13 July 2024 : PIB Summary For UPSC
1. The Government to soon launch an ‘Agri Fund for Start-Ups & Rural Enterprises’ (AgriSURE) to provide support to Startup and Agripreneurs
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2032838 )
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government Policies, GS3 – Agriculture – E-technology in the aid of farmers. |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- The Indian Government announced the launch of ‘Agri Fund for Start-Ups & Rural Enterprises’ (AgriSURE) during a stakeholder meet in Mumbai.
- AgriSURE is a Rs 750 crore Category-II Alternative Investment Fund (AIF) aimed at supporting start-ups and agripreneurs in the agriculture and allied sectors.
- It will provide equity and debt investments, focusing on innovation and sustainability across the agriculture value chain.
- The fund will be financed with Rs 250 crores each from the Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare and NABARD, with an additional Rs 250 crores raised from financial institutions.
- NABVENTURES, a subsidiary of NABARD, will manage the fund, which aims to enhance farm produce value chains, rural infrastructure, and support Farmers Producer Organizations (FPOs).
- Features include promoting IT-based solutions, machinery rental services for farmers, and fostering employment generation.
- Concurrently, NABARD launched the AgriSURE Greenathon 2024, addressing challenges such as cost-effective smart agriculture, utilising agri-waste profitably, and promoting regenerative agriculture practices.
- The initiative underscores collaboration between public and private sectors to drive agricultural innovation and growth.
| PYQ: How does e-Technology help farmers in production and marketing of agricultural produce? Explain it. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2023) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the importance and impact of financial support initiatives like the AgriSURE fund in fostering innovation and sustainability in agribusinesses in India. (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. Release of SDG India Index 2023-24 By NITI Ayog
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2032857 )
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context |
|
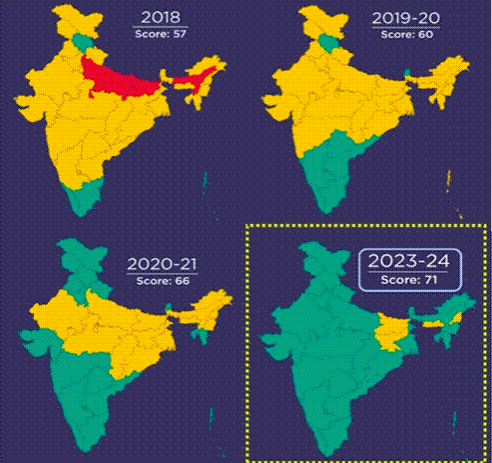
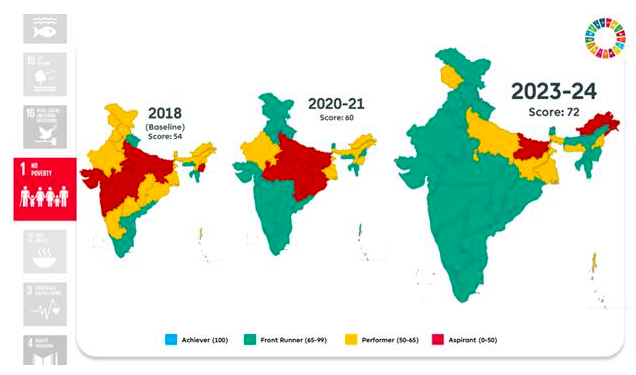
Goal 1: No Poverty
- Multidimensional poverty reduced significantly from 24.8% to 14.96% between 2015-16 and 2019-21.
- Employment generation through MGNREGA reached 99.7% coverage in 2023-24.
- Housing coverage expanded with nearly 95.4% of households living in pucca or semi-pucca houses.
- Health insurance coverage increased to 41% of households.
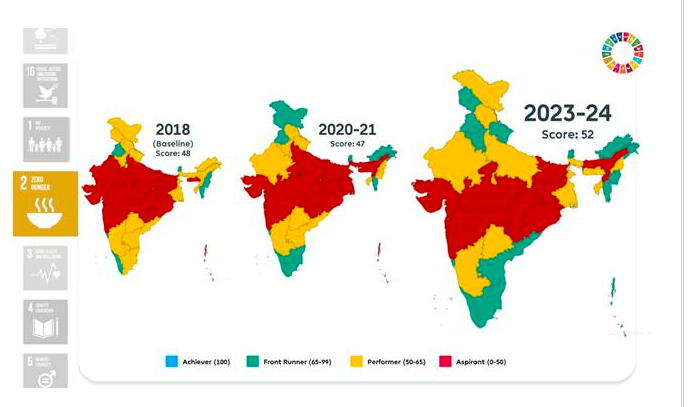
Goal 2: Zero Hunger
- NFSA coverage extended to 99.01% of beneficiaries.
- Productivity gains in agriculture with increased rice and wheat yields.
- Improved Gross Value Added (GVA) per worker in agriculture.
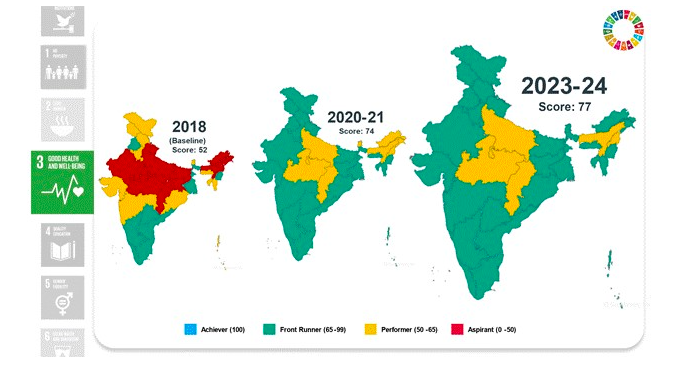
Goal 3: Good Health and Well-being
- Maternal mortality rate reduced to 97 per 100,000 live births.
- Under-5 mortality rate decreased from 36 to 32 per 1,000 live births.
- High immunisation coverage with 93.23% of children fully immunised.
- Significant progress in tuberculosis case notifications and institutional deliveries.
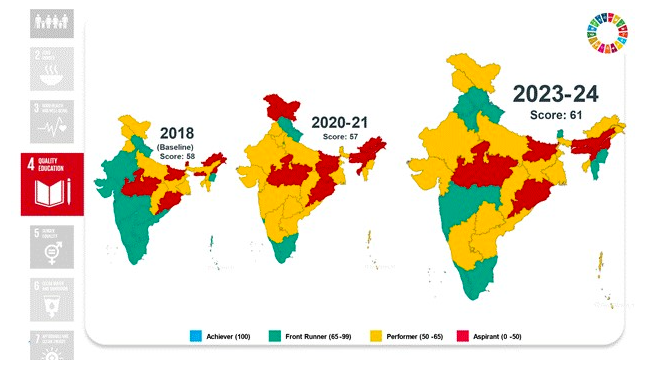
Goal 4: Quality Education
- Elementary education ANER at 96.5%, with 14 States/UTs achieving 100% enrolment.
- Pupil-teacher ratio improved to 18, meeting the target.
- Enhanced infrastructure with 88.65% schools having access to electricity and drinking water.
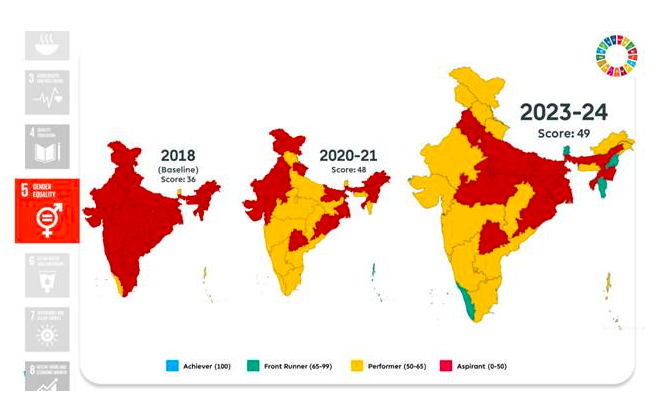
Goal 5: Gender Equality
- Improved sex ratio at birth of 929 females per 1,000 males.
- Increased female-to-male earnings ratio and labour force participation rate.
- Advancements in family planning met and mobile phone ownership among women.
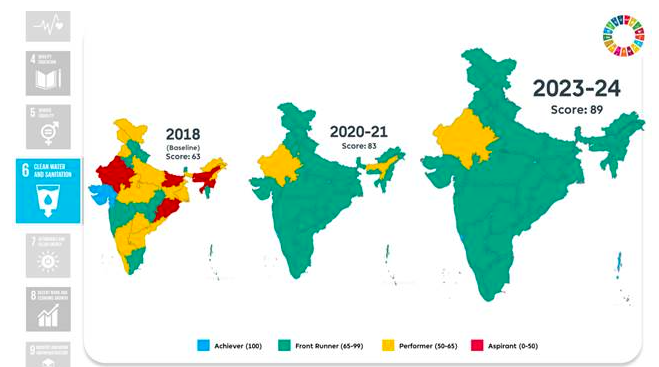
Goal 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
- Score improved from 63 to 89.
- Universal individual household toilet coverage under SBM (G).
- Significant rural household access to improved drinking water sources.
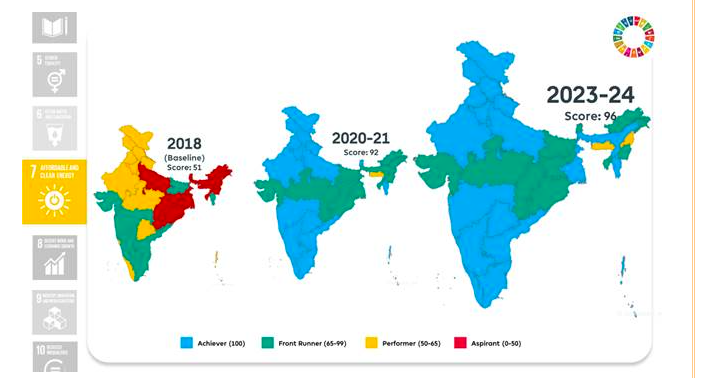
Goal 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- Highest score among SDGs with a score of 96.
- Saubhagya scheme achieving 100% household electricity access.
- Growth in clean cooking fuel connections (LPG + PNG) to 96.35% by 2024.
Goal 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- GDP per capita growth at 5.88% in 2022-23.
- Unemployment rate reduced to 3.40% in 2022-23.
- Increased LFPR and financial inclusion through PMJDY.
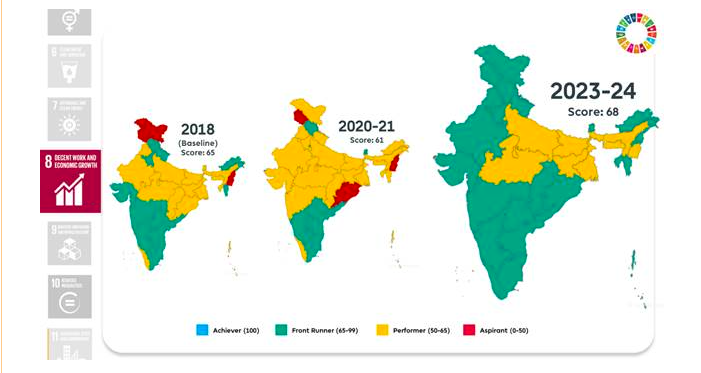
Goal 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Improved infrastructure connectivity with 99.70% habitations connected via PMGSY.
- High mobile phone penetration and improved internet coverage.
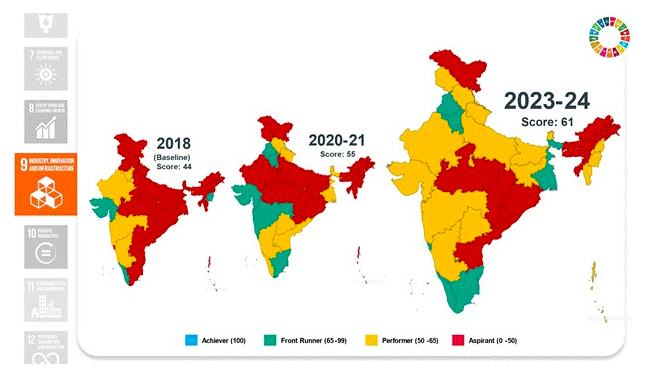
Goal 10: Reduced Inequalities
- Increased women’s representation in Panchayati Raj institutions to 45.61%.
- Enhanced SC/ST representation in state legislative assemblies to 28.57%.
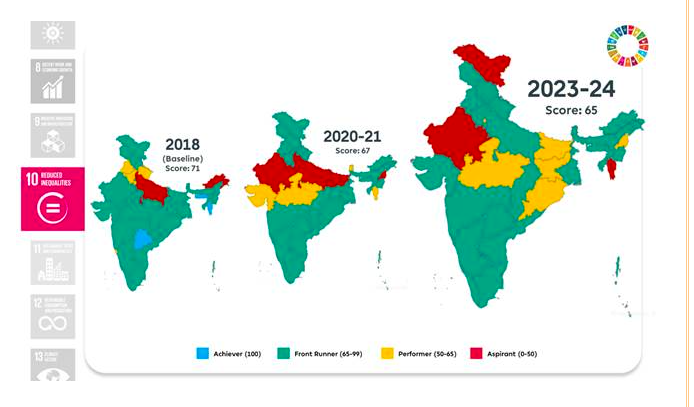
Goal 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Score improved from 39 to 83.
- Enhanced sewage treatment and municipal solid waste processing capacities.
- High coverage of door-to-door waste collection and source segregation under SBM (U).
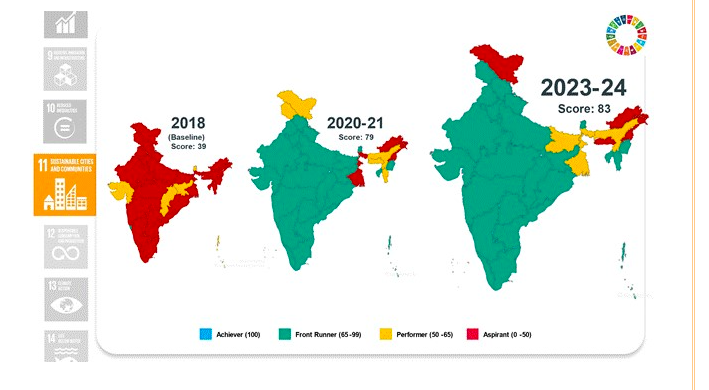
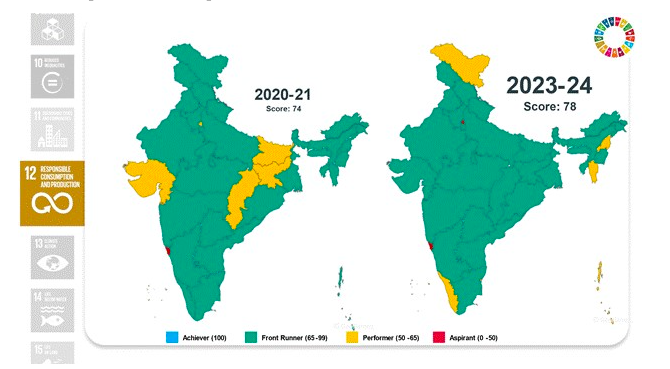
Goal 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- Biomedical waste treatment increased to 91.5% in 2022.
- Improved hazardous waste recycling to 54.99% in 2022-23.
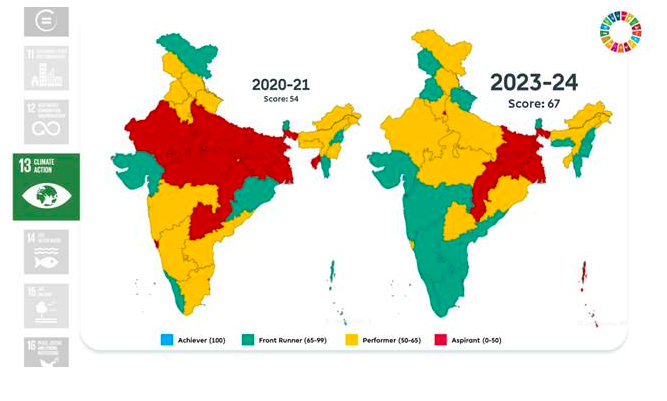
Goal 13: Climate Action
- Significant increase in score from 54 to 67.
- Improved disaster preparedness and renewable energy generation.
- High compliance with environmental standards among industries.
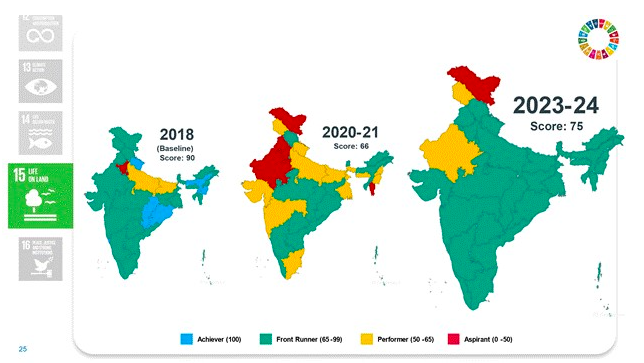
Goal 15: Life on Land
- Score increased from 66 to 75.
- Expanded forest and tree cover to nearly 25% of geographical area.
- Increase in carbon stock in forest cover.
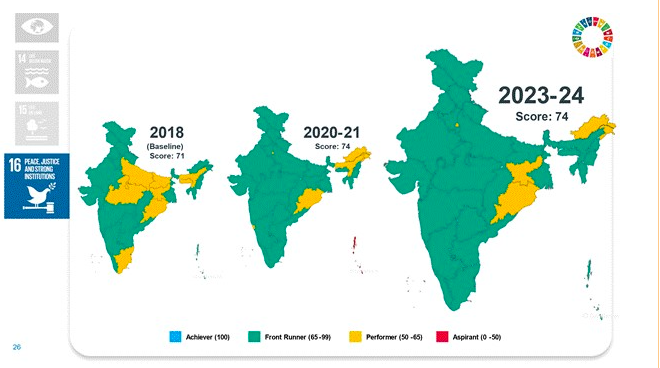
Goal 16: Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions
- High Aadhaar coverage at 95.5%.
- Improved birth registration rates and IPC crime charge sheeting.
| PYQ: Access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy is the sine qua non to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Comment on the progress made in India in this regard. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2018) |
| Practice Question: Discuss India’s progress and achievements in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) as highlighted in the SDG India Index 2023-24. Highlight key initiatives and their impact on national development. (250 Words /15 marks) |




