8 October 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
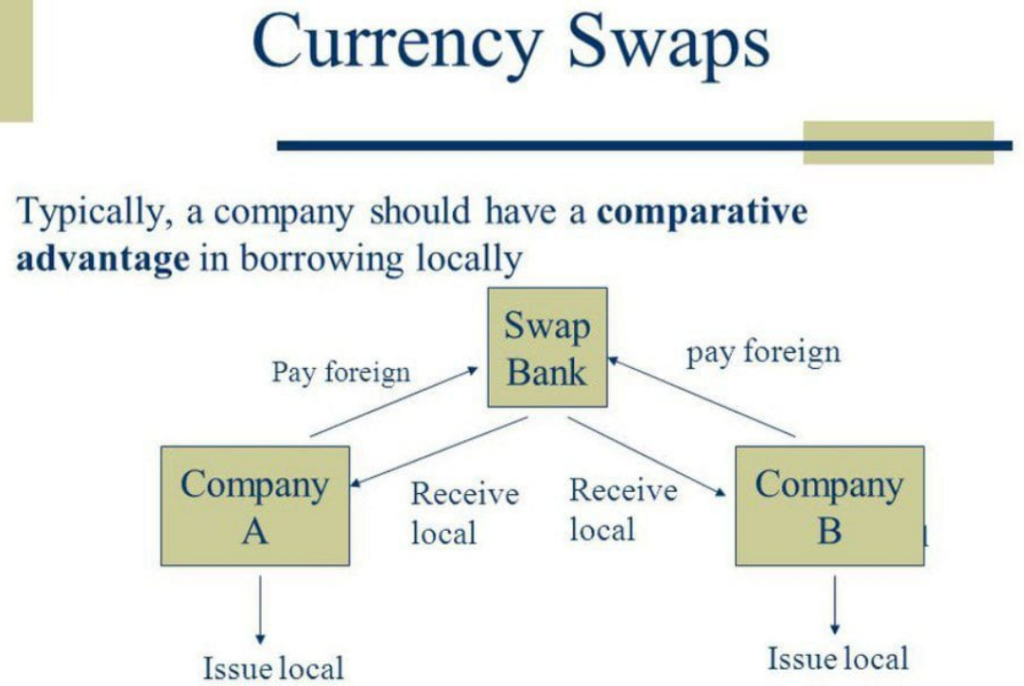
1. India signs $750-mn currency swap deal with forex-starved Maldives
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Topic: GS2 – International relations |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the News
| Currency Swap Agreement |
|
|
How this helps Maldives
- Foreign Exchange Stability: The swap agreement will help Maldives stabilise its foreign currency reserves, which are critically low, thus ensuring liquidity for international trade and payments.
- Economic Recovery: With increased access to foreign currency, the Maldives can manage its foreign debt repayments more effectively, aiding in long-term economic recovery.
- Boost Tourism: The agreement signals confidence in the Maldives’ economic stability, encouraging tourism—especially from India—one of its largest revenue sources.
- Infrastructure Development: The financial assistance and ongoing projects like the construction of homes and the airport runway will stimulate job creation and infrastructure growth.
- Strengthened Bilateral Ties: The agreement reaffirms India’s commitment as a reliable partner, offering not just financial support but also collaboration in security and trade sectors.
| Practice Question: Examine the evolving dynamics of India-Maldives relations in the context of recent engagements. How do these developments reflect India’s role as a “First Responder” in the region? (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. Genome editing is bringing clarity to the study of hereditary cancers
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
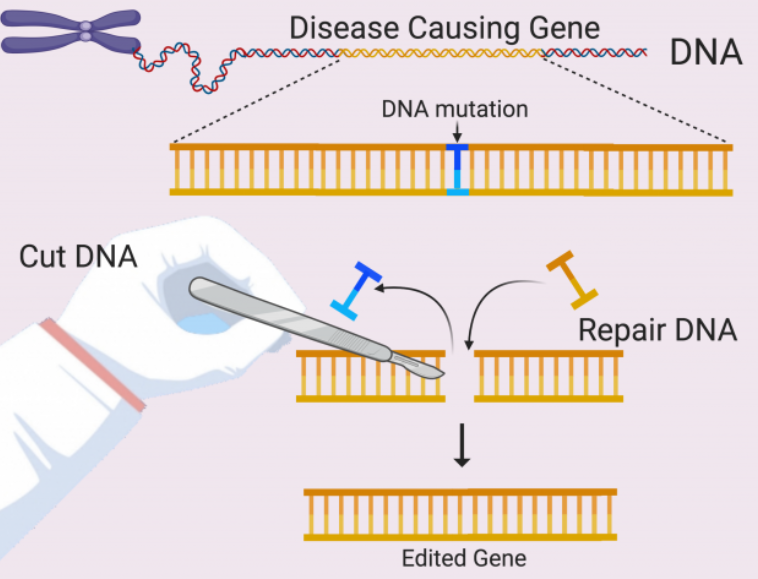
| What Is Genetic Editing? |
|
|
How Genetic Editing Can Help in Cancer:
- Correcting Mutations: Genetic editing can target and correct specific mutations responsible for causing cancer.
- Identifying Drug Targets: It allows researchers to understand the role of genes in cancer progression and identify new drug targets.
- Personalised Therapies: Genetic editing can be used to develop therapies tailored to an individual’s genetic profile, improving treatment outcomes.
- Drug Resistance: By studying cancer cells’ responses to treatments, genetic editing can help overcome drug resistance in therapies like chemotherapy.
- Early Detection: Gene editing tools can help identify early genetic changes that predispose individuals to cancer, enabling preventive measures.
| Practice Question: Discuss the potential of genetic editing technology like CRISPR in revolutionising cancer treatment. What are the ethical and regulatory challenges associated with its widespread adoption in medical science? (150 Words /10 marks) |
3. On ‘casteist’ provisions in prison manuals
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context |
|
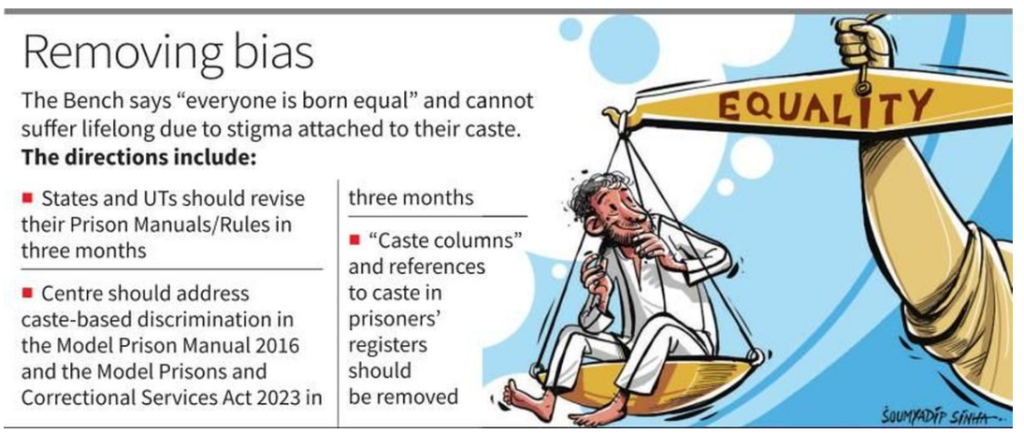
Colonial Legacy in Prison Manuals
- The court noted that prison manuals continued to reinforce colonial stereotypes, such as labelling certain communities as “habitual offenders.”
- These stereotypes originated from colonial laws like the Criminal Tribes Act, 1871, which stigmatised marginalised communities.
Fundamental Rights Violation
- The court ruled that using caste as a basis for segregation and labour division in prisons violated Article 14 of the Constitution, which guarantees equality before the law.
- Assigning cleaning duties to marginalised castes while reserving cooking for higher castes was considered direct discrimination under Article 15(1).
- These practices were also seen as perpetuating untouchability, prohibited by Article 17, and restricting prisoners’ right to dignity and reformation.
Court Directions and Reforms
- The Supreme Court directed all States and Union Territories to amend their prison manuals within three months to eliminate such discriminatory practices.
- It also ordered reforms to the Union government’s Model Prison Manual, 2016, and the Model Prisons and Correctional Services Act, 2023, to address similar issues.
- District legal services authorities and boards of visitors were instructed to ensure compliance through regular inspections.
| Practice Question: Discuss how caste-based practices in prison labour violate constitutional provisions. What measures can be taken to ensure equality and dignity for all prisoners? (150 Words /10 marks) |
4. How high-performance buildings are the next step towards a sustainable future
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 11)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy – Infrastructure |
| Context |
|
Importance of Sustainability in the Building Sector
- Buildings contribute significantly to global emissions, especially in rapidly growing cities.
- They account for 40% of total global energy consumption over their lifespan, leading to about 28% of energy-related carbon emissions.
- In India, buildings use over 30% of national energy and generate 20% of carbon emissions.
- As urbanisation increases, the demand for sustainable construction becomes more urgent to meet climate goals.
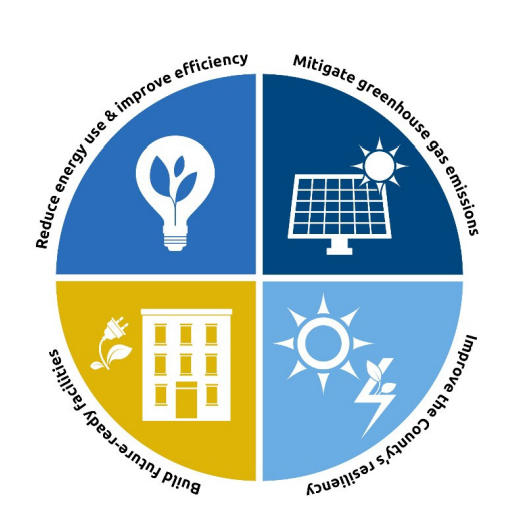
| High-Performance Buildings (HPBs) |
|
|
Benefits of High-Performance Buildings
- HPBs offer both environmental and operational benefits, helping buildings achieve long-term efficiency.
- Smart systems enable continuous monitoring, ensuring resource optimization and extending the lifespan of building systems.
- These buildings have higher property values and lower maintenance costs due to better design and automation.
- They also promote occupant well-being through superior air filtration, natural light, and thermal comfort.
HPBs and Urban Development in India
- HPBs help cities manage resource scarcity and rising temperatures by promoting resilience and self-sufficiency.
- They reduce the strain on public infrastructure and foster healthier indoor environments.
- By adopting HPBs, India can transition to a low-carbon economy while addressing the challenges of rapid urbanisation.
- HPBs are future-proof investments, delivering value while addressing environmental and economic pressures.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of high-performance buildings (HPBs) in promoting sustainable urban development in India. How can the adoption of HPBs help in rapidly urbanising regions? (250 Words /15 marks) |
5. Amazon River Faces Historic Low Water Levels as Climate Change-Induced Droughts Disrupt Transportation and Ecosystems
(Source: Indian Express; Section: The World)
| Topic: GS3 – Environment |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Impact on Transportation and Commerce
- The Amazon River, a crucial transportation route for remote regions in South America, has become gridlocked due to the severe drop in water levels. The drought has hampered the movement of people and goods, leaving boats unable to operate effectively.
- Communities, especially in the Brazilian state of Amazonas, are struggling to transport children to school, rush sick individuals to hospitals, and deliver essential supplies like medicine and drinking water.
- The city of Manaus, an important manufacturing hub, faces supply chain disruptions as shallow waters make it difficult for cargo ships to dock.
What is Dredging?
- Dredging is the removal of sediments and debris from the bottom of lakes, rivers, harbors, and other water bodies.
- It is a routine necessity in waterways around the world because sedimentation—the natural process of sand and silt washing downstream—gradually fills channels and harbors.
Dredging as an Unprecedented Solution
- In response to the crisis, Brazil has taken the extraordinary measure of dredging the Amazon River to ensure navigability during droughts.
- The dredging plan, initially used only in emergencies, will now be a continuous operation for the next five years. This effort reflects the global shift towards drastic measures to mitigate the impacts of extreme weather on daily life and transportation systems.
- The initiative underscores the harsh reality of climate change and its profound effects on vital ecosystems.
The Wider Implications of Climate Change on the Amazon
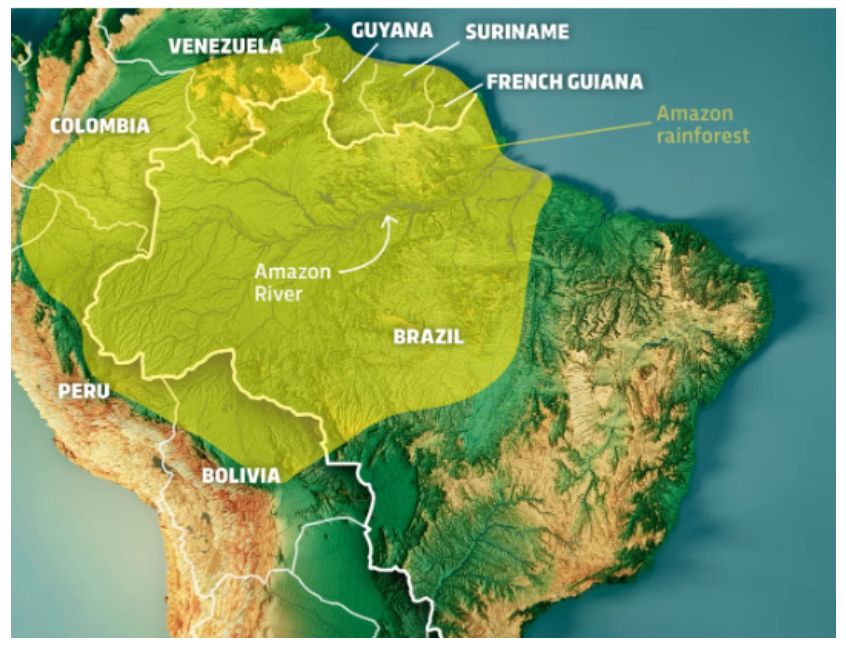
- The drying of the Amazon River also highlights the broader implications of climate change on the Amazon rainforest, which serves as the planet’s largest freshwater reservoir and plays a critical role in absorbing greenhouse gases.
- The ongoing droughts and their impact on the river ecosystem illustrate how a hotter, drier climate is reshaping not only the Amazon but also the global fight against climate change.
- As Brazil prepares for chronic drought conditions, it becomes clear that long-term solutions are necessary to protect this vital region.
| Amazon Rainforest |
|
| Practice Question: Analyze the impact of climate change on the Amazon River, focusing on the implications of record-low water levels and the broader ecosystem. What measures are being implemented to address these challenges, and what do they signify about the future of climate adaptation strategies in vulnerable regions? (150 words/10 m) |
6. India’s Farm Sector Growth Driven by Livestock and Fisheries, Crop Growth Lags: NITI Aayog Report
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 14)
| Topic: GS3– Agriculture |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
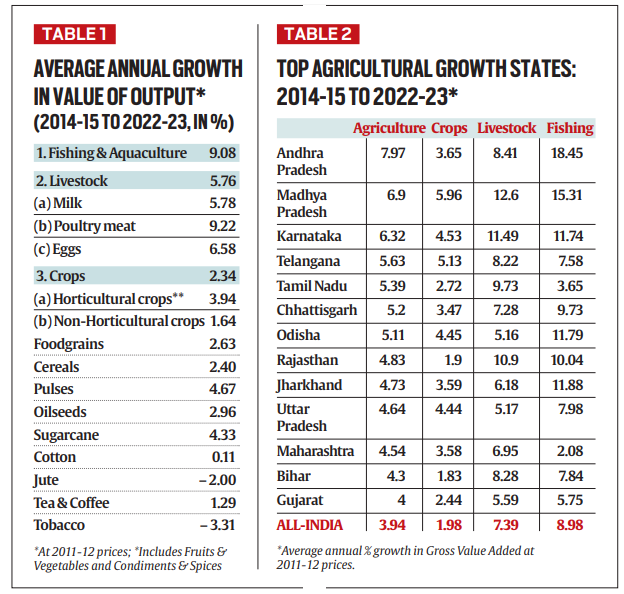
Subsector Performance Variations
- Agriculture growth under the Modi government has been primarily driven by the livestock and fisheries sectors, which recorded annual growth rates of 5.8% and 9.2%, respectively.
- In contrast, crop output grew by only 2.3%, lower than the 3.4% growth seen during the UPA period. Non-horticulture crops, such as cotton, jute, and tobacco, saw minimal growth, whereas poultry, fisheries, and horticulture performed better.
Regional Disparities
- Thirteen states, including Madhya Pradesh and Telangana, achieved over 4% annual agriculture growth from 2014-2023, largely due to livestock and fisheries.
- In contrast, agriculturally prominent states like Punjab, Haryana, and West Bengal saw slower growth, particularly in crop production.
Diversification and Market-Driven Growth
- The report attributes the sector’s growth to diversification into horticulture, livestock, and fisheries, driven by increasing consumer demand for protein-rich foods like vegetables, fruits, milk, and meat.
- New technologies, such as hybrid seeds and improved irrigation, have supported this shift. However, the benefits of diversification are uneven, with field crops seeing limited gains despite government support through Minimum Support Price (MSP) regimes.
Policy Implications
- The paper concludes that demand-side factors and advancements in production technology have been more effective in boosting agricultural growth than government subsidies or price interventions, especially in subsectors like livestock and horticulture.
- The need for targeted policy measures to enhance productivity in field crops remains a challenge.
| PYQ: Livestock rearing has a big potential for providing non-farm employment and income in rural areas. Discuss suggesting suitable measures to promote this sectors in India. (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2015) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the recent growth trends in India’s agriculture sector, with a focus on the role of livestock and fisheries. How do these trends highlight the challenges and opportunities for traditional crop farming? Evaluate the effectiveness of current policies in addressing these challenges. (150 words/10 m) |
Prelims Facts
1. India slipped on academic freedom index over the past decade: report
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- India’s academic freedom has sharply declined over the past 10 years, dropping from 0.6 to 0.2 points on the Academic Freedom Index from 2013 to 2023.
- India now ranks as “completely restricted,” the lowest since the mid-1940s.
- Major concerns include political control over universities and policies limiting student protests, particularly under the current ruling party.
- Restrictions on student expression were implemented by several universities, barring protests in academic spaces.
- The report highlighted ongoing conflicts between the central and state governments over control of higher education.
- Academic restrictions and government influence in states like Kerala, Tamil Nadu, West Bengal, and Punjab were noted.
- The global report documented 391 attacks on higher education communities across 51 countries between July 2023 and June 2024.
2. ‘miRNA ensures the correct set of genes is active in each cell type’
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 14)
| Context |
|
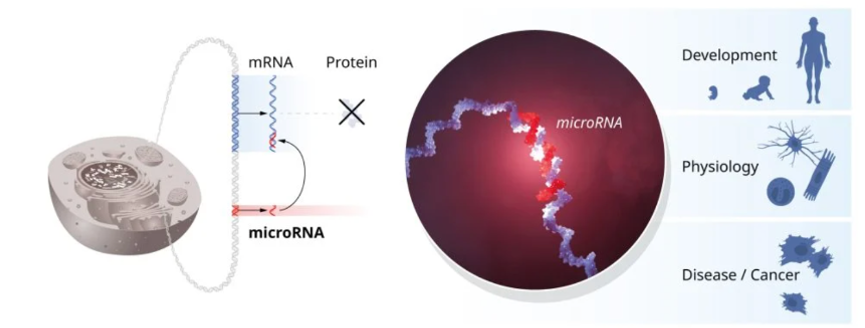
Nobel Prize In Medicine For 2024:
- Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun discovered microRNA (miRNA), a key regulator in gene activity.
- Before this, biologists believed that gene expression wasn’t controlled after transcription began.
- miRNA helps control which genes are active in specific cell types, allowing different cells like muscles or nerves to perform specialised functions.
- Defects in miRNA can cause diseases, including cancer, autoimmunity, and disorders related to sight, hearing, and growth.
- Their discovery opened a new layer of understanding in gene regulation and disease.
- Scientists are now researching if targeting miRNA can treat or prevent certain conditions.
- Their work also connects to the findings of Andrew Fire and Craig Mello, 2006 Nobel winners, who found a similar RNA process used by plants to fight viruses.

3. Bilateral Investment Treaty between India and the United Arab Emirates, comes into effect
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2062692®=3&lang=1 )
| Context |
|
Present Status:
- The Bilateral Investment Treaty (BIT) between India and the UAE was signed on February 13, 2024, in Abu Dhabi.
- The BIT came into effect on August 31, 2024, continuing investment protection after the expiration of the previous Bilateral Investment Promotion and Protection Agreement (BIPPA) on September 12, 2024.
- The UAE accounts for 3% of total Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in India, with approximately $19 billion invested from April 2000 to June 2024.
- India has invested about $15.26 billion (5% of total Overseas Direct Investments) in the UAE from April 2000 to August 2024.
How This BIT Aims to Increase Bilateral Investments?
- The BIT aims to boost investor confidence by ensuring minimum standards of treatment and non-discrimination.
- It provides an independent forum for dispute resolution through arbitration while balancing the state’s regulatory rights.
- Key features include a closed asset-based definition of investment, obligations against denial of justice, and exceptions for taxation and local governance.
- The treaty protects investments from expropriation, emphasises transparency, and mandates the exhaustion of local remedies for three years in dispute cases.
4. Indian Wild Ass Population in Gujarat Increases by 26.14% in Four Years, Reaching 7,672: WAPE 2024
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 12)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:

Key Facts about Indian Wild Ass:
- It is a sub-species of Asian Wild Ass, i.e., Equus hemionus.
- Scientific name: Equus hemionus khur
- It is characterized by distinctive white markings on the anterior part of the rump and on the posterior part of the shoulder and a stripe down the back that is bordered by white.
- Distribution: World’s last population of Indian WildAss is restricted to Rann of Kachchh, Gujarat.
- Habitat: Desert and grassland ecosystems.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN: Near threatened.
- CITES: Appendix II
- Wildlife Protection Act (1972): Schedule-I
District-Wise Population Distribution
- The latest WAPE data reveals that the highest number of wild asses were recorded in Surendranagar (2,705), followed by Kutch (1,993), Patan (1,615), Banaskantha (710), Morbi (642), and Ahmedabad (7).
- Patan, Kutch, and Surendranagar districts have seen significant growth since 2020, while populations in Morbi, Banaskantha, and Ahmedabad have declined.
Modern Enumeration Techniques
- The WAPE-2024 survey, conducted over 15,510 square kilometers, adopted the Direct Count Method.
- Enumerators were trained in traditional methods and provided with modern technology like drones, camera traps, and the e-Guj forest module, enhancing the accuracy of the census.
Broader Wildlife Census
- Along with the Indian Wild Ass, other species such as the Asian antelope, Indian gazelle, blackbuck, wild boar, and Indian jackal were also surveyed.
- The census recorded 2,734 Asian antelopes, 915 wild boars, 222 Indian hares, 214 Indian gazelles, and 153 Indian jackals.
5. Marburg Virus Outbreak Strains Rwanda’s Healthcare System
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 14)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
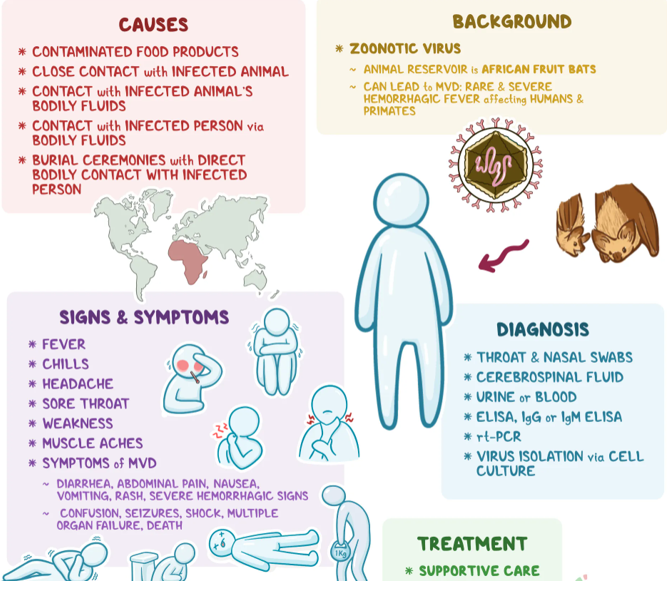
What is the Marburg Virus?
- Marburg virus is a highly fatal pathogen from the filovirus family, which includes Ebola. Marburg virus disease (MVD) has a case fatality rate between 24% and 88%, depending on the virus strain and medical response.
- The first outbreak was in Marburg, Germany, in 1967, and most subsequent outbreaks have occurred in Africa.
How Does MVD Spread?
- The virus originally spreads to humans through exposure to Rousettus bats. Human-to-human transmission occurs via direct contact with infected bodily fluids or contaminated materials.
- Medical workers are especially vulnerable during outbreaks due to the lack of stringent infection control.
Symptoms of MVD
- The incubation period ranges from 2 to 21 days. Early symptoms include high fever, severe headaches, muscle pain, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Hemorrhagic symptoms, such as internal and external bleeding, develop in many patients, leading to death within 8–9 days in severe cases due to blood loss and shock.
Prevention and Treatment
- There are no approved vaccines or specific treatments for MVD. Supportive care, such as rehydration and symptom management, improves survival.
- Rwanda’s health ministry is exploring experimental vaccines and treatments, with 700 doses of an experimental Marburg vaccine being provided to frontline healthcare workers.