4 October 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Annual Floods Ravage North Bihar: Geography and Embankments Worsen Crisis for 15.76 Lakh Residents
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 17)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
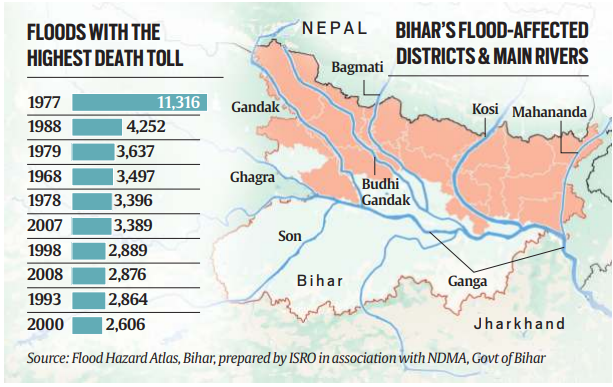
Geographic Factors Behind Recurrent Flooding
- Bihar is crisscrossed by many rain and snow-fed rivers, making it highly flood-prone.
- About 76% of North Bihar’s population lives under constant flood threats. Flash floods from Nepal, river floods, drainage congestion, and permanent waterlogged areas contribute to the flooding problem.
- Rivers like Kosi, Gandak, and Bagmati carry loose soil and sediment from the Himalayas, making it easy for these rivers to overflow.
The Kosi Embankments: A Double-Edged Sword
- Kosi, known as the “Sorrow of Bihar,” is the most destructive river in the state. Embankments were built to contain the river, but these have often been breached, worsening the flood situation.
- Accumulated sediment raises the riverbed by about 5 inches annually, making flooding more frequent and severe.
- Embankments have trapped over 15 lakh people in flood-prone areas with no escape.
Non-Engineering Solutions: The Way Forward
- While structural solutions like embankments and barrages have been considered, experts stress the need for non-engineering solutions such as better flood warnings, faster response times, and public awareness.
- Since the geography of Bihar cannot be changed, a focus on risk mitigation, preparedness, and flood management policies is crucial for reducing flood damage.
| Floods |
|
| PYQ: The frequency of urban floods due to high intensity rainfall is increasing over the years. Discussing the reasons for urban floods. highlight the mechanisms for preparedness to reduce the risk during such events. (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2016) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the factors contributing to the recurrent flooding in North Bihar. Critically analyze the effectiveness of structural solutions like embankments and propose non-engineering measures for sustainable flood management in the region. (250 words/15 m) |
2. India’s Diplomatic Tightrope: Navigating Rising Iran-Israel Tensions Amidst Strategic and Economic Stakes
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 17)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
India’s Diplomatic Role
- India maintains diplomatic relations with both Israel and Palestine. Prime Minister Narendra Modi has recently communicated with both Palestinian President Mahmoud Abbas and Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, expressing concern for peace and stability.
- However, India has not yet offered to mediate between the two sides. For meaningful mediation, India would need greater leverage beyond its current communication channels.
Balancing Relations with Israel and Iran
- India faces a delicate balancing act between Israel and Iran. Israel is a strategic partner, particularly in defense, and has been a reliable ally for India during times of crisis, such as during the Kargil War.
- On the other hand, Iran is crucial for India’s energy security and regional strategy, especially with projects like the Chabahar port.
- Tensions between these two nations, such as the 2012 attack on an Israeli diplomat in Delhi, have previously caused discomfort for India.
India’s Stakes in West Asia
- Indian Diaspora: There are around 18,000 Indians in Israel and 5,000-10,000 in Iran, with 9 million Indians living in the broader West Asian region. A wider conflict would pose significant risks to this large Indian community.
- Energy Security: West Asia provides 80% of India’s oil supplies. An escalation could drive up energy prices, impacting India’s economy.
- Strategic Interests: India has invested in relationships with major Arab countries, Israel, and Iran, and is actively pushing for the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor. A regional war would jeopardize these economic and strategic initiatives.

Conclusion
- India has a vested interest in maintaining peace in West Asia due to its diaspora, energy security, and strategic partnerships.
- While India has not positioned itself as a mediator, it will need to carefully navigate this conflict to protect its interests in the region.
| PYQ: ‘India’s relations with Israel have, of late, acquired a depth and diversity, which cannot be rolled back.” Discuss. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2018) |
| Practice Question: Examine India’s strategic and economic interests in West Asia in light of the escalating tensions between Iran and Israel. How can India balance its relations with both nations while safeguarding its regional stakes and security? (150 words/10 m) |
3. UK Cedes Sovereignty of Chagos Islands to Mauritius, Securing Military Presence at Diego Garcia
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 17)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
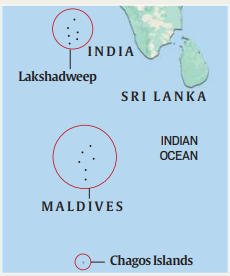
Historical Background
- The Chagos archipelago, a group of 58 islands located 500 km south of the Maldives, was uninhabited until the late 18th century.
- It was colonized by the French, who brought slaves to work on coconut plantations.
- The islands were ceded to the British in 1814. In 1965, the UK created the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) with Chagos as its centerpiece.
- When Mauritius gained independence in 1968, the Chagos Islands remained under British control, and the UK compensated Mauritius with £3 million for the islands’ “detachment.”
Strategic Importance of Diego Garcia
- Britain retained sovereignty due to the islands’ strategic military location. In 1966, the UK signed an agreement with the US to make the BIOT available for defense purposes, leading to the development of a military base on Diego Garcia.
- By 1986, the base became fully operational, playing a crucial role in US military operations, especially in West Asia and during conflicts such as the Gulf War.
- Diego Garcia remains critical for monitoring the Malacca Strait, essential for global trade and especially vital to China.
Dispute Over Sovereignty
- Mauritius has long contested the UK’s occupation of Chagos, raising the issue in international forums.
- In 2017, the UN General Assembly sought the International Court of Justice (ICJ) opinion on the legal status of Chagos.
- In 2019, the ICJ ruled that the detachment of Chagos from Mauritius was unlawful and called for the UK’s withdrawal.
- The UK-Mauritius agreement allows Mauritius to implement resettlement on Chagos islands, except Diego Garcia, while the military base remains operational for 99 years under British sovereignty.
Broader Implications
- The agreement has broader geopolitical significance, as unresolved disputes could push countries like Mauritius toward alternative partners such as China.
- India, having supported Mauritius’ claims in the UN, is also deepening its ties with Mauritius, especially in the Indian Ocean, as seen in its construction of infrastructure on Agaléga, another Mauritian dependency.
| Practice Question: What are the implications of the UK ceding sovereignty of the Chagos Islands to Mauritius while maintaining military operations at Diego Garcia? (250 words/15 m) |
PRELIMS FACTS
1. Union Cabinet Grants Classical Language Status to Marathi, Pali, Prakrit, Assamese, and Bengali
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt & Politics; Page: 07)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:

Historical Context of Classical Language Status
- The category of classical languages was introduced in 2004 with Tamil as the first language to receive this status.
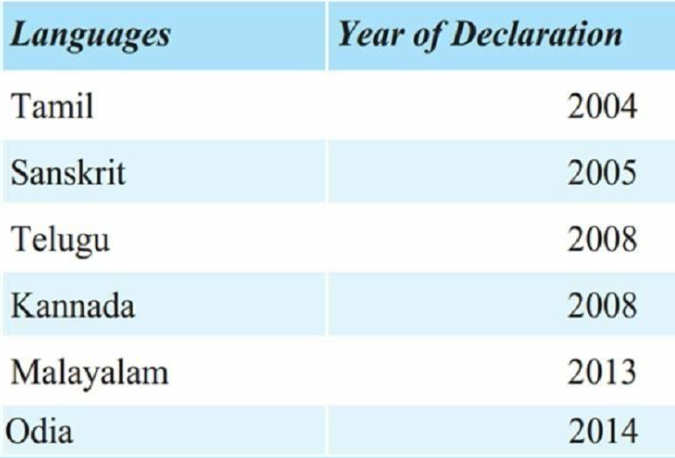
- Criteria include the antiquity of early texts and over 1,000 years of recorded history.
States Involved
- Marathi: Maharashtra
- Pali and Prakrit: Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh
- Bengali: West Bengal
- Assamese: Assam
National and International Impact
- The decision is expected to have wide-reaching cultural and academic implications both in India and globally.
Other languages that followed include:
- Sanskrit (2005)
- Telugu and Kannada (2008)
- Malayalam and Odia (2013 and 2014)
Benefits of Classical Status

The languages declared as ‘classical’ receive several benefits from the government to promote them further such as:
- Two international awards are instituted annually for scholars who have made exemplary research contributions, teaching or promoting the classical languages of India. This honours their service to preserving heritage.
- A Centre of Excellence is established by the Government to stimulate advanced research specifically focused on each of the classical languages declared. This powers further literary and linguistic study.
- The University Grants Commission(UGC) sponsors the creation of Professional Chairs related to the classical languages of India in central universities and research institutions. This enables focused teaching and research capacity building.
2. Centre Approves ₹10,103 Crore National Mission on Edible Oils to Boost Domestic Production
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt & Politics; Page: 07)
| Context: |
| The Union Cabinet, led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, approved the National Mission on Edible Oils–Oilseeds (NMEO-Oilseeds) with a financial outlay of ₹10,103 crore. |
Analysis of News:

Objective
- The mission aims to reduce India’s dependence on edible oil imports, currently at 58%, by increasing domestic production.
Key Targets
- Increase production from the current 12.7 million tonnes to 20.2 million tonnes by 2031.
Focus on key oilseed crops such as:
- Rapeseed-mustard
- Groundnut
- Soybean
- Sunflower
- Sesamum
Enhanced Efficiency
The mission will also emphasize improving extraction efficiency from secondary sources like:
- Cottonseed
- Rice bran
- Tree-borne oils
Scheme Reorganization
In parallel, the government has reorganized centrally-sponsored schemes under the Agriculture Ministry into two umbrella schemes:
- PM Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana
- Krishonnati Yojana (KY)
This restructuring aims to streamline efforts in the agricultural sector and enhance productivity.
3. Nepal, India, and Bangladesh Sign Tripartite Agreement for Cross-Border Electricity Trade
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Economy; Page: 15)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Key Details of the Agreement
- Nepal to Export Surplus Electricity: Nepal will export surplus hydroelectricity to Bangladesh during the rainy season (June 15 to November 15).
- India’s Role: India will provide its transmission line to facilitate electricity trade between Nepal and Bangladesh.
Phase 1: Electricity Export
- Initial Export Volume: Nepal will export 40 MW of hydroelectricity to Bangladesh via India.
- Transmission Line: The electricity will be transmitted through the Dhalkebar-Muzaffarpur 400 KV transmission line, with the metering point in Muzaffarpur, India.
Financial Aspects
- Rate: The unit price is set at 6.4 cents per unit.
- Annual Revenue: Nepal is expected to earn around $9.2 million annually from the export.
Approval and Delays
Delays: The agreement was delayed due to political turmoil and a change in government in Bangladesh.
Bangladesh’s Approval: Bangladesh’s Cabinet Economic Affairs Committee approved the import on December 6, 2023.




