4 September 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. India’s BioE3 Policy: Pioneering Sustainable Economic Transformation Through Biotechnology
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 16)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context: |
| The article discusses India’s BioE3 policy, which aims to drive sustainable economic growth by integrating biotechnology into industrial and manufacturing processes. |
Analysis of News:
Overview of the BioE3 Policy
- The BioE3 (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment, and Employment) policy, recently unveiled by the Indian government, is designed to stimulate growth in the biotech sector.
- However, its broader goal is to transform industrial and manufacturing processes to be more sustainable and less wasteful by leveraging biotechnology.
- This policy marks the beginning of what officials term the “industrialization of biology,” which could significantly impact the economy.
Potential of Biotechnology
- Biotechnology encompasses a wide range of fields, including genomics, genetic engineering, synthetic biology, and more. Advances in these areas have led to the development of environment-friendly alternatives to traditional products and processes, such as bioplastics and precision fermentation for animal-free milk.
- Additionally, biotechnology offers innovative solutions like carbon capture using microorganisms and the development of synthetic biology for creating novel organisms and biochemicals.
Benefits for India Through BioE3
- The BioE3 policy aims to prepare India for future economic transformations driven by biotechnology.
- While immediate economic returns are not expected, the policy focuses on building competencies, promoting research, and fostering talent to position India advantageously when these technologies mature.
- The potential economic impact of biomanufacturing alone is estimated to be between $2-4 trillion over the next decade.
Strategic Initiatives and Future Outlook
- The BioE3 policy aligns with other government initiatives like the Artificial Intelligence Mission and the Green Hydrogen Mission, which aim to develop and harness emerging technologies crucial for the global economy and addressing challenges like climate change.
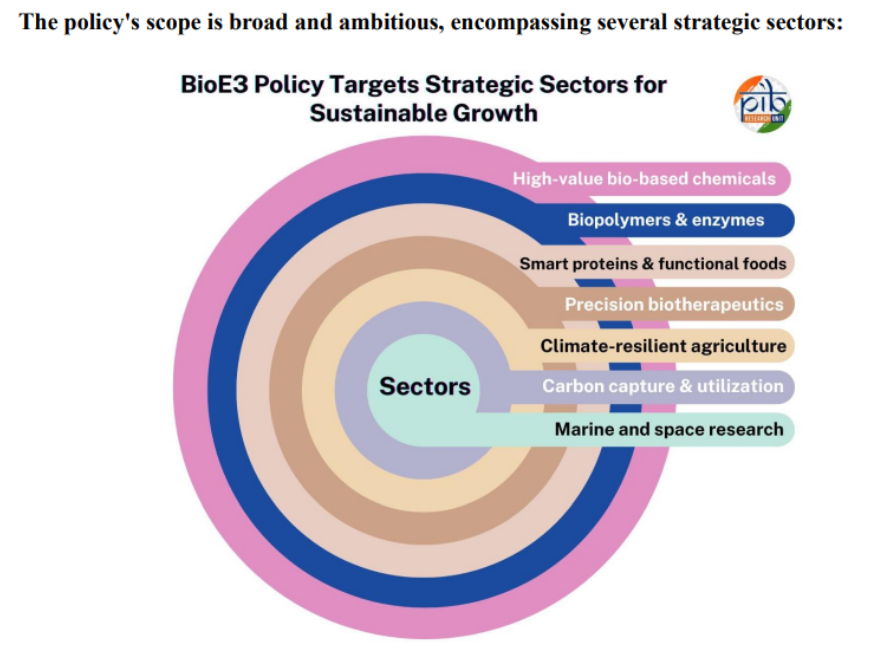
- The policy envisions creating biomanufacturing hubs across India to support the production of bio-based chemicals, smart proteins, and other specialized bio-products, with a focus on six key areas including climate-resilient agriculture and marine research.
Implementation Challenges
- The BioE3 policy, piloted by the Department of Biotechnology, requires collaboration across at least 15 government departments to succeed.
- Its implementation will involve overcoming scalability, financial, and regulatory challenges to fully realize the benefits of biotechnology in transforming India’s economy and industrial processes.
| What are the Challenges for Biotechnology in India? |
|
| PYQ: What are the research in developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poor sections of the society? (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2021) |
| Practice Question: Evaluate the potential impact of India’s BioE3 policy on the country’s industrial and manufacturing sectors. How might biotechnology-driven innovations transform these sectors, and what challenges must be addressed to achieve the policy’s goals? (250 words/15 m) |
2. Modi’s Landmark Visit to Brunei: Strengthening Defence and Strategic Ties Amid Indo-Pacific Tensions
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt & Politics; Page: 05)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations – Bilateral Relations |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
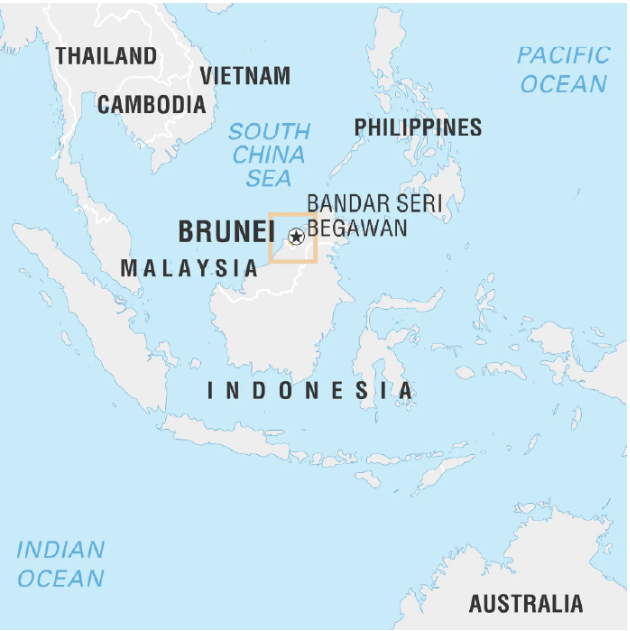
About Brunei Darussalam (Capital: Bandar Seri Begawan)
Political Features
- Location: Country in Southeast Asia consisting of two unconnected parts, situated on northern coast of island of Borneo.
- Border: Apart from northern coastline on South China Sea, it is completely surrounded by Malaysian state of Sarawak.
- It is a member of Commonwealth and ASEAN.
Geographical Features
- Landforms: Narrow coastal plain in north & rugged hills in south.
- Highest point: Pagon Peak
- Major rivers: Belait, Tutong, and Brunei, Pandaruan etc.
- Climate: Equatorial climate influenced by monsoon systems
Key Areas of Discussion
- Defence Collaboration: Talks included the potential establishment of a joint working group on defence cooperation. The existing defence relationship, governed by a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) signed in 2016 and renewed in 2021, covers regular high-level exchanges, naval visits, training, joint exercises, and participation in each other’s exhibitions.
- Commercial and Cultural Ties: Modi’s visit aims to enhance commercial and cultural relations, reflecting the historical ties between the two nations. The Indian diaspora in Brunei, particularly in sectors like healthcare and education, plays a significant role in strengthening these bonds.
Strategic Importance of Brunei
- Role in Act East Policy: Brunei is a key partner in India’s “Act East” policy and Indo-Pacific vision, particularly as India marks a decade of the “Act East” policy. Brunei’s strategic location and its role in the South China Sea disputes make it a vital ally for India in countering China’s influence in the region.
- Space and Defence Cooperation: Brunei has supported India’s space program, hosting a Telemetry, Tracking, and Command station since 2000. This collaboration extends to defence, with regular naval exchanges and joint exercises underscoring the strategic partnership.
Historical Context
- Diplomatic Relations: The visit coincides with the 40th anniversary of diplomatic relations between India and Brunei. Sultan Haji Hassanal Bolkiah, the world’s longest-reigning monarch, has visited India four times, emphasizing the longstanding and warm relationship between the two nations.
Conclusion
- Modi’s visit to Brunei is a strategic move to deepen ties in defence, commerce, and culture amid rising tensions in the Indo-Pacific.
- The visit not only strengthens bilateral relations but also reinforces India’s commitment to its “Act East” policy and its broader Indo-Pacific strategy.
| Practice Question: Discuss the strategic importance of Brunei in India’s “Act East” policy and Indo-Pacific vision. How can deepening defence and cultural ties with Brunei help India counter China’s influence in the region? (250 words/15 m) |
3. The harm principle: how John Mill’s theory defines the extent of liberty
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 11)
| Topic: GS4 – Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude |
| Context |
|
Philosophical Foundation
- John Stuart Mill, a 19th-century philosopher, is known for his influential work, On Liberty.
- Mill’s theory is a cornerstone of libertarianism and utilitarianism.
Harm Principle
- Mill proposed that the only justification for exercising power over an individual, against their will, is to prevent harm to others.
- He distinguished between ‘self-regarding actions’ (affecting only the individual) and ‘other-regarding actions’ (affecting others or society).
Libertarian View on Freedom
- Mill argued for minimal state intervention in individual liberties.
- He believed that individual actions should not be restricted unless they cause harm to others.
Free Speech
- Mill supported complete freedom of thought and expression, arguing it is essential for societal progress.
- He believed that suppressing opinions, even if they are false, deprives society of the opportunity to test and strengthen its beliefs.
Limits of Free Speech
- While advocating for freedom, Mill acknowledged that speech could be limited if it incites harm or causes societal disruption.
- He cited examples where speech could justifiably be restricted, such as inciting violence against a specific group.
Relevance Today
- Mill’s theory continues to influence contemporary discussions on free speech and its limits.
- His harm principle is used to evaluate the balance between individual liberties and societal protection.
| Practice Question: Discuss John Stuart Mill’s harm principle as presented in On Liberty. How does this principle justify limitations on free speech, and what relevance does it hold in contemporary legal and ethical discussions on individual freedoms? (150 Words /10 marks) |
4. Kavach expansion: Railways floats tenders worth over ₹2,200 crore
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 12)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy – Infrastructure – Railways |
| Context |
|
Kavach System – Overview
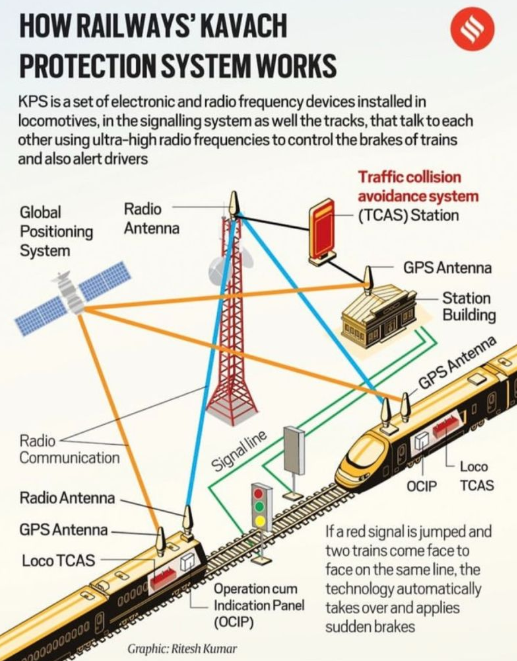
- Indigenous Automatic Train Protection System: Developed by Indian Railways to prevent collisions and enhance safety.
Key Components:
- Radio Frequency Identification (RFID): Installed on tracks and wireless devices to ensure real-time communication.
- RFID Readers: Located in the locomotive’s cabin, assisting in train control.
- Radio Infrastructure: Includes towers and modems placed at railway stations.
- Cabin Instrument Panels: Displays signal aspects and speed limits to drivers for safer operation.
Features:
- Automatic Brakes: Applied when red signals are ignored, preventing collisions.
- Onboard Display: Provides signal aspects and safety information, aiding operation in low visibility.
Deployment:
- Coverage: Set to cover 7,228 route kilometres, with tenders floated for ₹2,200 crore.
- Current Progress: Installation ongoing across 3,000 route kilometres, with plans for 9,000 kilometres by year-end.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of train safety measures in India with a focus on the Kavach system. How does it contribute to accident prevention and efficient railway operations? (250 Words /15 marks) |
5. Amid high tensions with Israel, Iran’s missile programme comes into focus
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 15)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations |
| Context |
|
Iran’s Missile Programme: Key Points:
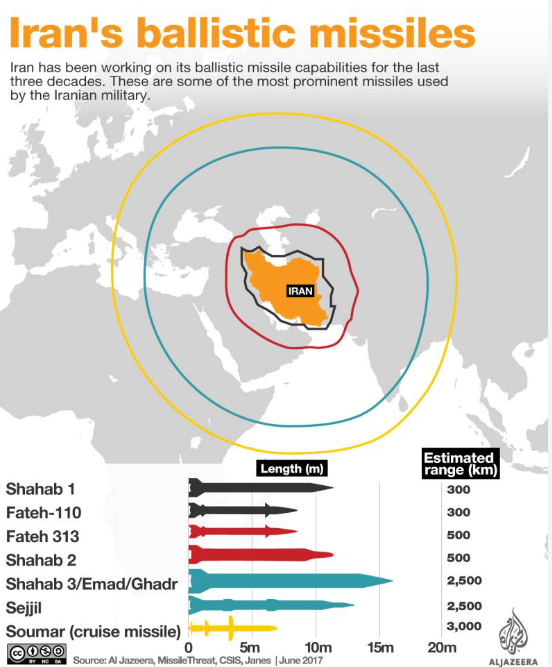
- Origins: Iran’s missile programme began in the 1980s during the Iran-Iraq War. Over time, it has become a core element of the country’s defence strategy.
- Capabilities: Iran possesses a range of missile types, including short-, medium-, and long-range ballistic missiles, cruise missiles, and drones. Key missile classes include Shahab, Sejjil, and Ghadr missiles.
- Ballistic Missiles: Iran’s long-range missiles, like the Shahab-3, can reach up to 2,000 km, putting Israel and U.S. bases in the Gulf within range. The missiles’ accuracy, however, remains questionable.
- Missile Production: The country claims to produce its missiles domestically, though some reports suggest outside technological support from countries like North Korea.
- April 2024 Attack: Iran launched 120 ballistic missiles, 30 cruise missiles, and 170 drones at Israel. Many failed to reach targets, raising concerns about missile reliability.
- Strategic Importance: Iran’s missile programme is seen as a deterrent to regional rivals like Israel and Saudi Arabia. It serves as a key tool in asymmetric warfare, where Iran cannot match conventional military power.
- Proxy Use: Iran’s missiles have been used by regional proxies like Hezbollah in Lebanon and the Houthis in Yemen.
6. New high-performance gas sensor can monitor low level nitrogen oxides pollution
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2051321 )
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
About New Invention:
- Scientists at the Centre for Nano and Soft Matter Sciences (CeNS) developed a new gas sensor using zinc ferrite (ZnFe2O4) nanostructures.
- This sensor can detect nitrogen oxides (NOx) at very low concentrations (parts-per-billion) even at room temperature.
- It addresses the limitations of existing gas sensors, which often need high temperatures to work and lack selectivity.
- The new sensor is highly sensitive, selective, and responds quickly, with excellent durability for over 3 months.
- It was tested on vehicle exhaust samples, successfully detecting trace NOx levels.
- The sensor’s low energy demand reduces operating costs, making it more affordable for monitoring air pollution.
- The findings were supported by computational studies, confirming the improved ability to detect NOx using this novel nanostructure.
| Nitrogen Oxides Pollution |
|
Causes of Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) Pollution:
Impact of NOx Pollution:
|
|
PYQ: Q. Which of the following add/adds nitrogen to the soil? (2013) Excretion of urea by animalsBurning of coal by manDeath of vegetation Select the correct answer using the codes given below: (a) 1 only Ans: Option C |
| Practice Question: Discuss the causes and environmental impacts of nitrogen oxides (NOx) pollution, and suggest measures to mitigate its harmful effects. (150 Words /10 marks) |
Prelims Facts
1. World Bank hikes India’s economic growth forecast to 7% for 2024-25
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- World Bank has revised India’s GDP growth forecast to 7% for FY 24/25, up from 6.6%.
- The report titled “India Development Update: India’s Trade Opportunities in a Changing Global Context” highlighted India’s resilience in a challenging global environment.
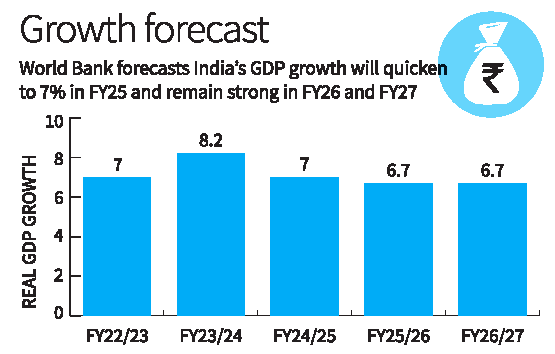
- India’s growth rate aligns with projections by IMF and ADB, both forecasting 7%.
- The Indian economy grew by 8.2% in FY 23/24, driven by public infrastructure investment and rising household real estate investment.
- The manufacturing sector grew by 9.9%, with strong performance in services but underperformance in agriculture.
- Urban unemployment has improved, especially for women, with female unemployment at 8.5% early in FY 24/25.
- However, youth unemployment remains high at 17%.
- The World Bank suggests India can further boost growth by diversifying exports, focusing on textiles, apparel, footwear, electronics, and green technology.
2. Centre gives nod to defence proposals worth ₹1.44 lakh cr.
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- The Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) has approved Acceptance of Necessity (AoN) for 10 capital acquisition proposals totaling ₹1,44,716 crore.
| Acceptance of Necessity (AoN) |
|
- Proposals include seven stealth frigates under Project-17B, future-ready combat vehicles (FRCV) to replace main battle tanks, air defence radars, Dornier-228 aircraft, and new patrol vessels.
- 99% of the cost is allocated to indigenous sources under Buy (Indian) and Buy (Indian-Indigenously Designed Developed and Manufactured) categories.
- The FRCV will feature advanced mobility, protection, and situational awareness.
- Seven stealth frigates will be built by Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE) and Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Ltd. (MDL).
- Air defence radars will track aerial targets and provide firing solutions.
- The Indian Coast Guard will receive Dornier-228 aircraft, next-gen fast patrol vessels, and offshore patrol vessels.
3. Could quakes explain why gold nuggets are found in quartz veins?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|

Analysis of the news:
- Gold nuggets often form in quartz veins found in mountainous areas.
- Quartz is a special crystal that generates an electric charge when squeezed or distorted.
- During earthquakes or similar stress events, quartz crystals are squeezed and create electric fields.
- These electric fields cause gold dissolved in surrounding fluids to be deposited on the quartz surface.
- Researchers tested this by straining quartz slabs in a solution with gold and observed gold deposits forming on strained slabs, but not on unstressed ones.
- This process, known as piezocatalysis, explains why gold accumulates in quartz veins: the piezoelectric effect during seismic activity helps deposit gold, leading to large nuggets over time.
4. Union Agriculture Minister Shri Shivraj Singh Chouhan Launches AgriSURE Fund
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2051466 )
| Context |
|

Analysis of the news:
- AgriSURE Fund is a ₹750 crore blended capital fund launched for start-ups and rural enterprises in the agricultural sector.
- It focuses on high-risk, high-impact, technology-driven ventures aimed at revolutionising agriculture in India.
- The fund is supported by the Government of India, NABARD, and private investors, with each contributing ₹250 crore.
- AgriSURE aims to promote innovative solutions for farmers across the agri-value chain, from input selection to post-harvest processes and marketing.
- The fund seeks to address challenges such as increasing production, reducing production costs, and preventing post-harvest losses.
- It provides financial support to start-ups creating tech-based solutions to help farmers, thereby boosting rural development.
- AgriSURE will enhance crop diversification and ensure farmers receive fair prices for their produce.
- It also integrates crop insurance solutions to safeguard farmers from losses.
- The initiative aims to foster growth, empower farmers, and contribute to the overall prosperity of the agricultural sector.
| PYQ: What are the impediments in marketing and supply chain management in industry in India? Can e-commerce help in overcoming these bottlenecks? (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2015) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the potential impact of the AgriSURE Fund on fostering innovation and addressing challenges in the Indian agricultural sector. (150 Words /10 marks) |
5. “VISHANU YUDDH ABHYAS”: A Mock Drill on Pandemic Preparedness conducted under National One Health Mission
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2051388 )
| Context |
|
Vishanu Yuddh Abhyas:
- Vishanu Yuddh Abhyas is a national mock drill conducted under the National One Health Mission (NOHM) in Ajmer, Rajasthan, from August 27 to August 31, 2024.
- It aimed to assess India’s preparedness and response to zoonotic disease outbreaks.
- The exercise involved the National Joint Outbreak Response Team (NJORT), composed of experts from human health, animal husbandry, and wildlife sectors.
- The mock scenario simulated a zoonotic disease outbreak to test investigation, identification, and containment strategies.
- The drill provided insights into pandemic response and identified areas for improvement.
- It emphasised a coordinated, multisectoral approach to enhance future outbreak preparedness and response, supporting the One Health concept for holistic health management.
6. Removing toxic chromium using sunlight can lower cost of wastewater treatment
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2051320 )
| Context |
|
More About New Invention:
- Researchers at the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST) developed a low-cost method to remove toxic hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) from industrial wastewater.
- The new technique uses sunlight as a catalyst combined with microfluidic technology to convert Cr(VI) to the less harmful trivalent chromium (Cr(III)).
- The process, known as continuous flow photoreduction, uses TiO2 nanoparticles and is monitored with a smartphone-based colorimetric technique.
- This method is cost-effective and utilises renewable energy, with a high removal efficiency of 95% achieved using a serpentine microreactor.
- The process is efficient, reusable, and can be tailored by adjusting microfluidic parameters like flow rate and reactor design.
- Potential for industrial use includes scaling up by setting up microfluidic reactors in parallel or texturing reactor surfaces.
| Chromium Pollution: |
|
| Practice Question: Examine the sources and impacts of heavy metal pollution in water bodies in India. Discuss the measures required to mitigate this issue and suggest policies for effective management and prevention. (250 Words /15 marks) |
7. OpenAI Set to Unveil Most Powerful AI Model Yet with Project Strawberry, Aiming for Advanced Reasoning and Autonomous Research
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 16)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Project Background
- Project Strawberry: Formerly known as Project Q* (Q-star), this secretive project is now codenamed Project Strawberry. It is designed to feature autonomous Internet research and enhance AI reasoning capabilities, pushing towards the creation of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) — AI with human-like cognitive abilities.
Model Capabilities
- Advanced Reasoning: Project Strawberry is expected to vastly improve mathematical and programming capabilities, outperforming any existing chatbot.
- Puzzle Solving: Demonstrations have shown the model’s ability to solve complex puzzles, indicating advanced levels of thinking.
Integration with ChatGPT
- Enhanced Chatbot: The integration of Project Strawberry with ChatGPT will likely make it the most powerful AI chatbot available. This integration aims to address issues like mathematical errors by incorporating more robust mathematical information into the training data.
Training and Data Challenges
- Capital and Data Needs: Project Strawberry aims to raise more capital for OpenAI’s next frontier model, Project Orion. A key focus is generating high-quality training data, which is scarce on the free Internet.
- Synthetic Data: Project Strawberry is also involved in creating synthetic data to overcome biases, errors, and incomplete information in existing datasets. This data can fill gaps, providing a more comprehensive and balanced training set.
Potential Impacts
- Scientific Breakthroughs: With improved reasoning and the ability to conduct autonomous research, the model could lead to scientific discoveries, including new drugs.
- Personalized Education: The model could revolutionize education by creating tailored educational content and interactive lessons, offering personalized learning experiences.
8. Government Establishes 23rd Law Commission to Review Obsolete Laws and Recommend Reforms
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 08)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Composition and Appointment
- Structure: The commission will consist of a full-time chairperson, four full-time members, Secretaries of the Legal Affairs and Legislative departments as ex-officio members, and up to five part-time members.
- Appointments: The government has not yet appointed the members. Typically, the chairperson is a retired judge, and members can include serving judges from the Supreme Court or High Courts or other qualified individuals.
Objectives and Mandate
- Law Review: The commission will review existing laws in light of the Directive Principles of State Policy and recommend reforms or new legislation to achieve the objectives outlined in the Preamble of the Constitution.
- Special Focus: The commission will also examine the impact of globalization on food security and unemployment and suggest measures to protect marginalized communities.
- Judicial System Review: Another key task is to review the judicial administration system to make it more responsive to contemporary needs.
Historical Context
- Previous Commission: The 22nd Law Commission, led by former Karnataka HC Chief Justice Ritu Raj Awasthi, worked on reports concerning the Uniform Civil Code and simultaneous polls but did not submit them before its term ended on August 31, 2024.
9. Union Ministry Directs Translation of ‘Zero FIRs’ to Ensure Legal Accuracy Across States
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 08)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:

Background and Legal Context
- Zero FIR: A ‘zero FIR’ can be filed at any police station, regardless of jurisdiction, and is then forwarded to the relevant police station for re-registration as a regular FIR. Under the new Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS), registering a ‘zero FIR’ is mandatory.
- New Criminal Laws: The BNSS, along with the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (replacing the IPC) and Bharatiya Sakshya Adhiniyam (replacing the Evidence Act), were introduced on July 1, 2024.
Directive Details
- Translation Requirement: The MHA’s directive mandates that ‘zero FIRs’ registered in local languages be translated into English when sent to states where a different language is spoken. This ensures accuracy and consistency in legal proceedings across state borders.
- Implementation: Following the directive, UTs have begun sending original ‘zero FIRs’ along with their English translations.
Implementation Review Meeting
- Challenges Identified: During a review meeting chaired by then Union Home Secretary Ajay Bhalla, Chief Secretaries and DGPs highlighted challenges in implementing the new laws. Concerns were raised about FIRs recorded in local languages potentially affecting the accuracy of investigations when used in other states.
- Forensic and Administrative Adjustments: The meeting also covered various UTs’ efforts to align with the new laws. For instance, the Lakshadweep administration coordinated with neighboring states for forensic support, and Chandigarh designated specific courts for cases under the new laws.