5 September 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Centre suggests measures to enhance security at hospitals
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Health |
| Context |
|
Measures suggested by the central government:
- Employ Ex-Servicemen: Use ex-servicemen and State security forces as security personnel in high-risk hospital areas to enhance safety.
- Action Plan: States and Union Territories must implement 11 safety measures and submit an action taken report by September 10, as directed by the Health Ministry.
- Hospital Prioritization: Identify hospitals with high footfall as high-priority for security improvements.
- Local Police Integration: Integrate with local police to share video footage of incidents promptly for swift responses and investigations.
- Background Checks: Conduct robust background checks for outsourced and contractual personnel in hospitals.
- Bereavement Protocols: Train healthcare workers to handle emotional situations and establish bereavement protocols to manage tensions among grieving families.
- Security Audits: Perform security audits with health and police authorities to assess and improve measures, focusing on high-risk areas like emergency rooms and ICUs.
- CCTV Installation: Ensure proper installation and functioning of CCTV cameras in high-risk areas, monitored from a central control room.
- Internal Security Committee: Establish an internal security committee in hospitals involving residents and students with clear incident response protocols.
| Practice Question: Considering the rising incidents of violence against healthcare professionals in India, assess the effectiveness of current policies and measures aimed at ensuring the safety of doctors and healthcare workers. What additional steps can be taken to improve their protection in healthcare settings? (250 Words /15 marks) |
2. What do we know about ANIIDCO?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 11)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context |
|
Information about ANIIDCO:
- Established on June 28, 1988, under the Companies Act.
- Based in Port Blair, Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Engages in trading petroleum products, liquor, and milk.
- Manages tourism resorts and infrastructure development for tourism and fisheries.
Mandate:
- Develop and commercially exploit natural resources in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Promote balanced and environment-friendly development.
- Focus on tourism, fisheries, and infrastructure projects.
- Support trading activities including petroleum products, liquor, and milk.
Challenges faced:
- Lacks an environmental policy and specialised human resources at the project’s initiation.
- Faced delays in recruiting experts like urban planners and environmental specialists.
- Conflicts of interest emerged with officials involved in both project approval and oversight.
- Struggled with issues related to environmental governance and compliance.
- Encountered criticism regarding its capacity to handle the ₹72,000 crore project effectively.
| Practice Question: Discuss the potential challenges and implications associated with the development of large-scale infrastructure projects in ecologically sensitive regions, using the ongoing infrastructure development in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands as a case study. (250 Words /15 marks) |
3. In a time of turmoil and crisis, the stoic roadmap to a meaningful life
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 12)
| Topic: GS4 – Ethics |
| Context |
|
Stoicism
- Origins: Founded by Zeno of Citium around 300 BC, Stoicism is a Hellenistic philosophy emphasising rationality and self-control.
- Core Principles: Focuses on living in harmony with nature and accepting things beyond one’s control, while managing emotions through reason.
- Major Figures: Roman philosophers Marcus Aurelius, Epictetus, and Seneca are key contributors.
- Key Texts: Notable works include Epictetus’ The Enchiridion, Seneca’s Letters to Lucilius, and Marcus Aurelius’ Meditations.
- Philosophy:
- It emphasises rational control over one’s emotions and acceptance of fate.
- It teaches that virtue, guided by reason, is the highest good and that individuals should focus on what they can control, accepting external events with equanimity.
- Stoicism advocates for resilience, self-discipline, and inner peace amidst life’s challenges.
Relevance in Today’s Life
- Coping Mechanism: Offers strategies to manage stress and anxiety by focusing on what is within personal control and accepting what cannot be changed.
- Emotional Resilience: Encourages maintaining equanimity in the face of adversity and setbacks, fostering mental strength.
- Practical Guidance: Provides practical advice on dealing with modern challenges, such as uncertainty and ethical dilemmas, through reflection and rational thought.
- Self-Improvement: Promotes personal growth and ethical living by aligning actions with core values and principles, enhancing overall well-being.
| Practice Question: Discuss the principles of Stoicism as propounded by ancient philosophers. How can Stoic philosophy be applied to contemporary challenges such as personal resilience and ethical decision-making (150 Words /10 marks) |
4. Ethanol push turns India into corn importer, shaking up global market
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 13)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context |
|
Ethanol Shift and Import Dynamics
- India’s increased focus on corn-based ethanol has turned it from Asia’s top corn exporter into a net importer for the first time in decades.
- The government raised the procurement price of corn-based ethanol in January to encourage a shift from sugarcane-based ethanol, aimed at reducing carbon emissions and ensuring a steady sugar supply.
- India is set to become a permanent net importer of corn, supporting global prices that are currently near four-year lows.
Impact on Local Industries
- Local poultry producers are struggling due to rising feed costs, with corn prices exceeding global benchmarks.
- They are advocating for the removal of import duties and lifting the ban on genetically modified (GM) corn, which limits their purchasing options.
- India’s corn exports are expected to drop to 450,000 tons in 2024, while imports are projected to reach a record 1 million tons, primarily from Myanmar and Ukraine.
Supply and Demand Imbalance
- The ethanol distilleries’ demand for corn has surged, following a government decision to curb sugarcane use due to a drought, creating a 5 million-ton shortfall.
- Ethanol distilleries are estimated to need 6 to 7 million tons of corn annually, a demand that will likely be met through imports.
Economic Impact and Adjustments
- The increase in corn prices has pushed poultry production costs higher, leading to financial strain for growers.
- Efforts to mitigate costs include substituting corn with cheaper alternatives in feed.
- Farmers are expanding corn cultivation due to higher prices, with a 7% increase in area under corn compared to last year.
Trade and Price Adjustments
- Indian demand has driven up corn prices in Myanmar, benefiting local farmers and exporters.
- Starch producers are importing duty-free corn from Ukraine through India’s Advance License Scheme.
- Overall, India’s corn imports surged significantly in early 2024, while exports plummeted, reflecting the shift in trade dynamics.
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of India’s policy shift towards increased ethanol blending. How does this policy impact local industries, such as poultry, and what are the potential long-term effects on global corn markets? (250 Words /15 marks) |
5. MoRTH Introduces Real-Time GIS-Based Toll Monitoring and Plans for Satellite-Based Tolling System
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 12)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology; GS2 – Governance |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
How the Monitoring System Works
- The software will provide real-time data on the name, location, queue lengths, wait times, and vehicle speeds at toll plazas.
- It will also generate traffic condition analyses on hourly, daily, weekly, and monthly bases, helping commuters avoid congested lanes.
Satellite-Based Tolling System
- MoRTH is also developing a Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)-based toll system, which will eventually replace the FASTag system.
- This system will enable distance-based tolling, allowing users to pay only for the distance traveled.
- GNSS-based tolling will initially operate alongside FASTag and will automate toll payments without the need for boom barriers.
Benefits to Users
- The satellite-based toll system is expected to make toll passage faster, reducing delays caused by current FASTag operations, which can take up to a minute per vehicle.
- The new system aims to minimize queues and improve traffic flow at toll plazas.
- Since its launch in 2015, FASTag has been responsible for over 98% of toll payments, as of March 2024.
| PYQ: Why is Indian Regional Navigational Satellite System (IRNSS) needed? How does it help in navigation? (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2018) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the potential impact of the GIS-based real-time toll monitoring system and the upcoming GNSS-based toll collection on traffic management and user convenience in India. (250 words/15 m) |
6. MNRE Exempts Export-Oriented Green Hydrogen Projects from Domestic Solar Module Mandate to Lower Costs
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Economy; Page: 13)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
What is the National Green Hydrogen Mission (NGHM)?

- India launched the National Green Hydrogen Mission (NGHM) in January 2023.
- The Ministry of New & Renewable Energy (MNRE) is implementing the NGHM with a target to achieve a production capacity of 5 million tonnes per annum of Green Hydrogen in the country by the year 2030.
- The Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition (SIGHT) programme, under NGHM, provides incentives for the manufacturing of electrolysers and the production of green ammonia.
- Under NGHM a dedicated portal was launched to provide information on the mission and steps for developing the green hydrogen ecosystem in India.
- India has also released scheme guidelines for the use of Green Hydrogen in steel, transport, and shipping sectors.
- The Department of Science and Technology has initiated Hydrogen Valley Innovation Clusters to foster innovation and promote the green hydrogen ecosystem in India.
Importance of Cost Reduction
- Lowering the cost of green hydrogen is essential to make it competitive with grey hydrogen, which is cheaper due to carbon-intensive production methods using natural gas.
- This cost reduction is critical to expanding green hydrogen’s demand globally and for India’s export market.
Solar Modules and Cost Impact
- Imported Solar Modules: 9.1 cents per watt (CIF basis, June 2024).
- Domestic Solar Modules: 18 cents per watt, making them twice as expensive as imports. The cost disparity between imported and domestic solar modules significantly influences the production cost of green hydrogen.
Impact on Domestic Industry
- MNRE Secretary Bhupinder S Bhalla emphasized that India’s fast-growing demand for solar modules will not be adversely affected by the exemption for green hydrogen projects.
Green Hydrogen Production Targets
- India aims to produce 5 million metric tons (MMT) of green hydrogen annually by 2030. Currently, 7.5 MMT of green hydrogen projects have been announced, and domestic demand is expected to replace grey hydrogen consumption.
Additional Incentives and Measures
- SIGHT Program: Rs 17,490 crore allocated for green hydrogen production and electrolyser manufacturing.
- R&D Investments: Rs 400 crore allocated, with 400 project proposals under review.
- Environmental and Transmission Incentives: Green hydrogen projects are exempt from prior environmental clearance and transmission charges for 25 years.
- Standards Development: 73 out of 100 recommendations for green hydrogen production and application have been notified by regulatory bodies, including BIS.
| What are the Reasons to Develop Green Hydrogen? |
|
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
Energy Security and Independence:
Creating New Industries and Jobs:
Decarbonizing in Sectors which are Difficult-to-Decarbonize:
Technological Advancements:
|
| PYQ: Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles produce one of the following as “exhaust” (2010) (a) NH3 (b) CH4 (c) H2O (d) H2O2 Ans: (c) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the government’s policy to exempt export-oriented green hydrogen projects from domestic solar module requirements. How will this decision impact the production costs of green hydrogen and contribute to India’s renewable energy goals? (250 words/15 m) |
7. Digital Agriculture Mission: Tech for Transforming Farmers’ Lives
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2051719 )
| Topic: GS3 – Agriculture, GS2 – Governance – Government Policies |
| Context |
|
Digital Agriculture Mission

Approval and Financial Outlay
- Launched by the Union Cabinet on September 2, 2024, with a budget of Rs. 2,817 Crore.
- Central government’s share: Rs. 1,940 Crore.
Objectives
- Transform agriculture through digital technologies.
- Create Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) and enhance farmer-centric services.
Key Component
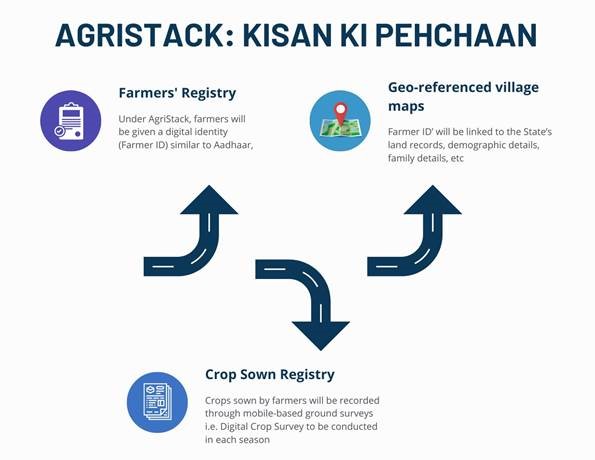
- AgriStack:
- Farmers’ Registry: Digital identity for farmers.
- Geo-referenced Village Maps: Detailed mapping of farming areas.
- Crop Sown Registry: Record of crops sown by farmers.
- Farmer ID: A digital ID akin to Aadhaar, linking various farmer-related data.
- Krishi Decision Support System (DSS):
- Integrates remote sensing data on crops, soil, weather, and water resources.
- Soil Profile Mapping:
- Mapping soil profiles at a 1:10,000 scale for 142 million hectares; 29 million hectares mapped so far.
- Digital General Crop Estimation Survey (DGCES):
- Provides precise yield estimates through crop-cutting experiments.
Implementation
- AgriStack Pilot Projects: Conducted in six states: Uttar Pradesh, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Haryana, Punjab, and Tamil Nadu.
- Targets:
- Create digital IDs for 11 crore farmers over three years.
- Nationwide Digital Crop Survey covering all districts by 2025-26.
Benefits
- Reduces paperwork and physical visits for accessing services.
- Enhances efficiency and transparency in government schemes and loan systems.
- Improves disaster response and insurance claims through accurate crop mapping.
- Provides tailored advisory services for crop management and irrigation.
Impact
- Aims to revolutionise service delivery, increase productivity, and enhance sustainability in Indian agriculture.
| PYQ: How does e-Technology help farmers in production and marketing of agricultural produce? Explain it. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2023) |
| Practice Question: Evaluate the potential impact of the ‘Digital Agriculture Mission’ on India’s agricultural sector. Analyse how digitalization could address challenges in agriculture and improve service delivery for farmers. (250 Words /15 marks) |
8. Government launches Vishvasya-Blockchain Technology Stack; To offer Blockchain-as-a-Service with a geographically distributed infrastructure
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2051934 )
| Topic: GS2 – Governance, GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
Vishvasya – Blockchain Technology Stack:
- Vishvasya is a Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) platform developed by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- It provides a secure, permissioned blockchain infrastructure that supports various citizen-centric applications.
- Hosted across geographically distributed data centres, Vishvasya is designed to enhance transparency, security, and trust in digital services by enabling decentralised applications on a reliable blockchain framework.
- It offers features like smart contracts, API gateways, and privacy protections to ensure the safe execution of blockchain-based solutions.
Potential Applications of Vishvasya – Blockchain Technology Stack:
- Citizen Services: Secure digital identities, verification processes, and tamper-proof records for public services such as land registries, healthcare, and education.
- Financial Services: Streamlined, secure transactions for banking, insurance, and financial operations, reducing fraud and enhancing transparency.
- Supply Chain Management: Traceability and verification for goods, ensuring authenticity and accountability in agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and logistics sectors.
- Governance: Transparent and accountable e-governance services, including voting systems and public policy execution.
- Legal Applications: Smart contracts for automating legal agreements, ensuring enforcement and reducing disputes.
- Academic and Research Collaboration: Platforms for educational institutions and startups to prototype blockchain applications and conduct research securely.
| Blockchain Technology |
|
|
PYQ: Q. With reference to “Blockchain Technology”, consider the following statements: (2020) It is a public ledger that everyone can inspect, but which no single user controls. The structure and design of the blockchain is such that all the data in it are about cryptocurrency only. Applications that depend on basic features of blockchain can be developed without anybody’s permission. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only Ans: Option D |
| Practice Question: Discuss the potential of blockchain technology in transforming governance, financial systems, and data management in India. Highlight the challenges associated with its implementation. (150 Words /10 marks) |
Prelims Facts
1. Latest ILO study links AI to dip in labour income
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- The ILO’s World Employment and Social Outlook: September 2024 Update highlights rising inequality worldwide due to stagnant labour income.
- A key factor behind this decline is artificial intelligence (AI), which, while improving productivity, has reduced workers’ income share.
- The global labour income share fell by 0.6 percentage points from 2019 to 2022 and has since remained flat, compounding a longer-term decline.
- The COVID-19 pandemic significantly contributed to this, with nearly 40% of the reduction occurring from 2020 to 2022.
- The ILO emphasises the need for stronger policy responses, including promoting collective bargaining, labour rights, and equitable economic distribution.
- The report also noted slow progress toward achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) as their 2030 deadline approaches.
2. Climate change threatens South Korea’s beloved kimchi
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
What is Kimchi?
- Kimchi is a traditional Korean dish made from fermented vegetables, most commonly napa cabbage and radishes.
- It is seasoned with a mixture of garlic, ginger, red chilli pepper, and other spices.
- The fermentation process imparts a tangy flavour and enhances its nutritional value.
- Kimchi is a staple in Korean cuisine, often served as a side dish or incorporated into various recipes.
- It is valued for its probiotic benefits, contributing to gut health and digestion.
3. Widespread human rights violations in Venezuela: HRW
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 15)
| Context |
|
Human Rights Watch (HRW):
- Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organisation founded in 1978.
- Mission: Dedicated to investigating and reporting on human rights abuses and advocating for justice and accountability globally.
- Activities: Conducts thorough research, publishes detailed reports, and campaigns to expose human rights violations and hold perpetrators accountable.
- Focus Areas: Includes issues such as conflict, discrimination, freedom of expression, and the treatment of refugees and displaced persons.
- Methodology: Utilises first hand interviews, documentation, and analysis to provide evidence-based reports.
- Advocacy: Engages with governments, international organisations, and the public to promote human rights policies and reforms.
- Global Presence: Operates in over 90 countries and has offices in various key locations around the world.
4. No Link Between Mobile Phone Use and Cancer, Finds Two-Decade WHO-Commissioned Study
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 09)
| Context: |
| A comprehensive WHO-commissioned study found no link between mobile phone use and brain or head cancers, even with prolonged or frequent usage. |
Analysis of News:
No Link Between Mobile Phone Use and Cancer
- A comprehensive review led by the Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency (ARPANSA) has found no link between mobile phone use and brain or head cancers.
- This study, commissioned by the WHO, reviewed data spanning nearly two decades from 22 countries.
Scope and Methodology of the Study
- The review analyzed 5,060 studies, selecting 63 key studies conducted between 1994 and 2022.
- These studies focused on examining the causal relationships between radio-frequency and electromagnetic radiation exposure and cancer development, specifically brain, spinal cord, and salivary gland cancers.
Stable Cancer Rates Despite Increased Phone Use
- Despite the significant rise in mobile phone usage, the research found no corresponding increase in cancer rates.
- Lead researcher, Professor Ken Karipidis, highlighted that brain tumor rates have remained stable despite the widespread use of mobile phones.
Expert Opinions on Mobile Phone Radiation
- Medical experts like Dr. Abhishek Shankar of AIIMS pointed out that mobile phone radiation is non-ionizing and does not have the cancer-causing potential of ionizing radiation, such as that from X-ray machines.
- Similarly, Dr. Pritam Kataria from Sir HN Reliance Foundation Hospital stated that mobile phones emit low-intensity radio waves that are not harmful compared to natural radioactive materials like thorium.
No Risk from Prolonged Use
- The study also ruled out any cancer risk from prolonged mobile phone use, even with frequent calls or extended call durations.
- Experts noted that other factors, such as smoking cessation and HPV vaccination, have a more significant impact on cancer prevention.
5. Rising Glacier Tourism Amid Climate Change Increases Risks and Safety Concerns
(Source: Indian Express; Section: The World; Page: 14)
| Context: |
| The article discusses the increasing popularity and risks of glacier tourism as climate change accelerates glacier melting, leading to safety concerns and adaptation strategies. |
Analysis of News:
Rising Popularity of Glacier Tourism
- The tragedy in Iceland where an American man died after ice collapsed while he was on a group tour to a glacier highlights the growing trend of “last-chance tourism”, where tourists rush to see receding glaciers before they disappear due to climate change.
- Iceland, in particular, has seen a boom in tourism, with half a million people visiting glaciers annually.
Hazards of Glacier Tourism
- As glaciers melt and recede, they become increasingly unstable, raising the risk of accidents.
- Ice caves, formed by meltwater, are particularly dangerous as they can collapse, especially during warmer months.
- Additionally, the moraine, or rock and soil left behind by glaciers, becomes unstable, increasing the likelihood of rockfalls or landslides.
Impact of Climate Change
- While the specific accident can’t be directly attributed to climate change, the incident underscores how rising temperatures are making glaciers more unpredictable.
- The combination of more tourists and less stable glaciers is leading to greater risks.
Adaptation Strategies
- Tour operators are developing adaptation strategies to mitigate these risks. For instance, insulating blankets are sometimes used to slow melting near ice caves.
- However, the expansion of glacier tours into summer has amplified safety concerns. Experts suggest the need for early warning systems and better contingency plans to address emerging hazards.
6. Centre and Tripura Government Sign Peace Pact with Insurgent Groups, Marking End to 35-Year Conflict
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt & Politics; Page: 08)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Significance of the Agreement
- Union Home Minister Amit Shah hailed the pact as a milestone for peace and progress in Tripura, marking the end of a 35-year-long insurgency.
- He emphasized the insurgents’ commitment to contribute to Tripura’s development and, by extension, India’s growth.
Broader Impact on the Northeast
- This is the 12th peace agreement for the Northeast and the third for Tripura, with around 10,000 insurgents having surrendered arms under various agreements.
- The pact reflects the Modi government’s emphasis on resolving conflicts through dialogue and development while preserving the culture, language, and identity of the region’s tribal groups.
Government’s Development Focus
- Shah credited Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s leadership for improving connectivity in the Northeast, bridging both physical and emotional gaps between the region and the rest of India.
- The agreement is part of the BJP-led government’s broader vision for a peaceful and prosperous Northeast.


