9 October 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. What does USCIRF report say about India?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations |
| Context |
|
USCIRF Report on India:
- The United States Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF) released a country update on India, highlighting deteriorating religious freedom conditions in 2024.
- The report claims individuals from minority communities have faced killings, lynchings, arbitrary arrests, and the destruction of places of worship throughout 2024.
- The Indian government has strongly rejected the report, calling USCIRF a biassed organisation with a political agenda.
What is the USCIRF?
- The USCIRF is a U.S.-based federal government agency that monitors religious freedom worldwide, based on international human rights standards, particularly Article 18 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
- It differs from the U.S. State Department’s Office of International Religious Freedom (IRF) and its recommendations do not directly affect bilateral relations.
- Although backed by extensive research, some view the USCIRF’s timing and reports as influenced by U.S. foreign policy goals, raising concerns about its objectivity.
USCIRF’s Role:
- USCIRF assesses religious freedom violations globally, producing an annual report recommending countries for designation as “Countries of Particular Concern” (CPC) or inclusion in the Special Watch List (SWL).
- CPC countries face the possibility of U.S. sanctions if their violations are deemed systematic, ongoing, and egregious.
USCIRF’s Findings on India:
- The report emphasises increasing suppression of minorities through discriminatory laws like the Citizenship (Amendment) Act, anti-conversion laws, and cow slaughter laws.
- It accuses Indian officials of promoting hateful rhetoric and perpetuating violence against religious minorities, while designating India as a CPC in 2024.
India’s Response:
- India’s Ministry of External Affairs dismissed the report as politically motivated, stating that it misrepresents facts and reflects an agenda-driven narrative.
| Practice Question: Critically analyse the implications of the USCIRF’s report on religious freedom in India for India’s international relations and internal policies. (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. Why is the textile industry struggling to perform better?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy – Changes in industrial policy and their effects on industrial growth. |
| Context |
|
Current Status of the Indian Textile and Apparel Sector
- Union Minister for Textiles Giriraj Singh announced that the Indian textile and apparel sector aims for a total business of $350 billion annually by 2030, which could generate 3.5 crore jobs.
- The industry’s size was estimated at $153 billion in 2021, with approximately $110 billion derived from domestic business.
- In FY22, India ranked as the third-largest textile exporter globally, with a market share of 5.4%, and possessed the second-largest manufacturing capacity in the sector.
- The textile industry contributed 2.3% to the country’s GDP and 10.6% to total manufacturing Gross Value Added (GVA).
- The sector employs around 105 million people directly and indirectly.
Reasons for Export Slump
- Economic Downturn: The industry faced a decline starting in 2022-2023, marked by significant reductions in exports and domestic demand due to geopolitical issues and decreased demand from purchasing countries.
- High Raw Material Prices: Rising prices for cotton and Man-Made Fibres (MMF) worsened the situation, with a 10% import duty on cotton making Indian cotton less competitive globally.
- Quality Control Orders: The introduction of quality control orders on MMF disrupted raw material availability and pricing, leading to industry calls for the removal of the import duty during the off-season from April to October.
Challenges Facing the Industry
- E-commerce Disruption: The sector is experiencing shifts due to e-commerce trends, with more manufacturers opting for direct retail to consumers.
- Sustainability Demand: International brands are prioritising sustainability, leading to increased demand for vendors who can meet specific environmental standards.
- Changing Consumer Preferences: There is a growing consumer preference for comfort wear, coupled with shifts in shopping habits, particularly in rural and semi-urban areas.
- Labour Costs: Labour constitutes around 10% of production expenses, with trained textile workers earning ₹550 daily and unskilled workers earning ₹450.
Future Outlook
- Investment Goals: To achieve the $350 billion target, the industry anticipates a $100 billion investment across various segments by 2030.
- Focus on Technology: The industry must emphasise technology adoption and workforce skilling to enhance productivity and reduce waste.
- Strengthening Supply Chains: Efforts will be made to strengthen supply chains to mitigate disruptions and ensure timely availability of raw materials and finished products.
| Practice Question: Discuss the challenges faced by the Indian textile and apparel industry in achieving its target of $350 billion annual business by 2030. How can the sector address these challenges to ensure sustainable growth? (150 Words /10 marks) |
3. Global Digital Compact: advancing digital innovation in a sustainable fashion
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 11)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations |
| Context |
|
Overview of the Global Digital Compact (GDC)
- The Global Digital Compact (GDC) was recently adopted at the ‘Summit of the Future’ organised by the United Nations.
- This groundbreaking instrument aims to harness and regulate digital technologies for the common good, marking a significant step in international digital governance.
Nature of the GDC
- The GDC is a non-binding diplomatic instrument that outlines shared goals for governments, institutions, firms, and stakeholders.
- While it is not legally binding, increased adherence could lead to its terms evolving into soft laws within individual countries.
Background and Objectives
- Building on previous UN initiatives, the GDC recognizes the transformative impact of digital technologies on society.
- While these technologies can facilitate the achievement of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), they also present significant challenges.
Goals and Structure
- The GDC focuses on ensuring human oversight of technologies to promote sustainable development.
- It aims for global cooperation in data governance and digital technologies, with member countries committing to establish two panels: an Independent International Scientific Panel on AI and a Global Dialogue on AI Governance.
Proposed Digital Public Goods
- To bridge the digital divide, the GDC advocates for digital public goods such as open-source software and open AI models.
- These goods are seen as crucial for creating a digital public infrastructure that can deliver essential services effectively.
Challenges and Criticisms
- The GDC faces several lacunae:
- Openness in public-private partnerships may be restricted by contractual requirements, limiting transparency.
- The Compact lacks new frameworks for internet governance and relies on self-regulation from digital technology companies, which has historically proven ineffective.
- It acknowledges the importance of interoperable data governance but fails to adequately address the risks associated with increased data collection and sharing.
- The GDC grants more power to corporate entities in data governance without emphasising necessary countervailing measures to prevent monopolistic control.
Conclusion
- Ultimately, the GDC may not radically transform global digital governance.
- However, it holds the potential for significant outcomes if member states engage seriously with its goals.
- It could foster capacity building and collaborations between nations in developing digital public goods, thus facilitating a more equitable digital landscape.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the Global Digital Compact (GDC) in the context of international digital governance. What challenges does it face in implementation, and how can member states address these challenges to promote effective digital governance? (250 Words /15 marks) |
4. AI Pioneers Hopfield and Hinton Awarded Nobel Prize for Revolutionizing Machine Learning with Neural Networks
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 19)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context: |
| The article highlights the groundbreaking contributions of John Hopfield and Geoffrey Hinton in developing neural networks, which have revolutionized artificial intelligence and earned them the Nobel Prize in Physics. |
Analysis of News:
Artificial Intelligence: A Game Changer
- Artificial intelligence (AI) tools have become a key part of modern life, enabling users to access information, create multimedia, and analyze large data sets in ways that were unthinkable just a few years ago.
- AI is transforming the way people work and live, with applications ranging from everyday tasks on computers and phones to complex problem-solving in scientific fields.
Nobel Prize for AI Foundations

- This year’s Nobel Prize in Physics recognized John Hopfield and Geoffrey Hinton for their groundbreaking work in artificial neural networks.
- These scientists, who made major contributions in the 1980s, laid the foundation for today’s AI revolution.
- Their research is only now being fully realized, as the capabilities of machine learning and AI continue to advance rapidly.
Mimicking the Human Brain
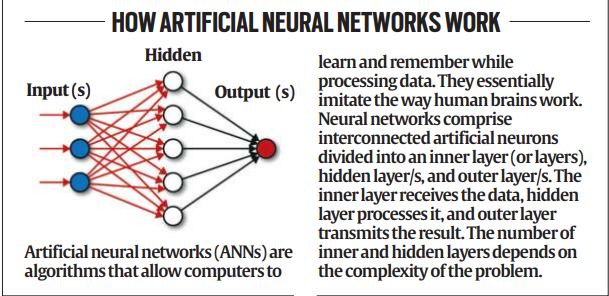
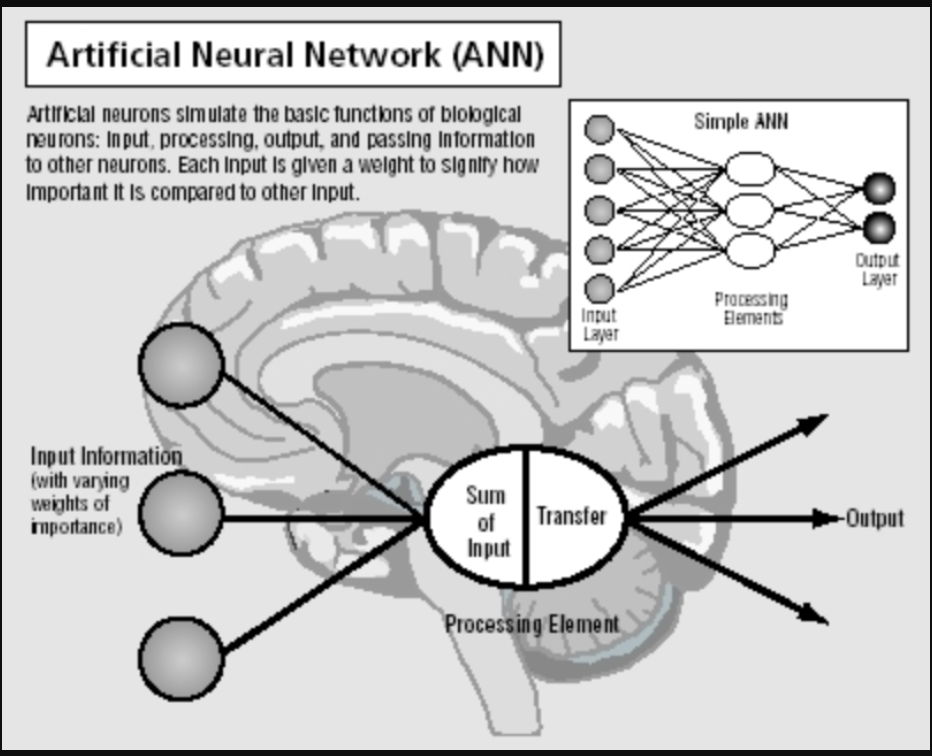
- Hopfield’s key contribution was the development of neural networks that mimic the functioning of the human brain.
- His work in the 1980s allowed machines to “remember” and “learn” by building neural networks similar to the nerve cells in the brain.
- This breakthrough helped enable pattern recognition, which powers modern technologies like facial recognition and image enhancement tools.
Deep Learning: A New Era
- Geoffrey Hinton expanded on Hopfield’s work, introducing deep learning techniques. His method, known as backpropagation, allowed neural networks to learn from their mistakes and improve accuracy.
- This innovation led to the development of deep neural networks, which are crucial for today’s AI systems like voice assistants, image recognition, and self-driving cars.
Real-World Impact of AI
- Hinton’s work gained global recognition when his team’s algorithm, AlexNet, demonstrated superior image recognition at the 2012 ImageNet competition.
- This marked a turning point in the AI field, solidifying the potential of deep learning. Today, AI is used across industries, from astronomy to healthcare, for analyzing vast amounts of data and identifying significant patterns.
Legacy of the Pioneers
- Both Hopfield and Hinton have left an indelible mark on AI and computer science.
- While Hopfield’s work drew from his background in physics and biology, Hinton’s deep learning advancements have revolutionized computer science.
- Together, their contributions continue to shape the future of AI, earning them a place among the pioneers of the digital age.
| What is an Artificial Neural Network? |
|
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the contributions of John Hopfield and Geoffrey Hinton in the development of artificial neural networks and their impact on the evolution of artificial intelligence. How have these advancements transformed modern technologies? (150 words/10 m) |
Prelims Facts
1. The Second Hanle Dark Sky Reserve Star Party observed in Ladakh
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2063296®=3&lang=1 )
| Context |
|

Why Is Hanle Ideal Site For Astronomy?
- Dark Skies: Hanle features some of the darkest night skies in India, minimising light pollution, which enhances visibility for astronomical observations.
- Clear Atmosphere: The region has exceptionally clear and transparent air, providing optimal conditions for observing faint celestial objects.
- High Altitude: Situated at a high elevation, Hanle reduces atmospheric interference, improving the clarity and quality of observations.
- Stable Weather: The area experiences stable weather patterns, leading to fewer cloudy nights and consistent opportunities for stargazing.
- Astrophysical Facilities: The Indian Astronomical Observatory is equipped with professional telescopes, offering advanced research and observation capabilities.
- Diverse Celestial Views: Unique celestial phenomena can be observed, thanks to Hanle’s geographic and environmental advantages.
| Practice Question: What are the key factors that make Hanle Dark Sky Reserve an ideal location for astronomical observations, and how do these conditions enhance the study of celestial phenomena?(150 Words /10 marks) |
2. PSLV C-37 rocket body re-enters the earth’s atmosphere: ISRO
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Context |
|

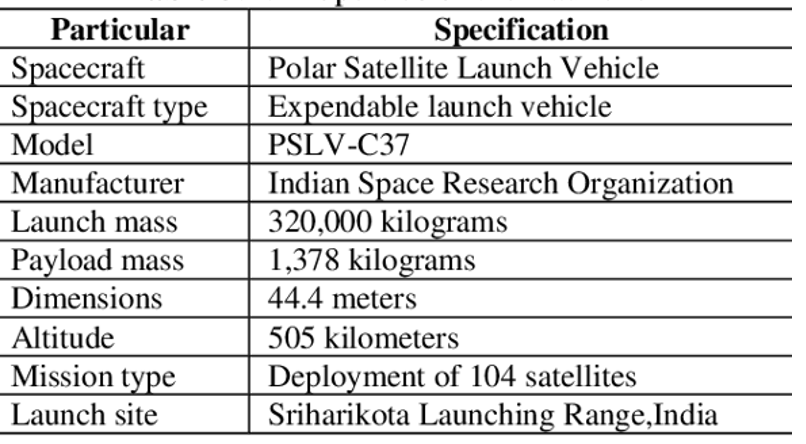
Analysis of the news:
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) announced that the upper stage of the PSLV-C37 rocket re-entered Earth’s atmosphere on Sunday.
- The PSLV-C37 mission was launched on February 15, 2017, carrying the Cartosat-2D satellite as the main payload along with 103 co-passenger satellites.
- This mission set a world record by launching 104 satellites in a single rocket.
- After deploying the satellites, the upper stage (PS4) was left in orbit.
- Due to atmospheric drag, the orbit of the PS4 stage gradually decayed over time.
- Since September, ISRO’s System for Safe and Sustainable Space Operations Management (IS4OM) monitored the orbital decay and predicted the re-entry in the first week of October.
- The atmospheric re-entry complies with international debris mitigation guidelines, specifically limiting the orbital life of defunct objects in Low-Earth orbit to 25 years.
3. Forests nearly the size of Ireland lost in 2023, says study
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 15)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- A major study revealed that deforestation in 2023 continued at rates exceeding pledges to end it by 2030.
- Forests equivalent to the size of Ireland were lost, with 15.7 million acres of trees felled and burned.
- The deforestation rate significantly exceeded levels needed to stay on track with the 2030 goal, set by over 140 leaders in 2021.
- Forests are vital for biodiversity, regulating water cycles, and absorbing CO2.
- The report highlighted worsening deforestation since the decade’s start, with tropical primary forests particularly affected.
- Bolivia saw a 351% rise in deforestation between 2015-2023, and Indonesia’s deforestation increased sharply in 2023 after declining from 2020-2022.
4. Study uncovers surprising new ‘spatial grammar’ of gene expression
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
Spatial Grammar In Gene Expression:
- What is Spatial Grammar?: It’s about how transcription factor binding sites are arranged near the starting point of genes.
- Effect of Location: The position of these binding sites can determine if a transcription factor helps turn on (activator) or turn off (repressor) a gene.
- Different Arrangements: Changing how these binding sites are organised can lead to different results in gene activity.
- Genetic Changes: Variations in the binding sites can affect how much a gene is expressed, depending on how close they are to the starting point.
- Experiment Findings: Tests with artificial binding sites show that their order and distance from the starting point greatly influence gene activity.
- Health Implications: Knowing about spatial grammar can help predict mutations that might cause diseases and lead to better treatments.
- Understanding Genes: This knowledge improves our grasp of gene control and how organisms adapt over time.
5. James Webb Telescope Detects Carbon Dioxide on Charon
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
| Scientists detected carbon dioxide on Charon using the James Webb Space Telescope, aiding understanding of icy celestial bodies’ formation and evolution. |
Analysis of the news:
- Research published on October 1 revealed that scientists using the James Webb Space Telescope detected carbon dioxide on Charon, Pluto’s largest moon, for the first time.

- This significant finding, along with the detection of hydrogen peroxide, enhances our understanding of the composition and processes occurring on icy celestial bodies.
- The discovery could provide insights into the formation and evolution of such worlds, helping scientists piece together the complex history of these distant, frozen environments in our solar system.
6. India has eliminated trachoma, says WHO
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Context |
|
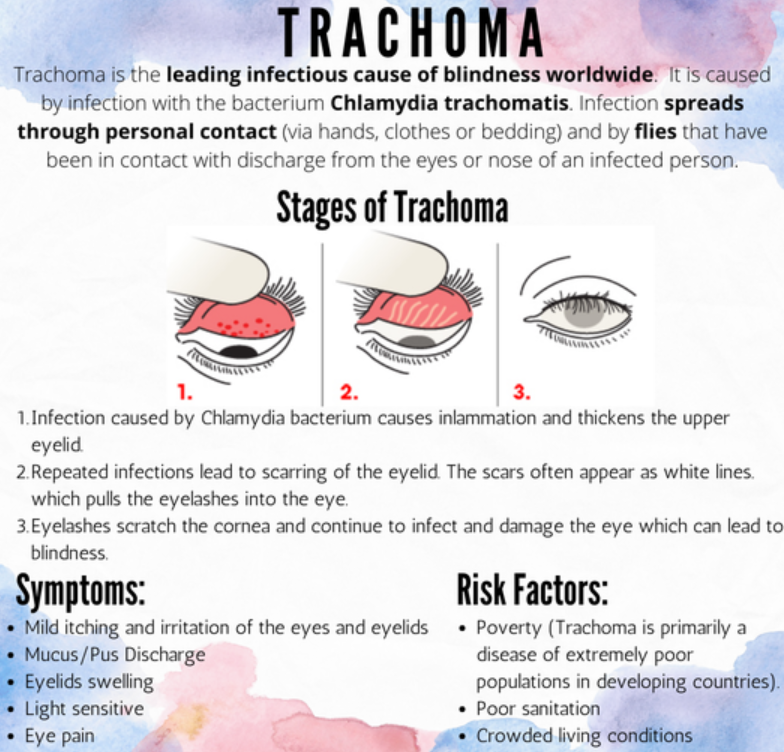
Analysis of the news:
- Trachoma is a bacterial eye infection that can lead to blindness.
- India becomes the third country in the Southeast Asia Region to achieve this milestone.
- Collaborative efforts with partners ensured effective surveillance, diagnosis, and management of active trachoma.
- The elimination of trachoma contributes to overall eye health and well-being in India.
7. India makes pledge of $300 million for WHO programme
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- A substantial portion, $250 million, will be allocated to establish a Centre of Excellence for Traditional Medicine.
- WHO has received pledges exceeding $2.2 billion toward a total funding gap of $7.1 billion.
- The funding aims to save at least 40 million lives over four years through various initiatives.
- These initiatives include increasing vaccine deliveries to priority countries and supporting 55 countries in training and employing 3.2 million health workers.
India’s funding commitment is the largest in Sou