9 July 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Hurdles in importing diamonds pose a quantum block to research ambition
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance, GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- The Customs Department’s diamond import decisions affect the National Quantum Mission (NQM), a ₹6,000-crore initiative for quantum technology.
- Quantum technology leverages “quantum-mechanical” properties to develop advanced computers, sensors, and encryption systems.
- Research in quantum technology is still evolving, requiring experiments involving diamonds.
- Quantum researchers value diamond “defects,” specifically nitrogen-vacancy centres, for their sensitivity to magnetic fields and potential as qubits in quantum computers.
| Qubits |
|
- Qubits enable calculations beyond the capability of current supercomputers.
- Researchers prefer lab-grown diamonds with specific defects, unlike jewellery-grade diamonds.
- The 2023 Union Budget announced a scheme for lab-grown diamond R&D, but India’s diamond industry is new to manufacturing these defect-specific diamonds.
- The Science and Technology Ministry aims to develop quantum computers with 50 to 1,000 qubits by the decade-end.
- Globally, quantum computers face challenges in maintaining qubit states, hindering their practical use.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the National Quantum Mission (NQM) in advancing India’s technological capabilities and global standing in quantum technologies. (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. Centre set to tweak criteria for according classical language status
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- The Union government plans to revise criteria for granting classical language status, based on recommendations from the Culture Ministry’s Linguistics Expert Committee.
- The new criteria will be issued after Cabinet approval, affecting the status of languages like Marathi.
- Marathi’s classical status has been under consideration, with repeated demands from States and literary circles for languages like Marathi, Bengali, Assamese, and Maithili.
- In 2014, Maharashtra’s then Chief Minister formed a committee, which concluded that Marathi meets the criteria for classical status.
- The Centre has assured consideration for Marathi’s status multiple times over the past decade.
- Classical language status entails Education Ministry support, including awards, a centre of excellence, and university chairs.
- With Maharashtra Assembly elections approaching, demands for Marathi’s status have intensified, with political efforts from both Congress and the Shiv Sena-BJP government.
| Classical Languages In India: |
|
India has six languages with classical status: Tamil (2004), Sanskrit (2005), Kannada (2008), Telugu (2008), Malayalam (2013), and Odia (2014).All classical languages are listed in the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution. The Ministry of Culture sets the guidelines for declaring a language as classical. Criteria for classical language status include:
Benefits provided by the Indian government for classical languages:
|
|
PYQ: Q. Which one of the following was given classical language status recently? (UPSC civil services prelims 2015) (a) Odia Ans: Option A |
|
Practice Question: Examine the significance of granting classical language status to regional languages in India and the implications of revising the criteria for such recognition. (150 Words /10 marks) |
3. What are new provisions for police officers?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context |
|
New Criminal Laws Implementation:
- Effective from July 1, 2023, new criminal laws were introduced with standard operating procedures (SOPs) issued by the Bureau of Police Research and Development (BPRD).
FIR Registration Rules:
- Zero FIR mandated; police cannot refuse to register based on jurisdiction disputes.
- FIR can be filed orally, in writing, or electronically, to be recorded by the officer within three days.
Videography Mandates:
- Mandatory videography during searches, crime scenes, and property seizures to ensure legal compliance.
- Use of ‘eSakshya’ mobile app for geo-tagged, time-stamped data capture in compliance with Inter-operable Criminal Justice System (ICJS).
Arrest Provisions:
- Information about arrests to be prominently displayed at police stations.
- Restrictions on arresting elderly or infirm persons without approval from a DySP or above.
- Handcuffs allowed only when necessary to prevent escape or harm, following Supreme Court guidelines.
Timelines and Procedures:
- Medical reports in rape cases to be forwarded within seven days.
- POCSO cases must be investigated within two months of reporting.
- Chain of custody for electronic devices emphasised for integrity; progress updates to informants/victims required within 90 days.
Terrorist Acts and Investigation:
- Section 113 defines ‘terrorist act’; SPs decide whether to invoke UAPA based on specified criteria.
- No explicit guidelines; factors include the nature of the accused and investigative requirements.
Challenges and Expectations:
- Requires sensitization of medical practitioners and police officers to new laws.
- Increased responsibility for cyber experts due to electronic evidence handling.
- Overall, aims to enhance legal compliance and transparency in criminal investigations.
| Practice Question: Discuss the impact of recent amendments in criminal laws on police procedures in India. How do these changes aim to enhance transparency and accountability in criminal investigations? (250 Words /15 marks) |
4. Hurricane Beryl Sets Record as Earliest Category 5 Storm Amid Rising Global Temperatures
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 14)
| Topic: GS1 – Geography |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Formation of Hurricanes
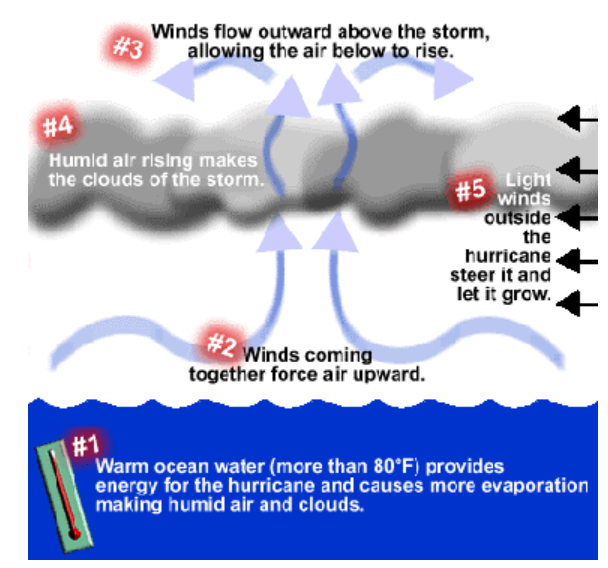
- Hurricanes, or tropical storms, form over warm ocean waters near the equator. When warm, moist air from the ocean surface rises, it creates a low-pressure area below.
- Air from surrounding areas with higher pressure rushes into this low-pressure zone, rising and becoming warm and moist. As this warm, moist air rises, it cools and forms clouds and thunderstorms.
- This system of clouds and winds strengthens, fueled by the ocean’s heat and evaporating water. When wind speeds reach 119 km/h or higher, the storm is classified as a hurricane.
- Hurricanes are categorized on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale from Category 1 to Category 5, based on their sustained wind speeds, with Category 5 hurricanes being the most severe.
Hurricane Beryl’s Unprecedented Development
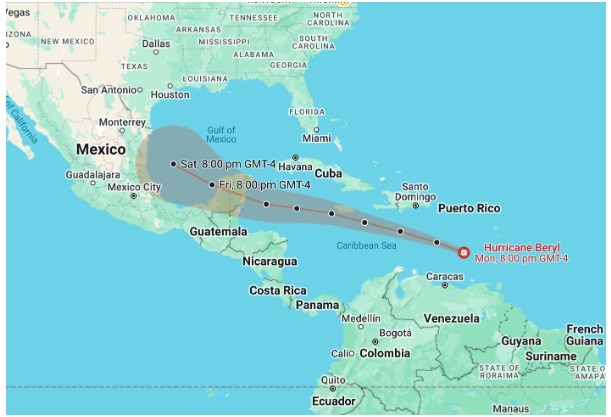
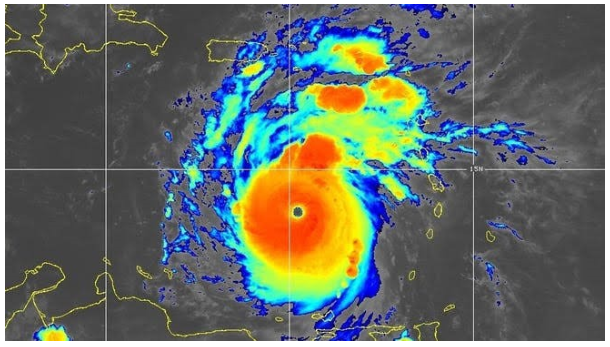
- Hurricane Beryl emerged as a tropical depression with winds of 56.3 km/h on June 28. Within 24 hours, it intensified into a hurricane and, over the next day, rapidly strengthened to become a Category 4 hurricane.
- This marked the first instance of a Category 4 hurricane forming in June. On July 1, Beryl made landfall on Grenada’s Carriacou Island as a Category 4 hurricane and continued to intensify, becoming a Category 5 hurricane on July 2.
- This made Beryl the earliest Category 5 hurricane recorded during the Atlantic hurricane season. Its peak winds reached 265.5 km/h, making it the strongest July Atlantic hurricane on record.
Factors Behind Early Intensification
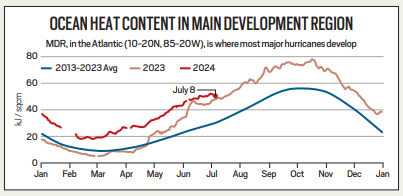
- The Atlantic hurricane season typically starts in June and lasts until November, with major hurricanes usually forming by September. The ocean is generally not warm enough at the surface or at deeper levels to fuel strong hurricanes until later in the season.
- However, Beryl’s early intensification is linked to unusually warm ocean temperatures, a phenomenon scientists attribute to global warming. Since last year, ocean temperatures in the Atlantic and globally have been at record-breaking levels.
- Sea surface temperatures and ocean heat content (OHC), which measures the heat present in ocean water, have significantly increased. The depth of warm water in the ocean plays a crucial role; deeper warm water means that hurricanes like Beryl can maintain their intensity by churning up more warm water, rather than cooler water that would typically reduce their strength.
Climate Change and Hurricane Intensity
- Scientists continue to study how climate change impacts hurricanes, but there is consensus that it contributes to rapid intensification, where maximum wind speeds increase quickly.
- The frequency and intensity of such events in the Atlantic have increased from 1971 to 2020, as noted in a 2023 study published in Nature. As global temperatures rise, the likelihood of more powerful hurricanes forming also increases.
- This trend suggests that extreme weather events like Hurricane Beryl could become more common in the future, posing significant challenges for affected regions.
Conclusion
- Hurricane Beryl’s early and unprecedented intensification underscores the complex interplay between ocean temperatures and hurricane formation. As climate change continues to warm the world’s oceans, the frequency and severity of such extreme weather events are likely to increase.
- Understanding these dynamics is crucial for preparing and mitigating the impacts of future hurricanes, ensuring communities are better equipped to handle such natural disasters.
| What is the difference between a hurricane and a tropical storm? |
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the unprecedented early intensification of Hurricane Beryl as the earliest Category 5 storm on record during the Atlantic hurricane season. Explain the factors contributing to its rapid development and analyze the role of climate change in influencing the frequency and intensity of hurricanes. What implications does this have for future hurricane preparedness and mitigation strategies? (250 words/15 m) |
5. Bihar Government Launches Bridge Maintenance Policy Amid Rising Incidents of Collapses
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt & Politics; Page: 08)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government policies – Interventions for development in various sectors GS3 – Disaster Management |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
What are the reasons for such incidents?
- Design: Faulty designs of infrastructure projects is responsible for accidents. Designs of coaches, highways, wagons, and bridges should be based on scientific guidelines.
- Poor maintenance: Infrastructure in India suffers from constant neglect from policymakers, officials, and people responsible for their work. Regular wear and tear leads to depreciating the life of the project and compromises safety. Eg: Morbi Bridge in Gujarat
- Improper safety and regulations: The regulations in place are not properly implemented and safety protocols are not deliberated upon leading to such accidents.
- Human error: Another major factor for the rise of such accidents is human error which could be due to negligence, fatigue, or even boredom.
- Lack of enforcement: Wilful flouting of norms and safety regulations by citizens and officials alike leads to mishaps that lead to loss of lives and destruction of property. There is no strict attitude to corruption and no strict penalty for those found guilty.
Implementation of the New Policy
- On the day of the policy rollout, Pratyaya Amrit, the additional chief secretary of the road construction department, emphasized the policy’s importance.
- The policy, drafted by the Bihar Rajya Pul Nirman Nigam Limited (BRPNNL), mandates that various departments issue “health cards” for bridges, detailing inspection and maintenance records. This requirement extends to bridges funded by MPs and MLAs.
Scope and Responsibilities
- The policy covers approximately 6,200 bridges constructed since 2005, coinciding with Nitish Kumar’s tenure as chief minister.
- While the BRPNNL will oversee the maintenance of major bridges, the respective departments will be responsible for maintaining other bridges.
- The policy also stipulates biannual physical and video inspections, with at least one inspection required before the monsoon season.
- Inspections related to desilting exercises must be supervised by experts and senior engineers.
Accountability and Expertise
- The policy aims to ensure accountability at all levels, from chief engineers to junior engineers.
- For larger bridges, the state may hire consultants to assist with maintenance. The department has studied maintenance policies from various countries to develop a robust framework suited to Bihar’s needs.
- The state boasts around 30 large bridges and 1,200 bridges over 60 meters in length.
Conclusion
- Bihar’s new bridge maintenance policy represents a significant step towards addressing the state’s infrastructure challenges.
- By mandating regular inspections, detailed maintenance records, and accountability, the policy aims to prevent future bridge collapses and restore public confidence in the state’s infrastructure.
- However, the successful implementation of this policy will require sustained effort and vigilance from all involved parties.
| What are measures needed to ensure safety in these projects? |
|
Politicians-contractor nexus:
Accountability:
Strict implementation of rules/protocols:
Training:
|
| Practice Question: Analyze the recent policy rollout by the Bihar government aimed at addressing the frequent collapse of bridges in the state. How can effective implementation of this policy contribute to better accountability and governance in the state’s public works sector? (250 words/15 m) |
6. India to Sign and Ratify High Seas Treaty for Ocean Conservation
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 12)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations – Agreements involving India or affecting India’s interests. |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Understanding the High Seas Treaty
- The High Seas Treaty, officially known as the agreement on Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdictions (BBNJ), was negotiated in March of the previous year.
- The high seas refer to ocean areas outside the national boundaries of countries, making up approximately 64% of the ocean surface. These areas are considered international commons, accessible to all and governed by international and regional laws.
- The most notable of these laws is the UN Convention on the Law of the Seas (UNCLOS), which outlines the rights and duties of countries and establishes general principles for acceptable conduct in the oceans.
- Once ratified, the High Seas Treaty will operate under the UNCLOS framework, becoming one of its implementing instruments.
Key Provisions of the High Seas Treaty
- The High Seas Treaty aims to define and establish marine protected areas in biodiversity-rich zones that are under stress.
- It also seeks to ensure that benefits derived from ocean life forms, such as drug development, are considered global commons, free from intellectual property rights, and equitably shared among all.
- The treaty will become international law 120 days after at least 60 countries submit their ratification documents.
- As of now, 91 countries have signed the treaty, but only eight have ratified it.
- The treaty’s implementation will mark a significant milestone in global efforts to protect ocean biodiversity and promote sustainable use of marine resources.
| What are the Other Conventions related to Seas? |
|
Convention on Continental Shelf 1964:
Convention on Fishing and Conservation of Living Resources of the High Seas 1966:
London convention 1972:
MARPOL Convention (1973):
|
|
PYQ: With reference to the United Nations Convention on the Law of Sea, consider the following statements: (2022 1) A coastal state has the right to establish the breadth of its territorial sea up to a limit not exceeding 12 nautical miles, measured from baseline determined in accordance with the convention. 2) Ships of all states, whether coastal or land-locked, enjoy the right of innocent passage through the territorial sea. 3) The Exclusive Economic Zone shall not extend beyond 200 nautical miles from the baseline from which the breadth of the territorial sea is measured. Which of the statements given above are correct? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (d) |
| Practice Question: What are the implications of India’s decision to sign and ratify the High Seas Treaty for global ocean conservation and biodiversity protection? (150 words/10 m) |
Prelims Facts
1. World’s oldest cave painting was created at least 51,000 years ago
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- Scientists discovered the world’s oldest-known confidently dated cave painting in Sulawesi, Indonesia, at least 51,200 years old.
- The painting, found in Leang Karampuang cave, depicts three human-like figures interacting with a wild pig.
- The Leang Karampuang painting shows cryptic interactions, with figures holding objects and engaging with the pig.
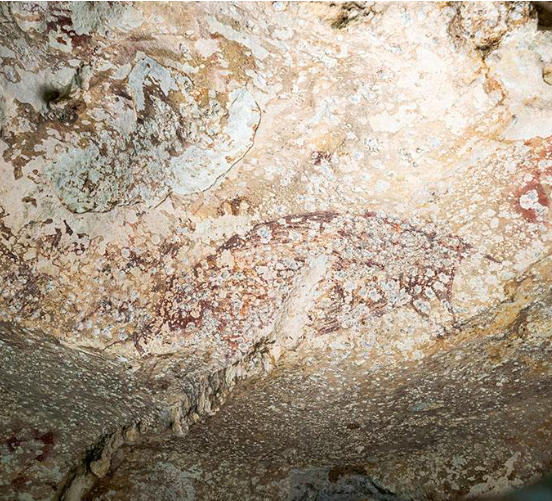

- Researchers used a laser to date calcium carbonate crystals on the painting, a significant advancement in rock art dating methods.
- The scene is painted in dark red pigment and is interpreted as the oldest-known evidence of storytelling in art.
- Another Sulawesi cave painting from Leang Bulu’ Sipong 4 was reassessed using the same method, dating it to at least 48,000 years old.
- These findings highlight the early human capacity for narrative storytelling through art.
2. In an electric vehicle, what is regenerative braking?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 11)
| Context |
| The concept of regenerative braking in vehicles, especially electric and hybrid types, involves converting kinetic energy during braking into reusable electrical energy, thereby enhancing energy efficiency and reducing reliance on traditional friction-based braking systems. |
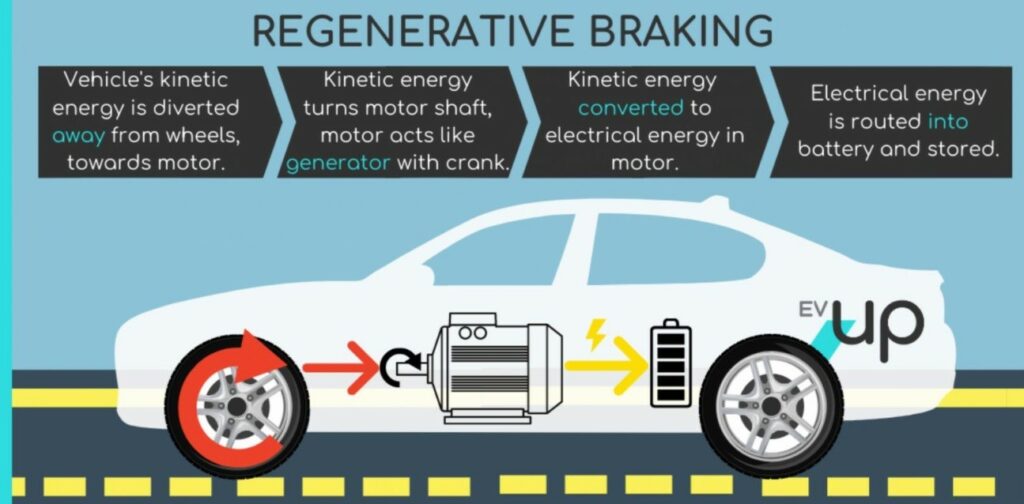
Analysis of the news:
- Definition: Regenerative braking is a mechanism used in vehicles, particularly electric and hybrid ones, to convert kinetic energy into a form that can be stored or reused.
- Purpose: It aims to improve energy efficiency by recovering energy during braking that would otherwise be lost as heat in traditional braking systems.
- Operation: When the vehicle brakes, the electric motor functions as a generator, converting mechanical energy back into electrical energy.
- Components: It involves components like the traction motor, which switches roles between propelling the vehicle and generating electricity during braking.
- Advantages: Enhances energy efficiency, extends battery range in electric vehicles, and reduces reliance on friction-based braking.
- Applications: Commonly used in electric cars, buses, trains, and some hybrid vehicles to maximise energy conservation and reduce emissions.
- Challenges: Limited effectiveness at low speeds and may require supplementary braking systems for complete vehicle control.
- Technological Variants: Includes systems like rheostatic braking and flywheel energy storage as alternatives or complements in different vehicle designs.
3. Govt. reopens PLI scheme for white goods till October 12
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 12)
| Context |
|
What are white goods?
- White goods refer to large household appliances such as refrigerators, washing machines, air conditioners, dishwashers, and other major kitchen appliances.
- They are called “white goods” due to their historical association with the colour white, which was predominant in their appearance.
- These appliances are typically durable and used for routine domestic tasks, contributing significantly to household comfort and efficiency.
- They are distinct from smaller appliances and are often considered essential in modern homes.
4. President Milei’s flagship economic reforms take effect in Argentina
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 14)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- Argentine President Javier Milei implemented economic reforms including privatisations, relaxed labour protections, and incentives for investment amid severe recession and protests.
- Reforms allow for declaring economic emergency, disbanding federal agencies, and privatising public companies.
- Critics, including left-wing opponents, oppose weakened labour protections as risking job security.
- Measures also include tax, customs, and foreign exchange incentives to stimulate investment amid the economic crisis.
- Milei’s government aims for zero budget deficit by 2024 through fiscal austerity, despite severe peso devaluation and economic contraction.
- Inflation has decreased due to reduced consumption amid the economic downturn.
- Milei called for a 10-point pact for a “new economic order” including fiscal balance, spending cuts, tax reform, labour reforms, and international market engagement, but faces opposition from governors, former presidents, Supreme Court members, and MPs.
5. India’s Employment Rate Rises by 6% in FY 2023-24, Reflects Positive Labor Market Trends
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Economy; Page: 13)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Increase in Employment Numbers
- Employment in India saw an increase of 4.67 crore, reaching a provisional total of 64.33 crore in the fiscal year 2023-24, up from 59.67 crore in 2022-23.
- In comparison, employment stood at 57.75 crore in 2022-23, reflecting a consistent upward trend from 56.56 crore in 2021-22.
- The data, sourced from the RBI’s India KLEMS database, underscores the growing number of employed individuals in the country.
Decline in Unemployment Rate
- According to the latest quarterly bulletin of the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) released by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) in May 2024, the unemployment rate (UR) in urban areas decreased from 6.8% during January–March 2023 to 6.7% in January–March 2024 for individuals aged 15 years and above.
- The female unemployment rate also showed a decline, from 9.2% in January–March 2023 to 8.5% in January–March 2024.
Increasing Labour Force Participation
- The Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) in urban areas exhibited an increasing trend, rising from 48.5% in January–March 2023 to 50.2% during January–March 2024 for individuals aged 15 years and above.
- This increase indicates a higher proportion of the working-age population entering the labor force.
Rising Worker Population Ratio
- The Worker Population Ratio (WPR) for individuals aged 15 years and above also showed an upward trend, increasing from 45.2% in January–March 2023 to 46.9% in January–March 2024.
- Notably, the female Worker Population Ratio in urban areas rose from 20.6% in January–March 2023 to 23.4% during January–March 2024, reflecting an overall increasing trend in the WPR and indicating improved labor market participation among women.
6. Supreme Court Rules Real-Time Tracking of Accused on Bail Violates Right to Privacy
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt & Policy; Page: 08)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Specific Case and Trial Court’s Condition
- The ruling came in response to a condition imposed by a trial court requiring a Nigerian national, facing charges under the NDPS Act 1965, to “drop a PIN on the Google map to ensure that” his “location is available to the Investigation Officer of the case.”
- Supreme Court found this condition to be an infringement on the accused’s privacy, as it allowed the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) to monitor his movements in real-time.
What is Right to Privacy?
- Generally understood that privacy is synonymous with the right to be let alone.
- The Supreme Court described privacy and its importance in the landmark decision of K.S. Puttaswamy v. Union of India in 2017 that – Right to Privacy is a fundamental and inalienable right and attaches to the person covering all information about that person and the choices that he/ she makes.
- The right to privacy is protected as an intrinsic part of the right to life and personal liberty under Article 21 and as a part of the freedoms guaranteed by Part III of the Constitution.
Restrictions (as stated in the Judgement):
The right may be restricted only by state action that passes each of the three tests:
- First, such state action must have a legislative mandate,
- Second, it must be pursuing a legitimate state purpose, and
- Third, it must be proportionate i.e., such state action- both in its nature and extent, must be necessary in a democratic society and the action ought to be the least intrusive of the available alternatives to accomplish the ends.




