6 May April 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis
1. Jobs picture in perspective
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government policies – Interventions for development in various sectors
GS3 – Indian Economy – Issues relating to development and employment |
| Context: |
|
What is India Unemployment Report?
- The India Employment Report 2024 is the third in the series of regular publications by the IHD on labour and employment issues.
- This report on Youth Employment, Education and Skills examines the challenge of youth employment in the context of the emerging economic, labour market, educational and skills scenario in India and changes over the past two decades.
- The report is primarily based on analysis of data from the National Sample Surveys and the Periodic Labour Force Surveys between 2000 and 2022, with a postscript for 2023.
Positive Developments in the Labor Market:
Employment Quality Improvement
- The report underscores a positive shift in employment quality, evidenced by a robust Employment Condition Index across all states.
- This improvement is particularly notable in the transition from agriculture-based employment to non-farm sectors, signaling a structural transformation in the economy.
- Moreover, there has been a steady increase in regular employment while the unorganized sector witnessed a decline, indicative of a more stable labor market.
Increase in Female Workforce Participation:
- A remarkable increase in the female workforce participation rate from 5% in 2019 to 37.0% in 2023 is highlighted.
- Although predominantly in the agricultural sector and involving own-account or unpaid family work, this surge signifies a positive trend towards greater gender inclusivity in the labor force.
Resilience Amidst Covid-19:
- Despite the global economic slowdown induced by the Covid-19 pandemic, the Indian labor market demonstrated resilience.
- Wages of casual workers increased, particularly among the bottom income groups, potentially mitigating extreme poverty and deprivation.
- Notably, both farm and non-farm job opportunities expanded during the pandemic period, indicating adaptability in the face of crisis.
Emerging Challenges:
Skewed Employment Patterns
- The report underscores persistent challenges, such as the skewed distribution of employment towards agriculture, which continues to employ nearly half of the workforce.
- Addressing this imbalance necessitates concerted efforts to accelerate non-farm job creation, particularly through labor-intensive manufacturing.
Youth Unemployment:
- Youth unemployment emerges as a principal challenge, with educated youth comprising a significant portion of the unemployed.
- This challenge is exacerbated by qualifications and skills mismatches, highlighting the need for enhancing the quality of education and skill development initiatives, in collaboration with the private sector.
Gender Disparities and NEET Population:
- Gender disparities persist, with women predominantly engaged in less remunerative agricultural and unpaid family work.
- Additionally, the proportion of youth not in employment, education, or training (NEET) remains high, particularly among females.
- Addressing these disparities requires targeted policies to boost women’s employment and cater to the needs of NEET populations.
Policy Recommendations:
The report proposes several policy measures to address emerging challenges and further enhance positive trends in the labor market:
(a) Prioritize labour-intensive production and growth strategies, with a focus on employment-generating sectors like manufacturing and agriculture.
(b) Improve the quality of jobs by strengthening social protection measures and promoting formalization.
(c) Address labour market inequalities, particularly by boosting women’s employment and implementing effective policies to tackle NEET populations.
(d) Enhance the effectiveness of skills training and active labor market policies, bridging the supply-demand gap in jobs and involving the private sector more actively.
(e) Generate reliable statistics to better understand the evolving dynamics of the labor market in the face of rapid technological changes.
Conclusion:
- The India Employment Report 2024 provides valuable insights into the evolving landscape of the Indian labor market, highlighting both positive developments and persistent challenges.
- By implementing targeted policy measures and fostering collaboration between public and private sectors, India can capitalize on its demographic advantage and achieve inclusive and sustainable growth in the coming years.
| What are the Government’s Initiatives Related to Employment? |
What is the International Labor Organization?
|
| PYQ: Most of the unemployment in India is structural in nature. Examine the methodology adopted to compute unemployment in the country and suggest improvements. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2023) |
| Practice Question: How does the India Employment Report 2024 assess the evolution of the Indian labor market over the past two decades, and what are the key findings and policy recommendations highlighted in the report? (250 words/15 m) |
2. LOOK EAST
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations – India and its neighbourhood |
| Context: |
|
Overview:
- Last week, Myanmar’s army claimed victory in retaking Myawaddy, a crucial point along its trade route with Thailand, after facing resistance from an anti-government coalition comprising ethnic armed groups and pro-democracy fighters.
- However, the real winner appears to be the Border Guard Force (BGF), which holds great autonomy on the ground and operates a vast criminal network along the Thai border.
About Myawaddy:
- Myawaddy is Myanmar’s most active trading post with Thailand.
- Myawaddyy is a trading town in Myanmar that connects with Mae Sot in Thailand.
- These are the endpoints of the India- Myanmar- Trilateral Highway.
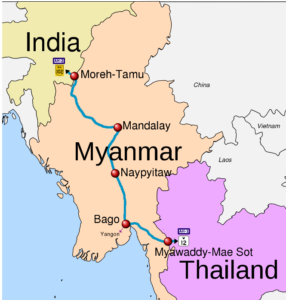
The Role of the Border Guard Force (BGF):
- The BGF, aligned with the military government in Yangon, is reported to play both sides to expand its regional dominance while overseeing illegal activities such as gambling, drug trafficking, and smuggling.
- The battle for Myawaddy underscores the breakdown of state authority in Myanmar, with the BGF emerging as a key player amidst the chaos.
Historical Context of Myanmar’s Fragile State Control:
- Myanmar has historically struggled to maintain control over its diverse territory due to conflicts between the majority Bamars and various ethnic minority groups.
- However, the situation has deteriorated since the 2021 coup, with the army losing control over significant portions of the country as pro-democracy and ethnic armed groups unite against military rule.
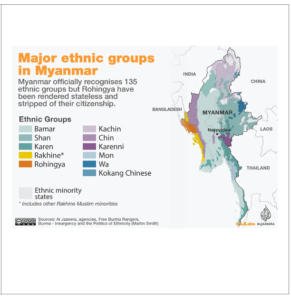
External Intervention and Regional Dynamics:
- As Myanmar’s authority weakens, external powers are increasingly involved in the nation’s affairs.
- China has deepened its intervention under the guise of stabilizing its frontier, while the US supports pro-democracy movements with substantial assistance.
- The inability of regional forums like ASEAN to address the crisis has further exacerbated the situation.
Implications for India’s Security:
Inadequate Response from India
- Despite profound implications for India’s security, there has been a lack of debate in Delhi on how to address the Myanmar crisis.
- India’s previous policy bias in favor of Myanmar’s army, which can no longer secure India’s interests, needs reevaluation.
The Need for Dialogue and Engagement:
- India must initiate dialogue with Myanmar’s National Unity Government, comprising democratic opposition and ethnic armed groups, while also engaging with local forces controlling regions along the shared border.
- Focusing solely on border defense through fencing is insufficient to address the challenges on India’s eastern frontier.
Conclusion:
- The battle for Myawaddy serves as a microcosm of Myanmar’s broader state breakdown, with the Border Guard Force emerging as a powerful player amidst internal strife.
- As external powers intervene and regional dynamics shift, India must reassess its approach, prioritizing dialogue and engagement with Myanmar’s diverse stakeholders to safeguard its interests and ensure stability along its eastern border.
| What are the Key Issues in the India-Myanmar Relationship? |
Internal Security Concern:
The Free Movement Regime (FMR):
‘Sick Man of Southeast Asia’:
Civil Liberty Index:
China’s Influence:
Infrastructure Project Delays:
Rohingya Crisis:
|
| PYQ: How far are India’s internal security challenges linked with border management, particularly in view of the long porous borders with most countries of South Asia and Myanmar?
(200 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2013) |
| Practice Question: What are the key dynamics and implications of the recent conflict in Myanmar, particularly focusing on the battle for Myawaddy and the involvement of various armed groups? (250 words/15 m) |




