30 November 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Sambhal’s Jama Masjid: A Historic Monument at the Heart of Legal and Communal Disputes
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 17)
| Topic: GS1 – History |
| Context: |
| The article explores the historical, architectural, and legal controversies surrounding Sambhal’s Jama Masjid, highlighting its significance and the communal tensions it has sparked. |
Analysis of News:

Historical Background of the Jama Masjid, Sambhal
- The Jama Masjid in Sambhal, Uttar Pradesh, constructed in 1526 by Mir Hindu Beg, an official under Mughal emperor Babur, is among the oldest surviving Mughal-era mosques in India.
- Its history reflects Sambhal’s evolution through various empires, from Ashoka’s reign to its role under the Delhi Sultanate and Mughals.
- Notable for its architectural significance, it combines local craftsmanship with Sultanate styles, as documented by historians like Catherine Asher and Ebba Koch.
- Despite later renovations, its design anticipates Babur’s subsequent mosques at Panipat and Ayodhya.
Legal and Religious Disputes
- The mosque has been embroiled in legal disputes for over a century. The Hindu side claims it was built by demolishing a Vishnu temple, citing features such as a path for circumambulation (parikrama) and temple-like columns.
- However, these assertions have been contested in courts since 1878. Earlier rulings dismissed such claims, citing uninterrupted Muslim use and lack of substantial evidence.
- Recent petitions reignited the controversy, with surveys and claims of historical artifacts fueling tensions.
Architectural and Historical Perspectives
- Historians are divided on whether temple remnants were incorporated into the mosque.
- While some highlight features suggestive of Hindu temple origins, others argue these reflect overlapping architectural styles rather than deliberate appropriation.
- Scholars emphasize that the mosque aligns more with decaying Sultanate architecture than distinct Mughal or Hindu traditions.
- Furthermore, the absence of a persistent historical conflict at the site undermines claims of intentional religious symbolism.
Contemporary Implications
- The renewed dispute over the Sambhal mosque mirrors broader patterns of communal and historical contestations in India.
- The Supreme Court’s involvement underscores the sensitivity of such cases, balancing religious sentiments and historical narratives.
- The ongoing legal processes and violent clashes surrounding the site highlight the need for careful adjudication, rooted in evidence rather than mythology.
- This case exemplifies the complexities of interpreting shared cultural and architectural legacies in a polarized socio-political context.
| Practice Question: Examine the historical and architectural significance of the Jama Masjid in Sambhal and discuss the implications of legal and communal disputes over heritage sites in India. (250 words/15 m) |
2. Economic drivers for communities, co-benefits of abandoned cattle for lions behind delicate human-lion co-existence in Gujarat, finds new study
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 10)
| Context: |
| The article examines the factors enabling human-lion coexistence in Gujarat, the challenges posed by increasing conflicts, and the need for sustainable conservation strategies. |
Analysis of News:

Human-Lion Coexistence: Key Drivers
- The coexistence of Asiatic lions and humans in Gujarat is sustained by a combination of economic incentives, cultural acceptance, and legal protections.
- Regulated wildlife tourism in Gir National Park and unregulated tourism on private lands provide financial benefits to communities, fostering tolerance.
- Additionally, cultural practices, such as abandoning old cattle, indirectly benefit lions by supplementing their diet.
Impact of Lion Population Growth
- The Asiatic lion population has grown at an annual rate of 6%, with their geographic range expanding by 36% between 2015 and 2020.
- Lions now inhabit areas beyond protected zones, aided by human acceptance and food availability from abandoned livestock.
- This expansion highlights successful conservation but also increases the risk of human-lion conflicts.
Challenges and Recommendations
Coexistence is fragile, requiring proactive measures to mitigate conflicts. Key recommendations include:
- Revising livestock compensation schemes to match market rates.
- Exploring livestock insurance programs.
- Monitoring high-risk areas using radio-collared lions with virtual geofences to reduce attacks on humans and livestock.
Conservation and Translocation Debate
- While Gujarat remains the sole habitat of Asiatic lions, conservationists advocate their translocation to Madhya Pradesh to ensure genetic diversity and guard against disease outbreaks. Despite Supreme Court orders, this has not been implemented, reflecting challenges in balancing state interests with ecological needs.
Community Perspectives on Coexistence
- Surveys across 277 villages revealed that even in high-conflict areas, people tolerate lions due to economic benefits, pride, and cultural perceptions of the species’ nobility.
- However, pastoralists, whose livelihoods are most affected, exhibit the highest intolerance, emphasizing the need for tailored conflict-mitigation strategies.
Conclusion
- The coexistence between humans and Asiatic lions in Gujarat represents a complex but remarkable example of mutual adaptation.
- To sustain this balance, focused conservation management, economic support, and scientific interventions are essential.
| Asiatic Lions (Panthera leo persica) |
|
The Asiatic lion, also known as the Persian lion or Indian Lion, is a population of Panthera leo leo that today survives in the wild only in India. Since the turn of the 20th century, its range has been restricted to Gir National Park and the surrounding areas in the Indian state of Gujarat. Historically, it inhabited much of southwest Asia to northern India. Until the 19th century, it occurred in Saudi Arabia, eastern Turkey, Iran, Mesopotamia, Pakistan, and from east of the Indus River to Bengal and the Narmada River in Central India. Characteristics of Asiatic Lions
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the key factors contributing to the coexistence of Asiatic lions and humans in Gujarat and evaluate the challenges and conservation strategies needed to mitigate human-lion conflicts. (250 words/15 m) |
3. Steps taken by Government of India to address the issue of addiction of children to online games
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2079098®=3&lang=1 )
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context |
| The Government of India has implemented various measures to address the risks associated with online gaming, such as addiction and financial harm.These include the IT Rules, 2021, advisory by the Ministry of Education, and guidelines from the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting. |
IT Rules, 2021:
- MeitY notified the Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021, to address concerns like online gaming addiction.
- Intermediaries (including social media platforms) must not host, store, or share unlawful content, including harmful material related to children, money laundering, and gambling.
- Intermediaries must act quickly to remove harmful content as per grievances and the IT Rules, 2021.
Ministry of Education Advisory:
- On 27th September 2021, an advisory was issued to parents and teachers about online gaming addiction, recognized as a gaming disorder.
- The advisory warns that unrestricted gaming without self-limits can cause addiction and lead to mental and physical stress in children.
- Parents and teachers were encouraged to circulate and act on these recommendations to manage gaming risks.
MIB’s Advertising Guidelines:
- The Ministry of Information and Broadcasting (MIB) issued guidelines on 4th December 2020 to regulate advertisements for online games and fantasy sports.
- Advertisements must carry a disclaimer about financial risks and addiction.
- Gaming ads must not feature individuals under 18 or present gaming as a viable employment option.
Cyber Crime Reporting and Assistance:
- The Ministry of Home Affairs launched the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) and the National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal.
- A toll-free helpline, 1930, is available for lodging online complaints.
| Issue of online gaming addiction among children: |
|
What is Online Gaming Addiction?
Signs and Symptoms:
Impact on Children:
Prevention and Intervention:
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the growing concern of online gaming addiction among children in India. Analyze the measures taken by the government to address this issue and suggest further steps that can be implemented. (250 Words /15 marks) |
4. Scientists, industry demand passage of new Seeds Bill, changes in policy
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Topic: GS3 – Agriculture |
| Context |
|
Challenges with the Seeds Bill of 2004

- The Seeds Bill, introduced in 2004, was not passed due to opposition from farmers.
- Experts stressed the importance of revising the Bill to address changes in the sector over the past two decades.
- Collaboration between public and private sectors was highlighted as crucial for delivering high-quality seeds to farmers efficiently and affordably.
Weak Seed Quality Assurance System
- The existing seed quality assurance mechanisms, established under the Seeds Act of 1966 and Seeds Rules of 1968, are outdated and fail to meet international standards.
- Experts called for strengthening the system to ensure adherence to global benchmarks.
Need for Clear Definitions
- There is a lack of clarity in defining “farmer seeds” and “commercial seeds,” which needs to be addressed in any revised policy or legislation.
Strategic Interventions Required
- Experts advocated for a balanced focus on innovation, farmer empowerment, and policy reforms to create a resilient and globally competitive seed industry.
Conclusion
- Modernizing the Seeds Bill and policy is imperative to address sectoral challenges, promote innovation, and empower farmers.
- Collaborative efforts between stakeholders can ensure quality seeds are accessible and affordable.
| Seed Quality And Indian Agriculture |
|
Importance
Challenges
Way Forward
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the need for revisiting India’s seed policies and the Seeds Bill of 2004 to address challenges in quality assurance, innovation, and farmer empowerment. Suggest measures to strengthen the seed industry for achieving global competitiveness. (150 Words /10 marks) |
PRELIMS FACTS
1. Cyclone Fengal
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Cover Page; Page: 01)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
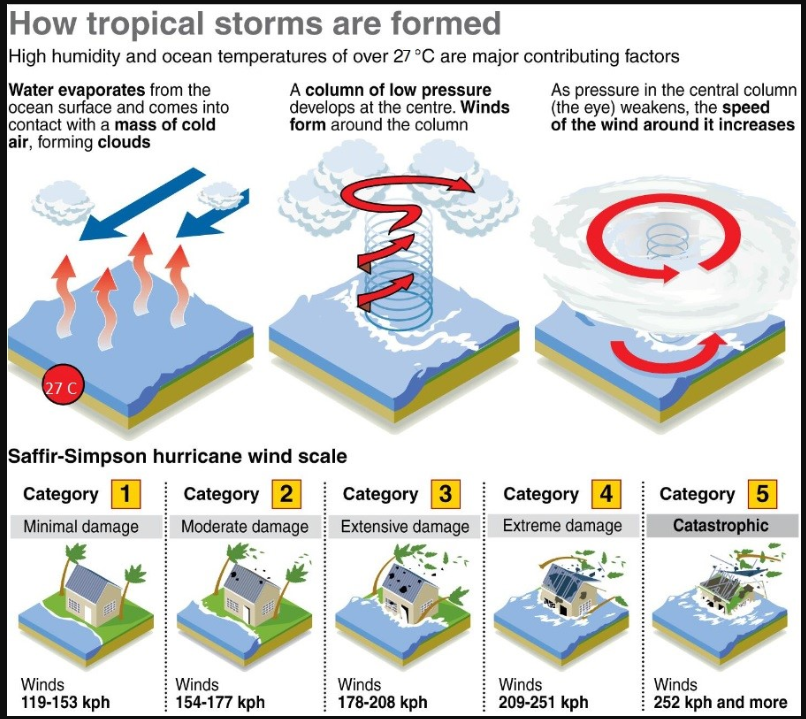
Origin of the Name ‘Fengal’
- The name ‘Fengal’ was proposed by Saudi Arabia and is rooted in Arabic.
- It reflects a combination of linguistic tradition and cultural identity.
Cyclone Naming Process:
- Cyclones in the North Indian Ocean are named by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP) panel.
- This panel includes 13 member countries, such as India, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and Pakistan, among others.
- Each member country submits a list of potential cyclone names, and these names are used sequentially as cyclones form in the region.
- This system, in place since 2004, ensures easy identification and effective communication of storms to the public
2. Odisha to Enact Stringent Law Against Cheating in Public Exams, Offenders Face Up to ₹1 Crore Fine and 10 Years Jail
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 17)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Scope of Offences
The proposed law identifies various unfair practices as offences, including:
- Leaking question papers.
- Providing unauthorised answers during exams.
- Tampering with answer sheets, documents, or computer systems.
- Manipulating seating arrangements.
- Creating fake websites for deceit or monetary gain.
The law also criminalises unauthorised use of alternative premises for exams without written approval.
Stringent Punishments
Offences under the Act will be cognisable, non-bailable, and non-compoundable, with strict penalties:
- Individuals: Imprisonment of 3-5 years and fines up to ₹10 lakh.
- Service providers: Fines up to ₹1 crore, liability for exam costs, and a four-year ban from conducting exams. Senior officials involved may face 3-10 years of imprisonment and fines up to ₹1 crore.
- Organised crimes: Involvement by institutions or individuals attracts 5-10 years imprisonment, fines of at least ₹1 crore, property forfeiture, and recovery of exam costs.
Need for the Legislation
- Protests by job seekers and discrepancies in recruitment processes, such as examinations held in unregulated cybercafés and question paper leaks, highlighted systemic issues.
- In 2022, Odisha Staff Selection Commission had to cancel exams due to question paper leaks, prompting the government to act decisively.
Investigation Protocols
Only officers ranked Deputy Superintendent of Police (DSP) or Assistant Commissioner of Police (ACP) and above will investigate offences under the law, ensuring a focused and robust probe into violations.
3. India Shines in Network Readiness Index 2024
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressNoteDetails.aspx?NoteId=153468&ModuleId=3®=3&lang=1 )
| Context |
|
India’s Improved Network Readiness in NRI 2024

- India has significantly improved its rank in the Network Readiness Index (NRI) 2024, rising from 60th place in 2023 to 49th position.
- The country’s score increased to 53.63 from 49.93, reflecting advancements in technology, governance, and infrastructure.
- India achieved the 1st rank globally for AI Scientific Publications, AI Talent Concentration, and ICT Services Exports.
- The country ranked 2nd for Fiber to the Home (FTTH) subscriptions, mobile broadband traffic, and international internet bandwidth.
- India also ranked 3rd for domestic market scale and 4th for annual investment in telecommunication services.
- Among lower-middle-income countries, India secured the 2nd position, demonstrating its leadership in digital progress within its income group.
| Network Readiness Index (NRI) Overview |
|
| Government Initiatives Driving Digital Transformation |
|
Government Initiatives Driving Digital Transformation Digital India Program: Launched in 2015, it has enhanced broadband access, digital literacy, and government services online, impacting millions in rural and remote areas. BharatNet Initiative: Aims to connect 2.5 lakh gram panchayats with high-speed broadband, narrowing the rural-urban digital divide and enhancing e-governance services. 5G and Future Telecom Technologies: India’s 5G rollout in 2022 has significantly boosted mobile broadband speeds, improving its global ranking from 118th to 15th.The government’s 5G Intelligent Village Initiative and Bharat 6G Vision aim to leverage 5G for rural innovation and position India as a leader in 6G technology. National Policies and Plans Supporting Digital Growth National Digital Communications Policy (NDCP) 2018: Focuses on improving connectivity and creating job opportunities through investments in the telecom sector. PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan: Launched in 2021, it integrates infrastructure development, including digital connectivity, to enhance seamless nationwide transport and logistics. National Artificial Intelligence (AI) Strategy: Promotes AI as a driver of economic growth, with India ranked top globally for AI talent and scientific publications. AI is also targeted for solving social challenges in sectors like healthcare and agriculture. Skill Development and Digital Literacy Programs Skill India and programs like PMGDISHA aim to equip the youth with digital and technical skills, enhancing India’s competitiveness in the global workforce. These initiatives have notably improved digital literacy, especially in rural areas, helping people access digital services and participate in the digital economy. |
| Practice Question: Discuss the factors contributing to India’s improved ranking in the Network Readiness Index 2024. How do government initiatives enhance the country’s digital transformation and global technological standing? (250 Words /15 marks) |
4. Uganda landslides: toll hits 20, many persons missing
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 12)
| Context |
|
Bulambuli, Uganda – Place in News
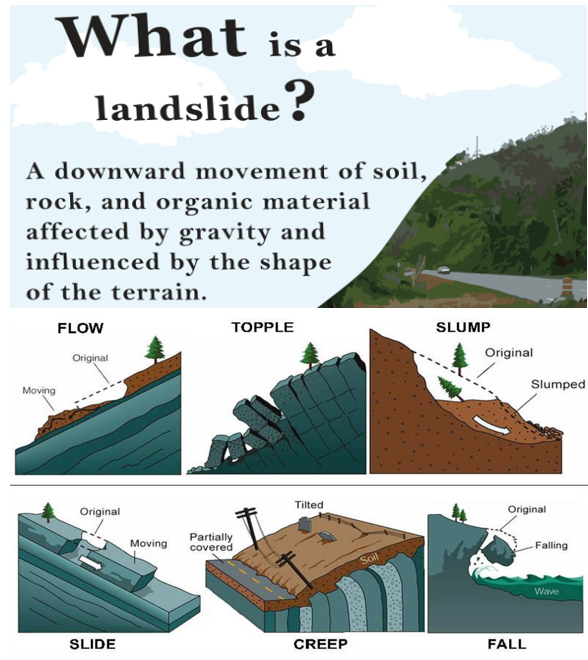
- Location: Bulambuli district, 280 km east of Kampala, Uganda’s capital, in a mountainous region.
- Event: Landslides triggered by heavy rains on Wednesday night affected six villages.
- Impact:
- Death Toll: 20 people confirmed dead, with bodies still being retrieved.
- Displacement: 750 people displaced, with 216 temporarily sheltered in a nearby school.
5. Notre Dame unveils its renewed interior five years after fire
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 13)
| Context |
|
Notre Dame Cathedral:
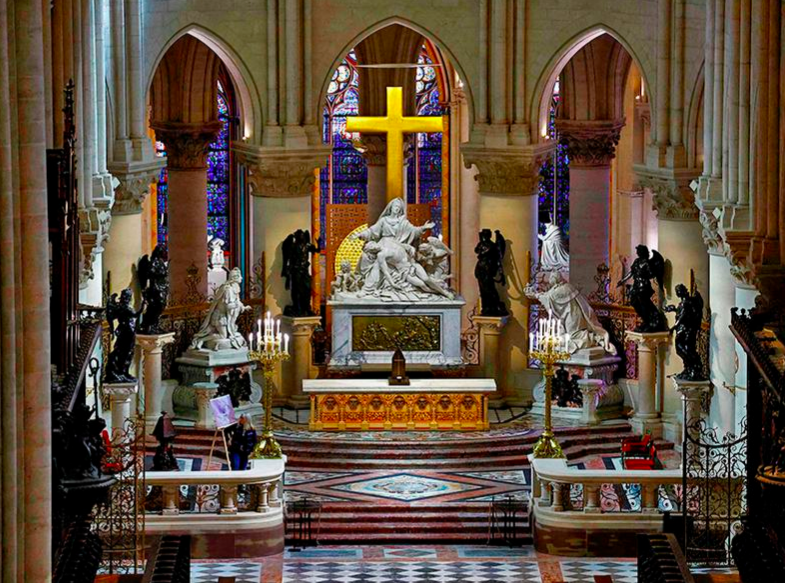

- Location: Situated in Paris, France, on the banks of Seine River.
- Built: Construction began in 1163, completed in 1345, spanning nearly 200 years.
- Architectural Style: French Gothic, with features like flying buttresses, ribbed vaults, and pointed arches.
- Famous Features:
- Rose Windows: Three large, iconic stained glass windows.
- Sculptures: Detailed carvings of biblical figures and scenes.
- Spire: Originally built in the 13th century, collapsed during the 2019 fire.
- Historical Significance: Hosted major events such as royal weddings, the coronation of Napoleon Bonaparte, and the beatification of Joan of Arc.
- Fire of 2019: Devastating fire severely damaged the roof and spire, prompting global efforts to restore it.
- UNESCO World Heritage Site: Recognized for its architectural and historical importance.
- Tourist Destination: Attracts millions of visitors annually.


