8 June 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Fish kill spotlights pangs of Periyar
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS3 – Environment – Environmental pollution and degradation |
| Context |
|
Industrial Pollution:
- The Periyar River ecosystem faces severe degradation due to industrial pollution from numerous industrial units along its banks.
- Effluents containing toxic chemicals and untreated wastewater are discharged into the river, leading to contamination of water and sediment.
Mass Fish Deaths:
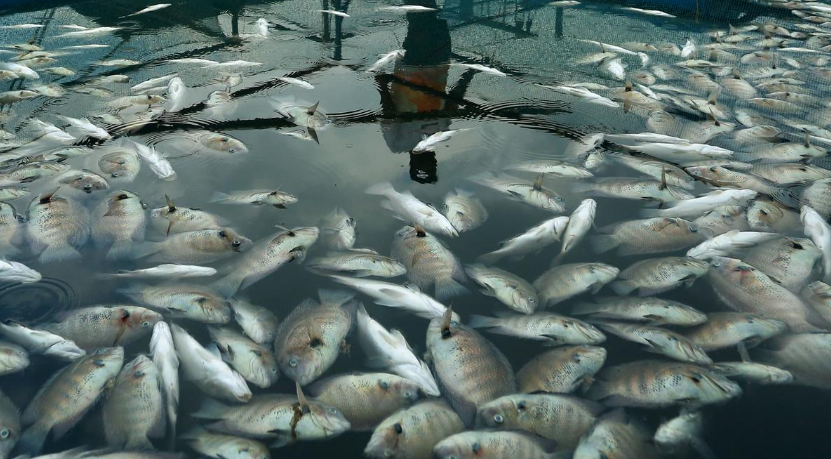

Dead fish found floating in a cage farm at Shappukadavu near Cheranalloor in Koch
- The river has witnessed multiple instances of mass fish deaths, indicating a significant decline in water quality.
- Fishermen and farmers report fish struggling to breathe and floating dead on the river’s surface, raising concerns about the ecosystem’s health.
Impact on Aquatic Life:
- Pollution in the Periyar River adversely affects aquatic biodiversity, including fish species and other aquatic organisms.
- Chemical pollutants and low oxygen levels pose threats to the survival of aquatic flora and fauna, disrupting the river’s ecological balance.
Human Health Risks:
- Contaminated water from the Periyar River poses serious health risks to communities reliant on it for drinking water and irrigation.
- Exposure to pollutants and toxins in the water can lead to waterborne diseases and long-term health complications for local populations.
Economic Consequences:
- The degradation of the Periyar River ecosystem has economic repercussions for communities dependent on fishing and agriculture.
- Loss of fish stocks, decline in agricultural productivity, and damage to livelihoods exacerbate poverty and economic inequalities in the region.
Environmental Activism:
- Environmental activists raise concerns about the deteriorating condition of the Periyar River and advocate for stricter regulations and enforcement measures.
- Calls for sustainable industrial practices and pollution control initiatives aim to mitigate further damage to the river ecosystem and protect human and environmental health.
Government Response:
- Government agencies conduct periodic monitoring of water quality and pollution levels in the Periyar River.
- Policy interventions, such as setting up a River Monitoring Authority and implementing pollution control measures, are proposed to address the degradation of the river ecosystem.
Long-Term Solutions:
- Long-term solutions to mitigate the degradation of the Periyar River ecosystem involve collaborative efforts between government, industries, and local communities.
- Implementing stricter pollution control measures, promoting sustainable industrial practices, and enhancing public awareness are essential for restoring the health and vitality of the river.
| PYQ: Enumerate the National Water Policy of India. Taking river Ganges as an example, discuss the strategies which may be adopted for river water pollution control and management. What are the legal provisions for management and handling of hazardous wastes in India? (200 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2013) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the challenges and solutions pertaining to the degradation of the Periyar River ecosystem in Kerala, emphasising the role of industrial pollution, its impacts on biodiversity, human health, and livelihoods, and the measures required for its restoration. (250 Words /15 marks) |
2. ASEAN FTA: govt. seeks industry inputs to up demand pitch
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 11
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations |
| Context |
|
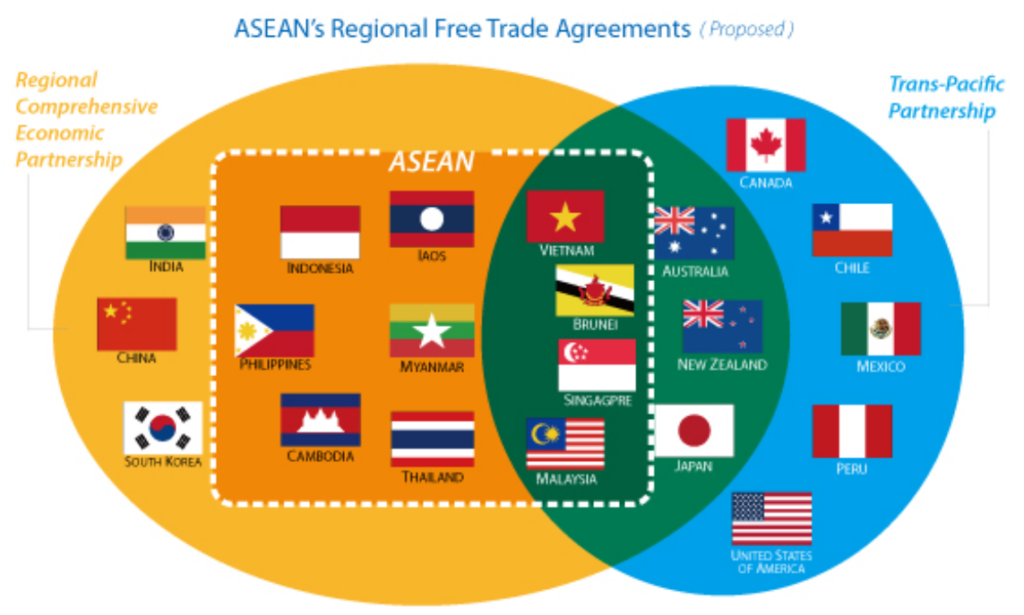
Analysis of the news:
- The Commerce Department aims to enhance its negotiation stance with ASEAN ahead of the ASEAN-India FTA review in Indonesia next month.
- Inputs are being gathered from industry and export promotion bodies regarding areas where deeper tariff concessions can be pursued.
- India seeks to address the disproportionate gains favouring ASEAN countries under the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITGA).
- The trade deficit with ASEAN widened to $38.46 billion in 2023-24, prompting India to push for greater market access, flexibility in rules of origin, and resolution of non-tariff barriers.
- Meetings between Commerce Ministry officials and industry representatives aim to align negotiation strategies and prioritise demands for lower duties.
- ASEAN comprises 10 member states: Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Brunei, Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar, and Cambodia.
- India has been advocating for a review of AITGA since its implementation in 2010, with the fifth joint committee meeting scheduled for July 29-31.
- India has emphasised the need for product specific rules in determining rules of origin to relax requirements for low value addition items.
| Potential advantages of India – ASEAN FTA: |
|
| PYQ: Q.1 Indian Diaspora has an important role to play in South-East Asian countries’ economy and society. Appraise the role of Indian Diaspora in South- East Asia in this context. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2017) Q.2 Evaluate the economic and strategic dimensions of India’s Look East Policy in the context of the post-Cold War international scenario. (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2016) |
| Practice Question: What are the potential advantages for India in the context of the India-ASEAN Free Trade Agreement (FTA), and how does it contribute to regional economic integration? (150 Words /10 marks) |
3. Human-Driven Climate Change Intensifies Severe Heatwave in North and Central India, Study Reveals
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 07)
| Topic: GS3 – Environment – Environmental Pollution and Degradation GS1 – Geography – Climate Change |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Record-Breaking Temperatures:
- More than 37 cities across North and Central India recorded temperatures exceeding 45° Celsius, triggering warnings for heat-related illnesses.
- Areas in Delhi, such as Najafgarh, Mungeshpur, and Narela, saw temperatures ranging between 47° and 49° Celsius.
- Even central and traditionally cooler areas like Safdarjung experienced highs of up to 46° Celsius.
- The widespread and extreme nature of these temperatures highlights the severity of the heatwave.
Historical Weather Comparisons:
- Researchers assessed atmospheric conditions, including surface pressure, temperature, and precipitation, comparing data from the late 20th century (1979-2001) with recent decades (2002-2023).
- Their findings indicate that recent heatwaves are approximately 1.5° Celsius more intense than those in the past.
- This increase aligns with the observed effects of climate change, which has become more pronounced over the years.
The Role of Climate Change:
- Experts emphasized the complex interplay between natural variations and climate change.
- They noted that climate change significantly contributes to changes in weather patterns in tropical and subtropical regions, potentially exacerbating future heatwaves.
- This perspective highlights the critical role of human activities in intensifying these extreme weather events.
Atmospheric Pressure Anomalies:
- The analysis revealed significant cyclonic anomalies over Northwest India and Southern Pakistan during the heatwave.
- These anomalies involved warm and moist air moving towards the coast, coupled with temperatures up to 5° Celsius higher than usual in some parts of Northwest India and Southern Pakistan.
- The presence of low to moderate winds further contributed to the unusual temperature highs, illustrating the complex dynamics of atmospheric pressure and climate change.
Conclusion:
- The ClimaMeter analysis concludes that the May heatwave in India was notably more intense than previous heatwaves, primarily due to human-driven climate change.
- The findings indicate that such heatwaves are now 1.5° Celsius warmer than the warmest previously recorded, reflecting the profound impact of global warming on extreme weather patterns.
- This unique event underscores the urgent need for climate action to mitigate the increasing severity of heatwaves and other climate-related phenomena.
|
PYQ: What are the possible limitations of India in mitigating global warming at present and in the immediate future? (2010) 1) Appropriate alternate technologies are not sufficiently available. 2) India cannot invest huge funds in research and development. 3) Many developed countries have already set up their polluting industries in India. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (a) |
| Practice Question: Examine the impact of human-induced climate change on the frequency and intensity of heatwaves in India. Discuss the findings of recent studies on temperature anomalies and atmospheric pressure patterns, and their implications for future climate-related events. (250 words/15 m) |
4. Indian Households Prioritize Beverages and Processed Foods, Varying State Preferences Highlight Regional Dietary Trends
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Economy; Page: 15)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy – Inclusive Growth |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
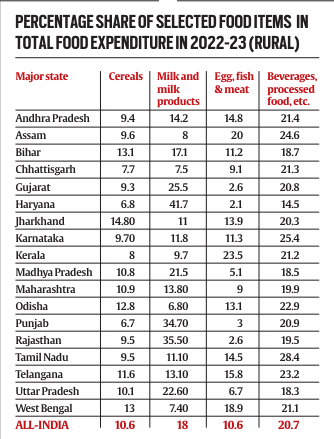
Rural Spending Preferences:
- In rural areas, households in Haryana spent the highest percentage of their food budget on ‘milk and milk products,’ with an allocation of 41.7%. Kerala, on the other hand, led in spending on ‘egg, fish & meat,’ dedicating 23.5% of its food expenditure to this category.
- States like Rajasthan (35.5%), Punjab (34.7%), Gujarat (25.5%), Uttar Pradesh (22.6%), and Madhya Pradesh (21.5%) also prioritized ‘milk and milk products’ over ‘beverages and processed food.’
Urban Spending Patterns:
- Urban areas showed a similar trend, with Rajasthan leading in spending on ‘milk and milk products’ at 33.2%, followed closely by Haryana (33.1%) and Punjab (32.3%).
- Kerala remained the top state for spending on ‘egg, fish & meat,’ with 19.8% of its total food expenditure allocated to this category.
- Overall, ‘beverages, refreshments, and processed food’ remained the top spending category in urban areas, with Tamil Nadu recording the highest share at 33.7%.
National Consumption Highlights:
- Nationally, rural households spent about 46% of their consumption budget on food, with ‘beverages, refreshments, and processed food’ accounting for the highest share at 9.62%. This was followed by ‘milk and milk products’ at 8.33% and vegetables at 5.38%. Cereals and cereal substitutes made up about 4.91% of the food consumption expenditure.
- In urban areas, food spending constituted about 39% of the average monthly per capita consumption expenditure (MPCE). Similar to rural areas, ‘beverages, refreshments, and processed food’ took the largest share at 10.64%, followed by ‘milk and milk products’ at 7.22%. Both fruits and vegetables each accounted for 3.8% of the total food expenditure.
State-Specific Preferences:
- The survey highlighted state-specific preferences that deviate from the national trend.
- For instance, Tamil Nadu’s highest expenditure share on ‘beverages, refreshments, and processed food’ stood out in both rural (28.4%) and urban (33.7%) areas. These variances underscore the diversity in dietary habits and preferences across different regions of India.
Conclusion:
- The Household Consumption Expenditure Survey for 2022-23 reveals significant insights into the spending habits of Indian households.
- While ‘beverages, refreshments, and processed food’ dominate overall food expenditure, preferences for ‘milk and milk products’ and ‘egg, fish & meat’ in certain states illustrate regional dietary variations.
- These spending patterns are crucial for policymakers and businesses aiming to address the nutritional needs and market demands of India’s diverse population.
|
PYQ: As per the NSSO 70th Round “Situation Assessment Survey of Agricultural Households”, consider the following statements: (2018) 1) Rajasthan has the highest percentage share of agricultural households among its rural households. 2) Out of the total agricultural households in the country, a little over 60 percent belong to OBCs. 3) In Kerala, a little over 60 percent of agricultural households reported to have received maximum income from sources other than agricultural activities. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 2 and 3 only (b) 2 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: c |
| Practice Question: Discuss the regional variations in household food expenditure in India as revealed by the Household Consumption Expenditure Survey 2022-23. What do these variations imply for policy-making in the areas of nutrition and food security? (250 words/15 m) |
Prelims Facts
1. President invites Modi to form new govt.; swearing-in tomorrow
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Context |
|
The President of India invites a leader to form the government based on the following order:
- The leader of the party or coalition with the majority of seats in the Lok Sabha.
- If no single party or coalition has a clear majority, the President may invite the leader of the largest party or coalition to demonstrate their ability to form a stable government through alliances and support from other parties.
- If no party or coalition is able to demonstrate majority support, the President may explore other options, such as inviting a leader to form a minority government with outside support.
- If no party or coalition can form a government, the President may recommend the dissolution of the Lok Sabha and call for fresh elections.
In the current situation, President Droupadi Murmu invited Narendra Modi to form the government as he was elected as the leader of the National Democratic Alliance (NDA), which secured a majority of seats in the Lok Sabha.
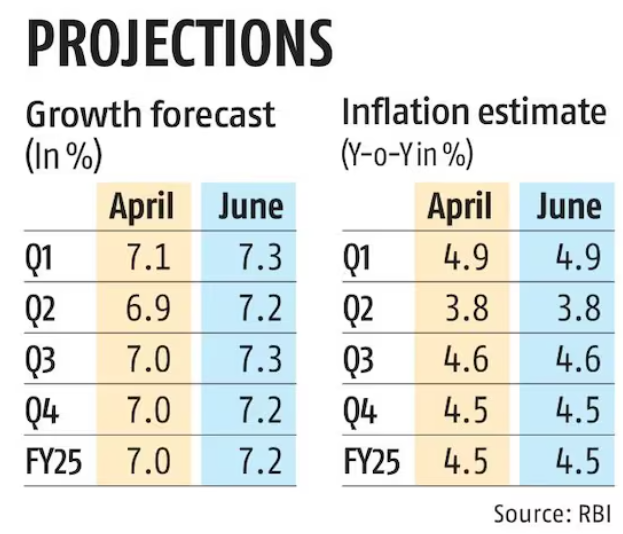
2. RBI keeps repo rate unchanged, raises GDP forecast to 7.2%
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Context |
|
About The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC):
- The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) is a statutory body constituted by the Government of India under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
- It is responsible for fixing the benchmark policy interest rate (repo rate) to achieve the inflation target set by the government.
- The MPC consists of six members, with three nominated by the Government of India and three from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), including the RBI Governor, who acts as a chairman.
- The committee meets at least four times a year to review macroeconomic conditions and determine monetary policy actions.
- Its decisions aim to balance the objectives of price stability and economic growth.
| Repo Rate: |
|
Repo Rate:
Repo Rate Significance:
|
| Reverse Repo Rate: |
|
Reverse Repo Rate:
Reverse Repo Rate Significance: Liquidity Management:
|
2. Modi Unanimously Elected NDA Parliamentary Party Leader in Historic Central Hall Meeting
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:

Historical Significance of Central Hall:
- The Central Hall, topped by a 98-feet diameter dome, has been a witness to numerous pivotal events since its establishment in 1927.
- Originally serving as the library for the members of the legislature, it gained monumental importance in 1946 when it was refurbished and renamed the Constituent Assembly Hall to host the Constituent Assembly deliberations on the Indian Constitution.
- This transformation marked the beginning of its use for high-profile and historically significant events.
The Parliament House Complex
- Located in the heart of New Delhi, the Parliament House Complex comprises several buildings, including the newly opened Parliament House, the old Parliament House now renamed Constitution House, Parliament House Annexe, and the Parliament Library Building.
- This complex provides office spaces and meeting venues for political parties, facilitating their organizational and strategic activities within close proximity to the legislative proceedings.
Historical Events in Central Hall
- Central Hall has a rich history of hosting formal and significant events. It has been the venue for the annual Presidential Address to Members of Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha, the swearing-in ceremonies of Presidents, and farewell events for outgoing Presidents.
- Additionally, it has hosted international dignitaries, such as the address by US President Barack Obama in 2010. The Hall has also been a venue for lectures by prominent academics, such as American economist Jeffrey Sachs and Nobel Laureate Amartya Sen during the 14th Lok Sabha term.
3. Japan Protests Armed Chinese Vessel Incursion Near Disputed Senkaku/Diaoyu Islands
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
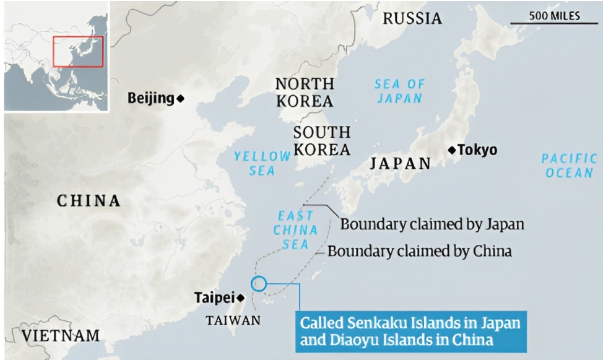
Escalation in a Long-Standing Dispute:
- The East China Sea islands, called Senkaku by Japan and Diaoyu by China, have long been a flashpoint in Sino-Japanese relations.
- Both nations lay claim to these strategically significant islands, which are surrounded by rich fishing grounds and potential energy resources.
- The recent intrusion by armed Chinese vessels represents a significant escalation in the territorial dispute, reflecting broader geopolitical tensions in the region.
4. RBI Proposes Digital Payments Intelligence Platform to Combat Fraud
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Rise in Domestic Payment Frauds:
- The urgency of this initiative is underscored by recent RBI data showing a significant rise in domestic payment frauds.
- During the six-month period ending in March 2024, payment frauds surged by 70.64%, reaching Rs 2,604 crore compared to Rs 1,526 crore in the same period the previous year.
- The volume of fraud cases also rose dramatically, from 11.5 lakh to 15.51 lakh during this timeframe. This alarming increase highlights the need for robust measures to enhance payment security.




