Science Reporter: India’s Future is in Innovation.
Article 1: Make Education more creative:
Context:
India is home to the world’s largest youth population. The future of our nation is lies on our youth Empowerment that only through creative education and it is the foundation for Atmanirbhar Bharat. The changing of society requires an education system that nurtures creativity and drives innovation. This would require major reforms in our education, especially in the way of teaching and learning happens now a days.
India’s education system:
- India has wider education system having network of 1.5Million Schools with 250M enrollments, 1k universities and over 40k higher education institutes with 40M students.
- India is also home to the world’s largest young learning population age group of 3-23 years may consists of 20% population but they are 100% of our future.
- In the development of creative skills, Education plays a very important role.
Crisis of creativity:
- Dearth of creative minds: There seems to be a dearth of creative minds leading to a crisis of creativity in India.
- Poor patent filing: India presently ranks 3rd in the world for research, 7th for highly cited papers and 10th for patent filings.
- Low density of researchers: India has just 250 scientists/researchers per 1M Population, No Indian scientist while working in India has been able to get a noble prize after CV Raman in 1930.
- Poor in Innovation: India has not been able to reproduce the magic of early part of that century created by eminent scientists, Now India ranks 40th in the Global innovation index 2022.
- The low spending on higher education budget is eventually affect quality of research in our HEIs and their world rankings.
Need for reforms:
- Education is not the learning of facts but the training of mind to think, we need a “well formed mind and not a well filled mind”.
- The NEP-2020 of India is needs to shift the focus of education system to conceptual clarity, critical thinking, problem solving, innovation and creativity.
- The method of teaching is traditional teacher-centric ‘talk and chalk’’ further it has many limitations such as mainly a monologue method which is very slow and time consuming.
- Teachers should embrace new learner-centric ways because learners learn best when they involved in the topic and get motivated to seek new knowledge, skills in order to solve the problem in hands.
- So the focus of teaching- learning should be on engaging the learners.
Nurturing creativity & innovation through education:
- Creativity is not an injection to give to someone, you need to create environment for curiosity. Albert Einstein once said, “I have to no special talent. I am only passionately curious”.
- The Ministry of Education (MoE), Govt of India recently launched (PMMMNMTT) Pandit Madan Mohan Malviya National mission on Teachers and teaching.
- It focuses primarily on enhancing the skills of teachers in higher education through various programs.
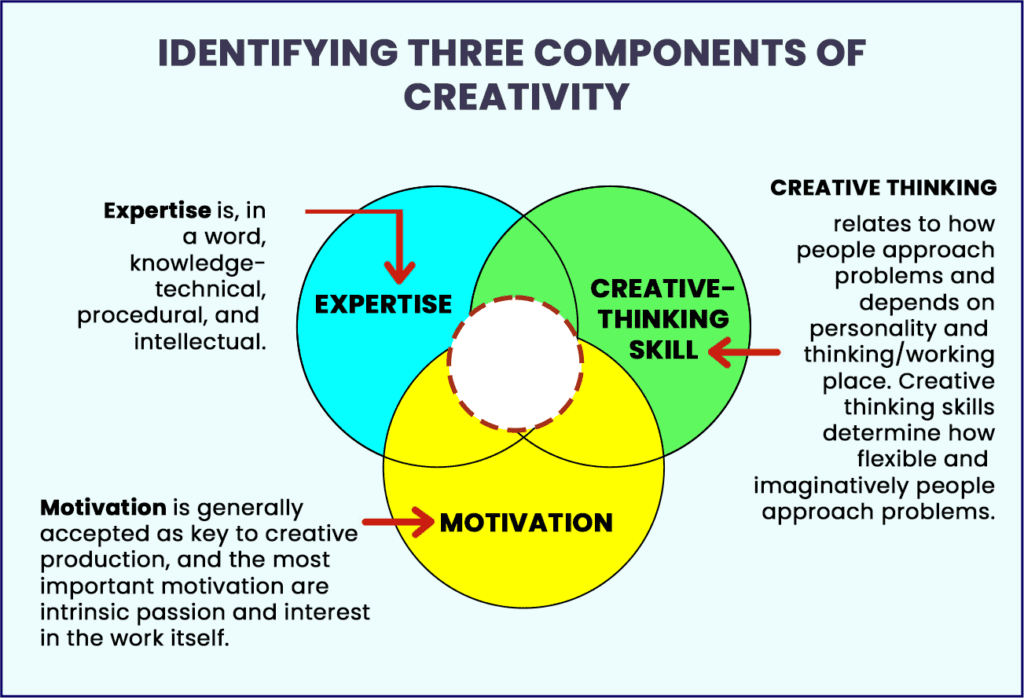
Ways to nurture creativity:
Some of the following are ways to nurture creativity amongst students:
- New teaching learning methods that encourage curiosity, creativity, to train students become independent, individually to Solve problems by their own thus nurturing their confidence and self belief.
- The age, Teachers needs to Empowered with new ICT empowered pedagogies such as blended learning, flipped classroom that helps to meet learning needs of the 21st century.
- There is immediate need to shift focus from passive learning to Experimental learning i.e., learning by doing.
- Focus on keen and strong observation skills are found to be strongly linked to greater creativity, originality, and flexible thinking.
- The main reason behind the lake of creativity in students is excessive use of internet. Now, we strongly recommend that to avoid as much as possible.
- The assessment driven learning process needs to be more scientific to encourage multiple skills of the students.
- The syllabus should be lighter consisting of only core essentials, teaching should be on conceptual clarity.
Conclusion:
- Creativity refers to the ability to generate the new and unique ideas, while innovation refers to the process of turning those ideas into practical solutions.
- In other words creativity is the fuel for innovation and it can drive creativity.
- The Creativity is the baseline for invention, innovation, and Entrepreneurship.
- Being Creative and innovative can helps to encourage the people to identify unique solutions for different types of problems that the entire nation encounters and thus, help to fulfill the dream of Atmanirbar Bharat.
Article 2: Promoting and nurturing grassroots innovations:
Context:
Grassroots innovations are essentially creative solutions devised by the common people who despite communities they live amongst and address it frugally. These are the different innovations from grassroots, which include innovations by students, professionals & formal R&D institutions which have applicability in the grassroots communities. The scope of this article is largely focuses on the contribution and challenges faced by the innovators from grassroots.
Grassroots innovations:
- Grassroots innovations emerge to address unmet social and technological needs.
- The honey bee network along with its institutions, GIAN, SRISTI, NIF, are several collaborators supporting grassroots innovators, traditional knowledge holders from the past 3 decades.
- GIAN is the world’s first incubator of grassroots innovations and technologies
- We do appreciate the role of innovations from the formal sectors to address the needs of the people at lower income levels
Problems face by innovators and support they need
- The documentation of grassroots innovations needs special efforts as most of our innovators from the rural parts of the country.
- Often are not fluent with Hindi much less with the English except some part of the south India due to The low literacy levels, they may not articulate or pitch their innovations.
- The vernacular innovation program Atal innovation mission is trying to bridge this gap for learning about design thinking.
- This needs grant support, not everything can be done through loan or equity investments particularly at a very lower stage.
- Innovations by and for women needs special attention because the rate of technological change found to be slower in the activities that women perform.
- The policy makers can provide dedicated funds and instrumental legitimacy, for such a partnership between formal and informal sectors.
- Mobile labs and testing facilities for standards of innovation are needed especially for small farmers, economically disadvantaged and hilly regions.
- Micro venture innovation fund(MVIF) is a risk fund needed to take these innovations in to the market most of the innovators come from economically constrained background
- GIAN invested 44 lakhs in 24 technologies with the help of SIDBI during the covid-19 pandemic and promoting DIY(do it yourself), IP protected solutions in a diversified ecosystem
Policy incentives:
- Direct innovation incubation fund –Every district Should have a fund of at least 5cr for scouting, supporting, rewarding local grassroots innovators and traditional knowledge holders and also include Public R&D fund for Laboratory, testing,
- All India coordinated project for Multi location trails of GRIs and TKs- one of existing gap in current ecosystem is the lake of funding for multi location pilots.
- Innovation week- Under the MGNREGA, at least one week will be celebrated as innovation week and MVIF is also a risk fund to provide soft loans without collateral.
Conclusion:
- India will lead in developing and diffusing the idea of grassroots innovations deserves to be highlighted even during G-20 meetings with all the diversity. The ecosystem is most important in present society. It is the GRI which will meet the emerging challenges in the country. Government and private initiatives should formulate good policies that to support the grassroots innovations, outstanding traditional knowledge, crafts, cuisines, new ideas for social development, etc.
Article 3: C-CAMP (A world class Model):
Context:
The center for cellular for and molecular platforms (C-CAMP) is helping set up an ecosystem that nurtures and catalyzes such deep science innovations of India in close collaborations with multiple govt agencies. Mainly it aims to harness the phenomenal scientific talent and potential that India already has and provide ecosystem support deep science ideas need to transform them into technologies that touch, save, and change lives.
Highlights from an Enviable Portfolio:
- Bug works– a drug discovery start-up whose genesis was in 2013-2014with a few scientists from India trying to address one of the 21st century medicine’s impending public health challenges- Antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
- Eyestem– one of the world’s best regenerative medicine start-ups with affordable stem cell therapy solutions to reverse vision loss in degenerative illnesses.
- String bio– the proprietary microbial and fermentation platforms convert methane- a potent methane gas into value added solutions for animal nutrition, crop inputs and biodegradable polymers.
- They were the winner of hello tomorrow 2017competation in Paris as the best deep tech agriculture startup and are India pioneers in clean tech solutions.
- There are the few more start ups i.e., Pandorum, innaccel, including the above start ups that are worth more than $600Mn in less than 10 years, which is unprecedented.
Conclusion:
- India has complex problems that are often highly region and population specific but problems like world class healthcare at affordable rates, high agri-production with high farmer income, Sustainable energy and the environment for environmentally vulnerable are common across India. Therefore it is imperative that indigenous innovations are built to solve these local problems with a global view. C-camp looks forward to collaborating with scientists, innovators and other eco system players across India and beyond to take these efforts to the next level and contributing towards India’s science and innovation story.
Article 4: Resilient India’s innovative and promoting culture of innovation:
Context:
India was ranked 40th in the global innovation index (GII) released in 2022 by WIPO and in 2015 India ranks 81, each year there has been improvement in Indian index aided by “Ease of doing business”, “Start up” programs promoting innovation and incubation.
The Global innovation:
The GII provides detailed information about 131 economies and countries performed globally in terms of innovation.
GII is the authoritative tool to analyze social and economic trends in their nations, it acts as a benchmark for measuring innovation in relation to SDG.
The GII 2022 also discuss positive and negative effects of two new innovation waves i.e.,
- Digital age innovation wave and artificial intelligence and role & impact of digital innovation enhancing the productivity in scientific research throughout the country
- Deep science innovation wave based on Bio & Nanotechnologies and sciences.
This ranking is based on objective and arbitrary data collected from various sources.
The WIPO released 15 Edition Report on GII with focused scheme of “what is the future of innovation-driven growth?”
The main goal & objective of this report were to incorporate innovations and technologies into socio economic challenges, changes by various governments to improve and strengthen existing policies and innovation ecosystem.
Challenges to India’s Innovation Ecosystem:
- Excessive focus on memory: the current educational system faces several challenges including an excessive focus on memory instead of innovation and creativity.
- There is a substantial gap between acquired and required knowledge because Companies expectations and objectives differ from educational institutions, students got qualification and struggle for jobs.
- Today schemes and programs like Atal innovation mission, jigyasa, vigynanajyoti, NIDHI etc. collaborating with international institutions and are promising results but still long way to go to bridge the gap.
- India’s new educational policy also calls for fostering innovation and creativity like STIP 2020 is intended to promote innovation.
- Low spending: India is still spending less than 1% of its GDP on Research and development whereas some of advanced countries spending up to 8% of their GDP.
Conclusion:
Institutions of higher education are committing to focus on nurturing winners by incorporating innovation in various modes of learning, in the form of teaching strategies, curricula, and institutional culture. Innovations are the only way forward towards an” Atmanirbhar Bharat” which not only promoting the nation’s resilience but also self-reliance too.
Article 5: Promoting a culture of innovation In India:
Context:
India with innovation and entrepreneurship high on development motive, for that there are several Government initiatives directed towards promoting and nurturing innovation at various levels of several sectors in India. Let’s go through some of programs.
Snapshot of government initiatives on promoting and nurturing innovation:
INSPIRE and INSPIRE-MANAK:
- DST (department of science and Tech) manages the scheme and this scheme encourages the young generation to pursue college or university education in natural science.
- The Scheme offers internship, Scholarship for higher education(SHE), faculty fellowship and it also motivates the youth to pursue their research careers in basic science.
- MANAK is an initiative of INSPIRE that fosters culture of innovation among talented school students and make them interested in science and research in early life.
- INSPIRE– innovation in science pursuit for inspired research and
MANAK– Million minds augmenting national aspiration and knowledge
SUNIL:
- It is a part of SEED & DST, the SUNIL programme (formerly TARA) provides technology delivery and social enterprise development models for economically weaker section of society.
- This programme also promotes the scientific and technological knowledge, skill development and capacity building.
- SUNIL– Strengthening, upscaling& Nurturing local innovation for livelihood.
- SEED– Science for equity, Empowerment & Development
ASPIRE:
- It is an initiative of government of India under the Ministry of MSME to set up a network of technology & incubation centers to promote entrepreneurship & culture, agro-industry innovation, creating new jobs
- ASPIRE– A scheme for promotion of innovation, rural industries and entrepreneurship.
NIDHI:
- DST fosters knowledge-based and technology- driven innovations into successful startups through the NIDHI programme.
- NIDHI- national initiative for developing and harnessing innovations
PRISM:
- The DSIR, individual innovators can receive grants, technical assistance and mentoring to transform their ideas into successful enterprises, it also aimed to help MSME clusters.
- PRISM– promoting innovations in individuals, startups and MSME
- DSIR– Department of scientific and industrial research
Atal innovation mission (AIM):
- NITI Aayog’s AIM is the government of India’s flagship initiatives to promote culture of innovation and entrepreneurship in the country.
- AIM created 4 programmes: Atal tinkering labs, Atal incubation centers, Atal new India challenges, and Atal grand challenges.
- Promoting entrepreneurship and fostering innovations are the core functions of AIM.
- NITI Aayog is a think tank of the government of India formed on 1st January 2015, Prime minister is the chairman.
BIRAC:
- It was established by the DBT (department of biotechnology).
- The aim of BIRAC is to address nationally relevant product development needs through interaction between industry and academia.
- BIRAC provides this through various initiatives including targeted funding, technology transfer, IP management, and handholding schemes that help biotech innovations
- BIRAC– Biotechnology industry research assistance council
Schemes under MoE (Ministry of education):
- Research parks: The main aim of this is to support government focus on developing indigenous R & D capabilities, boosting manufacturing and creating startup culture in India.
- IMPRINT: The MHRD-supported pan-IIT + IISC collaborative initiative guides and empowers India’s pursuit of inclusive growth and self-reliance by addressing major issues in the science and technology.
- School innovation council (SIC): this was launched across India for schools by MIC (Ministry of education’s innovation cell), to promote the culture of innovation, ideation, Entrepreneurship, creativity and design thinking.
Society for innovation & development (SID):
- SID is an initiative of IISc (Indian institute of science) Bangalore, for enabling Science and Tech innovations.
- It has three divisions-
- Core- Engages with large corporations in collaborative research.
- TIME- places midsized enterprises according to their innovation on journey of disruptive growth.
- STEM- which helps startups that have a big impact on science and society.
National innovation foundation (NIF):
- The NIF, DST, they aims to promote grassroots technological innovations and outstanding traditional knowledge.
- NIF helps to identify, support and spawn grassroots innovations developed by the local communities and individuals contributes to human survival without any support from formal sector.
- The GTIAF (Grassroots technological innovation acquisition fund) of NIF Address the challenges of grassroots innovators at commercial and technology levels.
National research development corporation (NRDC):
- The NRDC is an enterprise of DSIR and promotes, develops, Transfers technologies emerging from various national research and development organization.
CSIR- The innovation Engine of India:
- The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research is an organization with 37 National laboratories and many more research centers across India. The list of centers includes world class centers of research such as the National Physical Laboratory (NPL), National Chemical Lab (NCL), central road research Institute (CRRI).
- The past 80 years, the CSIR (council of scientific and industrial research) has been contributing to the research and innovation, promoting the cultural innovations.
Ministry of electronics & Information technology (MeitY):
- The Startup, innovation & IPR division of MeitY has undertaken a proactive, preemptive and graded measures to spur the technology led startup innovation ecosystem in the country giving an impulse to new and emerging technologies.
- Major initiatives of MietY are
- TIDE 2.0 (technology incubation and development of entrepreneurs
- Meity startup hub
- Stratup acceleration programmes
Department of space:
Atmanirbhar Bharat ARISE-ANIC:
- This program is a national initiative to promote research & innovation and increase competitiveness of Inidian stratups and MSMEs.
- The objectives of this program impulse research, Innovation and facilitate innovative solutions to sectoral problems.
- Also provide steam of innovative products & solutions where the central government ministries will become potential first buyers.
- It is a Self reliant India scheme announced by the union ministry of finance in May 2020 and also allocates almost 10% of GDP of the country.
Space enterprise encouragement & Development (SEED):
- This is an envisaged early stage encouragement program to innovative to startups and MSMEs in developing products/services in focus areas of interest to ISRO.
- SEED is an initiative of ISRO (Indian space research organization)
Article 6: What’s new in news?
Biodiversity of species:
The team of Punjab University found the two new species particularly in bio diversity hotspots like the Western Ghats and the northeast Himalayas.
Lordomyrma mewasinghi:
- They found this species in pampadum shola national park and karian shola national park in Western Ghats having daily temperature of 35 degrees.
- The analysis found that the ant belongs to genus called Lordomyrma.
Stictoponera lattkei:
- This was picked up from a tree trunk in a village near Rorathang town in east Sikkim having an average daily temperature of 30 degrees.
- The analysis found that the ant belongs to the genus called Stictoponera.
Cardiac imaging by wearable ultrasound device:
- The researchers from the University of California developed a wearable, non-invasive heart monitor device that can be worn easily for 24hrs.
- The portable wearable system uses ultrasound to continuously capture high quality images and provide real time data of the human heart.
Cost efficient carbon capture system:
- The Pacific Northwest national laboratory have created the new system that efficiently captures co2-the least costly to date and converts in to world’s most widely used chemicals, methanol it holds many uses.
BharOS:
- It is an indigenous mobile operating system developed by the IIT madras and it provides access to trusted apps from organization- specific private app store services (PASS).this means the user not forces to use apps that may not be familiar or not trust.




