6 September 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. PM Modi’s Southeast Asia Visit Strengthens Semiconductor Ties with Singapore, Expands Act East Engagement
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 10)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations; GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context: |
| Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to Brunei and Singapore focused on strengthening partnerships in trade, defense, and semiconductors, advancing India’s Act East Policy and Indo-Pacific vision. |
Analysis of News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s Visit to Southeast Asia
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi visited Brunei and Singapore as part of a two-nation trip.
- His visit to Brunei was the first by an Indian PM, highlighting Brunei’s role in India’s Act East Policy and Indo-Pacific vision, with discussions focused on trade, defense, space, and cultural ties.
- In Singapore, the focus was on signing agreements related to semiconductors, digital technologies, and skill development.
India’s Push for Semiconductors
- The partnership with Singapore on semiconductors is crucial for India’s geo-strategic and economic goals.
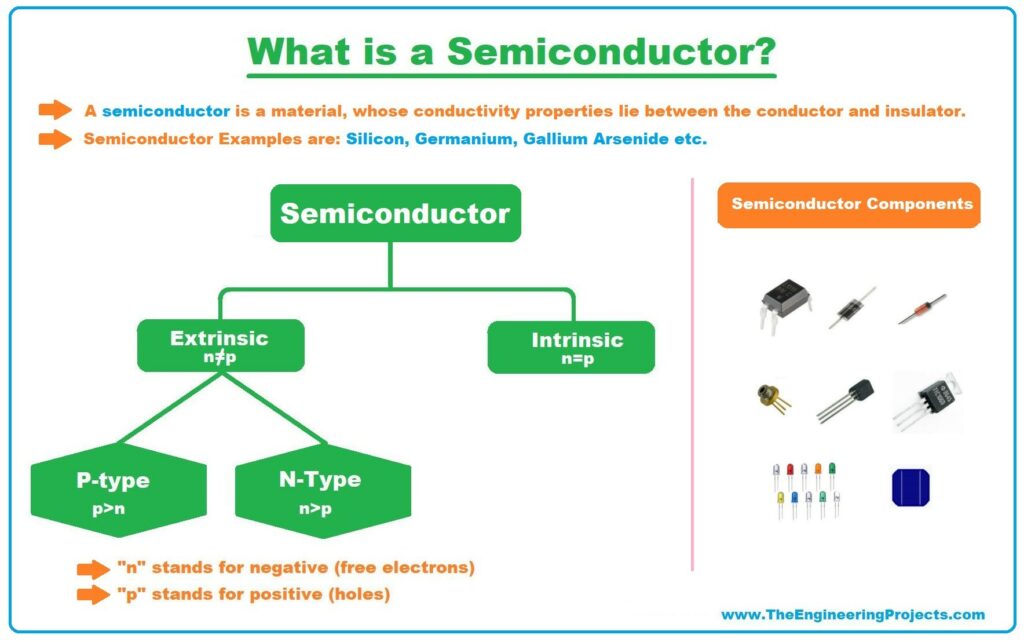
- The global chip shortage, exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic and tensions with China, has spurred India to develop its own semiconductor ecosystem.
- India’s Semiconductor Mission, launched in 2021, includes significant investment incentives, and collaborations with Taiwan and global semiconductor players to establish manufacturing units.
Singapore’s Semiconductor Industry
- Singapore has a well-established semiconductor industry, contributing around 10% of global output.
- The country’s success is rooted in early investments and government support in the 1970s. With a complete value chain, including design, fabrication, and testing,
- Singapore’s semiconductor industry plays a key role in its economy. Leading global semiconductor firms have set up operations there, enhancing its strategic importance in the global supply chain.
Opportunities for India-Singapore Collaboration
- While Singapore focuses on mature-node chips used in various industries, it faces challenges with increasing production costs and limited land and labor.
- This presents opportunities for India to collaborate with Singapore in talent development, knowledge sharing on semiconductor park management, and attracting semiconductor companies looking for expansion, leveraging India’s abundant land and competitive labor costs.

| What is the Overall Scenario of the Semiconductor Market? |
|
Global Scenario:
Indian Scenario:
|
| Practice Question: Examine the significance of Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s recent visit to Brunei and Singapore in the context of India’s Act East Policy and Indo-Pacific strategy, with a focus on strengthening trade, defense, and semiconductor partnerships. How can these engagements contribute to India’s economic and strategic goals? (250 words/15 m) |
2. Kerala tops citizen-centric reforms categories in Centre’s latest rankings
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 5)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context |
|
Announcement
- Kerala emerged as a top performer in two business-centric and seven citizen-centric reform categories in rankings by the Union Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Kerala’s Industries Minister, P. Rajeeve, received the Business Reforms Action Plan 2022 (BRAP 22) award from Union Minister of Commerce, Piyush Goyal.
Business-Centric Reforms
- Kerala excelled in two key business reforms:
- Facilitating utility permits for businesses.
- Improving the ease of paying taxes.
Citizen-Centric Reforms
- Kerala was recognized for top achievements in seven areas, including:
- Online single window system.
- Simplifying certificate issuance by Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) and the Department of Revenue.
- Utility permit facilitation.
- Public distribution system (Department of Food and Civil Supplies).
- Transport sector improvements.
- Employment exchange management.
Positive Feedback
- Kerala received over 95% positive feedback from businesses, recognizing improvements in these nine reform areas.
Technological Advancements
- The State upgraded service delivery using digital tools and cutting-edge technology, contributing to its success.
| PYQ: Many State Governments further bifurcate geographical administrative areas like Districts and Talukas for better governance. In light of the above, can it also be justified that smaller states would bring in effective governance at State level? Discuss. (200 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2013) |
| Practice Question: Examine the significance of citizen-centric reforms in enhancing governance and public service delivery. Discuss the role of digital tools in ensuring transparency, efficiency, and accountability in these reforms. (250 Words /15 marks) |
3. Close ties between agencies globally needed to tackle new-age crimes, says official
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations |
| Context |
|
Importance of Global Cooperation in Combating New-Age Crimes
- Transnational Nature of Crimes: New-age crimes, such as cyber-enabled frauds, terrorism, human trafficking, and drug smuggling, transcend borders, requiring international cooperation for effective prevention and investigation.
- Digital and Foreign Evidence: Investigations increasingly depend on digital evidence and information located abroad, making collaboration between nations crucial.
- Real-Time Coordination: Timely information sharing and real-time coordination between global law enforcement agencies are essential to counter rapid criminal activities.
Challenges in Global Cooperation
- Jurisdictional Conflicts: Differing legal frameworks and jurisdictional boundaries complicate cross-border investigations.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Striking a balance between privacy laws and the need for data exchange in criminal investigations remains a challenge.
- Limited Resources: Developing countries may face challenges in accessing advanced technology and expertise needed to combat sophisticated cybercrimes.
- Language and Cultural Barriers: Differences in language, legal practices, and cultural norms can hinder seamless international cooperation.
India’s Efforts in Combating New-Age Crimes
- Interpol and Europol Cooperation: Signed a working arrangement with Europol in 2024, enhancing cross-border law enforcement collaboration.
- CBI Global Operation Centre: Established in 2022 to facilitate international investigations and cooperation.
- Interpol Global Academy Network: Joined in 2023, allowing Indian law enforcement access to global best practices and training.
- Cybercrime Reporting Portal: Launched to streamline reporting and investigation of cyber-enabled crimes across India.
Way Forward
- Strengthening Legal Frameworks: Harmonising international laws and treaties can facilitate smoother cooperation.
- Capacity Building: Training law enforcement personnel and investing in digital infrastructure can help countries keep pace with evolving threats.
- Enhanced Information Sharing: Platforms like Interpol, Europol, and UNODC can be further strengthened for real-time data exchange and coordination.
- Public-Private Collaboration: Engaging tech companies to assist in cybersecurity and tracking digital crimes can boost crime prevention efforts.
| Practice Question: In the context of rising transnational crimes, critically analyse the need for enhanced global cooperation in combating new-age challenges such as cybercrime, terrorism, and human trafficking. Discuss the role of international organisations in facilitating this cooperation. (250 Words /15 marks) |
4. What is vertical fiscal imbalance?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS2 – Indian Polity – Federal Structure |
| Context |
|

Introduction to Vertical Fiscal Imbalance (VFI)
- The 15th Finance Commission highlighted that States in India face a significant Vertical Fiscal Imbalance (VFI).
- States incur 61% of the revenue expenditure but collect only 38% of the revenue receipts.
- This imbalance means that States rely heavily on transfers from the Union government for their expenditures.
Why VFI Needs Attention
- Constitutional Division of Duties: The Union and State governments have constitutionally defined financial responsibilities. The Union government collects major taxes like Personal Income Tax and Corporation Tax, while States handle expenditures on publicly provided goods and services.
- Efficiency Considerations: To maximise efficiency, it’s ideal for the government closest to the service users to manage expenditures. However, States struggle due to the revenue gap.
Finance Commission’s Role
- The Finance Commission addresses VFI by deciding on two key areas:
- How to distribute the Union government’s tax revenue to States.
- How to allocate these resources among individual States.
- VFI is related to the first area, focusing on how much tax revenue from the Union is devolved to States.
Current Financial Transfers
- Grants and Transfers: Besides tax devolution, Finance Commissions recommend grants under Article 275 of the Constitution for specific needs. Other transfers occur under Article 282 through centrally sponsored and central sector schemes, but these are conditional.
- Untied Transfers: Tax devolution is the only transfer that is unconditional and untied.
Estimating VFI in India
- There is a need to outline a method to estimate VFI at the aggregate level for all States, using a ratio of total own revenue receipts plus tax devolution to own revenue expenditure.
- If this ratio is less than 1, it indicates a VFI, with the deficit being used as a proxy for the imbalance.
- To eliminate VFI, the share of tax devolution needs to rise to about 48.94%, but the 14th and 15th Finance Commissions recommended only 42% and 41% respectively.
Call for Increased Tax Devolution
- Many States advocate for the 16th Finance Commission to fix the share of tax devolution at 50% of the net proceeds.
- Benefits: Higher devolution would provide States with more untied resources, align expenditures with local needs, and enhance the efficiency of spending, contributing to a more balanced fiscal federalism.
Conclusion
- Addressing VFI through increased tax devolution would support a more equitable distribution of fiscal resources and improve the efficiency of State expenditures, fostering a healthier system of cooperative fiscal federalism.
| PYQ: Though the federal principle is dominant in our Constitution and that principle is one of its basic features, it is equally true that federalism under the Indian Constitution leans in favour of a strong Centre, a feature that militates against the concept of strong federalism. Discuss. (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2014) |
| Practice Question: How does Vertical Fiscal Imbalance impact the financial autonomy of States, and what measures could be taken to address this imbalance? Evaluate the proposal for increasing tax devolution to States. (250 Words /15 marks) |
5. Can Kerala access funds from the Loss and Damage Fund?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS3 – Disaster and disaster management |
| Context |
|
India’s Role and Challenges

- Damage from Disasters: India has experienced over $56 billion in damages from weather-related disasters between 2019 and 2023.
- Focus on Mitigation: India’s National Climate Action Policy and budgets have prioritised mitigation over adaptation, resulting in less engagement in Loss and Damage dialogues.
- Need for Framework: There is an urgent need for a clear legal and policy framework in India to manage climate finance, especially for adaptation and loss and damage, and to support locally led adaptation efforts.
- Expectations: The introduction of a climate finance taxonomy in the Union Budget 2024 raises hopes for increased international climate finance but lacks clear guidelines for accessing loss and damage funds.
| What is the Loss and Damage Fund (LDF)? |
|
Need for State-Level Support:
- States like Kerala, which face acute climate impacts, bear substantial disaster recovery costs.
- The Rebuild Kerala Development Programme is an example of state-led recovery funded through international loans, highlighting the need for dedicated climate finance.
Challenges in Accessing the Fund:
- Bureaucratic Delays: Climate funds, including the Loss and Damage Fund (LDF), are often slow to disburse, particularly after disasters, affecting immediate relief efforts.
- Lack of Standardised Assessments: Absence of a comprehensive method for evaluating disaster-related damages, especially from slow-onset events, can hinder effective fund allocation.
- Centralised Systems: Current mechanisms for climate finance are largely centralised, potentially limiting the effectiveness of fund distribution at the local level.
Way Forward:
- Develop Local Frameworks: India needs clear legal and policy frameworks to streamline climate finance, focusing on locally led adaptation and clearer guidelines for accessing loss and damage funds.
- Advocate for Decentralization: In international forums, India should push for more decentralised disbursement methods to ensure funds reach affected communities more efficiently.
- Improve Assessment Processes: Establish standardised processes for assessing and quantifying disaster-related damages to better qualify for and utilise LDF resources.
| PYQ: Describe the major outcomes of the 26th session of the Conference of the ParSes (COP) to the United NaSons Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). What are the commitments made by India in this conference? (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2021) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the role of the Loss and Damage Fund (LDF) established under the UNFCCC in addressing climate-induced losses. Evaluate the challenges faced by India, particularly in relation to accessing and managing climate finance for adaptation and loss and damage. (250 Words /15 marks) |
6. Experts discuss on AI-driven solutions that can improve healthcare
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2052256 )
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Health, GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
AI-driven solutions that can improve healthcare:
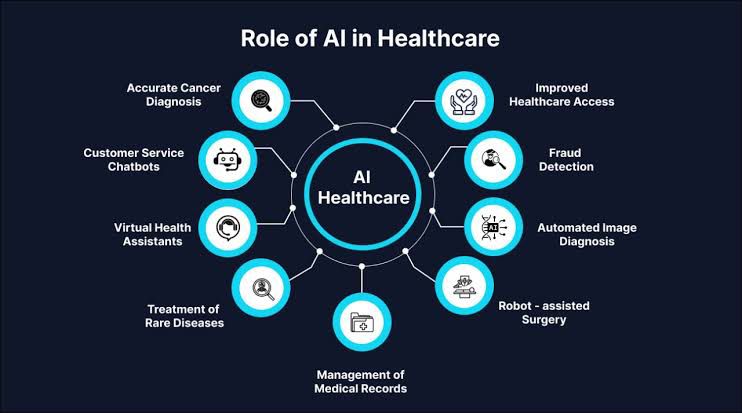
- AI-powered diagnostics: AI can analyse medical images (X-rays, MRIs, CT scans) to assist in early detection of diseases like cancer, reducing human error and improving accuracy.
- Predictive analytics: AI-driven models analyse patient data to predict potential health issues, enabling preventive care and reducing hospital readmissions.
- Personalised medicine: AI can process vast amounts of genetic data to tailor treatments specific to an individual’s genetic makeup, improving treatment efficacy and minimising side effects.
- Robotic surgeries: AI-powered robots assist in minimally invasive surgeries with higher precision, faster recovery times, and reduced risks of complications.
- Optimised clinical workflows: AI can automate administrative tasks such as scheduling, medical record management, and billing, allowing healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care.
- Drug discovery: AI accelerates the identification of potential drug compounds by analysing data sets from clinical trials, expediting the drug development process.
- Remote monitoring: AI-enabled wearable devices track vital signs in real-time, alerting doctors to changes in patients’ health status for timely interventions.
| PYQ: Introduce the concept of Artificial Intelligence (AI). How does AI help clinical diagnosis? Do you perceive any threat to privacy of the individual in the use of Al in healthcare? (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2023) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the role of AI-driven solutions in enhancing healthcare delivery in India. (150 Words /10 marks) |
PRELIMS FACTS
1. US, EU, and UK Sign First Global Treaty on AI to Safeguard Human Rights and Democracy
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 10)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Risk-Based Approach and Accountability
- The treaty adopts a risk-based approach for AI systems in both public and private sectors, holding signatories accountable for harmful or discriminatory AI outcomes.
- It mandates that AI outputs respect privacy and equality, ensuring legal recourse for victims of AI-related rights violations.
Obligations and Scope
- Member states must ensure their AI systems protect human rights and democratic institutions.
- However, the treaty exempts national security and R&D activities, and relies on monitoring rather than punitive sanctions for compliance, raising concerns about enforcement.
Global Context
- The treaty aligns with other recent global AI regulations, such as the G7 AI pact, Europe’s AI Act, and the Bletchley Declaration, addressing the rising risks of AI in a globally coordinated manner.
2. Saturn’s Rings to Disappear in 2025 (Briefly) Due to Optical Illusion
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 10)
| Context: |
| The article explains the brief optical disappearance of Saturn’s rings in March 2025 and the gradual loss of the rings over millions of years due to Saturn’s gravity. |
Analysis of News:

Optical Illusion of Disappearance (March 2025)
- Saturn’s rings will briefly “disappear” from Earth’s view in March 2025 due to an optical illusion.
- This occurs when Saturn’s rings align edge-on with Earth, making them appear invisible due to their thinness (tens of meters thick), reflecting minimal light.
- The planet’s tilt of 26.73 degrees and its 29.4-year orbit around the Sun cause this phenomenon, which last occurred in 2009.
Saturn’s Rings Won’t Last Forever
- NASA confirmed in 2018 that Saturn’s rings are gradually being pulled toward the planet due to its gravity and magnetic field.
- The process, called “ring rain,” is depleting the rings, which could vanish in about 300 million years.
Rings Composition and Evolution
- Saturn’s rings consist of billions of ice and rock chunks, ranging from dust-sized to mountain-sized.
- They likely formed 100 million years ago from a collision between two icy moons.
- While other gas giants (Jupiter, Uranus, Neptune) may have had rings, Saturn’s rings are uniquely massive and structured, spanning nearly five times Earth’s diameter.
3. Household Food Expenditure Falls Below 50%, Reflecting Dietary Diversity and Impact of Government Schemes
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Economy; Page: 11)
| Context: |
| The article highlights a significant reduction in household food expenditure, driven by government food distribution schemes, leading to greater dietary diversity and improved access to diverse food items. |
Analysis of News:
Decline in Food Expenditure Share
- Household spending on food has fallen below 50% of total monthly expenditure for the first time in modern India, indicating significant progress.
- This decline is driven by free distribution of wheat and rice under central and state government schemes, including the Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY).
Shift in Dietary Patterns
- The share of spending on cereals has significantly reduced, especially for the bottom 20% of households.
- Savings from reduced cereal expenditure have allowed families to diversify their diets, increasing spending on milk, fresh fruits, eggs, fish, and meat.
Impact of Government Schemes
- Government food security schemes have enabled the bottom 20% of households to diversify their diet by reducing the need to purchase cereals.
Anaemia and Dietary Diversity
- Despite efforts to improve iron intake through fortification, anaemia rates remain high.
- The paper suggests focusing on dietary diversity instead of relying solely on fortified cereals to reduce anaemia.
Regional and Infrastructure Improvements
- Northeastern states and regions like Bihar and Odisha have shown notable improvements in dietary diversity, aided by better infrastructure and accessibility to diverse food items.
4. Breastfeeding cuts chances of the child developing allergic disorders
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- Breastfeeding provides lower protein content (about 1%) compared to cow’s milk, which contains around 4% protein, reducing the allergy potential.
- Newborns absorb amino acids better than peptides; peptides from cow’s milk formula can trigger allergic reactions.
- Breastfeeding helps limit the intake of allergy-inducing peptides.
- Babies breastfed exclusively for the first six months have a reduced likelihood of developing allergy-related disorders like eczema and atopic dermatitis.
- The lower protein load from breast milk helps the child’s immune system develop without triggering allergic responses early in life.
5. China’s emissions nearing peak, says U.S. climate envoy
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 15)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- Climate envoys from the U.S. and China are meeting in Beijing this week to discuss emissions targets.
- China aims to peak its greenhouse gas emissions by 2030 but may reach this goal earlier due to significant increases in renewable energy capacity.
- China is installing wind and solar energy at an unprecedented rate, achieving its target for these technologies six years ahead of schedule.
- Despite heavy reliance on coal, China’s progress in renewable energy suggests it may reduce its dependence on fossil fuels sooner than expected.
- China’s role as the world’s top emitter underscores the global significance of its climate efforts.
6. Intellectual Property Awards 2024: Celebrating Innovation and Excellence
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2052254 )
| Context |
|
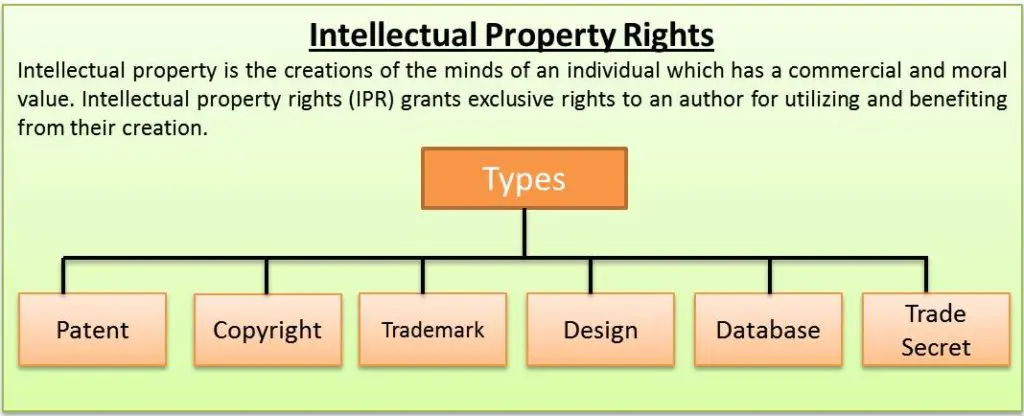
Intellectual Property Awards:
- The Intellectual Property Awards 2024 are organised by the Office of the Controller General of Patents, Designs, and Trademarks (CGPDTM) under the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT).
- The awards honour exceptional achievements in intellectual property (IP) across sectors like academia, R&D, MSMEs, startups, and large corporations.
- Categories include individuals, institutions, corporations, and organisations that have contributed to IP advancement in India.
- National IP Awards aim to acknowledge innovations, patents, designs, and trademarks.
7. Union Minister of Textiles Shri Giriraj Singh launches India’s first fashion forecasting initiative ‘VisioNxt’
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2052272 )
| Context |
|
VisioNxt Fashion Forecasting Initiative:
- VisioNxt is a fashion forecasting initiative launched by the National Institute of Fashion Technology (NIFT) with support from the Ministry of Textiles, India.
- It combines Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Emotional Intelligence (EI) to offer India-specific fashion trend insights.
- The initiative aims to elevate Indian design and culture in the global fashion industry, fostering healthy global competition.
- Launched in response to the gap in India-specific real-time trend data, identified at the 2017 Global Textile Summit.
- The “DeepVision” model identifies over 60 Indian and 40 Western wear categories, predicting fashion trends based on apparel attributes like style, colour, and regional accents.
- It seeks to reduce reliance on global trend agencies and empowers India’s fashion ecosystem.
| Practice Question: Discuss how the VisioNxt Fashion Forecasting Initiative can contribute to the growth of the Indian fashion industry and reduce reliance on global forecasting agencies. (150 Words /10 marks) |




