9 August 2024 : PIB Summary For UPSC
1. Impact of Glacial Lake Outburst Floods
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2042990 )
| Topic: GS1 – Geography, GS3 – Disaster and disaster management |
| Context |
|
What are Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs)?
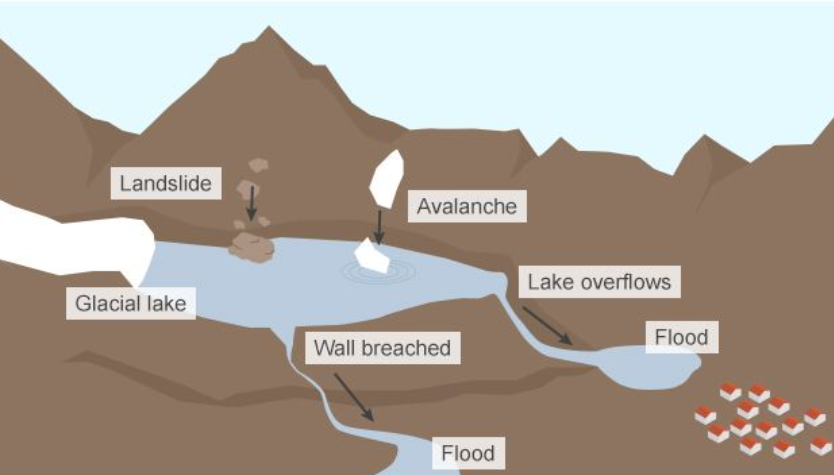
Definition
- Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs): A GLOF occurs when a glacial lake, formed by the melting of glaciers, suddenly releases a significant amount of water.
- This sudden release often results in catastrophic flooding downstream, causing damage to infrastructure, ecosystems, and communities.
Reasons
- Glacial Retreat: The melting of glaciers due to climate change leads to the formation and expansion of glacial lakes. As these lakes grow, the risk of their natural barriers (like moraines) failing increases.
- Ice or Rock Avalanches: Avalanches can destabilise the moraine or ice dam holding the glacial lake, causing it to collapse and release water.
- Seismic Activity: Earthquakes can trigger landslides or directly destabilise the lake’s dam, leading to a sudden outburst.
- Excessive Rainfall or Snowmelt: Heavy rainfall or rapid snowmelt can increase the volume of water in a glacial lake beyond its capacity, causing overflow and dam failure.
Way Forward
- Early Warning Systems: Implement and maintain robust early warning systems to monitor glacial lakes and detect signs of potential outbursts.
- Regular Monitoring: Conduct frequent assessments of glacial lakes and their surroundings using remote sensing technology and on-ground surveys to identify high-risk areas.
- Structural Mitigation Measures: Construct controlled drainage channels or reinforce moraine dams to reduce the likelihood of sudden breaches.
- Community Awareness and Preparedness: Educate local communities about GLOF risks and develop evacuation plans to minimise loss of life and property.
- Research and Collaboration: Encourage scientific research to better understand GLOF dynamics and collaborate internationally to share knowledge and strategies for risk reduction.
| Practice Question: Discuss the causes and potential mitigation strategies for Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs) in the Himalayan region. (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. WORLD HERITAGE SITES IN INDIA
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?P RID=2043018)
| Topic: GS1 – Indian Culture |
| Context |
|
World heritage sites in India:
| Site and State | Year | Information |
| Agra Fort, Uttar Pradesh | 1983 | A Mughal fortress known for its architectural grandeur. |
| Ajanta Caves, Maharashtra | 1983 | Ancient Buddhist cave monuments famous for their paintings and sculptures. |
| Ellora Caves, Maharashtra | 1983 | Rock-cut temples representing Buddhist, Hindu, and Jain traditions. |
| Taj Mahal, Uttar Pradesh | 1983 | Iconic white marble mausoleum built by Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan. |
| Group of Monuments at Mahabalipuram, Tamil Nadu | 1984 | Ancient rock-cut architecture and sculptures dating back to the Pallava dynasty. |
| Sun Temple, Konarak, Odisha | 1984 | 13th-century temple known for its massive chariot-like structure dedicated to the Sun God. |
| Kaziranga National Park, Assam | 1985 | Home to the world’s largest population of Indian one-horned rhinoceroses. |
| Keoladeo National Park, Rajasthan | 1985 | Renowned bird sanctuary hosting numerous migratory birds. |
| Manas Wildlife Sanctuary, Assam | 1985 | A biodiversity hotspot with rare and endangered species, including the Assam roofed turtle. |
| Churches and Convents, Goa | 1986 | Historical Portuguese churches and convents representing colonial architecture. |
| Fatehpur Sikri, Uttar Pradesh | 1986 | A Mughal city known for its stunning palaces and religious buildings. |
| Group of Monuments at Hampi, Karnataka | 1986 | The ruins of a medieval Hindu kingdom with impressive temples and palaces. |
| Khajuraho Group of Monuments, Madhya Pradesh | 1986 | Known for their exquisite erotic sculptures and intricate carvings. |
| Elephanta Caves, Maharashtra | 1987 | Rock-cut cave temples dedicated to Lord Shiva. |
| Great Living Chola Temples at Thanjavur, Gangaikondacholapuran and Darasuram, Tamil Nadu | 1987 & 2004 | Exemplary Chola dynasty temples showcasing Dravidian architecture. |
| Group of Monuments at Pattadakal, Karnataka | 1987 | Blend of northern and southern Indian architectural styles in Hindu and Jain temples. |
| Sundarbans National Park, West Bengal | 1987 | Largest mangrove forest in the world, home to the Bengal tiger. |
| Nanda Devi and Valley of Flowers National Parks, Uttarakhand | 1988 & 2005 | Known for high-altitude biodiversity and stunning floral displays. |
| Buddhist Monuments at Sanchi, Madhya Pradesh | 1989 | One of the oldest and most significant Buddhist complexes in India. |
| Humayun’s Tomb, Delhi | 1993 | A precursor to the Taj Mahal and an example of Mughal garden-tomb architecture. |
| Qutb Minar and its Monuments, Delhi | 1993 | A collection of Islamic architecture, including the world’s tallest brick minaret. |
| Mountain Railways of India (Darjeeling, Nilgiri, Kalka – Shimla), West Bengal, Tamil Nadu, Himachal Pradesh | 1999, 2005, 2008 | Historic narrow-gauge railways showcasing engineering marvels of the colonial era. |
| Mahabodhi Temple Complex at Bodh Gaya, Bihar | 2002 | The location where Buddha attained enlightenment. |
| Rock Shelters of Bhimbetka, Madhya Pradesh | 2003 | Prehistoric cave paintings and archaeological remains. |
| Champaner-Pavagadh Archaeological Park, Gujarat | 2004 | A blend of Hindu and Islamic architecture with historical significance. |
| Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus (formerly Victoria Terminus), Maharashtra | 2004 | An architectural masterpiece and historic railway station in Mumbai. |
| Red Fort Complex, Delhi | 2007 | A symbol of India’s Mughal era with significant historical importance. |
| The Jantar Mantar, Jaipur, Rajasthan | 2010 | An astronomical observatory with architectural innovations. |
| Western Ghats, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu | 2012 | Biodiversity hotspot known for its unique flora and fauna. |
| Hill Forts of Rajasthan (Chittorgarh, Kumbhalgarh, Jaisalmer, Ranthambhore, Amber, Gagron), Rajasthan | 2013 | A series of majestic forts reflecting Rajputana defense and architectural styles. |
| Rani-ki-Vav (the Queen’s Stepwell) at Patan, Gujarat | 2014 | An intricately designed stepwell showcasing Maru-Gurjara architectural style. |
| Great Himalayan National Park Conservation Area, Himachal Pradesh | 2014 | Known for its diverse ecosystems and conservation efforts. |
| Archaeological Site of Nalanda Mahavihara at Nalanda, Bihar | 2016 | Ancient university ruins reflecting early Buddhist education. |
| The Architectural Work of Le Corbusier, Chandigarh | 2016 | Modernist architecture by Le Corbusier, reflecting urban planning innovations. |
| Khangchendzonga National Park, Sikkim | 2016 | Known for its rich biodiversity and cultural significance. |
| Historic City of Ahmedabad, Gujarat | 2017 | Known for its blend of Hindu and Islamic architectural heritage. |
| Victorian Gothic and Art Deco Ensembles of Mumbai, Maharashtra | 2018 | Unique architectural style representing the colonial era in Mumbai. |
| Jaipur City, Rajasthan | 2019 | Known for its planned architecture and rich cultural heritage. |
| Dholavira: a Harappan City, Gujarat | 2021 | An archaeological site of the Indus Valley Civilization with impressive urban planning. |
| Kakatiya Rudreshwara (Ramappa) Temple, Telangana | 2021 | Renowned for its intricate craftsmanship and architectural brilliance from the Kakatiya period. |
| Santiniketan, India, West Bengal | 2023 | A cultural and educational center established by Rabindranath Tagore. |
| Sacred Ensemble of Hoysalas, Karnataka | 2023 | Known for its exquisite temple architecture from the Hoysala period. |
| Moidams – the Mound-Burial System of the Ahom Dynasty, Assam | 2024 | Ancient burial mounds of the Ahom dynasty, showcasing unique cultural heritage. |



