3 September 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Next-generation sequencing to map genetic blueprint of indigenous cattle
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 3)
| Context |
|

Analysis of the news:
- The National Institute of Animal Biotechnology (NIAB) is working to decode the genetic blueprints of indigenous cattle breeds using Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) and genotyping technology.
| Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) |
|
- The goal is to establish molecular signatures for registered cattle breeds for identification and conservation.
- NIAB is developing next-generation vaccine platforms for livestock diseases like brucellosis, crucial for animal health and reducing economic losses.
- The institute, under the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), aligns its efforts with the ‘BioE3’ policy to promote bio-manufacturing.
- NIAB aims to support biotech start-ups in transforming the livestock-based economy through vaccines, diagnostics, and biomolecules.
- Six thematic verticals under the BioE3 policy focus on circular bio-based economy, including alternative proteins.
2. Hectic negotiations on for control of House panels
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 5)
| Topic: GS2 – Indian Polity |
| Context |
|
| Parliamentary Standing Committees: |
|
Significance of Parliamentary Standing Committees:
- In-depth scrutiny: Provide detailed analysis of bills, budgets, and policies.
- Non-partisan discussions: Foster consensus-building across party lines.
- Expert inputs: Involve expert witnesses for specialised knowledge.
- Accountability: Enhance government accountability through questioning.
- Efficiency: Reduce Parliament’s workload by examining issues in smaller groups.
- Transparency: Facilitate greater transparency in the legislative process.
- Legislative quality: Improve the quality of legislation through recommendations.
Challenges:
- Political influence: Committees may face political pressure, reducing their independence.
- Limited time: Tight schedules often restrict thorough examination of bills and policies.
- Non-binding recommendations: Governments are not obligated to implement committee suggestions.
- Lack of expertise: Some committee members may lack domain-specific knowledge, affecting quality.
- Delayed constitution: Delay in forming committees can hinder legislative oversight and scrutiny.
- Resource constraints: Limited research and technical support affect in-depth analysis.
Way Forward:
- Strengthen independence: Committees should operate without political interference for unbiased recommendations.
- Enhance expertise: Include domain experts or provide training to members.
- Timely formation: Ensure timely constitution of committees to avoid delays in legislative scrutiny.
- Make recommendations binding: Consider making certain committee recommendations mandatory.
- Increase resources: Provide committees with better research and technical support for detailed analysis.
- Public engagement: Encourage transparency and citizen participation in committee discussions.
| PYQ: Explain the structure of the Parliamentary Committee system. How far have the financial committees helped in the institutionalisation of Indian Parliament? (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2023) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the role of Parliamentary Standing Committees in enhancing the legislative process and ensuring government accountability. How do their recommendations impact policymaking? (250 Words /15 marks) |
3. Use of regional languages in HCs remains limited
| Topic: GS2 – Indian Polity – Judiciary |
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 5)
| Context |
|
Use of regional languages in High Court:
- Current Status: Only four High Courts (Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, and Bihar) are permitted to use Hindi in their proceedings, while English remains the official language in all High Courts.
- Constitutional Provisions: Article 348(1) of the Indian Constitution mandates English for Supreme Court and High Court proceedings, unless Parliament decides otherwise. Article 348(2) allows State Governors to authorise regional languages in State High Courts with Presidential consent.
- Recent Discussions: Chief Justice of India D.Y. Chandrachud highlighted the need for regional languages in legal proceedings to make the justice system more accessible to common citizens.
- Proposals: Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Chhattisgarh, West Bengal, and Karnataka have proposed using regional languages in their High Courts. These proposals were reviewed but not accepted by the Chief Justice of India in 2012.
Challenges:
- Language Proficiency: Judges and lawyers may lack proficiency in regional languages, leading to communication difficulties and inefficiencies in court proceedings.
- Uniformity Issues: Ensuring consistent legal terminology and standards across different languages can be complex, potentially affecting the quality of justice.
- Training Requirements: Judges and legal professionals need extensive training to become proficient in regional languages, which may be time-consuming and costly.
- Resource Constraints: Developing and maintaining legal resources, such as case law and statutes, in multiple languages requires significant investment.
- Legal Documentation: Translating legal documents and maintaining accurate records in various languages can be challenging and may lead to errors.
- Resistance to Change: There may be resistance from the legal community accustomed to English, leading to delays and disputes.
- Implementation Issues: Coordinating and implementing language changes across different High Courts involves logistical complexities and administrative hurdles.
| Practice Question: Discuss the potential benefits and challenges of using regional languages in High Court proceedings in India. How can these challenges be addressed to improve access to justice for common citizens? (250 Words /15 marks) |
4. Union Cabinet Approves ₹2,817 Crore Digital Agriculture Mission to Revolutionize Farming with Advanced Digital Infrastructure
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 12)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government Policies |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:

Mission Components

AgriStack:
- Farmers’ Registry: A digital identity, similar to Aadhaar, will be created for each farmer, linking their data on land, crops, livestock, etc. Pilot projects have been carried out in six districts.
- Crop Sown Registry: Digital Crop Surveys will record crop details for each season. It is set to cover 400 districts in 2024-25 and the rest by 2025-26.
- Geo-Referenced Village Maps: These will connect land records to their physical locations.
Krishi Decision Support System (DSS):
- A geospatial system combining data on crops, soil, weather, and water resources to support crop mapping, drought/flood monitoring, and yield assessment.
Soil Profile Maps:
- Detailed maps of about 142 million hectares of agricultural land, with 29 million hectares already completed.
Digital General Crop Estimation Survey (DGCES):
- Aims to enhance the accuracy of crop yield estimates, addressing current concerns about data robustness. This will support more efficient schemes like MSP-based procurement and crop insurance.
Background and Funding
- The Mission, initially planned for 2021-22, was delayed due to COVID-19. With a budget of ₹2,817 crore, ₹1,940 crore will be funded by the central government, and the rest by states and UTs. The initiative is part of the Agriculture Ministry’s activities during the Modi government’s first 100 days in its third term.
Impact on Farmers and the Farm Sector
- Efficiency: Digital identities and services will streamline access to benefits, reducing paperwork and the need for physical office visits.
- Transparency: Improved crop data will make processes like MSP procurement, insurance claims, and credit more transparent.
- Informed Decisions: Farmers will have better access to information on crops, soil, and weather, enabling them to make informed decisions, optimize resources, and adapt to climate conditions.
- Data-Driven Policies: The government can use robust data for more accurate agricultural policies and initiatives, ensuring balanced fertilizer use and efficient irrigation.
The Digital Agriculture Mission is expected to transform the farm sector by integrating cutting-edge digital technologies, leading to a more efficient, transparent, and data-driven agricultural ecosystem.
| Practice Question: Discuss the potential impact of the Digital Agriculture Mission on the Indian agricultural sector. How can the creation of Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) address existing challenges and improve the efficiency and transparency of farming practices? (250 words/15 m) |
5. West Bengal Proposes Death Penalty for Severe Rape Cases in New Aparajita Woman and Child Bill
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt & Politics; Page: 05)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Key Provisions of the Bill
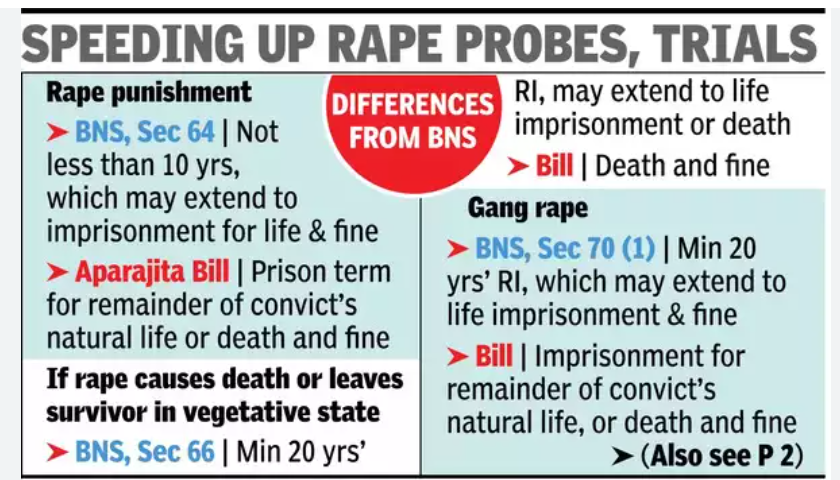
Capital Punishment for Severe Cases:
- The Bill proposes the death penalty for rape convicts if their actions lead to the victim’s death or leave the victim in a vegetative state.
Life Imprisonment:
- Convicts of rape and gangrape will face life imprisonment, which will last for the “rest of their natural lives.”
Amendments to Existing Laws:
- The Bill seeks to amend the Bharatiya Nyay Sanhita 2023, Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita 2023, and the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act 2012, specifically for West Bengal, to enhance punishments and streamline the investigation and trial processes.
Proposed Changes to Investigation and Prosecution
Expedited Investigations:
- The Bill mandates that investigations into rape cases be completed within 21 days, with a possible extension of 15 days, reducing the previous two-month deadline.
Fast-Track Courts:
- To ensure swift justice, the Bill proposes the establishment of fast-track courts and specialized investigation teams equipped with necessary resources and expertise. These courts aim to minimize the trauma experienced by victims and their families by handling cases efficiently and effectively.
Conclusion
- The Aparajita Woman and Child Bill reflects the West Bengal government’s commitment to enhancing the safety of women and children by introducing stringent punishments and expediting the legal process for sexual offenses.
- The proposed changes aim to deter crimes against women and children while ensuring timely justice for victims.
| Government Initiatives |
|
| PYQ: Is the National Commission for Women able to strategize and tackle the problems that women face at both public and private spheres? Give reasons in support of your answer. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2017) |
| Practice Question: Critically analyze the potential impact of the Aparajita Woman and Child Bill proposed by the West Bengal government. How might the introduction of stricter penalties and expedited legal processes influence the safety of women and children, and what challenges could arise in its implementation? (250 words/15 m) |
6. Cabinet approves one more semiconductor unit under India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2050859 )
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy, GS2 –Governance |
| Context |
|

Analysis of the news:
- India Semiconductor Mission (ISM) was launched in 2021 with a financial outlay of Rs 76,000 crore under the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY).
- It aims to develop a sustainable semiconductor and display ecosystem in India by offering financial support to companies investing in these sectors.
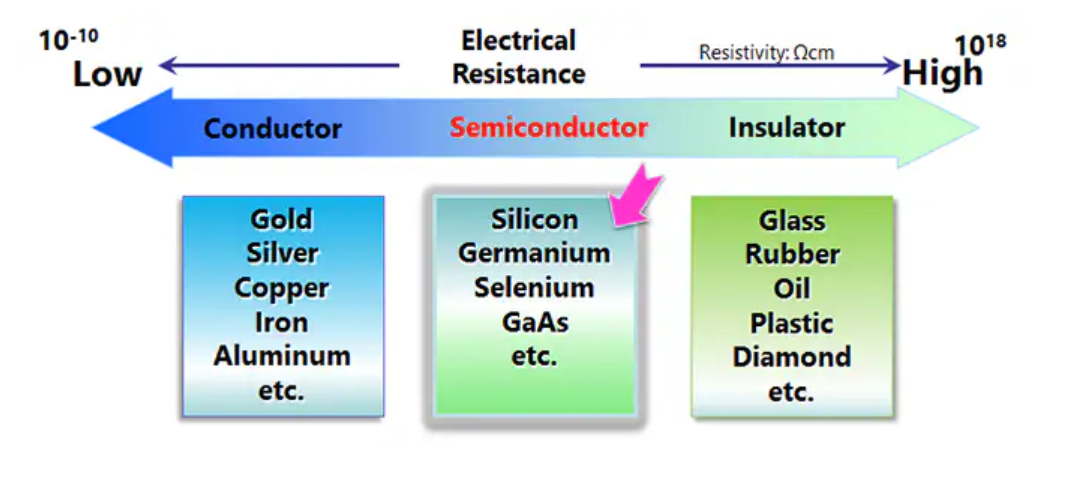
| What are semiconductors? |
|
|
- ISM is envisioned to be led by global experts from the semiconductor and display industries, acting as the nodal agency for scheme implementation.
- The mission includes various schemes:
- Scheme for setting up Semiconductor Fabs, providing fiscal support to eligible applicants to establish semiconductor wafer fabrication facilities.
- Scheme for setting up Display Fabs to attract investments for TFT LCD and AMOLED display fabrication facilities.
- Scheme for Compound Semiconductors, Silicon Photonics, and Sensors Fab, providing 30% fiscal support for setting up such facilities.
- Design Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme, offering financial incentives and infrastructure support for semiconductor design development.
- The vision is to build a robust semiconductor and display design ecosystem, positioning India as a global hub for electronics manufacturing and design.
| Need of Promoting Semiconductor Industry |
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the strategic importance of promoting the semiconductor industry in India and its role in fostering economic growth, technological advancements, and supply chain resilience. (150 Words /10 marks) |
7. Cabinet approves seven major schemes for improving farmers’ lives and livelihoods with total outlay of Rs 14,235.30 Crore
| Topic: GS3 – Agriculture |
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2050899 )
| Context |
|
- Digital Agriculture Mission (Outlay: Rs 2,817 crore)
- Uses technology and Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) to improve farming.
- Includes Agri Stack with registries for farmers, land, and crops.
- Krishi Decision Support System provides geospatial, weather, and groundwater data.
- Features AI, Big Data, and mobile-based knowledge dissemination, enhancing crop yield, loans, and buyer connections.
- Crop Science for Food and Nutritional Security (Outlay: Rs 3,979 crore)
- Aims to prepare farmers for climate resilience and ensure food security by 2047.
- Focuses on research, genetic improvement of crops, plant resources, and crop science.
- Enhances pulse, oilseed, and commercial crop productivity.
- Studies the impact of insects, microbes, and pollinators.
- Strengthening Agricultural Education, Management, and Social Sciences (Outlay: Rs 2,291 crore)
- Modernises agricultural education under the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
- Aligns with the New Education Policy 2020, using AI, Big Data, and remote sensing.
- Focuses on natural farming and climate resilience.
- Sustainable Livestock Health and Production (Outlay: Rs 1,702 crore)
- Aims to increase farmers’ income through improved livestock and dairy productivity.
- Includes animal health management, veterinary education, and genetic resource management.
- Enhances dairy production, nutrition, and small ruminant development.
- Sustainable Development of Horticulture (Outlay: Rs 1,129.30 crore)
- Promotes income growth through horticulture crops.
- Focuses on tropical, sub-tropical, and temperate crops, and root, tuber, and bulbous plants.
- Supports the cultivation of vegetables, spices, medicinal plants, and floriculture.
- Strengthening of Krishi Vigyan Kendra (Outlay: Rs 1,202 crore)
- Enhances the role of Krishi Vigyan Kendras in agricultural research and knowledge dissemination.
- Focuses on technology transfer and extension activities to support farmers’ productivity.
- Natural Resource Management (Outlay: Rs 1,115 crore)
- Aims to promote sustainable use and conservation of natural resources.
- Focuses on improving land, water, and soil management to ensure long-term agricultural productivity.
|
PYQ: Q.1 Assess the role of National Horticulture Mission (NHM) in boosting the production, productivity and income of horticulture farms. How far has it succeeded in increasing the income of farmers? (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2018) Q.2 What are the major reasons for declining rice and wheat yield in the cropping system? How crop diversification is helpful to stabilise the yield of the crop in the system? (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2017) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the recent government-approved schemes aimed at improving farmers’ livelihoods and promoting sustainable agricultural practices in India. How can these initiatives contribute to achieving food security and climate resilience? (250 Words /15 marks) |
Prelims Facts
1. Gene of thrones: rulers’ genomes reveal how empires rose and fell
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
What is Palaeogenomics?
- Palaeogenomics is the study of ancient DNA recovered from archaeological sites to understand historical human populations and their evolution.
- By analyzing genomes from ancient remains, scientists can trace migration patterns, cultural exchanges, and genetic adaptations.
- For instance, it has revealed the migration of Paleo-Eskimos from Siberia to Greenland and provided insights into ancient African populations and Bronze Age Eurasian migrations.
- Despite challenges like DNA degradation in tropical climates, advances in the field have significantly enhanced our knowledge of human history and evolution.
- Svante Pääbo’s pioneering work in palaeogenomics earned him the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2022.
2. What is the Unified Lending Interface by the RBI?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Context |
|
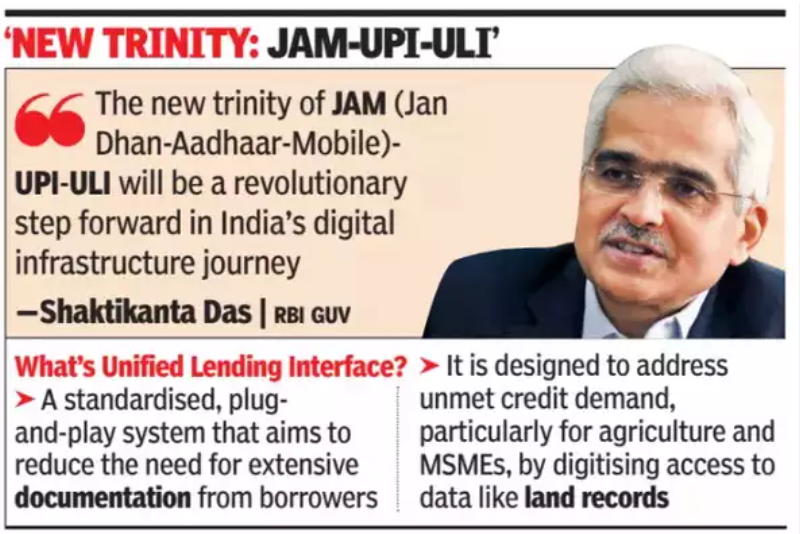
Unified Lending Interface (ULI):
- The Unified Lending Interface (ULI) is a new technology platform introduced by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to streamline credit access.
- It enables seamless and consent-based flow of digitized financial and non-financial data from various sources, including government databases and satellite imagery, to lenders.
- This platform aims to simplify credit underwriting by providing a standardized, ‘plug and play’ approach to data integration.
- ULI facilitates quicker credit appraisal, especially for borrowers without credit histories, by reducing the need for extensive documentation and enabling automated decision-making.
- It supports diverse borrowers, including farmers and MSMEs, by making credit processes more efficient and accessible.
3. Debate Erupts Over Proposal to Rename Ravenshaw University Due to Colonial Legacy
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 12)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:

Historical Context of the Famine and the College
- Na Anka Durbhikshya: The 1866 famine, caused by severe drought, decimated a third of Orissa’s population.
- Ravenshaw’s Role: As Commissioner, Ravenshaw proposed the establishment of a degree college in Orissa, which led to the foundation of Ravenshaw College in 1868. The college was later elevated to a degree institution in 1876 and named after him in recognition of his contributions to higher education in the region.
Contributions of Ravenshaw College
- Educational Impact: Ravenshaw College, established with significant contributions from local leaders, became a leading institution offering courses in various disciplines and played a vital role in advancing the Odia language and culture.
- Civic and Political Influence: The college was central to Orissa’s civic and political life, producing many eminent personalities, including Utkal Gourab Madhusudan Das, former Chief Ministers, and prominent writers and scholars. The college was also the venue for important events like the oath-taking ceremony of Orissa’s first Governor and the first sessions of the Provincial Legislative Assembly.
Debate on Renaming
- Opposition: Several alumni and scholars oppose the renaming, arguing that Ravenshaw made significant contributions to Odisha’s educational and cultural landscape.
- Support for Renaming: Supporters of the change point to Ravenshaw’s role during the 1866 famine, which they believe overshadows his contributions to education.