27 December 2024 : PIB Summary For UPSC
India’s Rural Connectivity Revolution
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2088194®=3&lang=1 )
| Context |
|
Role of Mobile and Internet Connectivity in Empowering Women and Driving Self-Independence
- Mobile and internet connectivity plays a crucial role in fostering self-independence (Aatma Nirbharta) and empowering women, particularly in rural areas, by providing access to opportunities that bridge gaps and transform lives.
- The Government e-Marketplace (GeM) has enabled rural entrepreneurs to expand their markets and increase their income by promoting products to a broader audience.
- This digital empowerment has enhanced their confidence and allowed them to compete in larger markets.
Government Initiatives to Improve Connectivity in Rural Areas
- The Indian government has made significant strides in extending mobile and internet coverage to rural and remote areas, ensuring digital inclusion and socio-economic development.
- As of September 2024, 6,22,804 out of 6,44,131 villages have mobile coverage, with over 6,14,564 villages having 4G connectivity.
- Under the Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM JANMAN) Mission, 1,136 out of 4,543 Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) habitations have been provided mobile coverage.
- By October 2024, 1,018 mobile towers have been sanctioned to enhance 4G coverage in PVTG habitations, with an estimated cost of Rs 1,014 Crore.
Key Government Programs for Digital Inclusion
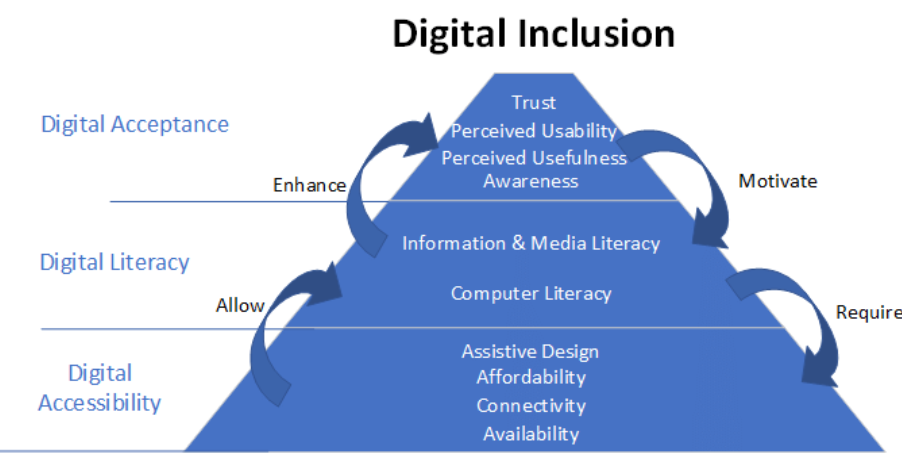
- Digital Bharat Nidhi (DBN): Previously known as the Universal Service Obligation Fund, DBN has funded the installation of mobile towers to provide communication services to underserved areas. As of December 27, 2024, 8,730 towers have been installed, covering 1.99 lakh villages.
- BharatNet Project: This initiative aims to provide affordable, high-speed internet to every Gram Panchayat in India. As of December 27, 2024, over 2.14 lakh gram panchayats are connected through BharatNet.
- PM-WANI: The Wi-Fi Access Network Interface aims to create a network of public Wi-Fi hotspots across India. As of December 27, 2024, 247,076 Wi-Fi hotspots have been established.
Protecting Telecom Users
- The government has implemented measures to protect telecom users, including the “Know Your Mobile Connections” facility and regulations to block unsolicited calls through the “Do Not Disturb” (DND) service.
- The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) uses Artificial Intelligence to detect unregistered telemarketers and imposes penalties on telecom service providers for non-compliance.
Impact of Connectivity on Socio-Economic Landscape
- The extension of mobile and internet coverage in rural areas has transformed India’s socio-economic landscape.
- Initiatives like DBN, BharatNet, and PM-WANI have laid the foundation for a digitally inclusive India.
| PYQ: Has digital illiteracy, particularly in rural areas, coupled with lack of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) accessibility hindered socio-economic development? Examine with justification. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2021) |
| Practice Question: Evaluate the effectiveness of government initiatives like GeM, BharatNet, and PM-WANI in bridging the digital divide and fostering socio-economic growth. (150 Words /10 marks) |
For more such UPSC related Current Affairs, Check Out –26 December 2024 : PIB Summary For UPSC


