8 July 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. New private investment plans slumped to 20-year low in Q1
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy. |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- Private capital expenditure in India hit a 20-year low in the April-to-June quarter, with only ₹44,300 crore in new investment plans.
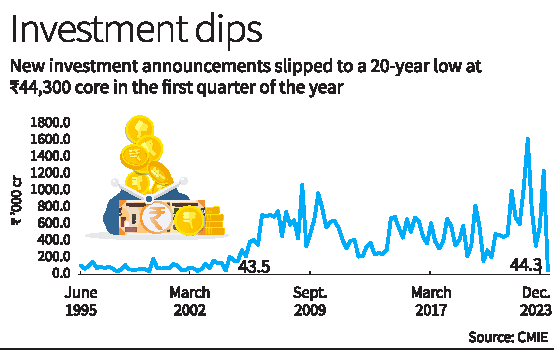
- Last year, investment announcements totaled ₹27.1 lakh crore, the second highest in a decade.
- Bank of Baroda’s chief economist, Madan Sabnavis, attributes the slowdown to a wait-and-watch approach by the industry.
- Historically, the April-June quarter has lower investment announcements, but this year’s figures are exceptionally low.
- Compared to previous Lok Sabha election years, Q1 investment in 2023-24 is significantly lower.
- High investment announcements in the last two years may have contributed to the slowdown.
- Corporate bond issuances and bank credit flows also indicate a slowdown in investment plans.
- Manufacturing dominated the investment outlays with a 46.4% share, followed by electricity and services.
- The transport services sector saw a 61% drop in investment value, linked to airline industry plans announced last year.
| Importance of private investment for economy: |
|
| PYQ: Explain the meaning of investment in an economy in terms of capital formation. Discuss the factors to be considered while designing a concession agreement between a public entity and a private enSty. (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2020) |
| Practice Question: Evaluate the significance of private investment in driving economic growth, generating employment, and enhancing infrastructure development in India. (250 Words /15 marks) |
2. Kerala varsity to launch genome editing mission to boost pearl spot production
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 3)
| Topic: GS3 – Agriculture – Technology in the aid of farmers. |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- Kerala’s pearl spot farmers traditionally rely on wild brood stocks, breeding in uncontrolled environments, and face slow growth rates, with fish reaching only 300-400 grams in a year.
- The Kerala University of Fisheries and Ocean Studies (Kufos) plans a genome editing mission to enhance pearl spot growth rates, similar to the success of genetically improved farmed tilapia (GIFT).
- The genome editing will target genetic factors inhibiting growth and improve breeding and seed production.
- Pearl spots have a high market value, sold at ₹650-₹700 per kg, compared to tilapia at ₹250-₹300 per kg.
- Tilapia grows to 600-700 grams in six months, whereas pearl spots take 12 months to reach 300-400 grams.
- Kerala produces 2,000 tonnes of pearl spots annually, against a market demand of 10,000 tonnes.
| Genome editing – It’s benefits for agriculture and animal husbandry: |
|
| Practice Question: Explain the role of genome editing in enhancing agricultural productivity and sustainability, highlighting its ethical considerations. (150 Words /10 marks) |
3. Bail cannot be withheld as a form of punishment, says SC
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Topic: GS2 – Indian Polity – Judiciary |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- The Supreme Court ruled that denying bail cannot be used as punishment regardless of the crime’s severity.
- Justices emphasised that an accused, presumed innocent until proven guilty, deserves bail to avoid unjust “prisonization.”
- The decision stemmed from Javed Gulam Nabi Shaikh’s appeal against Bombay High Court’s bail denial under UAPA.
- The National Investigation Agency (NIA) sought an adjournment, which the court denied, granting Shaikh bail after four years as an undertrial.
- The court criticised delays in trial proceedings despite no charges framed and 80 witnesses pending examination.
- Shaikh was accused of possessing counterfeit ₹2,000 notes smuggled from Pakistan to Mumbai in February 2020.
- The ruling stressed that bail should not be withheld punitively, reaffirming fundamental rights under Article 21 of the Constitution.
| Practice Question: Discuss the Supreme Court’s recent stance on bail as a fundamental right, emphasising its implications for justice and the presumption of innocence in criminal proceedings. (150 Words /10 marks) |
4. Modi’s Visit to Russia: Strengthening Historical Ties Amidst Geopolitical Tensions
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 12)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
A Statement of Prioritization
- Modi’s decision to visit Russia for his first bilateral visit after re-election, deviating from his previous practice of visiting neighboring countries first, signals the importance of Indo-Russian relations.
- This visit comes as NATO leaders gather in Washington to celebrate the alliance’s 75th anniversary, highlighting the contrasting diplomatic engagements of India and the Western bloc.
Historical Ties and Evolution
- India and Russia share a seven-decade-old relationship, deeply rooted in the camaraderie of the USSR era.
- Although the nature of this relationship has evolved, with India’s diversification of global partnerships, defense remains a cornerstone of Indo-Russian ties.
- Despite expanding its defense procurement to include the United States, France, and Israel, India continues to rely heavily on Russian military equipment, which constitutes 60-70% of its arsenal.
Defense Cooperation: A Strategic Pillar
- India’s defense partnership with Russia has progressed from a simple buyer-seller dynamic to joint research and development, co-development, and joint production of military hardware.
- Significant agreements include the supply of S-400 missile systems, MiG-29 aircraft, Kamov helicopters, and the production of T-90 tanks and Su-30MKI fighters.
- This cooperation is crucial for India, especially amidst the ongoing border tensions with China.
Economic Ties and Energy Security
- The Ukraine conflict has spurred India to purchase discounted Russian oil, significantly boosting bilateral trade.
- This move, although criticized internationally, is defended by India as essential for domestic economic stability.
- The bilateral trade volume reached an unprecedented $65.70 billion in FY 2023-24, driven largely by India’s imports of Russian oil and other commodities.
Diplomatic Balancing Act
- India’s stance on the Ukraine conflict has been delicate, balancing its strategic interests with its relationships with Western allies.
- While India has abstained from UN votes condemning Russia, it has also expressed concerns over the conflict’s humanitarian impacts. Modi’s past interactions with both Putin and Ukrainian President Zelenskyy illustrate India’s potential role as a mediator, though its actual involvement in peace processes remains cautious.
The Geopolitical Landscape
- Modi’s visit to Russia follows a series of high-level interactions between India and Western leaders, indicating India’s efforts to maintain a balanced foreign policy.
- The visit aims to reinforce Indo-Russian ties while ensuring that India’s strategic interests, particularly regarding China, are safeguarded.
Addressing Domestic Concerns
- One significant issue on Modi’s agenda is the situation of Indians in Russia who were reportedly misled into joining the Ukraine conflict.
- Ensuring their safe return and discussing defense cooperation in light of the Russia-China partnership are key concerns for India.
Strengthening Historical Ties
- The visit is part of the long-standing annual bilateral summits between India and Russia, reflecting a commitment to sustaining this strategic partnership.
- Modi aims to reaffirm historical ties and navigate the complex geopolitical landscape to ensure that Russia’s engagement with China does not undermine India’s strategic interests.
| PYQ: What is the significance of Indo-US defence deals over Indo-Russian defence deals? Discuss with reference to stability in the Indo-Pacific region. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2020) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to Russia amidst ongoing geopolitical tensions and the Ukraine conflict. How does this visit reflect India’s strategic priorities and its balancing act between maintaining historical ties with Russia and engaging with Western allies? (250 words/15 m) |
5. DoT Introduces Digital Bharat Nidhi to Enhance Rural Telecom Connectivity, Replacing USOF
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Economy; Page: 11)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government policies – Interventions for development in various sectors |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:

Background of USOF
- The USOF was established through a 5 percent Universal Service Levy charged on telecom operators’ Adjusted Gross Revenue (AGR).
- The primary objective of the USOF was to fund the expansion of telecom networks in underserved rural areas where private companies are reluctant to invest due to low revenue potential.
Transition to Digital Bharat Nidhi
- With the notification of parts of the Telecom Act, the government has proposed the transformation of USOF into the DBN, which will have a broader scope.
- The contributions made by telecom companies to the DBN will first be credited to the Consolidated Fund of India and then deposited into the Nidhi periodically.
Functioning of Digital Bharat Nidhi
- The DBN funds will support universal service by promoting access to telecommunication services in underserved areas, funding R&D in telecom technologies, supporting pilot projects, and introducing new telecom services and products.
- The draft rules specify that an “administrator” will be appointed to select DBN implementers through bidding or application invitations.
- Funding modalities will be determined on a case-by-case basis, including full funding, partial funding, co-funding, and risk capital.
Targeted Beneficiaries and Objectives
- The DBN will focus on providing telecom services to underserved groups such as women, persons with disabilities, and economically weaker sections.
- The schemes and projects funded by the DBN will aim to introduce next-generation telecom technologies, improve affordability, promote innovation and R&D, develop indigenous technologies, and encourage start-ups in the telecommunications sector.
Sharing and Non-Discrimination
- DBN implementers receiving funding will be required to share their telecom networks and services on an open and non-discriminatory basis, in accordance with instructions issued by the administrator.
Underutilisation of USOF
- Since its inception in 2003, the USOF has faced criticism for its underutilisation.
- Between 2017 and 2022, the government collected Rs 41,740 crore from telecom operators but utilised only Rs 30,213 crore, a utilisation rate of about 72 percent.
- The low spending can be attributed to the underspending of funds allocated for the BharatNet project aimed at providing fibre connectivity to villages.
Conclusion
- The establishment of the Digital Bharat Nidhi represents a renewed effort by the Indian government to address the connectivity gap in rural and remote areas.
- By expanding the scope and improving the utilisation of funds, the DBN aims to foster innovation, enhance telecom services, and ensure inclusive access to digital infrastructure across the country.
| What is the Status of the Telecom Sector in India? |
|
6. Raging Wildfires Darken Arctic Skies, Threatening Climate Stability
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 12)
| Topic: GS3 – Environment – Environment Pollution and Degradation |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:

Natural and Escalating Threat
- Wildfires have historically been a natural part of the Arctic’s boreal forest (snow forest) and tundra (treeless regions) ecosystems.
- However, in recent years, their frequency and scale have significantly increased, primarily due to global warming. These blazing wildfires are not only a natural hazard but also a factor fueling the climate crisis.
Reasons for Worsening Arctic Wildfires
Accelerated Arctic Warming
- The Arctic has been warming roughly four times as fast as the rest of the world. While the global average temperature has increased by at least 1.1 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, the Arctic has become on average around 3 degrees warmer than it was in 1980.
- This rapid warming has led to more frequent lightning in the Arctic, further increasing the likelihood of wildfires.
Increased Lightning and Thunderstorms
- Experts explained that thunderstorms, which can ignite wildfires, occur when there is differential surface heating leading to updraft-downdraft convection.
- This phenomenon is more likely to occur over ice-free land than land covered with ice, making the Arctic more susceptible to thunderstorms as it warms.
Polar Jet Stream Changes
- Soaring temperatures have also slowed down the polar jet stream, responsible for circulating air between the mid- and northern latitudes.
- The diminished temperature difference between the Arctic and lower latitudes causes the polar jet stream to often get “stuck” in one place.
- This stagnation brings unseasonably warm weather to the region, leading to intense heatwaves that can spark more wildfires.
Future Outlook
- Rising temperatures, more frequent lightning, and prolonged heatwaves are likely to worsen in the coming years, potentially leading to more wildfires in the Arctic.
Impact of Arctic Wildfires on Global Warming
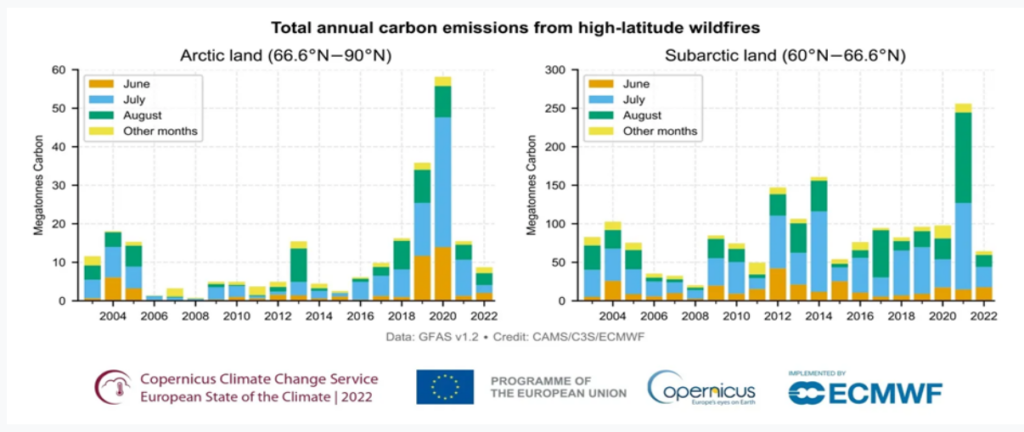
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- When wildfires ignite, they burn vegetation and organic matter, releasing heat-trapping greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere.
- The increasing frequency of wildfires globally contributes to climate change by releasing large amounts of these gases.
Permafrost Thawing
- The most significant concern with Arctic wildfires is the carbon stored underneath the region’s permafrost, which remains frozen for at least two consecutive years.
- Scientists estimate that Arctic permafrost holds around 1,700 billion metric tons of carbon, including methane and CO2, which is roughly 51 times the amount of carbon the world released as fossil fuel emissions in 2019.
- Wildfires make permafrost more vulnerable to thawing by destroying the upper insulating layers of vegetation and soil.
- This can lead to the decomposition of ancient organic materials, releasing stored carbon into the atmosphere.
- If large-scale thawing of Arctic permafrost is triggered, it would be impossible to stop the release of this vast amount of carbon.
| Practice Question: How are increasing wildfires in the Arctic affecting global climate change, and what factors are contributing to their rising frequency and intensity? (250 words/15 m) |
Prelims Facts
1. Red flags raised over silver imports from UAE through GIFT City
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Context |
|
Gujarat International Finance Tec-City (GIFT) City:
- Location: Situated in Gandhinagar, Gujarat, India.
- Establishment: Conceptualized in 2007, inaugurated in 2013.
- Objective: To create a globally benchmarked financial and IT services hub.
- Regulatory Framework: Governed by the International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA).
- Infrastructure: World-class infrastructure, including high-rise office buildings, residential complexes, and provides state-of-the-art facilities for IT and IT-enabled services (ITES) companies.
- It hosts India’s first International Financial Services Centre (IFSC), offering various financial services such as banking, insurance, and capital markets.
- Designed as a smart city with sustainable urban planning, including efficient waste management, green buildings, and energy-efficient systems.
- Attracts both domestic and international investors with various incentives and a conducive business environment.
2. Lakhs of devotees throng Puri to witness annual Rath Yatra
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Context |
|
Annual Rath Yatra or Chariot Festival:
- Significance: Celebrates the journey of Lord Jagannath, Lord Balabhadra, and Devi Subhadra from the Jagannath Temple to the Gundicha Temple.
- Typically held in the month of June or July, on the second day of the bright fortnight (Shukla Paksha) of Ashadha.
- Rituals: Priests perform special rituals to prepare the three massive chariots (Rathas) for the deities.
- Chariots: Three main chariots named Nandighosa (Jagannath’s chariot), Taladhwaja (Balabhadra’s chariot), and Darpadalana (Subhadra’s chariot) are adorned with colourful decorations and icons.
- Procession: Thousands of devotees pull the chariots with ropes through the streets of Puri amidst chanting, music, and festivities.
- Tradition: Symbolises the journey of the deities to their aunt’s place, reflecting familial ties and communal harmony.
- Spiritual Significance: Believed to cleanse sins and bestow blessings upon devotees who participate or witness the procession.
- Attracts pilgrims and tourists worldwide, recognized for its cultural richness and religious fervour.
- Accompanied by traditional dances, music performances, and religious discourses during the festival period.
3. Graphene: a simple wonder
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
Graphene:
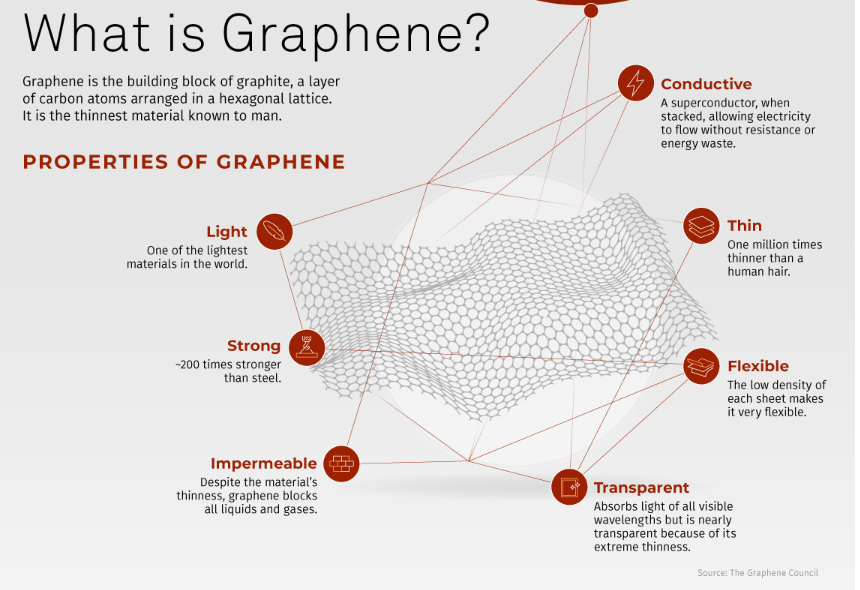
- Definition and Structure: Graphene is an allotrope of carbon consisting of a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice.
- Properties:
- Strength: Stronger than diamond, making it highly durable.
- Conductivity: More conductive than silver, facilitating efficient electricity and heat transfer.
- Flexibility: More elastic than rubber, allowing it to bend and stretch without damage.
- Lightweight: Lighter than aluminium, contributing to its versatility in various applications.
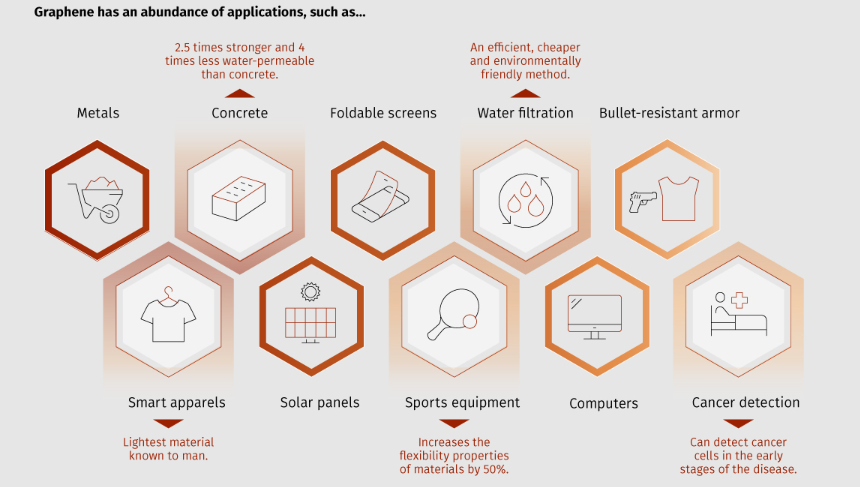
- Production Methods:
- Initially demonstrated by using scotch tape to peel graphite layers.
- Industrial methods like chemical vapour deposition (CVD) are used for large-scale production.
- Applications:
- Reinforcing materials such as car tires to improve strength and durability.
- Substituting silicon in electronics for faster and more efficient components.
- Enhancing concrete strength by 25% while reducing carbon emissions.
- Special Properties:
- Forms a superconductor when two graphene sheets are stacked and rotated at 1.1 degrees.
- Investigated for potential applications in quantum computing and other advanced technologies.
Graphene’s unique combination of properties makes it a promising material for revolutionising various industries, from electronics and construction to biomedical applications and beyond.
4. Jumping genes and RNA bridges promise to shake up biomedicine
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|
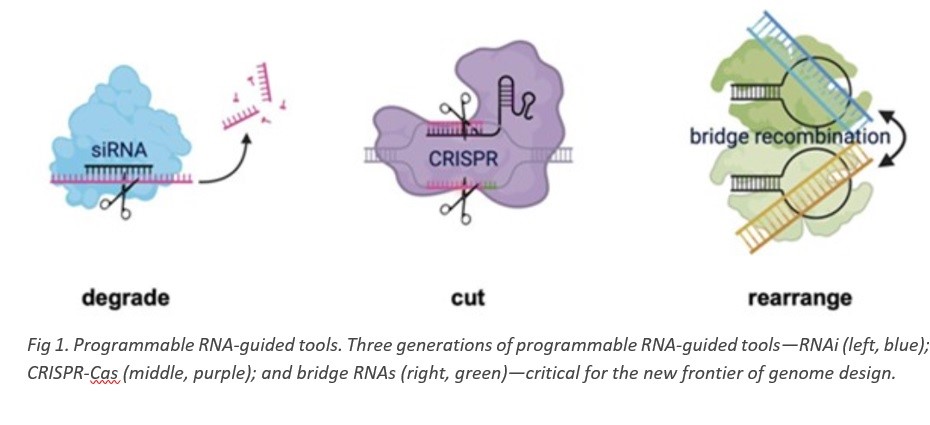
Jumping Genes:
- Definition: Jumping genes, or transposons, are DNA sequences that can change their position within the genome, “jumping” from one location to another.
- Characteristics: They can influence gene expression and genome evolution by moving around and altering genetic sequences.
RNA Bridges:
- Definition: RNA bridges refer to RNA molecules that can bind to two separate pieces of DNA, facilitating genome editing by guiding the insertion of DNA sequences into specific genomic locations.
- Function: They enhance precision in genetic engineering by targeting specific sites for DNA insertion and replacement.
5. Vadhavan, a global port in the making
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 13)
| Context |
|
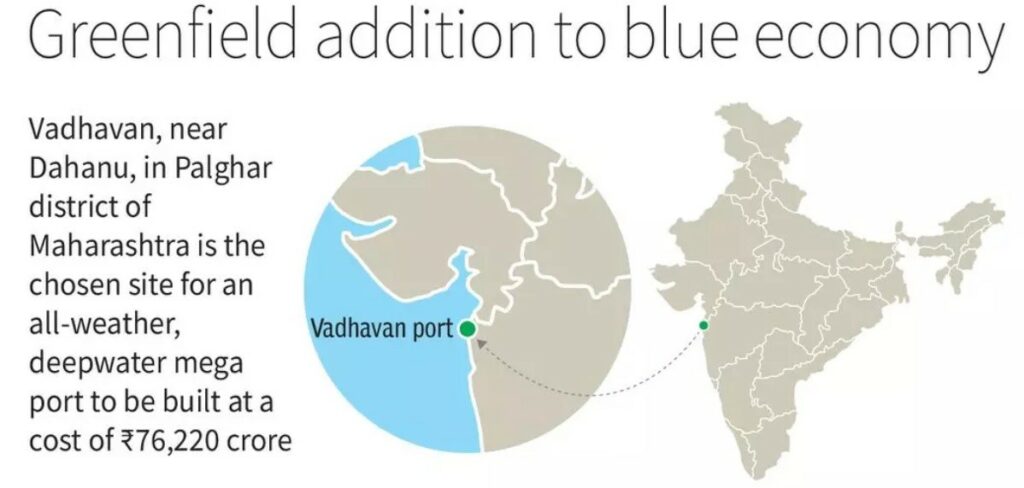
Analysis of the news:
- Location: Vadhavan port is situated near Dahanu in Palghar district, Maharashtra, India.
- Development: The port is being developed as an all-weather, deepwater mega port.
- Investment: Estimated to cost ₹76,220 crore, it is a joint venture between Jawaharlal Nehru Port Authority (JNPA) and Maharashtra Maritime Board (MMB).
- Ownership: JNPA holds a majority share of 74%, while MMB holds the remaining 26%.
- Infrastructure: Planned infrastructure includes nine container terminals, each 1,000 metres long, four multipurpose berths, four liquid cargo berths, a Ro-Ro ship berth, and a Coast Guard berth.
- Draft Capacity: The port will feature a draft of 20 metres, enabling it to accommodate large vessels.
- Cargo Handling Capacity: Once fully operational, the port aims to handle a cumulative cargo capacity of 298 million tonnes per annum (MTPA), including around 23.2 million TEUs (Twenty-Foot Equivalent Units) of container handling capacity.
- Regional Impact: It is expected to cater to industrial areas in Maharashtra, Gujarat, Rajasthan, NCR, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and other central and northern Indian states, enhancing logistics and reducing transit costs.
6. Bone Fragments in Tibetan Cave Reveal Denisovans’ Diverse Hunting Practices and High-Altitude Adaptations
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 12)
| Context: |
|
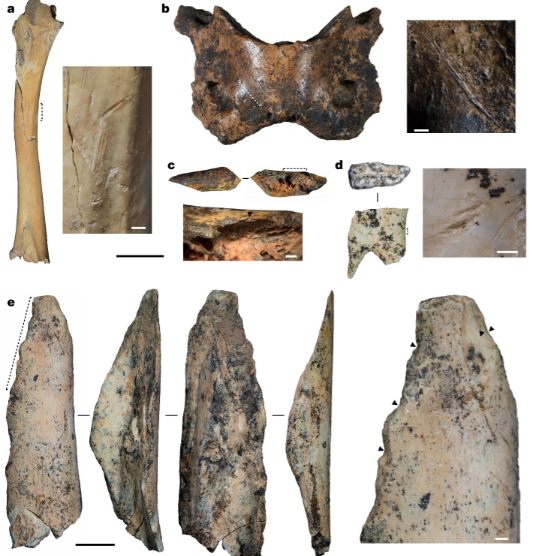

Examples of anthropogenically modified faunal specimens and bone tools.
Analysis of News:
Diverse Prey and Environment
- Most of the bones were identified as belonging to blue sheep, also called bharal, a goat species still seen in the Himalayas.
- Other bone remains came from woolly rhinos, yaks, small mammals like marmots, birds, and even from the spotted hyena, a large carnivore that prowled the region called the Ganjia Basin.
- This area was a grass landscape with small forested areas, teeming with life despite harsh conditions. The animals were butchered for meat, as evidenced by cut marks found on various bones, and there was also evidence of bone marrow extraction and skinning activities.
Subsistence Behaviors
- The findings provide the first understanding of the subsistence behaviors of Denisovans, showing that they were highly capable of accessing and utilizing a wide range of animal resources.
About Denisovan:
- The Denisovans are an extinct group of archaic humans that lived across Asia during the Lower and Middle Paleolithic periods. They are known primarily through DNA evidence, as physical remains are scarce.
- The first Denisovan individual was identified in 2010 from a finger bone found in Denisova Cave in Siberia. They are closely related to Neanderthals and interbred with both Neanderthals and modern humans.
- Genetic studies suggest that Denisovans had dark skin, eyes, and hair, and contributed to the genetic makeup of present-day Melanesians, Aboriginal Australians, and Filipino Negritos.
- The exact taxonomy of Denisovans is still debated, with some researchers suggesting they may be a separate species within the Homo genus.
7. Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, and Maharashtra Lead in Informal Sector Enterprises, Survey Reveals
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Economy; Page: 11)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
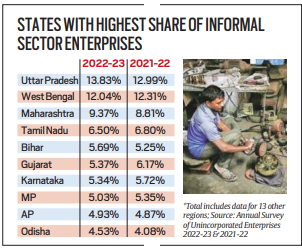
State-wise Changes
- Among the major states, Uttar Pradesh recorded a 13.83% share of informal sector enterprises in 2022-23, up from 12.99% in the previous year.
- West Bengal, which followed in the second position, saw a marginal dip in its share to 12.04% from 12.31% in 2021-22.
- Maharashtra’s share rose to 9.37% from 8.81% during the same period.
Comparison with Previous Data
- When compared with the National Sample Survey’s 73rd round on Unincorporated Enterprises for 2015-16, there was a decline in workers employed in states such as Andhra Pradesh, Assam, Uttar Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, and West Bengal in 2022-23.
- However, the share of informal sector workers increased in most states immediately after the pandemic compared to 2021-22.
Trends in Informal Sector Workers
- In Uttar Pradesh, the number of informal sector workers declined to 1.57 crore in 2022-23 from 1.65 crore in 2015-16 but rose from 1.30 crore in 2021-22.
- West Bengal saw a decline in informal sector workers to 1.05 crore in 2022-23 from 1.35 crore in 2015-16, with a marginal increase from 1.02 crore in 2021-22.
- Maharashtra recorded an increase in informal sector workers throughout this period, rising to 1.15 crore in 2022-23 from 91.23 lakh in 2015-16 and 98.81 lakh in 2021-22.
States with the Lowest Share
- State-wise data for unincorporated enterprises revealed that the lowest share of informal sector enterprises was recorded in Uttarakhand, Assam, Chhattisgarh, Delhi, and Jammu & Kashmir.
- However, Delhi saw a sharp jump from the previous year, rising to 1.43% in 2022-23 from 0.64% in 2021-22.




