24 July 2024 : PIB Summary For UPSC
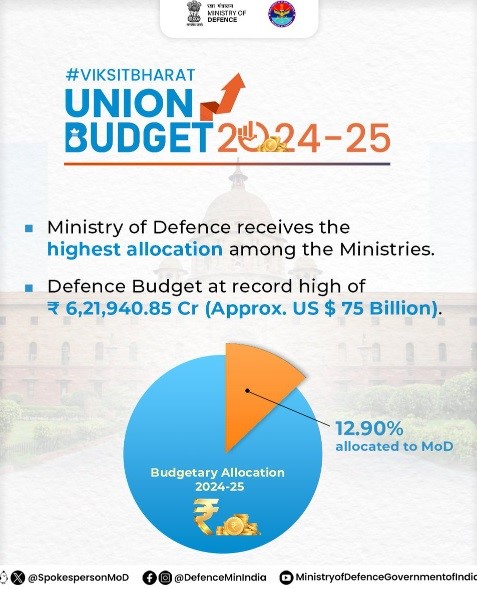
1. Rs 6.22 lakh crore allocated to MoD, highest among Ministries, in Regular Union Budget 2024-25; 4.79% higher than FY 2023-24
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2035748 )
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- The Union Budget 2024-25 allocated Rs 6,21,940.85 crore to the Ministry of Defence (MoD), the highest among ministries.
- Capital acquisition funding is Rs 1.72 lakh crore, a 20.33% increase from FY 2022-23 and 9.40% more than FY 2023-24.
- Rs 92,088 crore is allocated for sustenance and operational readiness, up 48% from FY 2022-23.
- Defence pensions have been allocated Rs 1.41 lakh crore, a 2.17% increase from the previous year.
- Rs 6,500 crore is designated for border roads development, and Rs 7,651 crore for coastal security.
- The iDEX budget is raised to Rs 518 crore from Rs 115 crore to foster defence innovation.
- The budget includes Rs 6,968 crore for the Ex-Servicemen Contributory Health Scheme (ECHS), a 28% increase from last year.
- Border Roads Organisation receives Rs 6,500 crore, a 30% increase from FY 2023-24.
- Indian Coast Guard’s allocation is Rs 7,651.80 crore, 6.31% higher than last year.
- DRDO’s budget is increased to Rs 23,855 crore, with a focus on capital expenditure and private sector partnerships.
- The allocation for Technology Development Fund (TDF) is Rs 60 crore to support start-ups and innovation.
- Raksha Mantri Rajnath Singh praised the budget for strengthening armed forces and promoting self-reliance in defence.
2. SUMMARY OF THE UNION BUDGET 2024-2025
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2035618 )
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context |
|
Summary of the Union Budget 2024:
- Economic Performance:
- India’s inflation is currently low and stable, approaching the 4% target set by the government. Core inflation, excluding food and fuel, is at 3.1%. The government is working on ensuring the effective supply of perishable goods to stabilise prices.
- Prime Minister’s Package:
- The government announced a ₹2 lakh crore package for 5 major schemes aimed at providing employment, skill development, and other opportunities to 4.1 crore youth over the next 5 years. An allocation of ₹1.48 lakh crore has been made this year for education, employment, and skilling initiatives.
- Budget Focus Areas:
- The budget emphasises nine key priorities:
- Productivity and resilience in agriculture
- Employment and skilling
- Inclusive human resource development and social justice
- Manufacturing and services
- Urban development
- Energy security
- Infrastructure
- Innovation and research
- Next-generation reforms
- The budget emphasises nine key priorities:

- Agriculture:
- Introduction of 109 new high-yielding, climate-resilient varieties of 32 field and horticulture crops.
- Over the next two years, 1 crore farmers will be trained in natural farming, supported by certification and branding.
- Establishment of 10,000 bio-input resource centers.
- Strengthening production, storage, and marketing of pulses and oilseeds.
- Implementation of Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) in agriculture, with a ₹1.52 lakh crore provision for agriculture and allied sectors.

- Employment and Skilling:
- Implementation of three new schemes under the ‘Employment Linked Incentive’ program focusing on EPFO enrolment, recognition of first-time employees, and support for both employees and employers.
- Upgrading 1,000 Industrial Training Institutes with a hub-and-spoke model.
- Revised Model Skill Loan Scheme to provide loans up to ₹7.5 lakh, benefiting 25,000 students annually.
- Financial support for higher education loans up to ₹10 lakh, with e-vouchers for 1 lakh students, including an annual interest subvention of 3%.

- Inclusive Human Resource Development:
- Enhanced implementation of schemes supporting craftsmen, artisans, self-help groups, and entrepreneurs, including PM Vishwakarma, PM SVANidhi, National Livelihood Missions, and Stand-Up India.
- The ‘Purvodaya’ plan for the all-round development of the Eastern states of Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha, and Andhra Pradesh.
- Launch of ‘Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan’ to improve socio-economic conditions in tribal-majority villages and aspirational districts, benefitting 5 crore tribal people.

- Establishment of more than 100 branches of India Post Payment Bank in the North East region to expand banking services.
- Allocation of ₹2.66 lakh crore for rural development, including infrastructure.
- Manufacturing and MSMEs:
- Special attention to MSMEs, with a self-financing guarantee fund offering guarantee cover up to ₹100 crore per applicant. Public sector banks will enhance their credit assessment capabilities for MSMEs.
- Enhanced Mudra loan limit to ₹20 lakh for entrepreneurs with previous successful loans.
- Financial support for setting up 50 multi-product food irradiation units and 100 food safety testing labs with NABL accreditation.
- Establishment of E-Commerce Export Hubs to help MSMEs and traditional artisans access international markets.
- Launch of a comprehensive internship scheme for 1 crore youth in 500 top companies over 5 years.
- Urban Development:
- PM Awas Yojana Urban 2.0 aims to address the housing needs of 1 crore urban poor and middle-class families with an investment of ₹10 lakh crore, including ₹2.2 lakh crore central assistance over 5 years.
- Water supply, sewage treatment, and solid waste management projects for 100 large cities in partnership with state governments and multilateral development banks.
- Development of 100 weekly ‘haats’ or street food hubs to support street vendors.
- Energy Security:
- Launch of PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana to install rooftop solar plants, providing free electricity up to 300 units for 1 crore households. The scheme has received over 1.28 crore registrations.
- Increased focus on nuclear energy as part of the energy mix for Viksit Bharat.
- Infrastructure:
- Allocation of ₹11.11 lakh crore for capital expenditure, representing 3.4% of GDP.
- Launch of Phase IV of PMGSY to provide all-weather connectivity to 25,000 rural habitations.
- Financial support for irrigation and flood management projects in Bihar, Assam, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and Sikkim.
- Innovation and Research:
- Operationalization of the Anusandhan National Research Fund with ₹1 lakh crore to support basic research and prototype development.
- Expansion of the space economy with a ₹1,000 crore venture capital fund.
- Next Generation Reforms:
- Formulation of an Economic Policy Framework to guide future reforms and employment generation.
- Integration of e-shram portal with other services and enhancement of compliance portals for labor.
- Simplification of Foreign Direct Investment and overseas investment regulations.
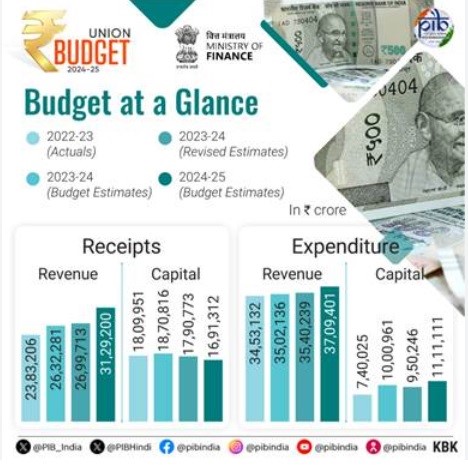
- Fiscal Estimates:
- Estimated total receipts (excluding borrowings) are ₹32.07 lakh crore, with total expenditure at ₹48.21 lakh crore. Fiscal deficit is projected at 4.9% of GDP.
- Gross and net market borrowings are estimated at ₹14.01 lakh crore and ₹11.63 lakh crore, respectively.
- The government aims to achieve a fiscal deficit below 4.5% next year.
- Tax Reforms:
- Increased standard deduction for salaried individuals to ₹75,000 and enhanced family pension deduction to ₹25,000.
- Abolition of angel tax, reduced corporate tax for foreign companies, and simplified TDS rates.
- Increase in capital gains exemption limit to ₹1.25 lakh per year and other provisions to enhance ease of doing business.




