3 September 2024 : PIB Summary For UPSC
1. Cabinet approves one more semiconductor unit under India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2050859 )
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy, GS2 –Governance |
| Context |
|

Analysis of the news:
- India Semiconductor Mission (ISM) was launched in 2021 with a financial outlay of Rs 76,000 crore under the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY).
- It aims to develop a sustainable semiconductor and display ecosystem in India by offering financial support to companies investing in these sectors.
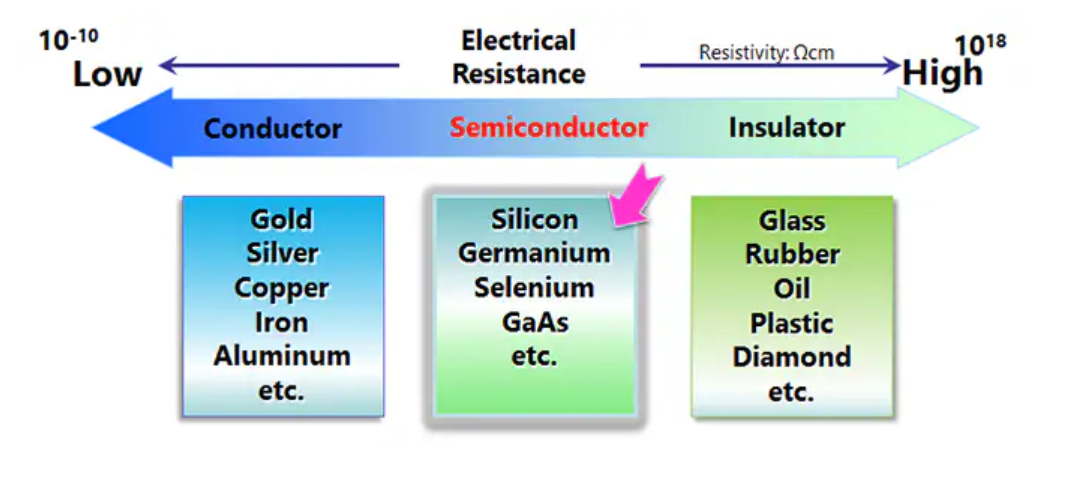
| What are semiconductors? |
|
|
- ISM is envisioned to be led by global experts from the semiconductor and display industries, acting as the nodal agency for scheme implementation.
- The mission includes various schemes:
- Scheme for setting up Semiconductor Fabs, providing fiscal support to eligible applicants to establish semiconductor wafer fabrication facilities.
- Scheme for setting up Display Fabs to attract investments for TFT LCD and AMOLED display fabrication facilities.
- Scheme for Compound Semiconductors, Silicon Photonics, and Sensors Fab, providing 30% fiscal support for setting up such facilities.
- Design Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme, offering financial incentives and infrastructure support for semiconductor design development.
- The vision is to build a robust semiconductor and display design ecosystem, positioning India as a global hub for electronics manufacturing and design.
| Need of Promoting Semiconductor Industry |
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the strategic importance of promoting the semiconductor industry in India and its role in fostering economic growth, technological advancements, and supply chain resilience. (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. Cabinet approves seven major schemes for improving farmers’ lives and livelihoods with total outlay of Rs 14,235.30 Crore
| Topic: GS3 – Agriculture |
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2050899 )
| Context |
|
- Digital Agriculture Mission (Outlay: Rs 2,817 crore)
- Uses technology and Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) to improve farming.
- Includes Agri Stack with registries for farmers, land, and crops.
- Krishi Decision Support System provides geospatial, weather, and groundwater data.
- Features AI, Big Data, and mobile-based knowledge dissemination, enhancing crop yield, loans, and buyer connections.
- Crop Science for Food and Nutritional Security (Outlay: Rs 3,979 crore)
- Aims to prepare farmers for climate resilience and ensure food security by 2047.
- Focuses on research, genetic improvement of crops, plant resources, and crop science.
- Enhances pulse, oilseed, and commercial crop productivity.
- Studies the impact of insects, microbes, and pollinators.
- Strengthening Agricultural Education, Management, and Social Sciences (Outlay: Rs 2,291 crore)
- Modernises agricultural education under the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
- Aligns with the New Education Policy 2020, using AI, Big Data, and remote sensing.
- Focuses on natural farming and climate resilience.
- Sustainable Livestock Health and Production (Outlay: Rs 1,702 crore)
- Aims to increase farmers’ income through improved livestock and dairy productivity.
- Includes animal health management, veterinary education, and genetic resource management.
- Enhances dairy production, nutrition, and small ruminant development.
- Sustainable Development of Horticulture (Outlay: Rs 1,129.30 crore)
- Promotes income growth through horticulture crops.
- Focuses on tropical, sub-tropical, and temperate crops, and root, tuber, and bulbous plants.
- Supports the cultivation of vegetables, spices, medicinal plants, and floriculture.
- Strengthening of Krishi Vigyan Kendra (Outlay: Rs 1,202 crore)
- Enhances the role of Krishi Vigyan Kendras in agricultural research and knowledge dissemination.
- Focuses on technology transfer and extension activities to support farmers’ productivity.
- Natural Resource Management (Outlay: Rs 1,115 crore)
- Aims to promote sustainable use and conservation of natural resources.
- Focuses on improving land, water, and soil management to ensure long-term agricultural productivity.
| PYQ: Q.1 Assess the role of National Horticulture Mission (NHM) in boosting the production, productivity and income of horticulture farms. How far has it succeeded in increasing the income of farmers? (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2018) Q.2 What are the major reasons for declining rice and wheat yield in the cropping system? How crop diversification is helpful to stabilise the yield of the crop in the system? (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2017) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the recent government-approved schemes aimed at improving farmers’ livelihoods and promoting sustainable agricultural practices in India. How can these initiatives contribute to achieving food security and climate resilience? (250 Words /15 marks) |