8 February 2025 : Daily Current Affairs
1. RBI slashes rate by 0.25% to revive growth
- 1. RBI slashes rate by 0.25% to revive growth
- 2. Private Bills seek sitting of Parliament for 100 days a year
- 3. SC Examines Governor’s Powers: Tamil Nadu Case to Set Precedent on Assent Delays
- 4. India Achieves Historic Milestone of 100 GW Solar Power Capacity
- Prelims Facts
- 1. 9 submarines, 65 ships taking part in TROPEX exercise
- 2. A surge of dead sea turtles in the sand
- 3. The men who play women under the stars
- 3. ‘Dunki Routes’: The Perilous Journey of Illegal Indian Migrants to the US
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context |
|
Repo Rate Cut After 57 Months
- This decision aims to boost economic growth amid expectations of inflation easing to 4.4% in this quarter and averaging 4.2% in 2025-26.
- The reduction in the repo rate may lead to lower borrowing costs for home, car, and other loans.

| What is Repo Rate? |
|
| Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) |
|
Economic Growth and Inflation Projections
- The RBI has projected real GDP growth at 6.7% for 2025-26, an increase from the 6.4% estimated for this year.
- Assuming a normal monsoon, inflation is expected to decline further and gradually align with the 4% target.
Mixed Demand Trends
- Rural demand is improving, while urban consumption remains weak.
- Higher employment, tax benefits from the budget, and lower inflation are expected to support household consumption.
Currency and External Sector Stability
- The RBI does not target a specific exchange rate but intervenes to reduce excessive market volatility.
- India’s foreign exchange reserves are at $630.6 billion (as of January 31, 2025), covering over 10 months of imports.
- The current account deficit is expected to remain at a sustainable level.
|
PYQ: Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)? (UPSC civil services prelims 2017)
Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 only Ans: Option (a) |
| Practice Question: Explain the role of the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) in maintaining price stability and fostering economic growth in India. How does the repo rate influence inflation and liquidity in the economy? (250 Words /15 marks) |
2. Private Bills seek sitting of Parliament for 100 days a year
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 3)
| Topic: GS2 – Indian Polity |
| Context |
|
Need for Such a Bill
- Declining Parliamentary Sittings: The number of parliamentary sittings has significantly reduced over the years. In the 1950s, Parliament met for around 120-140 days annually, but this has now declined to around 60-70 days.
- Ensuring Legislative Scrutiny: More sittings would allow better examination of bills, policies, and government decisions.
- Strengthening Democracy: A more active Parliament ensures better representation of public issues and enhances accountability.
- Preventing Disruptions: Frequent disruptions lead to lost working hours; a fixed calendar can ensure optimal legislative functioning.
- Recommendations from Reports: The National Commission to Review the Working of the Constitution (2002) and earlier parliamentary committees have recommended a minimum number of sittings.
Challenges
- Executive Hesitation: The government may resist due to administrative burden and fear of increased scrutiny.
- Opposition Coordination: Ensuring effective debates instead of mere disruptions remains a challenge.
- Lack of Political Consensus: Different political parties may have varying opinions on increasing parliamentary sittings, leading to delays in implementing such a reform.
- Legislative Overload: More sittings may not necessarily translate into better lawmaking if the focus remains on passing bills quickly rather than thorough debate and discussion.
Way Forward
- Fixed Parliamentary Calendar: A structured annual calendar with mandatory sittings can improve efficiency.
- Strengthening Parliamentary committee: To ensure detailed examination of bills even during non-sitting periods
- Compensating Lost Hours: Introducing mechanisms to recover hours lost due to disruptions.
- Multi-Session Model: Adding a short session to discuss opposition business and policy review.
- Incentivizing Constructive Participation: Introduce mechanisms such as performance-based evaluations for MPs, ensuring productive discussions and reducing disruptions in parliamentary proceedings.

| PYQ: Individual Parliamentarian’s role as the national lawmaker is on a decline, which in turn, has adversely impacted the quality of debates and their outcome. Discuss. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2019) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of mandating a minimum number of parliamentary sittings in a year. What challenges could arise in implementing such a provision, and how can they be addressed? (250 Words /15 marks) |
3. SC Examines Governor’s Powers: Tamil Nadu Case to Set Precedent on Assent Delays
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained – Page No. – 14)
| Topic: GS2 – Polity |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Governor’s Role in the Legislative Process
- Tamil Nadu argues that delays in granting assent to Bills could undermine democracy.
- The case holds national significance as similar petitions have been filed by other opposition-ruled states like Kerala, Telangana, and Punjab.
Understanding Article 200
Article 200 provides three options for a Governor when presented with a Bill:
- Give assent, making it law.
- Withhold assent and return it for reconsideration. If re-passed, the Governor must grant assent unless it derogates the High Court’s powers.
- Reserve the Bill for the President’s consideration in specific cases.
The Tamil Nadu Dispute
- Since Governor RN Ravi’s appointment in 2021, the Tamil Nadu government (DMK) has raised concerns over repeated delays in granting assent to Bills.
- In November 2023, the SC criticized Governors for withholding Bills indefinitely, stating that they “are not elected representatives” and should act before forcing states to approach the court.
- The Tamil Nadu Assembly re-passed the Bills, but Governor Ravi withheld assent again and referred two to the President.
Key Legal Issues Before the SC
- Can a Governor withhold assent twice after a Bill is re-passed?
- What are the limits on referring Bills to the President?
- Does the Governor’s indefinite withholding (pocket veto) have constitutional validity?
- Should there be a specific time frame for assent under Article 200?
SC on Time Frame for Assent
- Article 200 states that the Governor must act “as soon as possible”, but lacks a fixed deadline.
- The SC has ruled that Governors cannot indefinitely withhold assent, as seen in the Nabam Rebia (2016) case and reiterated in November 2023 during Punjab’s petition against similar delays.
- The Court emphasized that delays should not hinder the legislative process.
Conclusion
- The Supreme Court’s ruling on Tamil Nadu’s case will set a precedent for all states, clarifying the constitutional limits of a Governor’s role in lawmaking.
- A verdict enforcing a time-bound framework could prevent Governors from obstructing the legislative process and uphold the federal structure of democracy.
| Supreme Court Observations/Interpretations |
|
| Practice Question: The prolonged delay by Governors in granting assent to state Bills raises concerns about the federal structure and democratic governance in India. Examine the constitutional provisions related to the Governor’s role in the legislative process. Discuss the implications of indefinite delays in assent and suggest reforms to ensure timely decision-making. (250 Words /15 marks) |
4. India Achieves Historic Milestone of 100 GW Solar Power Capacity
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2100603®=3&lang=1 )
| Context |
|
Government’s Commitment to Green Energy
- Union Minister Pralhad Joshi highlighted India’s transformation in the energy sector under Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s leadership.
- Initiatives like solar panels, solar parks, and rooftop solar projects have significantly boosted solar energy production.
- The PM SuryaGhar Muft Bijli Yojana is helping households install rooftop solar systems, making clean energy more accessible.

Rapid Growth in Solar Power Sector
- Solar power capacity grew by 3,450% in the last decade, from 2.82 GW in 2014 to 100 GW in 2025.
- As of January 31, 2025, India has:
- 100.33 GW installed capacity
- 84.10 GW under implementation
- 47.49 GW under tendering
- In 2024, 24.5 GW of solar capacity was added, more than double that of 2023.
Top-Performing States
- Rajasthan, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, and Madhya Pradesh have contributed significantly to solar installations.
Growth in Rooftop Solar and Manufacturing
- The rooftop solar sector added 4.59 GW in 2024, a 53% increase from 2023.
- Solar module production grew from 2 GW in 2014 to 60 GW in 2024, with a target of 100 GW by 2030.
Conclusion
- With ongoing policy support, India is ensuring clean, sustainable, and affordable energy for millions while striving for energy independence.
| PYQ: India has immense potential for solar energy though there are regional variations in its development. Elaborate. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2020) |
| Practice Question: India has achieved a significant milestone by surpassing 100 GW of installed solar power capacity. Discuss the factors behind this rapid growth and the challenges that remain in achieving the target of 500 GW non-fossil fuel-based energy capacity by 2030. (250 Words /15 marks) |
Prelims Facts
1. 9 submarines, 65 ships taking part in TROPEX exercise
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|
Theatre Level Operational Readiness Exercise (TROPEX)
- Biennial Naval Exercise: TROPEX is the Indian Navy’s largest biennial operational exercise, conducted every two years in the Indian Ocean Region.
- Duration: The 2025 edition (TROPEX-25) is being held from January to March.
- Objectives: It aims to validate and refine the Indian Navy’s Concept of Operations, testing its ability to respond to conventional, asymmetric, and hybrid threats in a contested maritime environment.
- Participants: The exercise involves approximately 65 Indian Navy ships, 9 submarines, and over 80 aircraft, along with substantial participation from the Indian Army, Air Force, and Coast Guard.
- Exercise Phases: It includes harbour and sea phases, covering combat operations, cyber and electronic warfare, live weapon firings, and amphibious operations.
- Strategic Importance: The exercise enhances joint operational readiness, ensuring a synchronized, integrated response to safeguard India’s maritime security interests.
2. A surge of dead sea turtles in the sand
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- The death toll significantly exceeds the usual annual average, raising alarms among conservationists and local fisherfolk.
- Experts blame destructive fishing practices such as bottom trawling and frequent violations of marine regulations for the increased mortality.
- Turbulent monsoon currents have also contributed to the crisis, worsening the situation for the endangered species.
- The alarming rise in deaths has prompted government action and legal scrutiny to enforce stricter marine conservation measures.
- Conservationists and stakeholders are urging sustainable fishing solutions to protect Olive Ridley turtles and maintain marine ecosystem balance.
| Olive Ridley Turtle |
 |
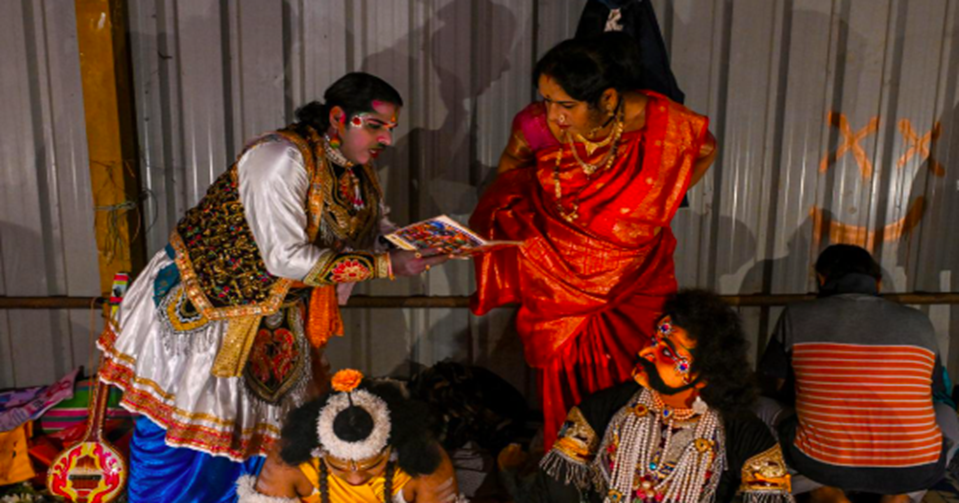
3. The men who play women under the stars
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 8)
| Context |
|
Dashavatar:
- Dashavatar is a traditional theatre form from Maharashtra’s Sindhudurg district and northern Goa, rooted in Hindu mythology.
- It has been performed for over 800 years and depicts the ten avatars of Vishnu.
- The performances take place after the paddy harvest until May, coinciding with village fairs (jatras).
- Only men traditionally perform, even in female roles, due to cultural beliefs.
- The form involves improvisation, music, and symbolic props. Artistes, often farmers or small traders, rely on Dashavatar for supplementary income.
- Despite evolving social norms, gender perceptions around the performances remain significant, influencing societal acceptance of actors playing female roles.

3. ‘Dunki Routes’: The Perilous Journey of Illegal Indian Migrants to the US
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained- Page No. – 14)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
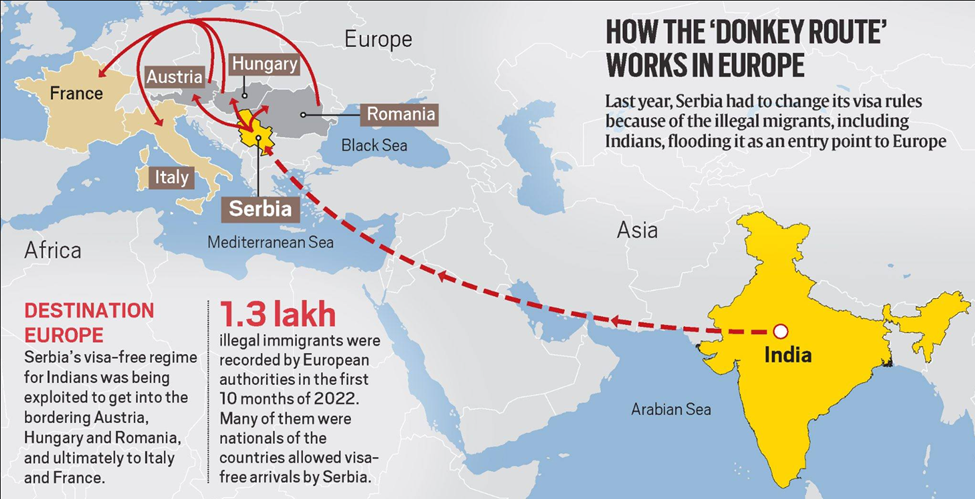
The Growing Trend of ‘Dunki Routes’
- Once prevalent in Punjab and Haryana, illegal migration via the dunki route is now expanding to Gujarat.
- Among the deportees, 33 were from Gujarat and Haryana each, and 30 from Punjab.
- Agents facilitate these perilous journeys, often charging exorbitant fees ranging from ₹30-40 lakh to ₹1 crore per person.
Illegal Route via South America
- Migrants typically begin their journey by entering Latin American countries with easier visa policies, such as Ecuador, Bolivia, and Guyana.
- Some agents also arrange Mexican visas via Dubai, though this route is riskier due to strict border controls.
- Once in Latin America, migrants are transported through multiple countries, eventually reaching Mexico before attempting to cross into the US.
High-Risk Journey to the US
- The most treacherous part of the journey involves crossing the Darién Gap, a dense jungle between Colombia and Panama, rife with wild animals, criminal gangs, and high risks of robbery and assault.
- Migrants must traverse multiple Central American countries, often facing arrests, deportations, or fatal accidents along the way.
- Many use ladders to scale border fences or cross the Rio Grande river to enter the US, where they are detained by American authorities.
Alternative Routes and Future Risks
- Some migrants bypass the Darién Gap by traveling via San Andrés in Colombia and then taking boats to Nicaragua.
- Others enter Europe first before flying to Mexico. The choice of route depends on agents’ connections and the level of scrutiny at different borders.
- Any crackdown on the existing routes could lead to the emergence of new, equally dangerous pathways.
2. National Commission for Safai Karamcharis gets 3-yr extension
(Source – Indian Express, Section – In Parliament- Page No. – 07)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:

Mandate and Functions
NCSK plays a crucial role in safeguarding the rights of safai karamcharis by:
- Recommending policies and action plans to eliminate social and economic inequalities.
- Monitoring the implementation of rehabilitation programs for safai karamcharis and manual scavengers.
- Investigating cases of non-implementation of laws and schemes, and addressing grievances with relevant authorities.
Evolution of NCSK: From Statutory to Non-Statutory Body
- Originally established as a statutory body under the National Commission for Safai Karamcharis Act, 1993, the NCSK lost its statutory status after the Act lapsed in 2004.
- Despite this, its scope has expanded, particularly after the enactment of The Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and Their Rehabilitation Act, 2013.
Financial Implication
- The decision entails a financial outlay of ₹51 crore and ensures the continued functioning of the Commission beyond its previous deadline of March 2024.
Significance of the Extension
- The extension underscores the government’s continued focus on uplifting safai karamcharis and eradicating manual scavenging.
- However, the non-statutory nature of the Commission limits its authority, raising concerns about the effectiveness of its recommendations.
- Strengthening its legal framework and ensuring strict enforcement of rehabilitation policies remain critical challenges.
Check more – 7 February 2025 : Daily Current Affairs



