7 August 2024 : PIB Summary For UPSC
1. Cultivation of Genetically Modified crops
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2042234 )
| Topic: GS3 – Agriculture |
| Context |
|
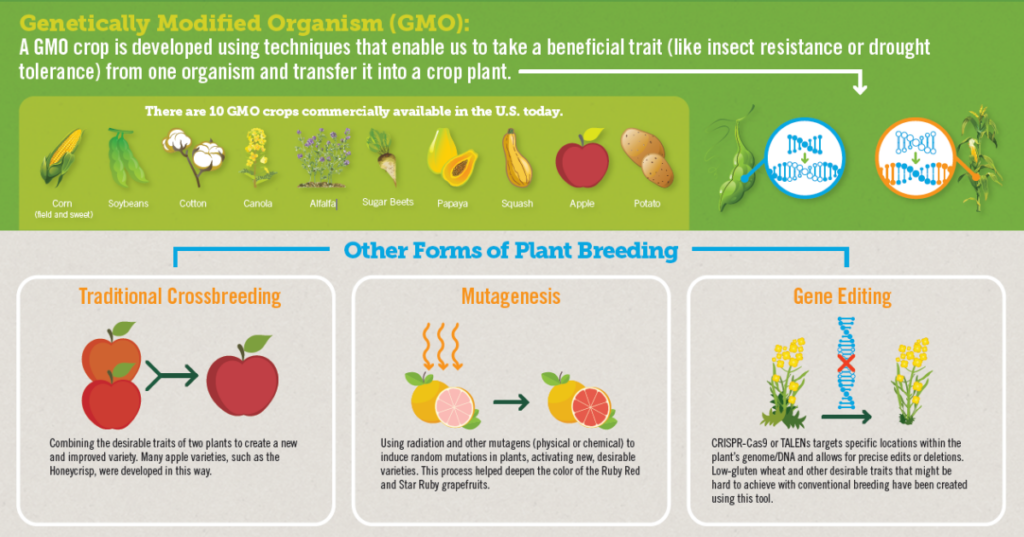
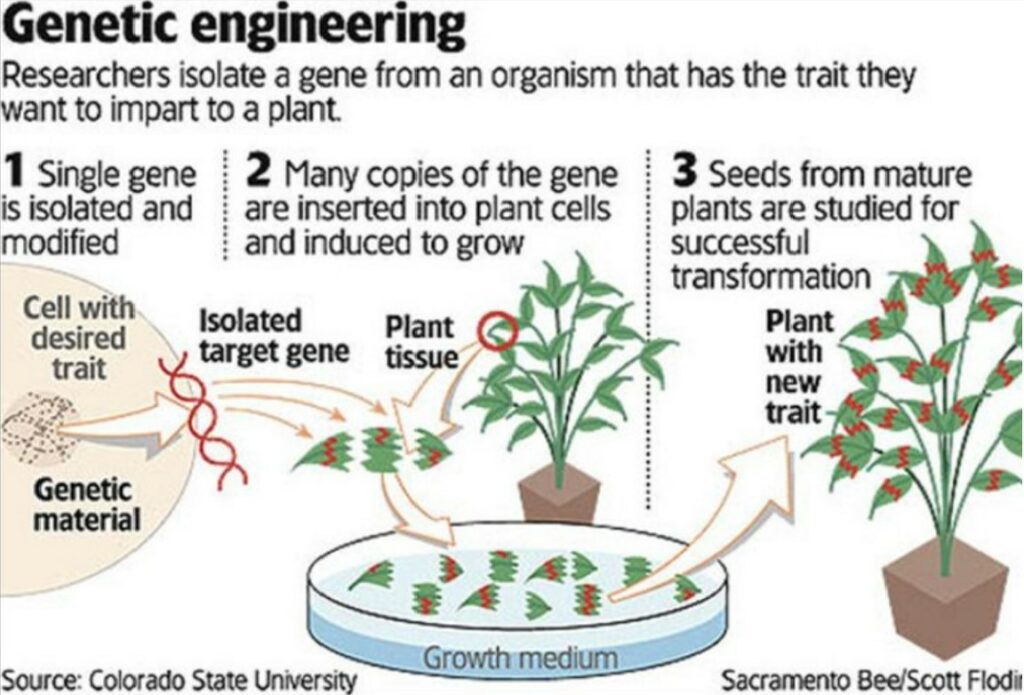
Analysis of the news:
- Bt. cotton is the only genetically modified crop approved in India for commercial cultivation since 2002 by the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) of the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
| Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC): |
|
- The Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) – Central Institute for Cotton Research (CICR), Nagpur, evaluated the impact of Bt. cotton in Maharashtra for the years 2012-13 and 2013-14.
Advantages of Bt. Cotton As per the study:
- Effective Pest Control: Bt. cotton significantly reduces bollworm infestation, a major pest, leading to healthier crops and lower damage.
- Reduced Insecticide Use: Farmers experience a decrease in insecticide applications from 8 to 4, lowering costs and minimising environmental impact.
- Increased Crop Yields: Adoption of Bt. cotton results in higher yields, with a difference of 3-4 quintals per acre compared to non-Bt. cotton.
- Higher Income for Farmers: Increased yields and reduced insecticide costs contribute to a rise in income, estimated at Rs. 25,000 per hectare under rainfed conditions.
- No Adverse Soil Effects: Studies show that Bt. Cotton cultivation does not negatively affect soil ecological parameters.
- Widespread Adoption: Over 96% of cotton cultivation area is occupied by Bt. cotton, indicating its acceptance and effectiveness among farmers.
- Enhanced Agricultural Sustainability: Bt. cotton supports sustainable farming practices by integrating pest resistance and reducing reliance on chemical inputs.
| Practice Question: Discuss the impact of Bt. cotton on agricultural productivity and environmental sustainability in India. Highlight key benefits and challenges based on recent studies. (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. New Blue Revolution
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2042167 )
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government policies |
| Context |
|
The New Blue Revolution:
- Overview: The New Blue Revolution aims to boost the fisheries and aquaculture sector in India with a focus on sustainable and responsible practices.
Information about government schemes:
- Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY):
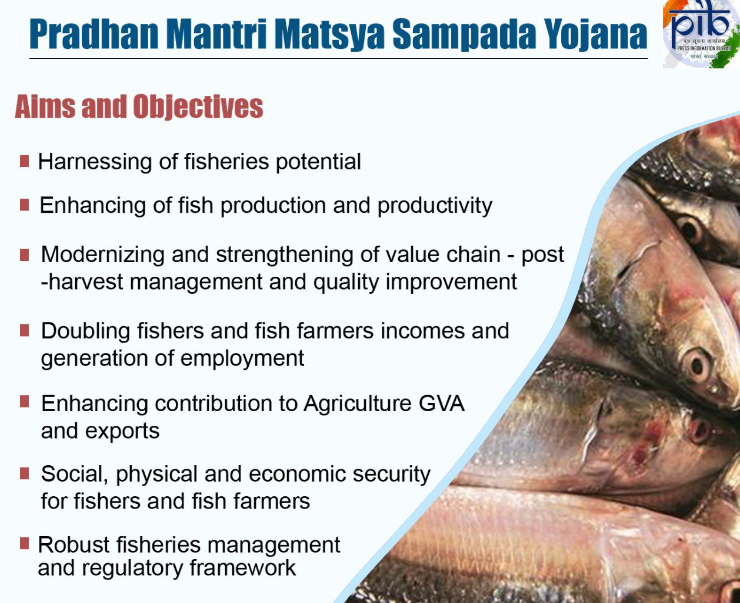
- Duration: 2020-21 to FY2024-25.
- Investment: ₹20,050 crore.
- Financial Assistance: Up to 40% for general beneficiaries and 60% for SC/ST/Women.
- Components: Pond and tank construction, hatcheries, technology infusion (e.g., Re-circulatory Aquaculture System, Bio-floc systems), seaweed and bivalve cultivation, fish transport infrastructure, cold storage, fish feed mills, value-added enterprises, and trout farming support.
- Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund (FIDF):
- Total Fund: ₹7,522.48 crore.
- Support: Concessional finance and interest subvention up to 3% for 12 years.
- Focus: Development of fisheries infrastructure, including trout farming facilities.
- Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah Yojana (PMMKSSY):

- Investment: ₹6,000 crore.
- Objectives: Formalization of the sector, incentivizing aquaculture insurance, improving value chain efficiency, and ensuring safety and quality.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC):
- Extension: Since 2018-19 for fishers and fish farmers.
- Purpose: Meets working capital requirements for fisheries and aquaculture activities.
| Practice Question: Discuss the objectives and impact of the New Blue Revolution in India’s fisheries and aquaculture sector. (150 Words /10 marks) |
3. PM-KUSUM SCHEME
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2042069 )
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government policies |
| Context |
|
PM-KUSUM scheme

Uttar Pradesh alone has benefited 51,097 farmers as of 29.07.2024.
Launch and Scaling: PM-KUSUM scheme launched in March 2019, scaled up in January 2024.
Ministry: Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE)
Objectives:
- Provide energy and water security to farmers.
- Enhance farmer income.
- De-dieselize the farm sector.
Reduce environmental pollution.
Component-A:
- Purpose: Set up Decentralized Ground/Stilt Mounted Grid Connected Solar or other Renewable Energy based Power Plants on farmers’ land.
- Capacity: Up to 2 MW.
- Implementation: Can be done by farmers themselves, or in partnership with cooperatives, panchayats, FPOs, or developers.
- Financials: Renewable energy purchased by DISCOMs at pre-fixed tariffs; land lease payments if leased to developers.
Incentives: DISCOMs receive Performance Based Incentive (PBI) of Rs. 0.40 per unit or Rs. 6.6 lakh per MW for five years, which can be passed to REPP owners for better tariffs.
Component-B:
- Purpose: Install Stand-alone Solar Agriculture Pumps.
Central Financial Assistance (CFA): 30% (50% for North Eastern Region/Hilly regions/Islands).
Component-C:
- Purpose: Solarisation of grid-connected Agriculture Pumps under Individual Pump Solarisation (IPS) and Feeder Level Solarisation (FLS).
Central Financial Assistance (CFA): 30% (50% for North Eastern Region/Hilly regions/Islands).
Beneficiaries:
- As of 30.06.2024, 4,11,222 farmers benefited nationwide.



