31 August 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Era of uninterrupted dialogue with Pak. is over, says Jaishankar
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 3)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations – India and its neighbourhood. |
| Context |
|
End of “Uninterrupted Dialogue”
- External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar stated that the age of “uninterrupted dialogue” with Pakistan has ended.
- India’s relationship with Pakistan has been frozen since at least 2016, following a surge in cross-border terrorist attacks, such as those in Pathankot and Uri.
Neighbouring Relationships
- The foreign minister emphasised that relations with neighbouring countries are ongoing and dynamic.
- He noted that every country faces issues with its neighbours, highlighting that such relationships inherently involve complications.
- Jaishankar cited political developments in Bangladesh and the Maldives to illustrate the nature of neighbouring relationships.
Current Status and Future Prospects
- Jaishankar declared that Article 370, related to Jammu and Kashmir, is no longer an issue.
- The focus now is on determining what kind of relationship can be envisioned with Pakistan moving forward.
- He assured that India is not passive and will respond to developments in the relationship with Pakistan, whether they are positive or negative.
| PYQ: Terrorist activities and mutual distrust have clouded India-Pakistan relations. To what extent the use of som power like sports and cultural exchanges could help generate goodwill between the two countries? Discuss with suitable examples. (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2015) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of ending the era of “uninterrupted dialogue” with Pakistan as highlighted by India’s External Affairs Minister. How might this shift impact India-Pakistan relations and regional stability? (250 Words /15 marks) |
2. China reasserts its claims in regional disputes, pushes rivals’ limits
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations |
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 13)
| Context |
|
China’s Assertive Campaign:
- China has increasingly adopted a confrontational stance across several contested regions, including the South China Sea, Taiwan, and the East China Sea.
- The strategy aims to wear down regional rivals by asserting territorial claims more aggressively as China’s military strength has grown.
Escalation in the South China Sea:
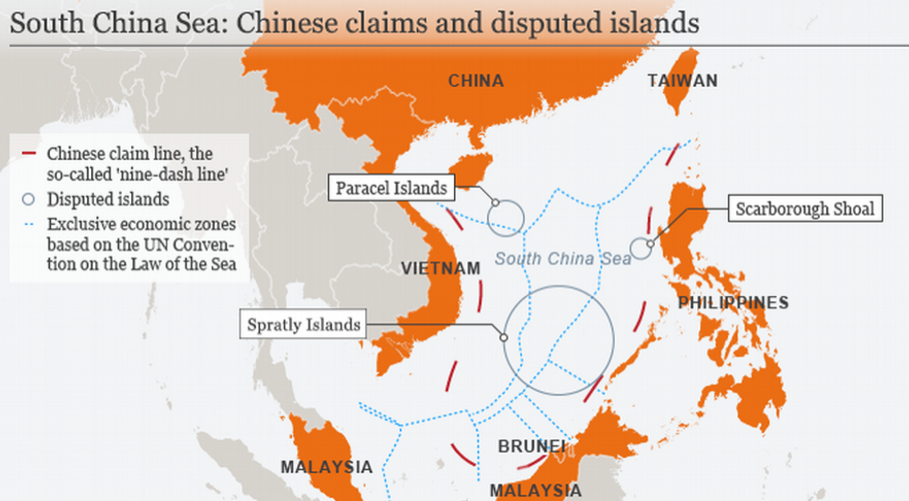
- Recent actions have seen China deploying military and coast guard vessels to challenge the Philippines over strategically important reefs and islands.
- The latest incident involves Sabina Shoal, located 140 km west of the Philippine island of Palawan, where China took measures against two Philippine Coast Guard ships, claiming they entered “illegally.”
- Manila countered by accusing China of disrupting regional peace and blocking Philippine ships from resupplying their own coast guard vessels in the area.
International and Regional Reactions:
- China has dismissed an international ruling that disputes its claims in the South China Sea.
- In June, Chinese coast guard personnel boarded Philippine vessels near Second Thomas Shoal, escalating tensions.
- The Philippines has strengthened its alliance with the U.S., which may help deter further aggression but also creates a distraction due to ongoing conflicts in West Asia and uncertainties surrounding the U.S. presidential election.
- The Philippines has considered seeking U.S. escorts for its resupply missions to counter Chinese actions.
China’s Broader Assertiveness:
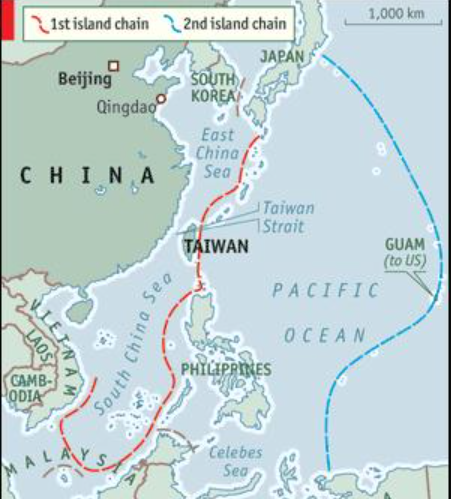
- Beyond the South China Sea, China has ramped up its military activities around Taiwan, sending more fighter jets, drones, and naval vessels to keep Taiwan vigilant against a potential invasion.
- The assertiveness extends to the East China Sea, where China has intensified pressure over a disputed island group controlled by Japan.
- Analysts suggest that these actions are interconnected as part of a broader strategy to establish more control across these regions.
Strategic Intent and Analysis:
- Analysts indicate that China’s actions are designed to test the limits of regional resolve while staying below the threshold of outright aggression.
- China aims to challenge the Philippines’ ability to manage and utilise its exclusive economic zone, and similarly, it seeks to assert control in Taiwan and the East China Sea by pushing the boundaries of regional stability.
| PYQ: South China Sea has assumed great geopolitical significance in the present context. Comment. (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2016) |
| Practice Question: Analyse China’s recent confrontational tactics in the South China Sea, Taiwan Strait, and East China Sea. Discuss the implications of these actions on regional stability and international relations, (150 Words /10 marks) |
3. DGTR Recommends Anti-Dumping Duty on Chinese Aluminium Foils Amid Market Concerns
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Economy; Page: 13)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
What is Anti-Dumping Duty?
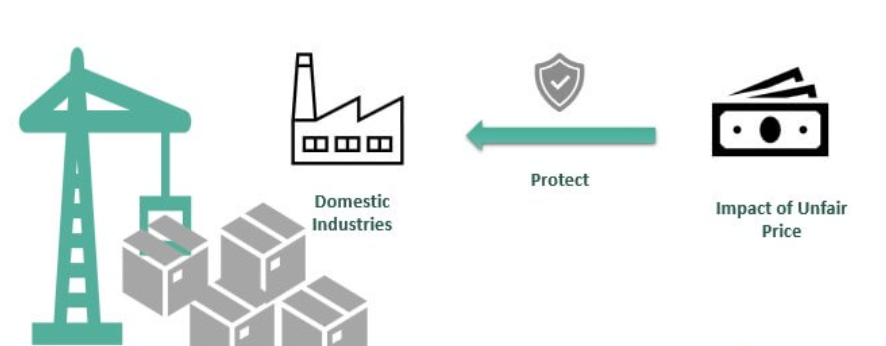
- Anti-dumping duty is a tariff imposed on imports manufactured in foreign countries that are priced below the fair market value of similar goods in the domestic market.
- The government imposes anti-dumping duty on foreign imports when it believes that the goods are being “dumped” – through the low pricing – in the domestic market.
- Anti-dumping duty is imposed to protect local businesses and markets from unfair competition by foreign imports.
- Thus, the purpose of anti-dumping duty is to rectify the trade distortive effect of dumping and re-establish fair trade.
- The use of anti-dumping measure as an instrument of fair competition is permitted by the World Trade Organization (WTO).
- The WTO allows the government of the affected country to take legal action against the dumping country as long as there is evidence of genuine material injury to industries in the domestic market.
- The government must show that dumping took place, the extent of the dumping in terms of costs, and the injury or threat to cause injury to the domestic market.
- While the intention of anti-dumping duties is to protect local businesses and markets, these tariffs can also lead to higher prices for domestic consumers.
Directorate General of Trade Remedies
- It is the apex national authority under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry for administering all trade remedial measures including anti-dumping, countervailing duties and safeguard measures.
- It provides trade defence support to the domestic industry and exporters in dealing with increasing instances of trade remedy investigations instituted against them by other countries.
Inquiry Initiated by Domestic Producers
- The investigation was initiated following a request from Hindalco, one of India’s largest aluminium manufacturers, along with other companies like Shyam Sel & Power Ltd, Venkateshwara Electrocast Pvt. Ltd, and Ravi Raj Foils Ltd.
- They argued that the surge in cheap imports from China was harming domestic industries.
Impact on Domestic Industry
- The DGTR found that the prices of Chinese aluminium foil imports, particularly those up to 80 microns, were undercutting the prices of the domestic industry, forcing Indian producers to sell below the cost of production.
- The recommended anti-dumping duty ranges from $619 to $873 per tonne.
Domestic Production Capacity
- During the period of investigation (POI), the combined capacity and production of the domestic producers were 1,32,140 MT and 69,572 MT, respectively, representing 45% of capacity and 54% of production in the Indian market.
Concerns Over Market Monopoly
- Some industry stakeholders have expressed concerns that imposing duties could create a monopoly in the market.
- They warned that it could adversely affect downstream producers by limiting their ability to source aluminium foils with good product quality and lead times, potentially impacting their ability to meet customer demands.
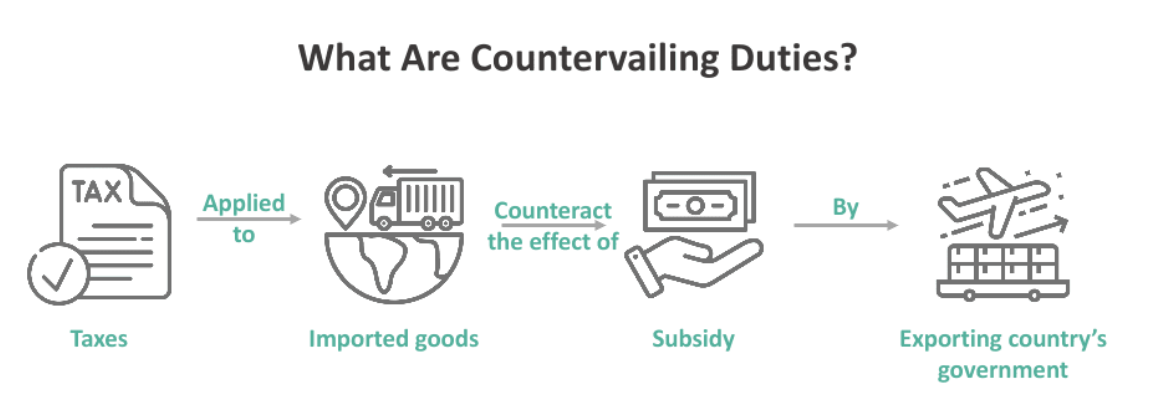
| What is Countervailing duty (CVD)? |
|
It is a specific form of duty that the government imposes to protect domestic producers by countering the negative impact of import subsidies. CVD is thus an import tax by the importing country on imported products. Why is CVD imposed?
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of imposing anti-dumping duties on imported goods for the domestic industry and the broader economy. In the context of the recent recommendation by the DGTR to impose anti-dumping duties on aluminium foils imported from China, evaluate the potential benefits and challenges this measure might create for India’s industrial ecosystem? (250 words/15 m) |
PRELIMS FACTS
1. NASA Confirms Long-Hypothesized Planet-Wide Electric Field, Key to Earth’s Atmospheric Evolution
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 17)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
The Ambipolar Electric Field
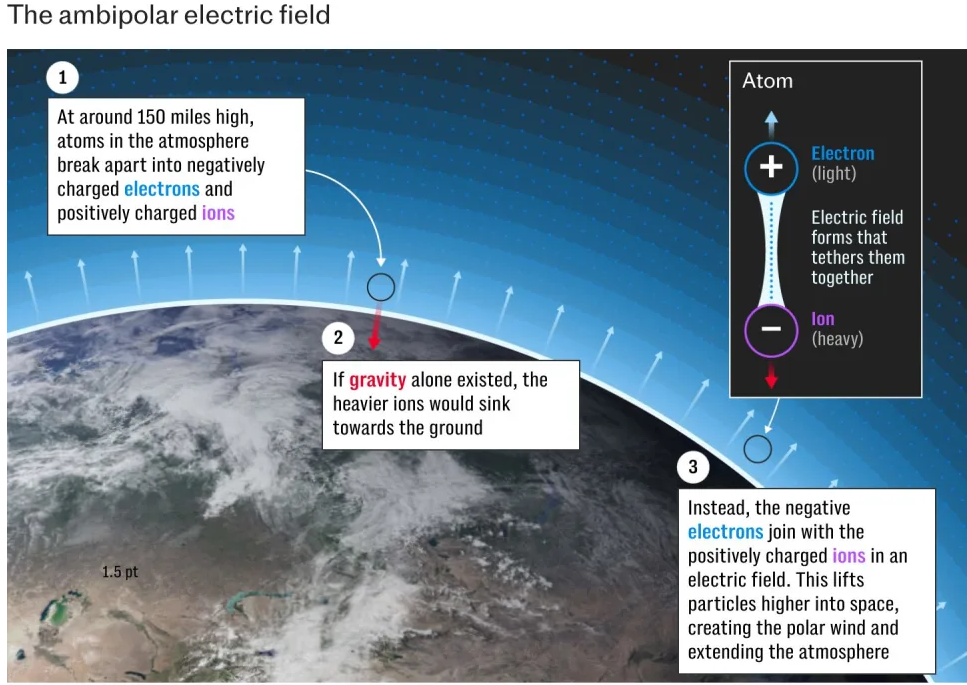
- The ambipolar electric field is formed at an altitude of around 250 km in Earth’s atmosphere, where atoms split into negatively charged electrons and positively charged ions.
- This weak electric field, with a potential of 0.55 volts as measured by Endurance, keeps these charged particles tethered together.
- It prevents the heavier ions from sinking back to Earth and stops the lighter electrons from drifting into space.
- The field is bidirectional, with ions pulling electrons down and electrons lifting ions up, which sometimes allows ions to escape Earth’s atmosphere.
Impact on Earth’s Evolution
- This newly confirmed electric field is believed to have continuously influenced the evolution of Earth’s atmosphere, shaping it into what it is today.
- The discovery opens up possibilities for further research into how this electric field has affected Earth and potentially other planets over time.
2. HAL and SAFHAL to Develop New ‘Aravalli’ Engine for Next-Generation Indian Helicopters
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt & Politics; Page: 06)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
About Indian Multi Role Helicopters
- The Indian Multi Role Helicopter (IMRH) is a medium-lift helicopter currently under development by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) for Indian Armed forces for air assault, air-attack, anti-submarine, anti-surface, military transport and VIP transport roles.
- IMRH is aimed to replace all the current Mil Mi-17 and Mil Mi-8 helicopters across the Indian armed forces.
- The planned rotorcraft is expected to have a maximum takeoff weight of 13 tonnes with a five bladed main rotor and 4 bladed rotor on tail.
- The navalised version further will have longer range and higher payload capacity. HAL estimates requirement of over 314 rotocraft of same class across Indian Armed Forces replace existing Mil Mi-17 helicopters in service in India.
Applications of the Aravalli Engine
- The Aravalli engine will be used in the 13-tonne Indian Multi-Role Helicopter (IMRH) and the 12.5-tonne Deck-Based Multi-Role Helicopter (DBMRH).
- The IMRH is expected to be ready within the next 8 to 10 years and is set to replace the aging Russian Mi-17 helicopters, which will begin phasing out by 2028.
- The DBMRH is being developed specifically for the Indian Navy.
Role of SAFHAL in the Project
- SAFHAL, a joint venture between Safran Helicopter Engines SAS and HAL, is responsible for the design, development, production, and sales of these new-generation helicopter engines in India.
- The partnership aims to boost indigenous capabilities in high-power helicopter engine technology, contributing to India’s defense self-reliance.
3. Rajasthan Launches Roadshows to Attract Global Investments Ahead of 2024 Summit
(Source: Indian Express; Section: The Second page; Page: 02)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
MoUs and Investment Prospects
- During the event, several Memorandums of Understanding (MoUs) were signed across sectors like cement, chemicals, petrochemicals, civil aviation, ITI upgradation, and renewable energy, amounting to a total of ₹4.50 lakh crore.
- The Chief Minister emphasized Rajasthan’s ongoing transformation and commitment to providing a favorable business environment with strong returns.
Supporting Infrastructure and Promotion
- A dedicated website for the summit was launched to offer potential investors comprehensive information about investment opportunities and Rajasthan’s economic landscape.
- Industry leaders shared positive experiences of investing in the state, supported by a short film highlighting recent developments and investments, underscoring Rajasthan’s potential as a leading investment hub.
| Rising Rajasthan Global Investment Summit 2024 |
|
4. At 6.7%, growth slid to five-quarter low in Q1
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Context |
|
Reasons For This Slowdown :
- Election-related expenditure drop: Government spending, including capital expenditure, slowed due to the conduct of general elections, reducing public investments.
- Public capital expenditure decline: Public capital expenditure, including projects funded by the Centre, States, and public sector firms, fell by 33.3% compared to the previous year.
- Statistical base effects: High growth in certain sectors during the previous quarters created a base effect, leading to slower growth in the current quarter.
- Global uncertainties: External factors like global economic uncertainties, inflationary pressures, and fluctuating commodity prices affected private investment and consumption.
- Monetary policy tightening: Hawkish policies by the RBI, aimed at controlling inflation, may have dampened growth in some sectors.
- Slower services sector growth: Key services, such as trade, hotels, and transport, registered slower growth due to a high base from last year and weaker demand recovery in these areas.
5. Cyclone Asna forms over Kutch; heavy rain batters Gujarat
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Context |
|
Cyclone Asna:
- Formation: Cyclone Asna formed over the Kutch coast in Gujarat and adjoining areas of Pakistan.
- Impact: Caused light to moderate rainfall in Gujarat, with heavy to very heavy rainfall in Kutch and Saurashtra.
- Movement: Expected to move away from the western coast in the next 48 hours, heading towards the Arabian Sea.
- Historical Context: This is the first cyclonic storm in the Arabian Sea in August since 1976. Previous August cyclones occurred in 1976, 1964, and 1944.
- Name Origin: “Asna” means “the one to be acknowledged or praised” in Pakistan.
6. Dr. T.V. Somanathan takes over as the new Cabinet Secretary
(Source –https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2050110 )
| Context |
|
Cabinet Secretary in India:
- Position: The Cabinet Secretary is the highest-ranking civil servant in the Indian government.
- Role: Serves as the principal advisor to the Prime Minister and the Cabinet.
- Responsibilities:
- Oversees the administration of government policies and their implementation.
- Coordinates and ensures effective communication between various ministries and departments.
- Provides administrative support for the Cabinet and its meetings.
- Handles sensitive and high-priority government matters.
- Appointment: Appointed by the Prime Minister, typically from among senior Indian Administrative Service (IAS) officers.
- Tenure: Generally serves a fixed term of two years, but extensions are possible.
| Practice Question: Discuss the role and responsibilities of the Cabinet Secretary in the Indian government. How does this position contribute to the effective functioning of the executive branch? (150 Words /10 marks) |
7. WAVES | Create in India Challenge Season 1
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2050221 )
| Context |
|

Analysis of the news:
- WAVES (World Audio Visual & Entertainment Summit) is an inaugural event hosted by the Government of India to enhance the global influence of India’s Media & Entertainment industry.
- Launched on August 22, 2024, by Union Minister Shri Ashwini Vaishnaw, the summit aims to spotlight Indian talent and innovation across various media sectors.
- It features 25 challenges under the ‘Create in India Challenge – Season 1,’ covering animation, gaming, esports, comics, film, music, and emerging technologies.
- WAVES will serve as a significant platform for showcasing creative works, offering networking opportunities, and exploring advancements in entertainment economics and technology, engaging both amateurs and professionals.
3. Solar Energy Corporation of India Ltd (SECI) attains Navratna Status
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2050232 )
| Context |
|
Solar Energy Corporation of India Ltd (SECI):
- Established: 2011, as a public sector enterprise under the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), Government of India.
- Purpose: Promote and facilitate the development of solar energy projects in India.
- Functions:
- Develop and operate solar power projects.
- Facilitate project implementation through policy support and financial assistance.
- Promote solar energy technology and innovation.
- Key Initiatives:
- Solar park development.
- Implementation of various solar power schemes.
- Support for large-scale solar projects and rooftop solar installations.
- Capacity: Cumulative generation capacity of 69.25 GW
- Mission: Enhance the deployment of solar energy, contributing to India’s renewable energy goals and reducing carbon emissions.
- Headquarters: New Delhi, India