3 October 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Israel suffers 8 casualties in Lebanon operation
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations |
| Context |
|
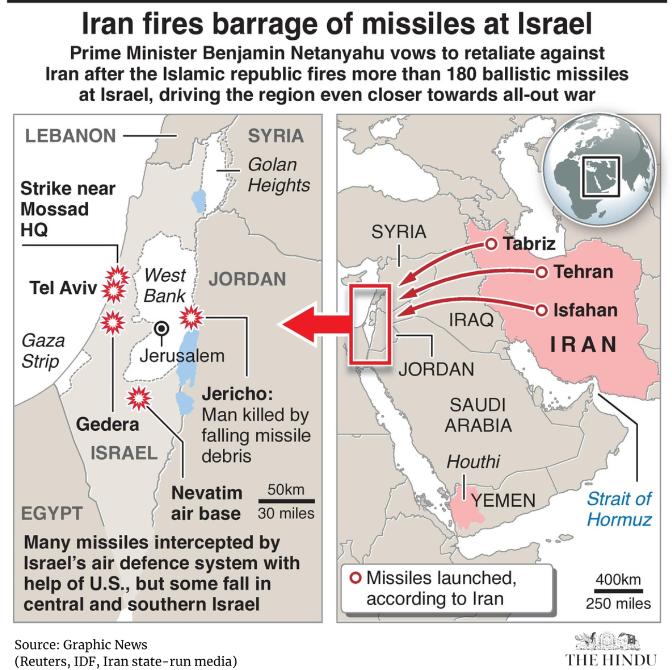
Israeli Ground Incursion:
- Israel launched a ground incursion into Lebanon to battle Hezbollah, leaving eight Israeli soldiers dead.
- Seven soldiers were killed in two separate attacks, following the earlier death of a 22-year-old captain.
- The incursions came on the eve of Rosh Hashana, the Jewish new year.
Iran’s Ballistic Missile Attack:
- Iran conducted its largest attack on Israel, targeting three Israeli military bases.
- Israeli air defences, supported by a U.S.-led defensive coalition, intercepted most of the missiles.
- Israeli PM Benjamin Netanyahu called Iran’s attack “a big mistake” and vowed retaliation.
Responses and Warnings:
- Iran’s President Masoud Pezeshkian stated the attack was over unless further provoked, warning of a stronger response.
- Hezbollah claimed to have repelled an Israeli infiltration into southern Lebanon, destroying three Merkava tanks.
- Israel carried out two brief incursions into Lebanon, urging residents to evacuate over 20 areas.
U.S. Position:
- U.S. President Joe Biden announced more sanctions on Iran but opposed any Israeli strike on Iran’s nuclear facilities.
- Biden emphasised the need for Israel to respond proportionally, with discussions ongoing among G-7 nations.
India Calls For Restraint:
- India expressed deep concern over the escalating crisis in West Asia following Iran’s missile strikes on Tel Aviv.
- India urged restraint from all parties involved, emphasising the need to prevent the conflict from expanding into a wider regional crisis and calling for a peaceful resolution.
Impact on Lebanon:
- Nearly 1,900 people have been killed and over 9,000 wounded in Lebanon in nearly a year of cross-border fighting.
- More than a million people have been displaced, with significant escalation in the past two weeks.
| Practice Question: Examine the ongoing crisis in West Asia, highlighting the dynamics between Israel, Hezbollah, and Iran, and discuss the broader implications of this conflict on regional stability and India. (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. Nanodiamonds spun at a billion RPM to test the limits of physics
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
| About Nanodiamonds: |
|
What are Nanodiamonds
Properties of Nanodiamonds Size: Typically range from 1 to 100 nanometers. Stability: Stable under prolonged light exposure. Non-Toxic: Safe for use in biological applications. Fluorescence: Emit light with a lifespan greater than 10 nanoseconds. Dopability: Can be modified with elements like nitrogen to enhance properties. High Surface Area: Offers significant reactive surface for interactions. Thermal Conductivity: Efficient heat conduction. Mechanical Strength: Exhibits high toughness and hardness. Biocompatibility: Compatible with biological tissues. |
How Nanodiamond Spin Can Help in Scientific Research
- Quantum Computing: Spin qubits in NDs can encode and process quantum information.
- Berry Phase Measurement: Enables measurement of Berry phase, crucial for understanding quantum effects and topological materials.
- Gravity Testing: Potential to test quantum mechanics and gravity reconciliation through rapidly rotating spin qubits.
- Sensor Development: Sensitivity to acceleration and electric fields aids in creating advanced sensors for high-value industries.
- Gyroscopes: The Berry phase effect from rotation can be harnessed to develop precise gyroscopes for rotation sensing.
- Long-term Observations: Stable behaviour of spin qubits allows for long-term tracking and observation in experimental setups.
- Innovative Materials: Doping NDs can lead to new materials with tailored properties for various scientific applications.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of fluorescent nanodiamonds (FNDs) in advancing scientific research and technology. Highlight their unique properties and potential applications in fields such as biomedicine, sensing, and quantum computing. (150 Words /10 marks) |
3. New Food Safety Directives Spark Legal and Social Debate Over Transparency and Discrimination Concerns
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 11)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Regulatory Framework for Food Businesses in India
- Under the FSSA, 2006, food businesses are required to register or obtain a license from the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI).
- For small-scale businesses (e.g., hawkers and vendors), registration is necessary, while larger businesses must acquire a license.
- Both the registration certificate and license must be displayed prominently at the business premises.
State Government Powers Under FSSA
- While the FSSA is a central legislation, state governments do have certain powers to make additional rules. Section 94 of the FSSA allows states to make rules, with the approval of the Food Authority, for implementing the Act.
- States can introduce measures as long as they don’t contradict the central regulations. However, state directives must be placed before the legislature for approval.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
- Under Section 63 of the FSSA, any operator running a food business without proper registration or license can be imprisoned for up to six months and fined up to Rs. 5 lakh.
- If other provisions or rules are violated, the food authority can issue an Improvement Notice, leading to suspension or cancellation of the license in case of non-compliance.
Controversy Over the Directives
- The display of owner details raised concerns about potential discrimination. Petitioners argued that the UP and Uttarakhand orders violated Article 15(1) of the Constitution by forcing individuals to disclose religious or caste identities, leading to fears of economic discrimination, especially against minority communities.
Rationale Behind the New Directives
- The UP government cited concerns about public health, pointing to incidents of food adulteration, as the reason for implementing stricter regulations. The government has also introduced additional measures such as the installation of CCTV cameras in food establishments.
Conclusion
- The recent directives by state governments under the FSSA aim to enhance transparency and food safety.
- However, they have sparked a legal and social debate about their broader implications, particularly regarding discrimination and constitutional rights.
| What is the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India? |
|
|
PYQ: Consider the following statements: (2018) The Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006 replaced the Prevention of Food Adulteration Act, 1954. The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is under the charge of Director General of Health Services in the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only Ans: (a) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the legal and constitutional implications of state directives requiring food establishments to prominently display personal details of owners and operators, in light of the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006. How do such directives intersect with issues of privacy, discrimination, and public health? (150 words/10 m) |
4. India’s Elephant Population Drops by 20%: Unreleased Report Cites Habitat Loss and Developmental Threats
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Cover Page; Page: 01)
| Topic: GS3 – Environment – Conservation |
| Context: |
| The article highlights a significant 20% decline in India’s elephant population, primarily due to habitat loss and developmental activities, based on an unreleased government census report. |
Analysis of News:
Delay in Publication
- Reason for Delay: The report has been delayed due to incomplete census data from the Northeast. The Ministry cited the use of new methods like DNA profiling and camera traps, which require more time and resources.
- Northeast Data Extrapolation: Figures for the Northeastern states were based on the 2017 census, as primary data collection was limited.
Key Findings
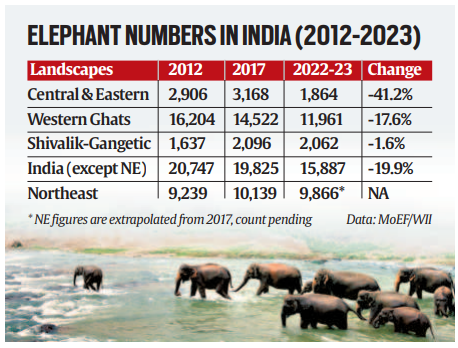
Elephant Population Decline: The report indicates a 20% drop in the elephant population nationwide, compared to five years ago.
- Central India & Eastern Ghats: These regions saw a 41% decline, with West Bengal, Jharkhand, and Odisha recording the sharpest drops (84%, 68%, and 54%, respectively).
- Western Ghats: An 18% overall decline, with Kerala experiencing a 51% drop.
- Shivalik Hills & Gangetic Plains: The population here remained stable, with only a 2% decline.
Causes of Decline
- Developmental Threats: The report highlights “unmitigated mining” and “linear infrastructure construction” as major threats to elephant habitats, causing fragmentation and disruption of movement corridors.
- Human-Wildlife Conflicts: Elephants are venturing into new areas due to habitat loss, leading to increased conflicts with humans.
- Other Threats: Poaching, railway collisions, and electrocution were identified as significant threats.
Regional Threats and Fragmentation
- Central and Eastern Ghats: Habitat loss due to mining and infrastructure has displaced elephants, exacerbating conflicts.
- Western Ghats: Fragmentation from land use changes, including plantations and encroachment, is isolating elephant populations.
- Northeast: The landscape is dominated by human settlements, plantations, and mining, making elephant movements difficult and dangerous. Poaching for ivory is a significant concern.
Call for Action
- Habitat Protection: The report recommends enhancing protection, restoring habitats, and improving corridors to safeguard the species.
- Conservation Strategies: It urges a focus on community support, mitigating developmental impacts, and targeted conservation efforts in high-risk areas.
| Significance of Elephants in Ecosystem |
Elephants in India:
|
|
PYQ: With reference to Indian elephants, consider the following statements: (2020) The leader of an elephant group is a female. The maximum gestation period can be 22 months. An elephant can normally go on calving till the age of 40 years only. Among the States in India, the highest elephant population is in Kerala. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 and 2 only Ans: (a) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the key factors contributing to the decline in India’s elephant population as highlighted in the recent elephant census report. What conservation measures can be adopted to mitigate these challenges? (150 words/10 m) |
Prelims Facts
1. 2 women Navy officers begin voyage around the world
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Context |
|
- The voyage, named Navika Sagar Parikrama, was flagged off by Navy chief Admiral Dinesh K. Tripathi from INS Mandovi, Goa.
- They will sail on the INSV Tarini, a 56-foot vessel equipped with advanced navigation, safety, and communication systems.
- The expedition consists of five legs, with stopovers for replenishment at four ports: Fremantle (Australia), Lyttleton (New Zealand), Port Stanley (Falkland), and Cape Town (South Africa).
- The journey aims to contribute to national scientific research, including studies on marine microplastics and large sea mammals.
- Both officers have extensive sailing experience and have trained for over three years for this voyage.
2. Brazil’s coast eroding faster than ever as Atlantic Ocean advances
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
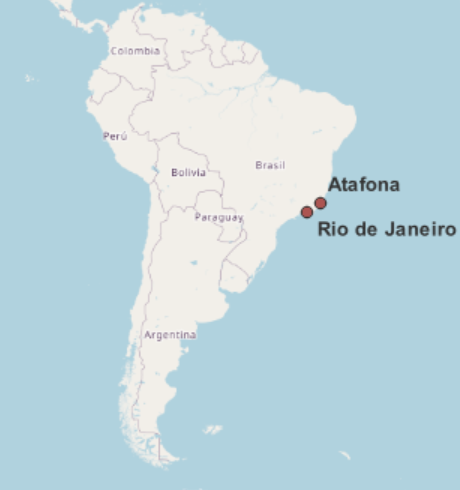
Analysis of the news:
- Coastal erosion in Brazil’s Atafona is exacerbated by climate change and river silting.
- Sea levels have risen 13 cm in the last 30 years, with predictions of an additional 16 cm by 2050.
- Coastal areas may experience up to 150 m of inland ocean advance in the next 28 years.
- The beach in Ponta Negra has lost 15 m of sand in two decades, prompting costly restoration efforts.
- Saltwater intrusion into the Amazon River threatens biodiversity and local fishing communities, particularly during severe droughts.
- The IPCC reports that sea level rise has accelerated, now at 0.48 cm annually, more than double previous rates.
3. Little Prespa Lake on Albanian-Greek border slowly dying
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 15)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
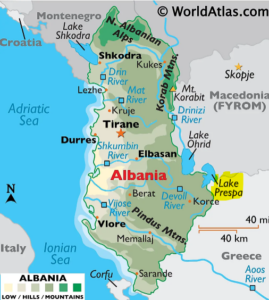
- Little Prespa Lake is located on the border of Albania and Greece, with most of its area in Greek territory.
- It has largely transformed from a clear lake into a marshy area, with only 20 hectares remaining as water.
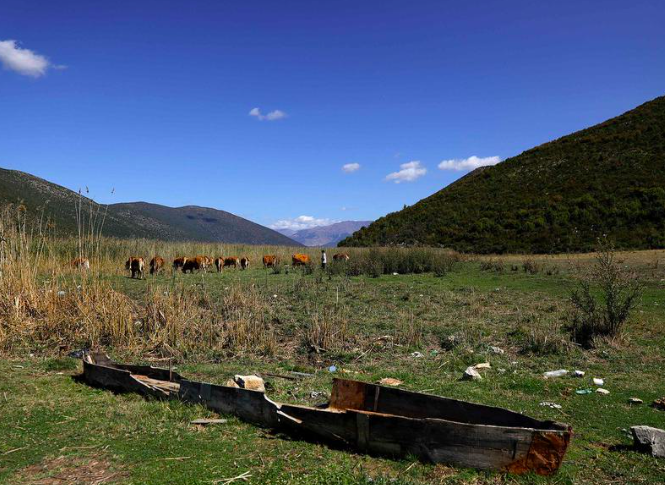

- The lake’s deterioration began in the 1970s when the Devoll River was diverted for irrigation purposes.
- Climate change, characterised by rising temperatures and reduced precipitation, has worsened the lake’s condition.
- Local fishing communities have been severely affected, with fish populations dwindling and livestock replacing fishing as a primary livelihood.
- Abandoned boats are now found on dry land, symbolising the lake’s decline.
- Experts warn that continued dry winters and hot summers could lead to complete desiccation of the lake.
4. New Study Unveils How Psychedelics May Help Treat Anxiety, Paving the Way for Targeted Therapies
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Cover Page; Page: 01)
| Context: |
| The article discusses a groundbreaking study that reveals how psychedelics may reduce anxiety by targeting specific brain cells, offering insights for developing new anxiety treatments. |
Analysis of News:
Growing Promise in Treating Anxiety and Depression
- Psychedelics, long associated with counterculture and spiritual experiences, are now being researched for their potential therapeutic benefits in treating anxiety and depression.
- Traditional therapies often fail to alleviate symptoms, and psychedelics offer new hope for patients.
Study by Indian Neuroscientist Vidita Vaidya
Research Collaboration and Findings
- Study Location: Conducted at Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Mumbai, in collaboration with Cornell, Yale, and Columbia.
- Publication: Results published in the journal Neuron.
- Breakthrough: The study identified specific neural mechanisms showing how psychedelics reduce anxiety-like symptoms.
Mechanism of Action
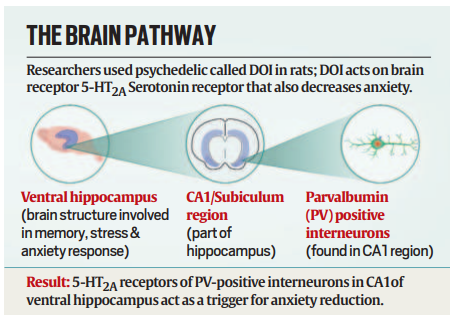
Serotonergic Psychedelics and the Brain
- Psychedelics’ Interaction with Serotonin: These substances affect the brain’s serotonin system, primarily through the 5-HT2A receptor, which influences mood and emotions.
- Study Substance: The psychedelic 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine (DOI) was used to observe effects on specific brain regions and cells.
Ventral Hippocampus and Anxiety Regulation
- Target Area: The ventral hippocampus (vHpc) was found to be the critical brain region involved in emotional regulation.
- Key Neurons: PV-positive interneurons in the vHpc, which help manage anxiety signals, were activated by DOI, reducing anxiety symptoms.
Implications for Future Treatments
Towards Targeted Anxiety Drugs
- Selective Pathways: Understanding how psychedelics work in specific brain areas enables the development of targeted anxiety treatments without causing hallucinogenic effects.
- Potential Drug Development: The research paves the way for new anxiety drugs inspired by psychedelics, focusing on the beneficial pathways while avoiding unwanted side effects.
5. Langurs Deployed to Control Rhesus Monkey Menace: A Solution Fraught with Ethical and Legal Challenges
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 11)
| Context: |
| The article discusses the use of langurs to control the increasing rhesus monkey menace in urban areas, highlighting ethical concerns, legal protections, and the need for better long-term solutions. |
Analysis of News:
Langur Physical Characteristics:
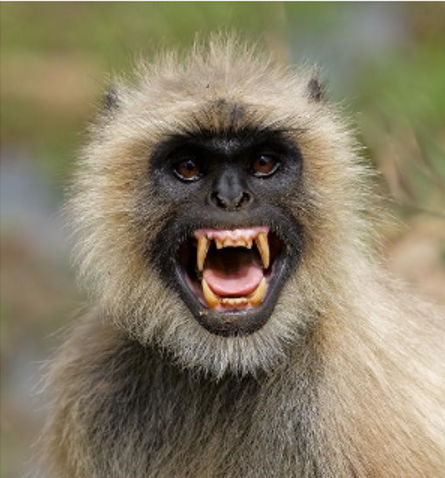

- Coloration: Langurs are typically gray or black in color, although some species may have white markings on their face or body.
- Tail: They have long, slender tails that can measure as long as their bodies, often used for balance.
- Face: Langurs have a relatively flat face with a narrow, pointed nose.
- Eyes: Their eyes are relatively large, adapted for good vision.
Rhesus Monkey Physical Characteristics
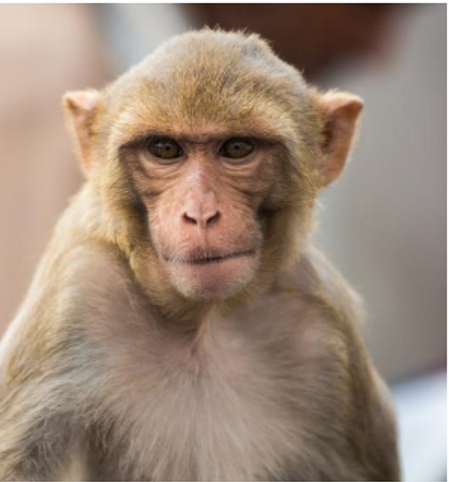

- Coloration: Rhesus macaques typically have brown or grayish fur with a pinkish face.
- Tail: They have a relatively short tail compared to langurs.
- Face: Their faces are rounder and less pointed compared to langurs.
- Eyes: Rhesus macaques have distinctive red or brown eyes.
Use of Langurs to Ward Off Monkeys
- The UP Cricket Association hired langurs to deter food-grabbing rhesus monkeys during a cricket match at Kanpur’s Green Park Stadium.
- Langurs have long been deployed across India to scare away rhesus monkeys, particularly in urban areas like Lutyens’ Delhi.
Are Langurs Natural Enemies of Rhesus Monkeys?
Coexistence in Nature
- Contrary to popular belief, langurs and rhesus monkeys often coexist peacefully in the wild.
- Studies, including those by Michigan University researchers, show that the two species can interact amicably, with examples of interspecies grooming and play behavior in natural habitats.
Why Are Langurs Effective Against Rhesus Monkeys?
The Role of Training
- Langurs are effective against rhesus monkeys not due to any natural hostility, but because of their trained behavior.
- Rhesus monkeys are naturally jumpy and nervous, which makes them respond to the presence of langurs.
- However, training langurs often involves cruelty, such as capturing them from the wild and subjecting them to harsh conditions.
Legal and Ethical Concerns
Protection and Prohibition
- Langurs are protected under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, and their use to scare monkeys is prohibited by the Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB).
- Despite legal protections, enforcement remains lax, and authorities sometimes use langur cutouts or impersonators to deter monkeys.
The Rising Rhesus Monkey Problem
Habitat Loss and Human Interaction
- Deforestation and urban expansion have forced rhesus monkeys into closer contact with humans, leading to conflicts in both rural and urban areas.
- Cultural veneration of monkeys and improper waste management provide a steady food source, exacerbating the issue.
Human-Monkey Conflict
Impact on Humans
- Rhesus monkeys cause extensive damage to crops, invade urban spaces, and attack humans, with monkey bites accounting for a significant portion of animal bite injuries in India.
- It is estimated that cities in India experience about 1,000 monkey bites daily.
Recommendations for Mitigating the Monkey Menace
Conservation and Management Solutions
- Conservationists suggest improving the protection of natural habitats, implementing mass translocation measures, and enforcing restrictions on feeding monkeys to address the problem at its root.
6. Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India celebrates its Eighth Annual Day
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2060974®=3&lang=1 )
| Context |
|
Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI)
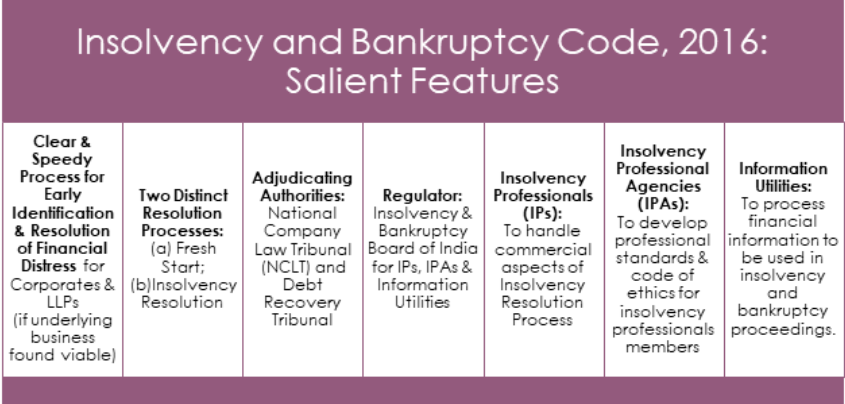
- The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI) was established in October 2016 under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), 2016, to regulate and oversee insolvency proceedings in India.
- IBBI is responsible for ensuring the effective implementation of the IBC and promoting a transparent and efficient insolvency regime.
- The board aims to protect the interests of stakeholders, including creditors, debtors, and other entities involved in insolvency processes.
- IBBI develops and enforces regulations governing insolvency professionals, professional agencies, and information utilities.
- It conducts research and analysis on insolvency law, facilitating informed policy decisions and enhancing the insolvency framework.
- The board plays a crucial role in enhancing the Ease of Doing Business in India by providing a robust framework for corporate insolvency resolutions.
- It promotes awareness and education regarding insolvency processes among stakeholders through various initiatives and publications.
- IBBI collaborates with various regulatory bodies and stakeholders to strengthen the insolvency ecosystem.
- It has initiated capacity-building programs for insolvency professionals to ensure the quality and consistency of services in the field.
- The board regularly publishes annual reports and research studies to assess the effectiveness of the IBC and its impact on the economy.
| Practice Question: Discuss the role of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI) in enhancing the corporate insolvency framework in India. Analyse its impact on the Ease of Doing Business and the resolution of non-performing assets (NPAs). (250 Words /15 marks) |




