19 July 2024 : PIB Summary For UPSC
1. India and Malaysia to increase cooperation in the field of Oil palm and other sectors
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2034036 )
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- The Union Minister for Agriculture & Farmers Welfare and Rural Development of India, Shri Shivraj Singh Chouhan, met with the Minister for Plantations and Commodities of Malaysia, Shri Datuk Seri Johari Abdul Ghani, on July 18, 2024.
- The Malaysian Minister is visiting India from July 16-19, 2024.
- The meeting focused on enhancing bilateral cooperation in agriculture, particularly in the oil palm sector.
- Discussions included collaboration on the National Mission on Edible Oil- Oil Palm, addressing market access issues for agricultural and allied products, institutionalising agricultural cooperation, and applying digital technology in the plantation sector.
| India – Malaysia Relations |
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of Malaysia for India in terms of strategic, economic, and cultural relations. (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. Report on “Electronics: Powering India’s Participation in Global Value Chains” by NITI Aayog released today
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2034096 )
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context |
|
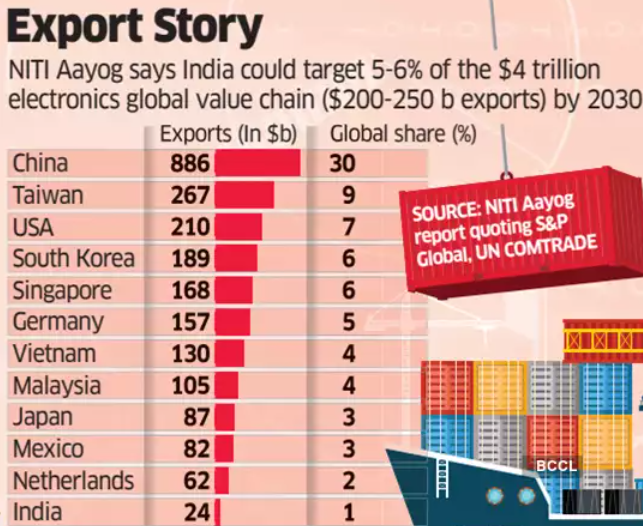 Analysis of the news:
Analysis of the news:
- NITI Aayog’s report titled “Electronics: Powering India’s Participation in Global Value Chains” highlights India’s potential and challenges in the electronics sector.
- Global Value Chains (GVCs) are crucial, accounting for 70% of international trade; electronics represent 75% of its exports.
- India’s electronics sector grew to USD 155 billion in FY23, with production nearly doubling from USD 48 billion in FY17 to USD 101 billion.
- Mobile phones drive the sector, now constituting 43% of production, and India manufactures 99% of smartphones domestically.
- Despite progress, India holds only 4% of the global electronics market, mainly focusing on assembly with limited design and component capabilities.
- The global electronics market is valued at USD 4.3 trillion, with India exporting about USD 25 billion annually.
- Projections show India’s electronics manufacturing could reach USD 278 billion by FY30 in a Business As Usual scenario, generating 3.4 million jobs and USD 111 billion in exports.
- For India to achieve its target of USD 500 billion by FY30, including USD 350 billion from finished goods and USD 150 billion from components, it needs substantial policy support and strategic interventions.
- The strategy includes enhancing production in mobile phones, expanding into wearables, IoT devices, and automotive electronics, and improving components manufacturing.
| Practice Question: Discuss the key strategies proposed in NITI Aayog’s report to transform India into a global leader in electronics manufacturing by FY30. Evaluate the potential impact of these strategies on India’s economic growth and job creation. (250 Words /15 marks) |



