5 June 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. The bacteria that write new genes to cope with infections
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
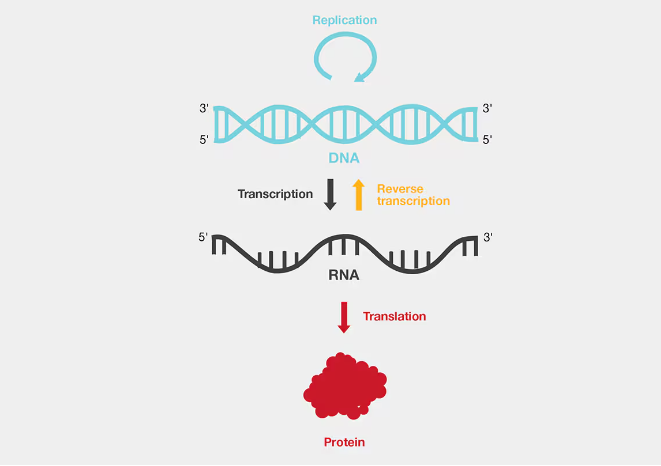
| Amid the COVID-19 pandemic, the enzyme reverse transcriptase gained prominence for its role in molecular diagnostics, enabling rapid SARS-2 virus detection and tracking.Its discovery revolutionised molecular biology, impacting viral research and treatment, particularly for HIV, and revealing significant evolutionary insights in human and bacterial genomes. |
The Rise of Reverse Transcriptase amid the COVID-19 Pandemic
- The COVID-19 pandemic brought unprecedented challenges, highlighting an obscure enzyme called reverse transcriptase.
- Laboratories worldwide used this enzyme for reliable diagnostic tests to detect the SARS-2 virus.
- Reverse transcriptase became a cornerstone of molecular diagnostics, facilitating rapid and accurate testing.
- Along with genome-sequencing, it played a crucial role in tracking the virus’s spread.
- This facilitated better public health surveillance, improved healthcare, and aided in vaccine development.
Discovery of Reverse Transcriptase
- The discovery of reverse transcriptase is noteworthy, independently discovered by researchers in two different laboratories.
- Both teams published their findings in the journal Nature in 1970.
- One of the researchers suggested that in the vesicular stomatitis virus, a protein called RNA polymerase was involved in reverse-translating RNA to DNA.
- The editor of Nature coined the term “reverse transcriptase” in an article discussing the significant advance.
| A Molecular Biology Revolution |
|
The discovery was transformative, challenging the prevailing Central Dogma which stated that hereditary information flowed only from DNA to RNA and then to protein. The new finding showed that information could also flow from RNA to DNA.This revolutionised research methods in molecular biology, allowing researchers to reverse-transcribe messenger RNAs to DNA, clone that DNA into bacterial vectors, and study gene functions. In diagnostics, reverse transcriptase was used to convert RNA to DNA, helping estimate viral material in samples, especially in the study of RNA viruses such as hepatitis B and the human immunodeficiency virus. |
Impact on HIV Management and Treatment
- The discovery had a significant impact on managing and treating human immunodeficiency virus infections and Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome in the 1980s.
- Antiviral agents targeting reverse transcriptase helped convert a deadly disease into one that could be managed, improving long-term outcomes and survival rates for people living with Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome.
- Subsequent studies provided mechanistic insights into how viruses use reverse transcriptase for replication.
Retroelements in the Human Genome
- Reverse transcriptases played a significant role in shaping the human genome.
- The human genome contains sequences, known as retroelements, believed to have originated from retroviruses and transferred horizontally over millions of years.
- These retroelements were initially considered “junk” DNA but recent evidence suggests they play important roles in various physiological processes.
- A study reported in Nature Communications linked the expression of endogenous retroviruses to neuropsychiatric disease risk, suggesting a profound impact on human biology and evolution.
Evolutionary and Functional Significance
- Retroelements and bacterial reverse transcriptases share a common evolutionary history and functional mechanisms.
- Bacterial reverse transcriptases, discovered in 1989, are believed to be the precursors of their eukaryotic counterparts.
- In bacteria, retroelements are categorised into three groups: Group II introns, retrons, and diversity-generating retroelements.
Reverse Transcriptase in Bacterial Defence
- Researchers suggested that when Klebsiella pneumoniae is infected by bacteriophages, they use non-coding RNA with specific motifs that bind to reverse transcriptase to create DNA.
- This DNA copy has multiple copies of a gene that can create a specific protein.
- The protein, named ‘Neo’ for “never-ending open-reading frame,” can block the replication of the bacterial cell and the invading bacteriophage, stopping the infection.
Innovative Applications and Future Potential
- Recent discoveries highlight the potential of reverse transcriptase in innovative biotechnological and medical applications.
- These include combating antimicrobial resistance, where disease-causing microbes resist the effects of substances designed to kill them.
- Exploring reverse transcriptases could reveal novel mechanisms of genetic evolution and viral resistance.
- This research could lead to new therapeutic strategies and biotechnological tools, demonstrating the enzyme’s fundamental role across different domains of life and its remarkable evolutionary continuity and functional versatility.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of reverse transcriptase in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic and its broader impact on molecular biology and viral research. (150 Words /10 marks) |
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 25)
2. SEBI forms panel to review economic structure of clearing corporations
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context |
|
SEBI has formed a committee under Usha Thorat to review the ownership and economic structure of clearing corporations. This move aims to ensure these entities operate independently and effectively manage risk, following concerns from the 2018 Gandhi Committee about concentrated ownership and potential conflicts of interest. |
Analysis of the news:
- SEBI forms an ad-hoc committee led by Usha Thorat to review the ownership and economic structure of clearing corporations and recommend measures for resilience, independence, and neutrality.
- The 2018 Gandhi Committee report recommended widely dispersed ownership for Market Infrastructure Institutions (MIIs), noting the high-risk nature of clearing corporations.
| What are clearing corporations? |
|
Clearing corporations are entities that facilitate the settlement of trades in financial markets. They act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers, ensuring the transfer of securities and funds.Their role includes managing counterparty risk by guaranteeing the completion of transactions.Clearing corporations maintain margin requirements and settlement guarantee funds to cover potential defaults.They enhance market stability and confidence by ensuring smooth and secure trade settlements. |
- Gandhi Committee emphasised clearing corporations should not be listed due to their sensitive and risk-managing roles.
- Currently, most Indian clearing corporations are 100% owned by a single parent exchange, exposing them to shareholder expectations and financial dependencies.
- Dominance of parent exchanges may conflict with the economic interests of clearing corporations, affecting their capital infusion and reserve augmentation.
- SEBI highlights the need to eliminate any perverse incentives that could compromise the independent risk management role of clearing corporations.
- Gandhi Committee suggested no specific profit stipulation for MIIs but recommended monitoring the reasonableness of charges and fees.
- Clearing corporations must prioritise market stability and development over profit, given their critical roles in technology, settlement guarantee funds, and regulatory resources.
- Rising trading volumes, especially in derivatives, necessitate enhanced settlement guarantee funds for clearing corporations.
- SEBI underscores the importance of clearing corporations as public utilities making reasonable profits to sustain operations while ensuring overall market stability.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of ensuring independent ownership and economic structure of clearing corporations in India’s securities market. How do SEBI’s recent initiatives address the concerns raised by the Gandhi Committee? (150 Words /10 marks) |
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 22)
INDIAN EXPRESS NEWS: 05TH JUNE 2024
3. Navigating a New Era: The Third Modi Government and the Return to Coalition Politics
| Topic: GS2 – Polity |
| Context: |
| The third Narendra Modi government will inevitably differ from its predecessors due to the changing political landscape and the composition of the Eighteenth Lok Sabha. Here are some key aspects that highlight these differences and the evolving dynamics of Modi’s leadership. |
Analysis of News:
Return to Coalition Politics:
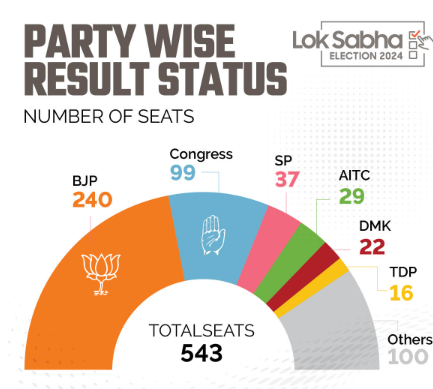
- Coalition Dynamics: After a decade of single-party dominance by the BJP, India is transitioning back to a coalition era. The BJP with 240 seats falls short of the 272 majority mark, necessitating reliance on allies such as the Telugu Desam Party (TDP), Janata Dal (United) (JD(U)), Shiv Sena, and Lok Janshakti Party (Ram Vilas) (LJP). This contrasts sharply with 2014 and 2019, when the BJP held a strong majority on its own.
- Impact on Governance: The necessity of coalition politics means that the BJP will need to consult and accommodate its allies more actively. This will impact policy-making and the stability of the government, as allies now hold significant influence over the BJP’s legislative agenda and decision-making processes.
Increased Federalism and Accountability:
- Federal Dynamics: The concept of a “double-engine sarkar” (same party at the Centre and state) has often been criticized for undermining federalism. The return to coalition politics will likely enhance respect for federal principles, as regional parties with distinct ideologies gain a stronger voice in governance.
- Enhanced Institutional Accountability: A coalition government is expected to improve checks and balances across institutions, from the judiciary to financial regulators. This environment fosters greater innovation and resistance to top-down policies, ensuring more robust democratic practices and accountability.
Composition and Functioning of the Eighteenth Lok Sabha:
- Representation of Opposition: The BJP’s reduced presence in the Lok Sabha allows for greater representation of opposition parties in parliamentary panels and committees. This will lead to more rigorous debate and scrutiny of legislation, reducing the likelihood of fast-tracking bills without adequate discussion.
- Legislative Challenges: The opposition’s increased strength means that the government will face greater challenges in passing legislation. The need for consensus and negotiation will be more pronounced, necessitating a collaborative approach to governance.
Economic Reforms and Coalition Compromises:
- Economic Reform Challenges: Despite a decade of majority rule, the BJP struggled to implement key economic reforms, such as land acquisition and farm laws. A coalition government, with its inherent need for broader consensus, may find it even more challenging to push through controversial reforms.
- Privatization and Disinvestment: While the government successfully privatized Air India, significant progress in other disinvestment initiatives, including the privatization of public sector banks, remains limited. The coalition context may slow down these processes further as different stakeholders negotiate their interests.
Conclusion:
- The third Modi government, characterized by coalition politics, the rise of regional leaders, recalibrated internal dynamics, enhanced federalism, and greater opposition representation, marks a significant shift from the previous two terms.
- This new phase will require a more collaborative and inclusive approach to governance, reflecting the diverse and dynamic nature of India’s political landscape.
| Features of Coalition Government |
|
The features of a Coalition Government are highlighted below:
In India, coalitions have come up before or after elections.The pre-poll coalition is considered advantageous as it provides a common platform for all parties to woo the electorate on the basis of a joint manifesto.A post-election union is intended to enable constituents to share political power and run the government. |
| Practice Question: What are the positive and negative aspects of a coalition government? (150 words/10 m) |
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 28)
PRELIMS FACTS
1. Israeli Airstrikes in Syria Kill Iranian General: Escalation Unlikely Amidst Domestic Crisis
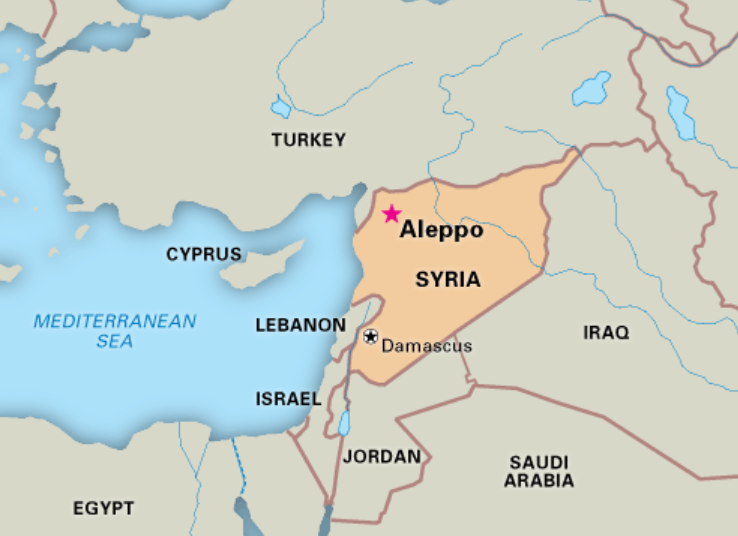
| Context: |
| Israeli airstrikes near Aleppo, Syria, killed General Saeed Abyar of Iran’s Revolutionary Guards Corps, who was serving as an advisor in the region. This marks the first Iranian casualty by Israeli actions since tensions nearly led to war between the two nations in April. |
Analysis of News:
Implications:
- The attack comes amid a period of reduced direct confrontations between Israel and Iran, influenced by intense international pressure to avoid escalating into a broader regional conflict.
- The incident underscores ongoing hostilities but occurs against a backdrop of Iran’s current domestic leadership crisis, suggesting that a significant escalation is unlikely in the near future.
What is the IRGC?
- The Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) is Iran’s elite military force established after the 1979 revolution to safeguard the Islamic system.
- It operates parallel to Iran’s regular military forces and includes its own army, navy, air force, and the Quds Force, which manages overseas operations.
What is the IRGC’s primary role?
- The primary role of the IRGC is to protect the Islamic Republic’s regime and its values, both domestically and internationally.
- It plays a crucial role in Iran’s security policies and has more influence than the regular armed forces.
What does the Quds Force do?
- The Quds Force is responsible for the IRGC’s clandestine operations abroad. It supports and arms various groups such as Hezbollah in Lebanon and Hamas in the Palestinian territories and has played a significant role in supporting President Assad’s regime during the Syrian civil war.
Why is the Quds Force a significant part of the IRGC?
- The Quds Force enables Iran to project its power beyond its borders, predominantly through proxy warfare rather than direct military engagement.
- This branch of the IRGC is critical for Iran’s strategy of influence in geopolitical conflicts in the Middle East.
2. China’s Chang’e-6 Probe Successfully Departs from Moon’s Far Side, Heading Back to Earth
| Context: |
| The Chang’e-6 probe has successfully lifted off from the far side of the moon and is on its way back to Earth, as announced by China’s space agency. This successful departure marks a significant step for China, potentially making it the first country to return samples from the moon’s far side, which is always facing away from Earth. |
Analysis of News:
Details:
- The China National Space Administration (CNSA) noted that Chang’e-6 endured the high temperatures on the moon’s far side, demonstrating its robust design.
- Unlike its predecessor, Chang’e-5, which collected samples from the near side of the moon, Chang’e-6 faced the additional challenge of operating without direct communication with Earth-based ground stations.
- This required overcoming significant technical hurdles, highlighting the mission’s complexity and the advancements in China’s space technology.
About Chang’e-6:
- It is the first human sampling and return mission from the far side of the moon for the first time.
- It was launched by a Chinese Long March-5 rocket from Wenchang Space Launch Center on the southern island of Hainan.
- Chang’e-6 consists of an orbiter, a returner, a lander and an ascender.
- The lander was equipped with multiple sensors, including microwave, laser and optical imaging sensors which can measure distance and speed, and identify obstacles on the lunar surface.
- It has adopted two methods of moon sampling, which include:Using a drill to collect subsurface samplesGrabbing samples on the surface with a robotic arm.
- It has achieved a breakthrough in the design and control technology of the lunar retrograde orbit and aims to realize key technologies of intelligent and rapid sampling.
- It marks the second time a mission has successfully reached the far side of the moon. China first completed that historic feat in 2019 with its Chang’e-4 probe.



