Science Reporter July 2023
Article 1: INDIAN CLASSICAL MUSIC
The origin of Indian classical music can be traced back to the Vedas (Sam Veda), which contained slokas that were set music. Indian music can be divided into three major periods, i.e., Ancient, Medieval and Modern.
Around the 14th century, it got divided into two branches, i.e., Hindustani Music (popular in northern India) and Carnatic Music (primarily popular in southern India). There are three main pillars of Indian classical Music Raga, Tala and Swara.
- Raga is the repetition of Musical notes such as SA, RE, GA, and MA. A collection of musical notes represents a set. A subset from the set of all 12 notes is known as Thaat, a subset of 7 notes from 12.
- Tala refers to rhythmic beat groupings.
- Swara: 12 notes on which Hindustani classical music is based are called Swara or Sargam. In Indian music, there is a concept called Saptak, also known as Octave. Saptak means gamut or series of seven notes. Out of 7 , generally 3 are used i.e.,mandra saptak, madya satak, tar saptak.
Article 2: Purveyors of doom… instil anxiety and helplessness
| 12 Musical notes | Set |
| Thaat (7 notes) | subset |
| Raga (5-7 notes) | A kind of subset of Thaat. Aesthetical permutation of an element of the subset
Bound in the structure of aTaal. |
Doomscrolling is endlessly scrolling through negative feeds and has become a pervasive habit for many. According to a study, Participants who spent more than six hours on media coverage per day were nine times more likely to experience symptoms of high acute stress than those who watched a minimal amount of news.
Ill-effects of Doomsrolling
- Doomscrolling amplifies anxiety, leaving people mentally exhausted.
- The constant stream of negativity hinders the ability to think critically and empathise.
- It can negatively impact the attention span and hinders cognitive functioning.
- Engaging before bed can disrupt the sleep pattern leading to feelings of fatigue and anxiety.
Conclusion
Conscious efforts may be required to bring a shift in media consumption. Further engaging in mindful media consumption is the key instead of passively scrolling through newsfeeds.
Article 3: Cold Plasma-based Nitrogen-Fixing Technology
What is nitrogen fixation?
The process of converting relatively non-reactive atmospheric nitrogen into more reactive compounds, i.e., Nitrates, Nitrites, or Ammonia, is nitrogen fixation.
Traditional agriculture depended on nitrogen fixed through biological nitrogen-fixing microbes and atmospheric nitrogen-fixing reactions.
Haber-Bosch process
It was an breakthrough in industrial chemistry. The haber-Bosch process converts atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia by reacting with hydrogen gas using high temperatures and pressures.
- This process produces over 90% of the world’s ammonia, sustaining 40% of the global population.
- However, it releases around 300 million tons of carbon dioxide.
- Therefore there is a growing need for green nitrogen for sustainable farm practices. Cold plasma-based nitrogen fixation technology could help to achieve this goal.

What is plasma?
Plasma is a state of matter in which atoms are ionised, meaning they have lost or gained electrons and become electrically charged.
Plasma can be classified into hot plasma and cold plasma, depending on the temperature of the electron and ions.
- Hot plasma: it is plasma where the electron and ions have the same energy or temperature.
- Cold plasma or non-thermal plasma: involves a state of matter where heavy atomic particles are at room temperature and are non-thermalised.
- Cold plasma is generated by applying energy to a gas that makes them lose electrons of the outer shells and become ionised at temperatures below 40o
- This property has enabled the application of cold plasmas to various biological systems.
Plasma Agriculture
Plasma agriculture is a term used for a cluster of cold plasma-based applications such as decontamination of seeds, germination enhancement in seeds, enhancement of plant growth, insect and fungal control in stored diseases and reclamation of contaminated soil.
Uses of cold plasma
- Cold plasma-activated water is known to enhance seed germination and crop growth.
- A Korean group at the applied plasma medicine centre, Kwang Woon University, has fabricated an AC-driven non-thermal atmospheric pressure nitrogen plasma jet that causes nitrogen reduction to ammonia. This will enhance seed germination and plant growth in corn plants.
- The developed plasma applicator reduces air nitrogen reacting it with oxygen forming nitrogen oxides.
- A Norwegian firm has developed a new technology for fortifying liquid organic manure with atmospheric nitrogen. This will reduce air nitrogen, reacting it with oxygen and forming nitrogen oxides.
- This causes about a 20% reduction in the dependence on chemical fertilisers made from fossil fuel or coal.
Conclusion
Cold plasma-based nitrogen fixation is a promising technology, and its adoption under Indian conditions should be feasible in the foreseeable future.
Article 4: A Catalyst to produce sustainable Green Hydrogen Fuel
Catalysts created by the Indian Institute of Technology in Guwahati may liberate hydrogen gas from wood alcohol without producing any carbon dioxide as a by-product.
Benefits
- This method produces formic acid, which is helpful in industrial chemicals.
- This development makes methanol a promising Liquid Organic Hydrogen Carrier (LOHC) and contributes to the concept of the hydrogen methanol economy.
- The process involves environmentally safe.
Methods
- Hydrogen is produced by either:
- the electrochemical splitting of water or
- bio-derived chemicals such as alcohol.
- In this method, hydrogen is typically produced from methyl alcohol (wood alcohol) using a catalyst.
A problem associated with the catalytic production: Two problems are associated with the catalytic production of hydrogen from wood alcohol.
- Firstly, the process involves as high as temperatures in the range of 300oC and at high pressures.
- Secondly, the reaction coproduces carbon dioxide (greenhouse gas).
The solution to the second problem, i.e., the reaction coproduces carbon dioxide
The IIT Guwahati team developed a catalyst called Pincer Catalyst. It contains central metals and few organic ligands.
This pincer catalyst becomes very specific and selective because the organic ligands are like the claws of a crab that hold the metal in place. Thus, formic acid is generated as wood alcohol is broken into hydrogen.
Article 5: New non-toxic powder uses sunlight to disinfect contaminated drinking water quickly
- A low-cost, recyclable powder that kills thousands of waterborne bacteria per second when exposed to sunlight is developed by scientists from Stanford University and SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory.
Benefits
- Access to drinking water: This will be helpful to nearly 30% population with no access to clean water.
- It is a harmless metallic powder that absorbs both UV and high energy visible from the Sun.
- This non-toxic powder is recyclable and requires low cost.
- This powder might also be useful in wastewater treatment plants using UV lamps to disinfect treated water.
Article 6: PRECISION MEDICINE – REVOLUTIONISING HEALTHCARE
Precision medicine, also known as personalised medicine. It aims to provide customised medical treatment and prevention plans based on an individual’s unique genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. To address the root causes of their illness, Tailor-made treatment is provided.
Key technologies used in precision medicine
Under precision medicine, Specifically designed treatments are provided to each patient. Different technologies used in Precision Medicine are:
- Genomics: Genomics is the study of an individual’s genes, and their interaction advances in genomic sequencing technologies have made it possible to sequence an individual’s entire genome, allowing researchers and healthcare providers to identify the specific mutations associated with particular diseases. This helps develop targeted treatments tailored to the patient’s genetic makeup.
- Proteomics: Proteomics is the study of an individual’s protein. With the help of Proteomics, healthcare providers can identify biomarkers that are associated with specific diseases and develop targeted treatments that address those biomarkers.
- Metabolomics: Metabolomics is a study of an individual’s metabolomics processes; by analysing individual metabolic profiles, the specific metabolites associated with particular diseases can be identified, based on which targeted treatments can be developed.

Apart from the technologies mentioned above, Artificial Individuals (AI) and information from Big Data can be used to develop personalised treatment plans according to the needs of individual patients.
Impact of Precision Medicine
The followings are areas where Precision Medicine has made a significant impact:
- Rare Diseases: According to World Health Organisation (WHO), Rare diseases, defined as one with a frequency of less than 6.5 per 10,000 people, are often caused by a single genetic mutation. Recently an FDA-approved therapy for Spinal Muscular Atrophy (a rare genetic disorder that causes muscle weakness and atrophy) has been developed, which targets the underlying genetic Mutation causing diseases.
- Mental health: Precision Medicine has the potential to identify specific genetic and environmental factors contributing to mental health. Recent studies have identified genetic variants associated with depression and bipolar disorder, providing new targets for drug development and enabling personalised treatment.
- Cancer: Targeted therapies have been developed that kill cancer cells. For example, in the case of Breast cancer, identifying specific genetic mutations, such as the HER2 gene, has led to the development of targeted therapies that can improve patient outcomes.
- Infectious Diseases: Rapid diagnostic tests that can identify the specific pathogen causing an infection allow for targeted treatment with antibiotics and antivirals, potentially reducing the overuse of antibiotics and preventing the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Current Status and Future Prospects of Precision Medicine
- Diagnostics: Rapid diagnostic tests can identify the pathogen causing an infection in infectious diseases, allowing targeted treatment.
- In cardiovascular diseases, genetic tests can identify individuals at risk, enabling early intervention with lifestyle changes or medication.
- Mental health-targeted therapy facilitates an individual by identifying different factors contributing to mental health.
Some of the factors that make Precision Medicine promising include:
- It offers tailored made treatments to address the root cause of diseases.
- It reduces healthcare costs by reducing the need for trial-and-error treatment and reducing hospital stays.
- It helps with the large amount of data that can be used to improve understanding of diseases and develop new treatments.
Challenges and Drawbacks in Precision Medicine:
While there are many potential benefits to precision medicine, it also comes up with challenges and drawbacks. Some of these include;
- Unaffordable: Due to its high cost, Precision medicine treatment may not be accessible to all.
- Privacy concerns: A considerable amount of data generated may raise concerns about privacy and data security.
- Ethical Concerns: There are ethical concerns around using it to select certain traits, such as eye or hair colour, for non-medical purposes, such as enhancement or selection.
Way forward
- Regulation will be needed to protect the privacy and security of genomic data.
- Training: Healthcare facilitators will need to be trained in the use of these technologies and the use of genomic data
- It will require significant funding and investment in research, infrastructure and data management.
Conclusion
Although Precision medicine is a new and innovative idea, it also comes with a great responsibility to ensure that the right balance is struck between innovation, ethics, and public health.
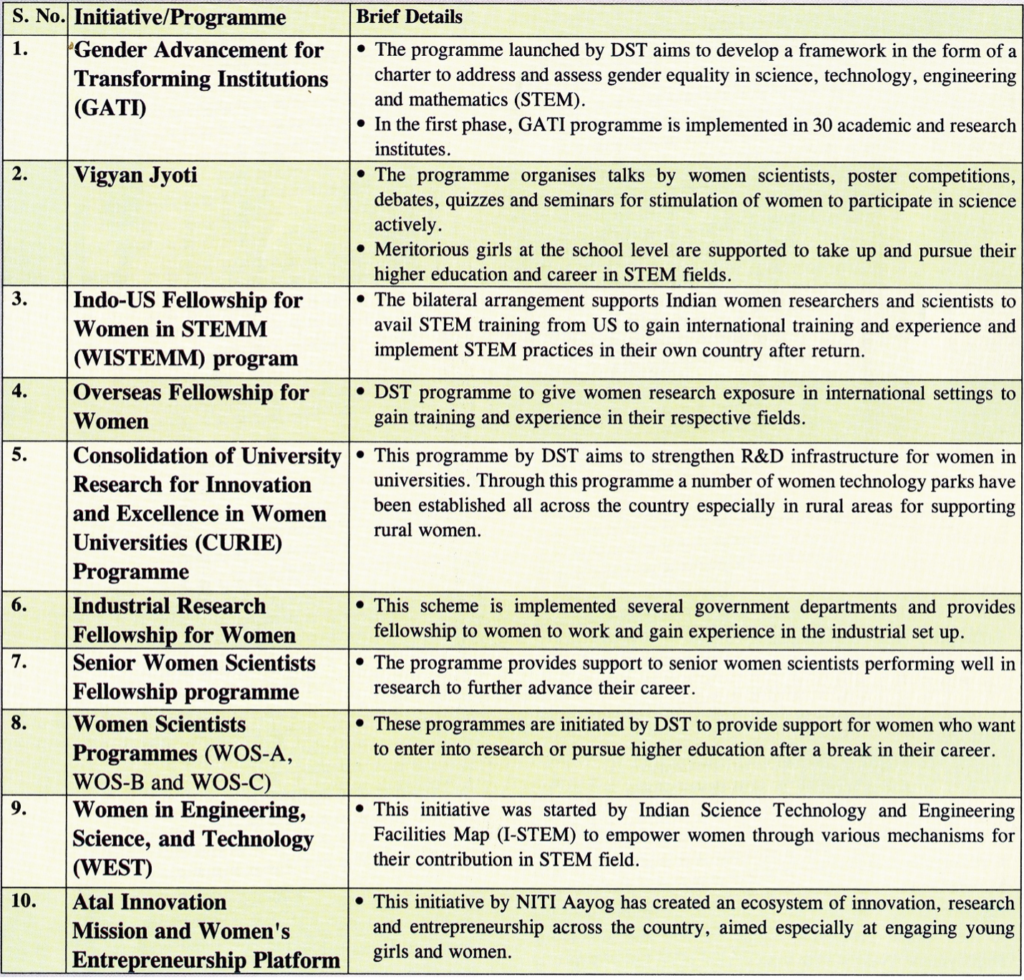
Article 7: EMPOWERING WOMEN IN SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY -A Push for sustainable national growth
The 108th Indian science congress was organised in Nagpur.
Role of Women
- The role of women’s empowerment is crucial in achieving sustainable economic development.
- According to UN World Population Prospects 2019, females contributes to 48% of the total Indian Population, which shows the potential for female in our progress.
- By enhancing women’s participation in the labour force, India can achieve nearly 700 billion USD in gross domestic product (Mckinsey Global).
- As per the SDG Index Report 2020, women are primarily responsible for providing nutrition, household and childcare.
Women Welfare schemes
- Ujjawala: a free gas cylinder scheme that helps minimise the risk associated with toxic smoke generated through traditional cooking systems.
- Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao and Sukanya Samridhi Yojna: to address the issue of declining child sex ratio in India and promote education and empowerment of girls.
- Unique Mahila E-Haaat: It is an online marketing platform to empower women to sell their products.
- SWADHAR Greh: provides shelter and rehabilitation services to women who are victims of violence or trafficking.
- Support to Training and Employment program for women (STEP): Assure employment by providing training in skill and development.
- Mahila Shakti Kendras: set up to provide training and support to women’s self-help groups.
Women in National Development:
Increased women’s participation in the political system:
- As per the SDG Index Report, Women’s participation increased from 11.6% to 14% in 2019.
- Women’s representation in Panchayati Raj has increased to 44%.
- Women’s count on voting has also increased in the past decade.
Women taking the lead in the MSME sector.
Women account for nearly 23% of labour force participation and hold almost 30% of senior management roles, higher than the global average of 24%.
Women and entrepreneurship
Women contributed approximately a 10% increase in entrepreneurship-oriented employment, with 8 million women in India.
Women in Science
Recently, Dr N Kalaiselvi was appointed as the first-ever Women Director General of the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), highlighting the emergence of women in science leadership.
The number of women researchers has increased to 18.7% (2018) from 13.9% (2015) and is also projected to further increased to 30% by 2030.
 Way forward
Way forward
- To promote inclusive science and technology, several efforts have to be made to promote gender equality.
- Participation of Women in the decision-making process should be encouraged because, despite holding several crucial positions, their participation is meagre.
- There is a need to bring cultural change by removing various obstacles women face in science.
- There is also a need to create safe working environments for women with safe accommodations and daycare facilities for their children.
Conclusion
However, a lot have done, and a lot still needs to be done in this area. Women empowerment is a gradual process that can be achieved by changing the overall perception of those at the bottom of the pyramid.
Article 8: The journey of crop improvement
An integrated approach is required to improve crop productivity, minimise land and water degradation, restore soil fertility, farm mechanisation and prevent post-harvest losses.
A look at the journey of crop improvement
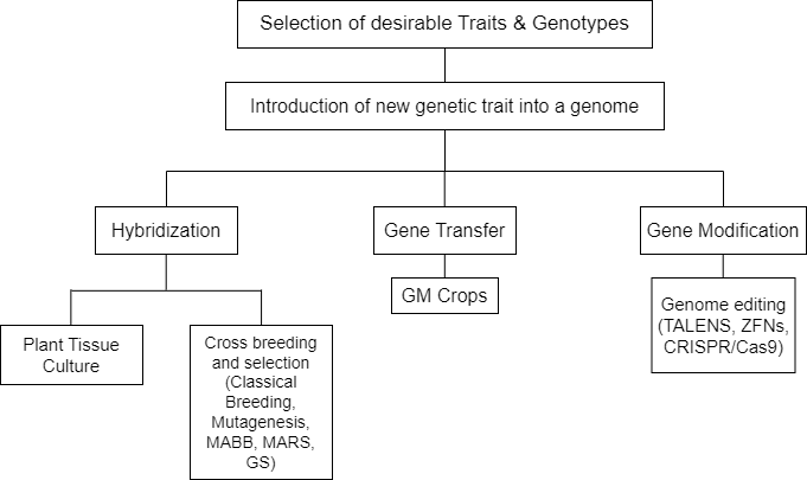
A journey from the earliest selection forms to post-Mendelian plant breeding, which involved the systematic crossing of parental lines to modern-day genome editing techniques.
The different methods can broadly be classified as Hybridisation-based methods, which involve the selection and crossbreeding of two or more accession or gene transfer and modification through biotechnological means.
A. Crop Improvement Through Hybridisation
1. Traditional Breeding Methods
- Cross-Breeding: Over the past ~10,000 years, crops were mainly improved through the selection of superior individuals that shows desirable traits. However, it gained momentum only after the formulation of Mendelian laws that enforced cross-breeding for trait improvement.
- Inducing Mutation through artificial means was the next breakthrough to achieve limited genetic variation in the germplasm in the crop species. The first step in plant breeding is identifying genotypes among the existing varieties. It might be helpful to create variation in th absence of variation found in nature.
- Mutagenesis is the formation of Mutation in DNA molecules. Mutagenesis as a breeding tool became popular from 1950 onwards when an extensive range of crop and ornamental plant species were treated by irradiation to increase variation for certain desirable traits.
New varieties are developed by generating and utilising genetic variability.
2. Modern Breeding Methods
- The selection of superior genotypes with the desired genetic combination has become precise and efficient.
- One such selection strategy is Genomic Estimated Breeding values, the time taken to develop new varieties with desired traits is reduced.
- Other breeding methods include MAS, MARS, etc.
B. Gene Transfer and Modification
1. Genetic Modification or Transgenesis
- Genetically Modified Organism (GMO): According to FAO and European Commission, a GMO is a product that does not occur naturally by mating or natural recombination.
- GM foods refer to foods produced from genetically modified plants or animals.
- Shortcomings in conventional breeding and mutation breeding are:
- Lack of sufficient genetic variation in the gene pool
- Random nature of genetic change (mutation, recombination)
- Reproductive barrier encountered while attempting interspecies gene transfer
- GM technology is much more precise as it transfers only the desired gene or the genes to the recipient plant.
- Has the potential to ensure the availability of adequate or nutritionally enhanced foods.
2. Genome Editing
- Genome Editing is a type of genetic engineering in which DNA is inserted, deleted, modified or replaced in the living organism’s genome.
- Compared to GM crops, the risks involved in altering the genome through genome-editing technology are considered significantly lower.
- Because most of the editing in the genome caused by genome editing tools (collection of advanced molecular biology technique) is confined only to a few nucleotides, producing minor changes as prevalent in natural populations.
- The need of the hour is to devise different approaches to accelerate the crop breeding process.Different crop improvement strategies
 Conclusion
Conclusion
A more progressive, scientifically-backed outlook that allows the selection of the best crop improvement method is required to accelerate the pace of sustainable crop improvement.
Article 9: Is India’s Solar Energy Transition Sustainable?
An initiative named, One Sun-one World, one grid is announced by India and the United Kingdom to improve the viability of solar power, complementing India’s focus on harnessing the Sun’s energy.
It will generate solar energy by interconnecting generators and loads across the continents and with international power gridlines.
Facts related to Solar Energy
- India’s installed capacity for solar energy potential reached 8 GW (2022), as per the Ministry of Power.
- In terms of overall installed renewable energy capacity, India ranks Fourth.
- As per the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, India’s potential has increased by 286% in 7.5 years.
- India surpassed Italy to achieve the 5th global position in solar power deployment.
India declared five ambitious targets declared at COP26 in UNFCCC 26th COP session held in Glasgow. These were :
- An energy capacity of 500 generated from non-fossil fuel sources by 2030
- By 2030, 50% of energy requirements from renewable energy
- One billion tonnes diminution in total carbon emissions by 2030
- 45% carbon reduction in carbon intensity by the Indian Economy by the year 2030, over 2005 levels
- Accomplish net Zero emissions by 2070
Threats and Concern
- The manufacturing of solar panel involves substances that are not eco-friendly and has a long-term environmental impact. For instance, Nitrogen Trifluoride and Cadmium.
- Silicon-based solar panels consist of glass which cannot be recycled.
- Regular disposal of solar panels in landfills contaminates soil leaching from landfills.
- Storage and disposal of batteries used cause threats.
- India anticipated producing around 34,600 tonnes of collective solar waste by 2030.
What can we do? Lessons from other countries
- Responsible Consumption: The European Union, under its waste electrical and electronic equipment directives, imposes the responsibilities of safe solar waste disposal on manufacturers or distributors.
- Take back scheme: Industry-managed take back, buy back and recycling scheme for solar waste introduced by the United Kingdom.
- Extended producer responsibility(EPR): Washington and California have strict cradle-to-grave responsibilities for solar waste disposal on producer responsibility.
Recommendation for solar waste management in India
- The waste generated needs specially designed treatment and management based on the waste characteristics.
- Separate rules for PVC waste management should be introduced.
- The cost of solar panel recycling should be reduced.
- Incentive-based systems and revenue-generating business models should be promoted to encourage the participation of recycling industries.
- Research development and innovation in design at education should be promoted, which may help decrease waste from future installations.
The need of the hour is a far-sighted vision to make solar a sustainable energy resource in the long term.
NEWS IN BRIEF
Jellyfish Bot-Underwater Cleaning Robot
It is an underwater Robot that can collect waste from oceans. It is noise-free, energy efficient and capable of trapping the trash without being in touch. It is by Roboticists from Max plank Institute for Intelligent Systems (MPI-IS), Stuttgart.
Testmyteeth- Smartphone App to Test Dental Plaque
Using this app, one can scan the teeth for better hygiene and detect the plaque level in the teeth. A Mechanical Engineering graduate of the University of Bath launches this app.
Portable screening device to assess the risk of cardiovascular diseases
It is developed by the Indian Institute of Technology Madras(IIT-M) to assess the health and age of blood vessels and thus help in early screening for cardiovascular diseases.
Soft E-Skin that talks to the brain
E-skin is a single, multilayered, soft, and stretchable material with integrated nerve-like electronics. Just like our natural skin, it can sense pressure, temperature, etc., and is developed by researchers from Stanford University.

