9 December 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Oilfields Amendment Bill, 2024
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 14)
| Topic: GS2 – Polity |
| Context: |
| The article discusses about the Oilfield Bill which was recently passed by Rajya Sabha. |
Analysis of News:

What is the Oilfields Bill?
- The Oilfields Bill amends the Oilfields (Regulation and Development) Act of 1948, which originally governed both oil and mineral operations.
- The amendment seeks to delineate the regulation of petroleum from mining activities, aligning it more closely with contemporary needs in the oil and gas sector.
- By doing so, it aims to boost domestic production and reduce reliance on imports.
Key Provisions of the Oilfields Bill
Definition of Mineral Oil
- The Bill defines “mineral oils” comprehensively, encompassing hydrocarbons like crude oil, natural gas, and petroleum in various forms.
- It excludes resources like coal, lignite, and helium associated with coal or shale, which remain under the Mines and Minerals Act.
Petroleum Leases
- The Bill introduces “petroleum leases” as a replacement for “mining leases.” These leases cover activities like prospecting, exploration, development, production, and disposal of mineral oils.
- It aligns with the goal of clearly demarcating the regulatory framework for petroleum operations.
Private Investment and Lease Protections
- Provisions in the Bill encourage private sector participation by safeguarding existing mining leases and offering guarantees against adverse changes during the lease period.
- It removes criminal penalties for violations and replaces them with higher financial penalties, fostering a more investment-friendly environment.
Criticisms and Concerns
Impact on State Rights
- Critics argue that reframing the Act’s focus from mining leases to petroleum leases could diminish state powers to tax and collect royalties from petroleum activities, potentially shifting control to the Union under Entry 53 of the Union List.
- Despite assurances from the Union Minister, concerns about reduced state autonomy persist.
Environmental Risks
- The push for private sector involvement raises questions about environmental safeguards. Opposition members have emphasized the need to prioritize public sector enterprises like ONGC, which have stricter environmental oversight, over private companies.
Demand for Greater Scrutiny
- Some opposition leaders, such as DMK MP N R Elango, have called for the Bill to be reviewed by a select committee, citing apprehensions about its implications for federal structure and state interests.
Conclusion
- The Oilfields (Regulation and Development) Amendment Bill, 2024, represents a significant policy shift aimed at enhancing domestic petroleum production and fostering private investment.
- However, its potential to centralize regulatory power, impact state revenues, and pose environmental challenges requires careful scrutiny and balanced implementation.
| Significance of the Amendment |
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the key provisions and implications of the Oilfields (Regulation and Development) Amendment Bill, 2024. (250 words/15 m) |
2. Study brings Indian star tortoise to evidence-based conservation
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
| Indian Star Tortoise |
|
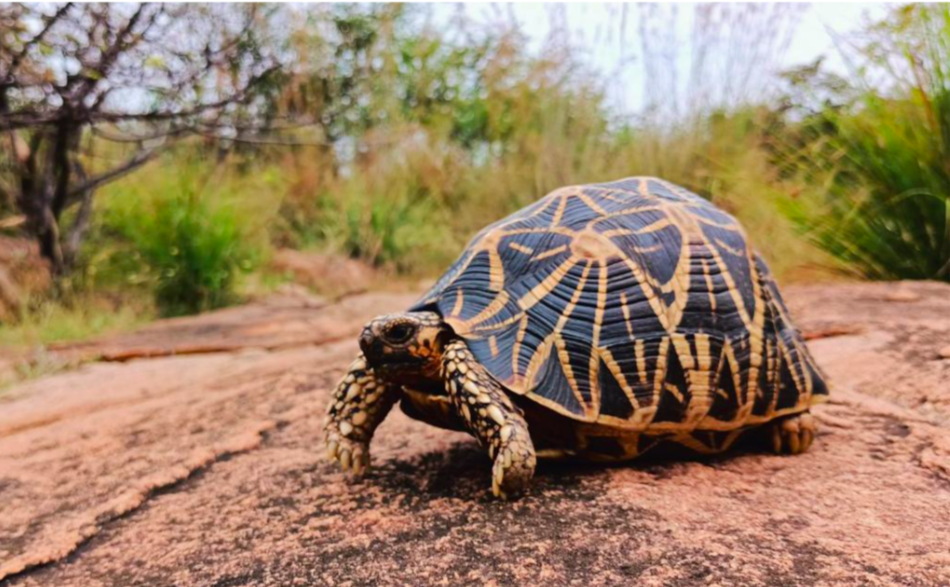
Appearance The Indian star tortoise (Geochelone elegans) is known for its striking obsidian shell adorned with sun-yellow star patterns. The shell itself is quite domed and can grow up to 10 inches long. They have strong, sturdy legs to help them navigate their dry, scrubland habitats. Their coloration helps them blend in with their surroundings, providing camouflage from predators. It is a herbivore and popular as an exotic pet, though it is illegal and unethical to own one in India, as the species is vulnerable in the wild. Habitat and Global Presence Endemic to northwest India, South India, and Sri Lanka, the species has been found in countries as distant as Canada and the U.S. Increasing demand as pets has led to its involvement in one of the largest global wildlife trafficking networks.
Legal Protection The Indian star tortoise is listed in Appendix I of CITES and in Schedule I of India’s Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, ensuring the highest legal protection. Despite this, hundreds of tortoises have been seized at airports and borders, highlighting the persistent trafficking problem. |
Concerns Over Unscientific Release
- The unscientific release of confiscated tortoises is a concern, as it could worsen their fate.
- The focus is now on finding alternative methods of releasing and conserving them.
- A study was conducted to understand the diversity and natural distribution of the tortoises through genomic sequencing of samples from various locations.
Genetic Differentiation of Tortoise Groups
- The study identified two genetically distinct groups of Indian star tortoises: one from the northwestern region and the other from the southern region of India.
- The genetic divergences correspond to differences in physical features, which can guide the strategies for conserving and releasing rescued tortoises.
Evolutionary History
- Millions of years ago, the Indian star tortoise group spread across the subcontinent after it separated from Gondwana.
- This led to the splitting of the species into northern and southern groups about 2 million years ago.
Findings and Conservation Implications
- The study revealed that the northwestern group remains genetically stable, while the southern group has higher genetic diversity.
- The findings confirm the presence of two distinct evolutionary significant units (ESUs), which are important for conservation efforts.
- It is essential to avoid mixing these populations during releases, as it could reduce genetic diversity and affect breeding success.
Conclusion
- The study’s findings provide vital information for both national and international conservation efforts, helping to ensure a scientifically sound approach to the conservation of the Indian star tortoise.
| Practice Question: Discuss the conservation challenges faced by the Indian star tortoise, focusing on the implications of illegal wildlife trade, unscientific releases. Highlight the importance of genetic research in formulating conservation strategies. (150 Words /10 marks) |
3. India’s Digital Revolution: Transforming Infrastructure, Governance, and Public Services
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2082144®=3&lang=1 )
| Topic: GS2 – Governance, GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context |
|
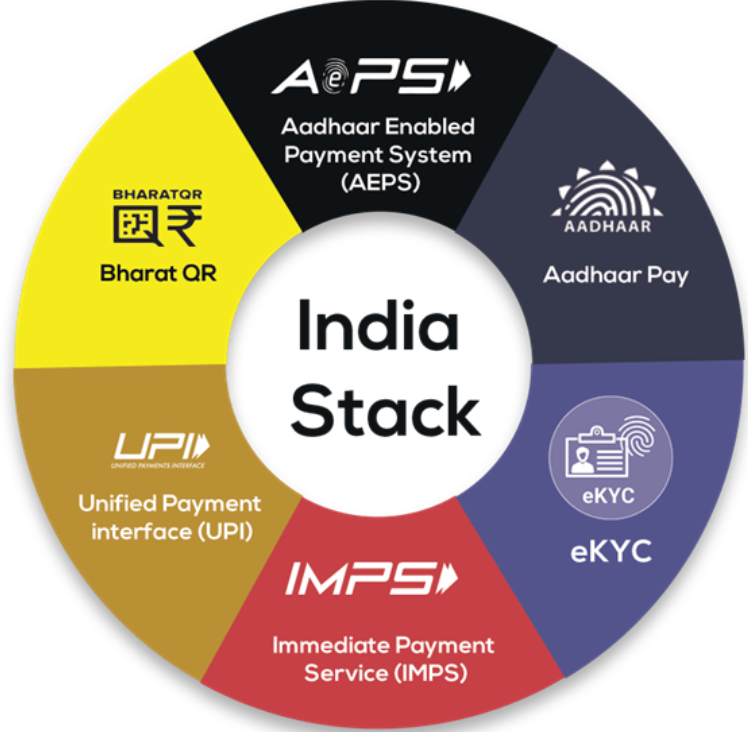
India’s Digital Public Infrastructure
India’s Digital Infrastructure Landscape
- India has rapidly evolved as a global leader in digital adoption, driven by innovations in cloud computing, AI, machine learning, and digital governance.
- The country’s digital infrastructure aims to ensure accessibility, scalability, and security in delivering government services and fostering economic growth.
Expansion of Data Centres
- Data centres are essential for supporting India’s increasing demand for cloud computing and data storage.
- The National Informatics Centre (NIC) has set up National Data Centres (NDC) in cities like Delhi, Pune, Bhubaneswar, and Hyderabad, offering cloud services to various government entities.
- These data centres provide disaster recovery and hosting services, with storage capacities expanding to approximately 100PB.
- The NDC-North East Region (NDC-NER), launched in 2020, aims to bridge the digital divide in Northeast India.
Enhancing Cloud Services: NIC and MeghRaj
- The NIC National Cloud Services project, launched in 2022, upgrades cloud infrastructure to support over 300 government departments.
- The GI Cloud (MeghRaj) initiative ensures the optimal use of IT infrastructure and accelerates the development of e-Gov applications, including digital payments and data sharing.
Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)
- DPI plays a critical role in transforming India’s digital economy, with key initiatives like Aadhaar, UPI, DigiLocker, and DIKSHA.
- Aadhaar, with over 138 crore registrations, provides a digital identity to citizens.
- UPI has facilitated 24,100 crore transactions, enhancing financial inclusion.
- DigiLocker has served 37 crore users for digital document verification.
- DIKSHA is the world’s largest education platform, with over 556 crore learning sessions.
National Knowledge Network (NKN)
- NKN connects national and state data centres, promoting resource sharing and collaborative research, with 1,803 institutional links and 637 district centre links.
Common Services Centres (CSCs)
- With over 5.84 lakh CSCs operational – this initiative brings essential e-services to rural India, including government schemes, education, telemedicine, and financial services.
Citizen-Centric Digital Services
- UMANG, with over 7.12 crore users, simplifies access to government services across various sectors.
- Platforms like MyGov and API Setu encourage citizen engagement and open data exchange, facilitating over 312 crore transactions.
Revolutionizing Government Operations
- Platforms like DigiLocker and GovDrive have transformed document management, enabling paperless governance.
- The Gov Intranet Platform streamlines workflow management for government officials, ensuring efficient communication and coordination.
Conclusion
- India’s digital infrastructure is revolutionizing governance and public service delivery, positioning the nation as a global leader in digital innovation.
- Through initiatives like Aadhaar, UPI, and DigiLocker, India is creating scalable digital solutions that empower citizens and promote socio-economic growth.
| PYQ: How have digital initiatives in India contributed to the functioning of the educational system in the country? Elaborate your answer. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2020) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the role of Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) in enhancing governance and socio-economic development in India. Highlight key initiatives like Aadhaar, UPI, and MeghRaj in this context.(250 Words /15 marks) |
PRELIMS FACTS
1. Moths Use Plant Sounds to Choose Egg-Laying Sites, Study Finds
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 14)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:

Study Overview
Research and Objectives
- The study, conducted by a team of 17 researchers from Israel, examined how Egyptian cotton leafworm moths respond to the ultrasonic clicks emitted by stressed plants.
- This research builds on previous findings that plants emit ultrasonic sounds when dehydrated or under stress.
Experimental Setup
- Researchers placed two healthy tomato plants in an experimental arena, one emitting recorded distress sounds and the other silent.
- They observed the oviposition (egg-laying) behavior of female moths to understand their decision-making process.
Key Findings
Preference for Silent Plants
- The study found that moths consistently preferred to lay their eggs on the silent plant.
- This behavior suggests that moths are not only capable of detecting plant-generated sounds but also interpreting these signals as indicators of plant health.
Ecological Implications
- By avoiding stressed plants, moths enhance the survival chances of their offspring, as healthy plants are more likely to provide adequate nourishment for the larvae.
- This highlights the evolutionary significance of such acoustic communication.
Expert Opinions and Unanswered Questions
Validation of Findings
- Experts have praised the robustness of the study, emphasizing the strong evidence provided for moths’ responsiveness to plant sounds.
Open Questions
- While the study establishes that moths attend to these sounds, the exact reason for this behavior—whether it is a direct response to stress signals or a learned association—remains unclear and requires further investigation.
2. Militants in Syria capture Damascus as Assad flees
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Context |
|
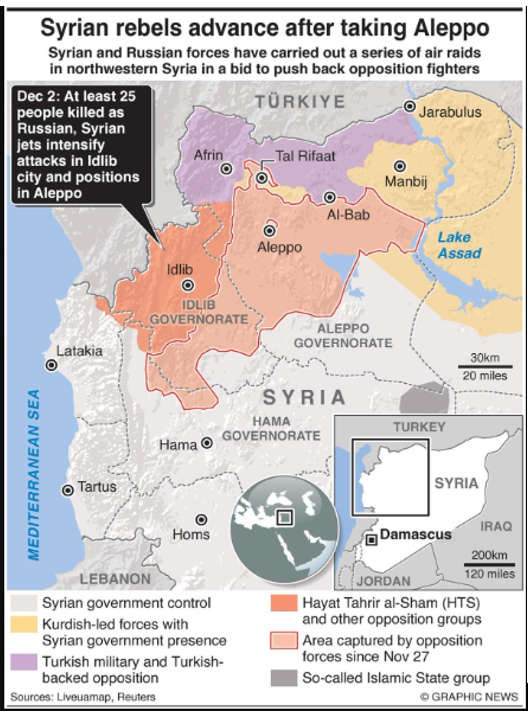
Analysis of the news:
- Hayat Tahrir al-Sham (HTS) militants seized control of Damascus, ending President Bashar al-Assad’s 13-year rule in Syria after a prolonged civil war.
- President Assad reportedly fled Damascus, with Russian sources stating he and his family are now in Moscow.
- The ouster marked a significant blow to the influence of Russia and Iran, Assad’s key allies during the conflict.
- Iran’s embassy in Damascus was stormed by HTS militants following their capture of the capital.
- Prime Minister Mohammad Ghazi al-Jalali called for free elections and engaged with HTS leader Abu Mohammed al-Jolani to discuss a transitional government.
- HTS, formerly an al-Qaeda affiliate, severed ties with the group in 2016 and is Syria’s strongest militant group.
- Concerns persist over HTS’s potential for Islamist rule and attacks on Kurdish-led forces, drawing resistance from the U.S. and regional powers.
| Places in news |
|
Damascus: Syria’s capital, a historic city, became the center of a power shift as HTS militants seized control. Hama: Syrian city where the Army claims to be continuing operations against militant groups despite losing other key territories. Homs: A major city in Syria, recently captured by militants, marking a significant advance in the civil war. Deraa: Southern Syrian region where Army operations against “terrorist groups” are reportedly ongoing amid militant advances. Manbij: Northern Syrian town under attack by HTS militants targeting U.S.-allied Kurdish-led forces. Saydnaya: Site of a notorious prison near Damascus, where detainees were freed by HTS militants during their takeover. Aleppo: Syria’s largest city, recently captured by HTS, symbolizing a major militant victory during their rapid advances. |
3. Foreign direct investment inflows into India cross $1 tn
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Context |
| India has reached over $1 trillion in Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) from April 2000 to September 2024.This achievement highlights India’s growing stature as a secure and attractive investment destination globally. |
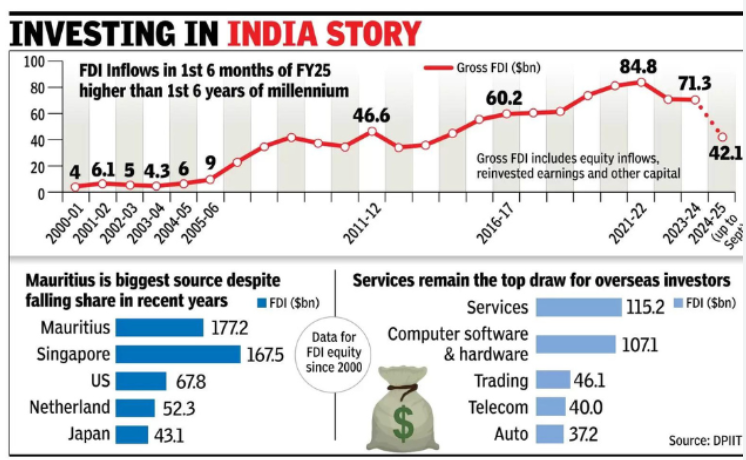
Analysis of the news:
- Foreign direct investment (FDI) inflows into India have surpassed $1 trillion during the April 2000 to September 2024 period.
- The cumulative FDI amount, including equity, reinvested earnings, and other capital, stands at $1,033.40 billion.
- This milestone reinforces India’s reputation as a safe and preferred global investment destination.
- The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) reported the latest figures, reflecting strong investor confidence.
- India’s consistent FDI growth is driven by reforms in the business environment, ease of doing business, and market potential.
- The sectors attracting significant FDI include services, computer software, telecommunications, and construction.
- India’s strong economic growth, large consumer market, and political stability contribute to this sustained investment inflow.



