official working language of the SCO Secretariat is Russian and Chinese.
The SCO’s Strategic Importance
- The SCO is an influential economic and security bloc comprising India, China, Russia, Pakistan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan.
- The summit in Astana is expected to draw significant international attention, with notable attendees including Russian President Vladimir Putin, Chinese President Xi Jinping, and Pakistan Prime Minister Shehbaz Sharif.
- The participation of these leaders highlights the strategic importance of the SCO in fostering regional stability and cooperation.
About Astana:
- Nursultan, formerly Astana, is the capital city of Kazakhstan. It the second-largest city in Kazakhstan, behind Almaty.
- Location: It is located on the banks of the Ishim River.
- History: Nursultan (then Astana) became the capital city of Kazakhstan in 1997
2. Bringing to light
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|
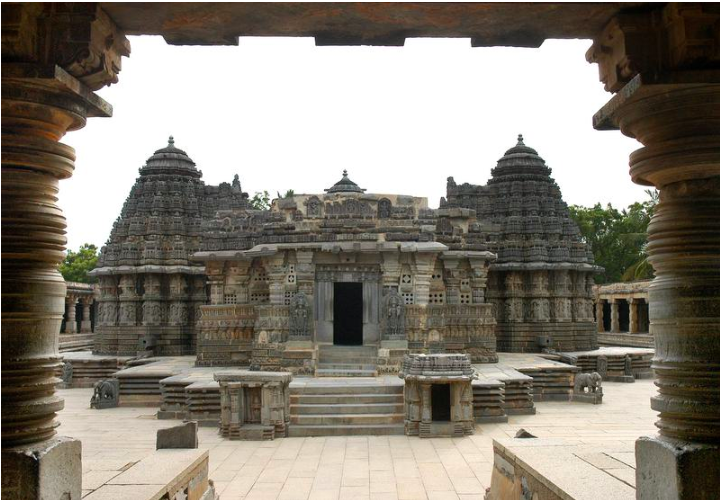
UNESCO World Heritage Site, Somanathapur:
- Location: Somanathapur is located in the state of Karnataka, India, approximately 35 kilometres east of Mysuru city.
- Historical Significance: The site is renowned for the Chennakesava Temple, a masterpiece of Hoysala architecture built in the 13th century during the reign of King Narasimha III.
- Architecture: The Chennakesava Temple is a prime example of Hoysala architecture known for its intricate carvings, detailed sculptures, and ornate pillars. The temple is dedicated to Lord Vishnu and showcases exquisite craftsmanship typical of the Hoysala period.
- Design Elements: The temple features a star-shaped platform (jagati), an impressive sanctuary (garbhagriha), and a large open hall (mandapa) with intricately carved ceilings supported by ornate pillars.
- Artistic Detailing: The outer walls of the temple depict various mythological scenes, deities, and celestial beings, each intricately carved with meticulous attention to detail.
- UNESCO Recognition: The Belur temple complex, along with the nearby Hoysaleswara Temple at Halebidu and the Keshava Temple at Somanathapura, was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 2023 as part of the Sacred Ensembles of the Hoysalas.

3. Fiscal deficit at 3% of target by May end
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 11)
| Context |
| In the first two months of FY25, India’s fiscal deficit was ₹50,000 crore, or 3% of the year’s projected figure, with strong non-tax revenue and controlled expenditure, prompting economists to foresee enhanced fiscal consolidation opportunities for the government. |
Analysis of the news:
- The Centre’s fiscal deficit in the first two months of FY25 was ₹50,000 crore, representing 3% of the full-year projected figure in the Interim Budget.
- Receipts stood at 18.6% of the target, bolstered by a ₹2.1 lakh crore dividend transfer from the central bank in May.
- Expenditure was lower at 13.1% of the projection, with capital expenditure accounting for ₹1.43 lakh crore of the ₹6.23 lakh crore total by May 2024.
- Economists suggest these numbers provide room for the Centre to achieve greater fiscal consolidation than the 5.1% of GDP target set in the Interim Budget.
- Increased non-tax revenue indicates potential for higher expenditure and faster fiscal consolidation efforts, according to ICRA chief economist Aditi Nayar.
Value addition/Mains Fodder points:
India Becomes World’s Third-Largest Domestic Aviation Market
Topic: GS Paper-3– Indian Economy
Source: AIR
- According to data compiled by aviation analytics firm Official Airline Guide (OAG), India has become the world’s third-largest domestic aviation market after the U.S. and China.
- The data show India’s domestic airline capacity doubled in the last 10 years from 7.9 million seats in April 2014 to 15.5 million in April 2024.
- The country’s domestic airline capacity has seen an impressive annual growth rate of 6.9%, the fastest in the world.
Important Quotes for UPSC Mains:
Topic: Democracy
- “I Understand democracy as something that gives the weak same chance as the strong.”
-Mahatma Gandhi







