4 July 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Spike in pollution levels may raise death rates in cities with cleaner air, says study
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Topic: GS3 – Environment – Environmental pollution and degradation |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
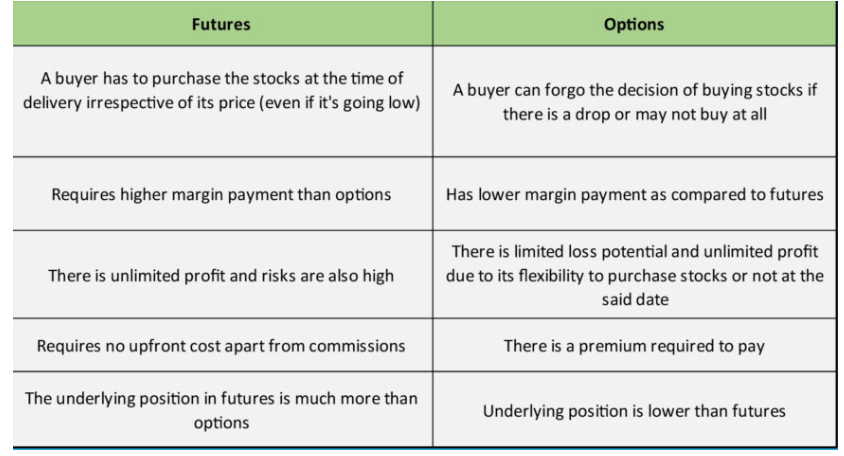
- A spike in air pollution in cleaner Indian cities can raise death rates more than in cities with higher pollution.
- The same pollution increase in Bengaluru can increase death rates more than in Delhi.
- High pollution cities still saw a greater fraction of annual deaths due to air pollution:
- Delhi: 11.5% of annual deaths attributable to air pollution.
- Bengaluru: 4.8% of annual deaths attributable to air pollution.
- Bengaluru residents had 30% of the daily air pollution exposure compared to Delhi residents.
- A multi-city analysis in India, published in Lancet Planet Health, studied health effects of short-term air pollution exposure.
- Scientists analysed pollution and death registry data from 10 cities: Ahmedabad, Bengaluru, Chennai, Delhi, Hyderabad, Kolkata, Mumbai, Pune, Shimla, and Varanasi.
- Nearly 30,000 deaths, or 7.2% of annual deaths in these cities, were due to short-term PM 2.5 exposure.
- Total daily deaths in these cities increased by 1.42% for every 10 microgram per cubic metre increase in average PM 2.5 exposure over a two-day period.
- From air pollution, Delhi had about 12,000 deaths per year and Shimla had the lowest at 59 deaths per year (2008-2019).
- Mortality risk rose quickly at lower PM 2.5 levels but plateaued at higher levels.
- Mortality risk was very high (2.65%) even on days with PM 2.5 levels below India’s national air quality standard of 60 micrograms per cubic metre.
- The study’s authors are from multiple institutes in Europe and India.
| PYQ: Mumbai, Delhi and Kolkata are the three mega cities of the country but the air pollution is a much more serious problem in Delhi as compared to the other two. Why is this so? (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2015) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of short-term air pollution spikes on mortality rates in Indian cities with varying pollution levels, as highlighted by recent studies. How can this inform policy decisions? (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. Spiral galaxies evolved 4 billion years sooner than expected
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|

A Hubble Space Telescope image of the spiral galaxy Messier 77, March 28, 2013
Discovery of More Spiral Galaxies in Universe’s Youth
- A new study revealed more spiral galaxies in the universe’s early years than previously thought.
- Age of Universe: Approximately 13.8 billion years old with various galaxy types, including spiral and elliptical.
- Previous Belief: Spiral galaxies were believed to have formed around 6 billion years ago.
| Spiral Galaxies: |
|
Formation and Evolution of Galaxies
- Initial Universe State: As the universe cooled from a dense plasma, it formed hot gas clumps that became galaxies.
- Traditional Theory: Early galaxies were irregular and lacked disks; over billions of years, they cooled and formed spiral arms.
- New Insight: The cooling and spiral formation may have occurred simultaneously.
Research Methods and Technology
- Detecting Early Galaxies: Utilised infrared and optical wavelengths.
- James Webb Space Telescope: Enabled deeper observations into the universe’s past.
- Study Sample: Examined 873 galaxies and identified at least 216 spiral galaxies dating to 1.5 billion years after the Big Bang.
- Researchers manually classified each galaxy image as spiral or non-spiral.
Increased Fraction of Spiral Galaxies
- Researchers compared the number of spiral galaxies to the total number of galaxies.
- Between 3 billion and 7 billion years after the Big Bang, the fraction of spiral galaxies increased from about 8% to 48%.
- Prior observations indicated an increase from 5% to 30%.
Impact on Star Formation Understanding
- New findings could alter the understanding of star formation rates in the early universe.
- Crucial for understanding formation earth-like planets, dependent on the presence of elements heavier than iron.
Future Galaxy Evolution
- Spiral Galaxies’ Evolution: Became more populous even as star formation peaked.
- Gas Depletion: Over time, spiral galaxies have less gas in their arms, slowing new star formation.
- Galactic Collisions: Predicted collisions, such as between the Milky Way and Andromeda, could restart star formation and create elliptical galaxies.
Uncertainties and Future Research
- The cycle of forming galaxies, stars, and earth-like planets is increasingly complex.
- Uncertainty remains about the exact processes and timeline of galaxy formation.
- Astronomers must continue refining models and expanding observations to better understand galaxy formation.
3. Till Russia do us part? NATO at 75, an enduring alliance
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 11)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations – Important International institutions. |
| Context |
|
Overview and Formation
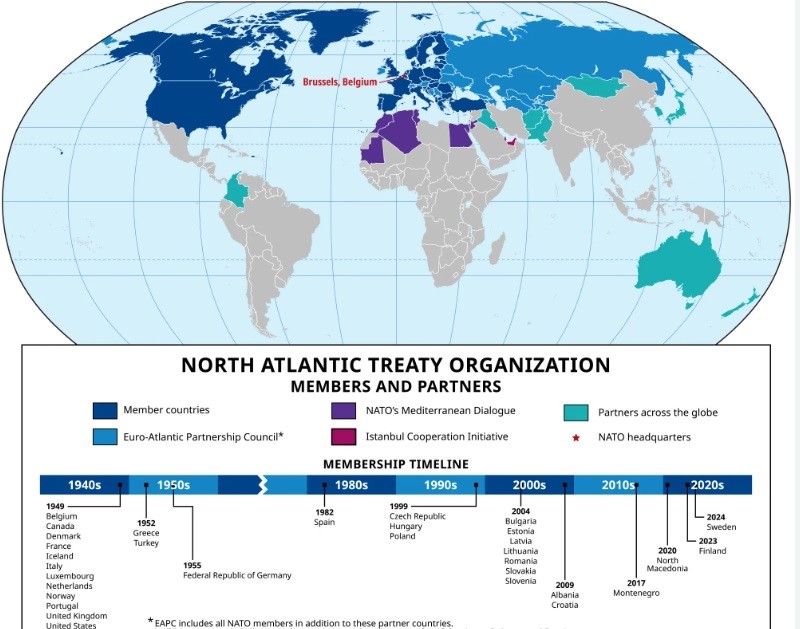
- NATO Formation: Established on April 4, 1949, as the ‘Atlantic Alliance’ with 12 founding members including the U.S., Canada, U.K., France, and several European countries.
- Purpose: Aimed to deter Soviet expansion during the Cold War.
- Historic Context: Created in response to Soviet threats post-WWII, such as the Berlin Blockade and Communist coups in Eastern Europe.
Key Developments
- Berlin Blockade: Stalin’s blockade of Berlin in 1948 led to the Berlin Airlift, a significant moment in NATO’s early history.
- Expansion: NATO has grown to 31 members as of 2023.
- In 1954, Soviet Foreign Minister Molotov suggested the Soviet Union apply for NATO membership, a move reflecting the tense Cold War dynamics.
NATO During the Cold War
- Eisenhower’s Role: Dwight D. Eisenhower’s leadership as NATO’s supreme commander highlighted the transition from WWII alliances to Cold War defence strategies.
- Secret Armies: NATO and the CIA established clandestine networks like the Gladio network to counter Soviet influence in Europe.
Post-Cold War and Modern Era
- Adaptation: NATO has adapted to post-Cold War realities, addressing new security challenges such as terrorism and cyber threats.
- Failures and Successes: The alliance faced criticism for its role in Afghanistan but gained renewed relevance with recent Russian aggression.
- NATO’s strategy has been characterised by unprecedented levels of integration and transparency among its members.
- Contrast with Pre-NATO Alliances: Unlike earlier alliances based on opportunism and mutual suspicion, NATO members have sought deeper cooperation and openness.
Current Relevance
- 75th Anniversary: Celebrated 75 years in 2024, reflecting on its legacy and ongoing strategic importance.
- Continues to adapt to contemporary security threats, ensuring its relevance in global geopolitics.
Conclusion
- NATO remains the longest-lasting military alliance in history, marked by its evolution from a Cold War deterrent to a multifaceted security organisation addressing diverse global challenges.
| PYQ: The expansion and strengthening of NATO and a stronger US-Europe strategic partnership works well for India.” What is your opinion about this statement? Give reasons and examples to support your answer. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2023) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of NATO’s adaptability and relevance in addressing contemporary global security threats as it celebrates its 75th anniversary. (150 Words /10 marks) |
4. Hindenburg vs. Adani: SEBI’s Show Cause Notice Sparks Controversy Over Short-Selling Allegations and Regulatory Practices
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 16)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
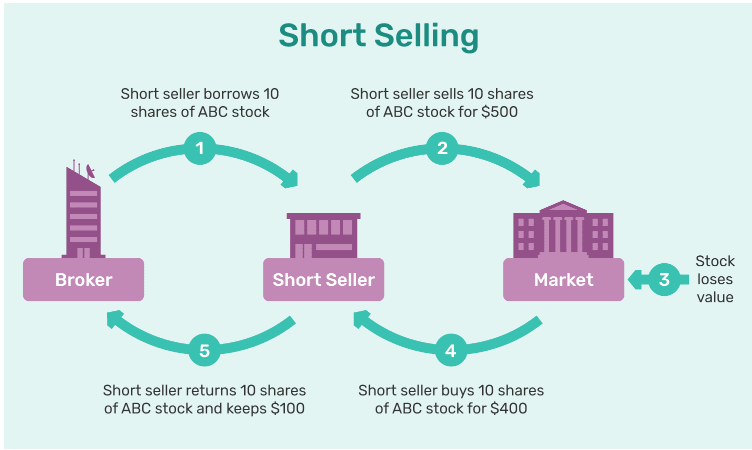
What is Short Selling?
- Short selling is the practice wherein an investor borrows a stock or security, sells it in the open market, foreseeing a potential future price decline, aiming to repurchase the same asset at a lower price point later on.
- SEBI defines short selling as selling a stock that the seller does not own at the time of trade.
SEBI’s Show Cause Notice to Hindenburg:
- On July 1, Hindenburg Research announced it had received a show cause notice from India’s capital markets regulator, SEBI, on June 27. The notice outlined suspected violations of Indian regulations and accused Hindenburg of colluding with entities to use non-public information to short-sell AEL shares, thereby making significant profits.
- SEBI named Hindenburg Research, its founder Nathan Anderson, partner-investor Mark Kingdon, and three entities owned by Kingdon in the notice.
- It alleged that Kingdon Capital Management used advance knowledge of Hindenburg’s report to take short positions in AEL futures, profiting Rs 183.24 crore after the report’s release.
Hindenburg’s Rejection of SEBI’s Allegations:
- Hindenburg dismissed SEBI’s allegations as “nonsense” and criticized the regulator for not pursuing the Adani Group’s alleged fraudulent activities.
- The research firm emphasized that their investment stance was transparent and well-known, countering SEBI’s claims that their short positions in Adani were secretive or misleading.
- Hindenburg also alleged that SEBI pressured brokers to close short positions in Adani stocks, artificially supporting the stock price at a critical time.
Involvement of Kotak Mahindra Bank
- Hindenburg highlighted SEBI’s omission of Kotak Mahindra Bank’s role in the matter. The bank allegedly created and managed the offshore fund structure used by Kingdon to bet against Adani.
- Hindenburg accused SEBI of protecting powerful Indian businessmen, implying that the regulator deliberately masked Kotak’s involvement by using the acronym ‘KMIL’ instead of the full name.
- In response, Kotak Mahindra Bank clarified that KIOF, the fund in question, was a SEBI-registered FPI established in 2013 and had no knowledge of Hindenburg’s involvement with its investors.
Conclusion: Implications and Controversies:
- The conflict between Hindenburg Research and the Adani Group, and the subsequent involvement of SEBI and Kotak Mahindra Bank, highlights significant issues within India’s financial regulatory framework.
- While SEBI aims to uphold market integrity, the allegations and counter-allegations suggest a complex interplay of interests and potential regulatory shortcomings.
- The outcome of this dispute will likely have profound implications for investor confidence, market transparency, and regulatory practices in India.
| Regulation of Short-selling in India |
|
SEBI has recently stated that investors across all categories will be allowed for short-selling, but naked short-selling will not be permitted. Consequently, all investors are required to fulfill their duty of delivering securities during the settlement period Naked short selling occurs when an investor sells stocks or securities without first arranging to borrow them or ensuring they can be borrowed. Institutional investors must disclose upfront whether a transaction is a short sale, while retail investors can make a similar disclosure by the trading day’s end. Also, short selling is permitted for securities traded in the F&O (Futures & Options) segment, subject to SEBI’s periodic review of eligible stocks. Futures and Options (F&O) are derivative instruments. Futures involve an obligation to buy/sell assets at an agreed price on a set date, carrying unlimited risk. Options grant the right (but not obligation) to buy/sell assets by a certain date, with a premium paid upfront limiting potential losses.
|
|
PYQ: In the parlance of financial investments, the term ‘bear’ denotes (2010) (a) An investor who feels that the price of a particular security is going to fall (b) An investor who expects the price of particular shares to rise (c) A shareholder or a bondholder who has an interest in a company, financial or otherwise (d) Any lender whether by making a loan or buying a bond Ans: (a) |
| Practice Question: Examine the implications of the recent show cause notice issued by SEBI to Hindenburg Research concerning the short-selling of Adani Enterprises Ltd. How do such regulatory actions impact market integrity and investor confidence in India? Discuss the broader issues related to regulatory oversight and the potential influence of powerful business interests in this context. (250 words/15 m) |
5. UK-India FTA Talks: Political Stability and Key Challenges in Immigration and Climate Policies
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 16)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations – Bilateral relations |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
What is a Free Trade Agreement?
- It is a pact between two or more nations to reduce barriers to imports and exports among them.
- Under a free trade policy, goods and services can be bought and sold across international borders with little or no government tariffs, quotas, subsidies, or prohibitions to inhibit their exchange.
- The concept of free trade is the opposite of trade protectionism or economic isolationism.
- FTAs can be categorized as Preferential Trade Agreement, Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement, Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA).
Not an ‘Anti-India’ Labour Party
- Under the leadership of Keir Starmer, the Labour Party has shifted its stance significantly. Unlike his predecessor Jeremy Corbyn, who called for international intervention in Kashmir, Starmer has recognized the political importance of the UK’s Indian-origin population, the largest immigrant group in the country.
- Labour has actively tried to eliminate ‘anti-India sentiments’ within the party.
- Labour Party Chair Anneliese Dodds recently stated that the party is confident it has removed members with extremist views on India.
- Starmer’s Labour has even criticized the Conservative Party for delaying the FTA with India, indicating a more favorable stance towards India in trade negotiations.
Visas a Likely Sticking Point
- Immigration is a highly contentious issue in British politics. While there are disagreements between the Tories and Labour on how to manage immigration, there is a consensus that it should be restricted.
- This poses a challenge for the FTA with India, as New Delhi seeks temporary visas for its service sector workforce, expecting significant gains from this provision.
- The UK, with its strong IT and financial services sectors, stands to benefit from integration with India’s service sector.
- However, given the UK’s political climate, Labour is likely to negotiate rigorously on the visa issue, aiming to balance trade benefits with immigration control.
Tougher Negotiations on Climate
- A Labour government is expected to bring tougher negotiations on climate issues.
- Labour has frequently criticized the Tories for not adhering to the UK’s 2030 net-zero goals. India has sought a relaxation on the carbon tax that the UK plans to implement, similar to the EU’s carbon border adjustment mechanism.
- New Delhi argues that this mechanism could negate the tariff concessions agreed upon during the FTA.
- Labour’s firm stance on climate goals might lead to more stringent demands on India regarding environmental regulations and carbon emissions, adding another layer of complexity to the FTA negotiations.
Conclusion: Balancing Trade, Immigration, and Climate Goals
- The negotiations for the FTA between New Delhi and London highlight the intricate balance required between trade liberalization, immigration policies, and climate commitments.
- Political stability in the UK could facilitate the progress of the FTA, but the negotiations will likely face significant hurdles.
- The Labour Party’s changing stance towards India and its emphasis on climate goals suggest that while the prospects for the FTA might improve, the road ahead will involve tough negotiations on critical issues such as visas and environmental regulations.
| How has Been India-UK Trade Relations? |
What can be the Significance of FTA between India & the UK?
|
|
PYQ: Consider the following countries: (2018) 1) Australia 2) Canada 3) China 4) India 5) Japan 6) USA Which of the above are among the ‘free-trade partners’ of ASEAN? (a) 1, 2, 4 and 5 (b) 3, 4, 5 and 6 (c) 1, 3, 4 and 5 (d) 2, 3, 4 and 6 Ans: (c) |
| Practice Question: The Ministry of Mines is planning to introduce a Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme to enhance the recycling of critical minerals in India. Discuss the significance of such a scheme in fostering a circular economy and strengthening domestic supply chains. What challenges might arise in its implementation, and how can they be addressed? (250 words/15 m) |
PRELIMS FACTS
1. New Discovery: Mosquito Hormones Regulate Blood Cravings, Offering Hope for Disease Control
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 16)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Hormones and Feeding Behavior:
- Female mosquitoes consume animal blood to develop their eggs. However, after a blood meal, they temporarily lose their appetite until they lay their eggs.
- Experts from the University of Georgia in Athens, investigated the factors controlling this feeding cycle.
- They discovered that the levels of a gut hormone called Neuropeptide F (NPF) spike when mosquitoes are seeking a host and decrease after feeding.
- This hormone’s levels closely mirror mosquitoes’ interest in humans.
Opposing Actions of NPF and RYamide
- Another gut hormone, RYamide, was found to have the opposite effect. As NPF levels fall after a blood meal, RYamide levels rise, and vice versa.
- The researchers concluded that NPF and RYamide work together to stimulate and suppress mosquitoes’ attraction to humans and other hosts.
- This tandem action regulates their feeding behavior and interest in seeking hosts for blood meals.
Implications for Disease Control
- Mosquitoes are vectors for diseases such as malaria, dengue, West Nile virus, yellow fever, Zika, chikungunya, and lymphatic filariasis, which collectively result in approximately 700,000 deaths worldwide each year.
- The situation is exacerbated by climate change, which allows mosquitoes to thrive in previously too cold regions.
- The recent discovery of the interplay between NPF and RYamide provides scientists with potential new targets for pesticides, aiming to prevent mosquito reproduction and disease transmission.
2. Smart Cities Mission period extended till March 2025
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|
Smart Cities Mission:
- Launch and Aim: Launched in June 2015, the Smart Cities Mission (SCM) aims to develop 100 cities in India into smart cities through an area-based development plan.
- Selection: 100 cities were selected through a competitive process to become model areas, expected to influence surrounding regions positively.
- Projects: Over 8,000 multi-sectoral projects are being developed under the mission, with a total investment of around ₹1.6 lakh crore.
- Progress: As of July 3, 2024, 7,188 projects (90% of the total) have been completed, amounting to ₹1,44,237 crore.
- Remaining Projects: 830 projects, worth ₹19,926 crore, are in advanced stages of completion.
- Funding: The mission has a budget of ₹48,000 crore, with ₹46,585 crore (97%) already released and 93% utilised.
- Extension: The mission period has been extended until March 31, 2025, to allow for the completion of the remaining projects without additional costs.
3. Japan issues first new bills in two decades, designed against fakes
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 13)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- Japan issued new yen banknotes with 3-D hologram technology to combat counterfeiting.
| 3D holography: |
|
- Prime Minister Fumio Kishida called the new ¥10,000, ¥5,000, and ¥1,000 bills “historic.”
- The new bills feature:
- ¥10,000: Eiichi Shibusawa, “father of Japanese capitalism.”
- ¥5,000: Umeko Tsuda, feminist and educator.
- ¥1,000: Shibasaburo Kitasato, physician and bacteriologist.
- Backs of the bills feature Tokyo Station, wisteria flowers, and Mount Fuji by Katsushika Hokusai.
- Bills have larger printing for easier reading, especially for the ageing population.
- Older bills remain valid and necessary for vending machines and bus fares.