SCIENCE REPORTER SUMMARY: APRIL 2024
ARTICLE 1: Genome India Project: Unveiling India’s Genetic Tapestry for Health and Innovation
- ARTICLE 1: Genome India Project: Unveiling India’s Genetic Tapestry for Health and Innovation
- ARTICLE 2: Unraveling Vitiligo: Insights into Autoimmunity and Innovative Treatments
- ARTICLE 3: Unlocking the Gut-Brain Connection: The Enteric Nervous System and Gut Microbiota in Health and Disease
- ARTICLE 4: Combatting Antimicrobial Resistance: Understanding the Global Challenge and Path Forward
- ARTICLE 5: Advancements in Psychosurgery and the Mental Health Care Act, 2017: A Renewed Hope for Treatment-Resistant Mental Health Conditions
- ARTICLE 6: Revolutionizing Pain Management: Exploring the Promise of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
- Top of Form
- ARTICLE 7: National Centre for Disease Informatics and Research (NCDIR) Spearheads Cancer Surveillance Efforts in India through Innovative Digital ToolTop of Form
- ARTICLE 8: Unlocking the Potential of Northeast India: Shiitake Mushrooms Spearhead Economic Growth and Nutritional RenaissanceTop of Form
- ARTICLE 9: Nanorespirocytes: Transforming Healthcare with Advanced Nanotechnology
- ARTICLE 10: Exploring the Culinary Delights of Edible Flowers: Unveiling Nutritional Riches and Health Benefits
- ARTICLE 11: Survival Strategies of Lithops: Mimicry, Water Storage, and Adaptability
- NEWS IN BRIEF
- 1) University of Washington Researchers Unveil Wireless Smart Thermal Earring: A Fusion of Fashion and Functionality
- 2) MIT Engineers Develop Wearable Ultrasound Sticker for Early Disease Detection
- 3) IIT Jodhpur Engineers Develop Breakthrough ‘Make in India’ Breath Sensor for Disease Detection
- 4) Washington State University Researchers Develop Novel Surgical Implant to Combat Bacterial Infections
Introduction:
- The Genome India Project (GIP) achieves a significant milestone in scientific exploration with the completion of its initial phase.
- Led by Dr Jitendra Singh, Union Minister of State for Science and Technology, this project, hosted at the National Institute of Immunology (NII) in New Delhi, marks a pivotal moment in understanding the genetic diversity of the Indian population.
Understanding the Human Genome:
- The human genome, comprising Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, and Cytosine nucleotides, spans three billion units within 23 pairs of chromosomes.
- These genetic codes shape individual characteristics and heredity, with approximately 1 in every 1000 positions exhibiting variation between individuals.
- These variations form the foundation for genetic diversity, influencing disease susceptibility and medication responses, with certain variations more common in specific populations.
Significance of Population-Specific Data:
- India’s vast population and diverse ethnicities necessitate understanding genetic variability within its population.
- The Genome India Project, initiated in January 2020 and funded by the Department of Biotechnology, aims to sequence 10,000 genomes across diverse ethnic groups to create a comprehensive catalogue of Indian genetic variations.
- This data promises invaluable insights into disease risks, drug responses, and evolutionary history, crucial for personalised healthcare strategies and medical research in India.
Implications and Future Directions:
- With over 19,200 blood samples collected and whole-genome sequencing completed for more than 10,000 individuals, the project has yielded initial findings, revealing rare variations with clinical significance.
- This marks the dawn of personalised medicine in India, with plans for global dissemination of research findings and various scientific investigations through specialised working groups.
Collaborative Approach and Achievements:
- The project involves scientists from 20 renowned institutions and entails sample collection, whole-genome sequencing, analysis, and method development.
- Samples are meticulously biobanked at CBR, Bengaluru, and data is archived at the Indian Biological Data Centre (IBDC), Faridabad.
- Furthermore, the project envisions designing genetic chips for low-cost diagnostics and fostering research in personalised medicine.
Conclusion:
- The Genome India Project exemplifies collaborative scientific partnerships aimed at unravelling the genetic tapestry of the Indian population.
- Government-funded and mission-oriented, this initiative sets the stage for advancements in public health interventions, drug development, and personalised medicine, showcasing India’s commitment to scientific exploration for the benefit of its citizens.
| PYQ: With reference to agriculture in India, how can the technique of ‘genome sequencing’, often seen in the news, be used in the immediate future? (2017) 1) Genome sequencing can be used to identify genetic markers for disease resistance and drought tolerance in various crop plants. 2) This technique helps in reducing the time required to develop new varieties of crop plants. 3) It can be used to decipher the host-pathogen relationships in crops. Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (d) |
ARTICLE 2: Unraveling Vitiligo: Insights into Autoimmunity and Innovative Treatments
Understanding Vitiligo:

- Vitiligo, a skin disorder characterised by depigmented patches, transcends racial and ethnic boundaries, affecting millions globally.
- The condition arises from the destruction of melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing skin pigment, leading to the loss of skin colour.
- While the precise triggers remain elusive, research points to a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors.
Role of Autoimmunity:
- Autoimmunity plays a central role in vitiligo, where the body’s immune system erroneously targets its melanocytes, destroying them.
- This autoimmune response involves cytotoxic T cells attacking melanocytes, resulting in depigmented skin patches.
- Understanding this immune dysregulation has spurred research into therapeutic interventions that modulate immune responses to halt vitiligo progression.
Harnessing Regulatory T Cells (Tregs):
- Research highlights the therapeutic potential of suppressor T cells, or Regulatory T cells (Tregs), in restoring immune balance in vitiligo.
- By enhancing the suppressive activity and quantity of Tregs, scientists aim to counteract the autoimmune attack on melanocytes, thereby preventing further depigmentation.
- Innovative approaches like Treg cell therapy, which involves isolating, expanding, and reintroducing Tregs into the body, offer personalised treatments with promising outcomes for vitiligo patients.
Advancements in Immunotherapy:
- Recent strides in immunotherapy have revolutionised vitiligo treatment, with approaches focusing on enhancing Treg function.
- Techniques such as CAR-Tregs, engineered immune cells targeting the aberrant immune response, hold significant potential in preserving melanocytes and promoting repigmentation.
- Additionally, researchers explore small molecules and biological agents to boost Treg activity, offering non-invasive alternatives to cell-based therapies.
Celebrating Diversity:
- As research deepens our understanding of vitiligo and its underlying immunological mechanisms, there’s a growing appreciation for the intricate workings of the human immune system.
- With each breakthrough, the vision of a future where skin pigmentation is celebrated, not battled, draws closer.
- Armed with knowledge and innovation, Regulatory T cells emerge as pivotal players in transforming vitiligo treatment and embracing diversity in all its forms.
ARTICLE 3: Unlocking the Gut-Brain Connection: The Enteric Nervous System and Gut Microbiota in Health and Disease
Understanding the Enteric Nervous System (ENS) and Gut Microbiota:
- The Enteric Nervous System (ENS), often called the second human brain, forms an extensive network of neurons within the gastrointestinal tract, interacting closely with the gut microbiota.
- The gut microbiota, consisting of various microbes, influences the ENS and plays a crucial role in maintaining intestinal homeostasis.
Interactions Between ENS and Gut Microbiota:
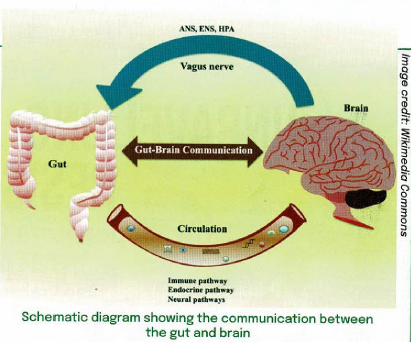
- The ENS regulates key enteric processes such as immune response, nutrient detection, motility, and intestinal barrier functions.
- Meanwhile, the gut microbiota, comprising predominantly Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes phyla, interacts with the ENS by producing metabolites like Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFA) and neurotransmitters.
- This interaction influences colonic metabolism, immune responses, and stress regulation.
The Gut-Brain Axis and Cognitive Health:
- The bidirectional Gut-Brain Axis (GBA) connects the ENS to the Central Nervous System (CNS), affecting human feelings, appetite, and behaviour.
- Dysbiosis in the gut microbiome can disrupt the GBA, leading to mood swings and cognitive impairments.
- The microbiota also influences neurotransmitter production, particularly serotonin, and Brain Derived Neurotropic Factor (BDNF) expression, affecting cognitive functions and memory.
Impact of Dysbiosis and Therapeutic Interventions:
- Dysbiosis, characterised by an imbalance in the gut microbiome, can lead to gastrointestinal and cognitive disorders.
- Probiotics, antibiotics, and dietary changes significantly affect the gut microbiome composition and function, influencing sympathetic nervous system activity and immune responses.
- Probiotics have been shown to alleviate anxiety, depression, and gastrointestinal disorders, highlighting their therapeutic potential.
Role of Food and Water Quality:
- Food and water quality directly impact the gut microbiome, with poor-quality food and water-containing pathogens that disrupt microbiota balance.
- Water and food-borne contaminants compromise intestinal barrier integrity, triggering inflammatory responses and dysbiosis.
- Ensuring access to clean water and maintaining a balanced diet rich in fibre, prebiotics, and probiotics are essential for supporting a healthy gut microbiome and mitigating the effects of contaminants.
Implications for Medical Research and Healthcare:
- Understanding the intricate relationship between the ENS and gut microbiome offers promising avenues for improving overall health.
- Manipulating this system through dietary interventions, probiotics, and therapeutic strategies can potentially prevent or treat various diseases, emphasising the importance of maintaining a healthy gut microbiome for optimal physical and mental well-being.
ARTICLE 4: Combatting Antimicrobial Resistance: Understanding the Global Challenge and Path Forward
Rapid Emergence of Antimicrobial Resistance:
- The global emergence of antimicrobial resistance has recently escalated, surpassing previous predictions.
- This phenomenon, characterised by microorganisms’ ability to withstand the effects of once-effective antimicrobial drugs, presents a significant global challenge to public health systems.
- These drug-resistant microbes, often called “superbugs,” can persist and increase even in the presence of antimicrobial treatments.
Factors Leading to Antimicrobial Resistance:
- Various factors, including the overuse and misuse of antimicrobial drugs, influence the development and spread of antimicrobial resistance.
- Widespread and inappropriate use of antibiotics, particularly in resource-constrained settings with limited access to clean water and proper sanitation, contribute to the selection and proliferation of antibiotic-resistant microbes.
- Additionally, the non-therapeutic use of antimicrobials in agriculture for growth promotion and disease prevention in livestock further exacerbates the issue.
- Global travel and trade facilitate the dissemination of resistant strains between countries, making antimicrobial resistance a shared concern globally.
Types of Antimicrobial Resistance:
- Antibiotic resistance can be categorised into three main types: intrinsic, acquired, and adaptive.
- Intrinsic resistance is inherent to certain microbial species and is not acquired through exposure to antimicrobial agents.
- Acquired resistance arises after antibiotic exposure, either through genetic mutations or the acquisition of resistance genes from other microbes.
- Adaptive resistance involves temporary changes in microbial physiology in response to antimicrobial exposure, reducing drug susceptibility.
Mechanisms Leading to Antimicrobial Resistance:
- Antimicrobial resistance develops through various mechanisms, including genetic mutations, horizontal gene transfer, enzymatic inactivation, efflux pumps, altered permeability, and phenotypic variation.
- These mechanisms allow microbes to evade the effects of antimicrobial agents, making infections more challenging to treat and control.
Ramifications of Antimicrobial Resistance:
- Antimicrobial resistance has significant ramifications, including increased morbidity and mortality, healthcare complications, economic burden, limited treatment options, compromised public health, and threats to modern medicine.
- The overuse and misuse of antibiotics in agriculture also contribute to environmental contamination, further exacerbating the spread of resistance.
Significant Initiatives for Controlling Antimicrobial Resistance:
- Governments and international organisations have launched various initiatives to combat antimicrobial resistance globally.
- These initiatives focus on enhancing surveillance and monitoring, promoting responsible antimicrobial use, strengthening infection prevention and control measures, and investing in research and development for new treatments.
Conclusion:
- Addressing antimicrobial resistance requires a multifaceted approach involving collaboration and information sharing at the global level.
- The “One Health” approach recognises the interconnectedness of human health, animal health, and the environment, which is crucial in guiding efforts to combat antimicrobial resistance.
- Through responsible antimicrobial use, strengthened infection prevention and control measures, and investment in research and development, the battle against antimicrobial resistance can be effectively waged.
| PYQ: Which of the following are the reasons for the occurrence of multi-drug resistance in microbial pathogens in India? (2019) 1) Genetic predisposition of some people 2) Taking incorrect doses of antibiotics to cure diseases 3) Using antibiotics in livestock farming 4) Multiple chronic diseases in some people Select the correct answer using the code given below. (a) 1 and 2 (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1, 3 and 4 (d) 2, 3 and 4 Ans: (b) PYQ: Can overuse and the availability of antibiotics without doctor’s prescription, the contributors to the emergence of drug-resistant diseases in India? What are the available mechanisms for monitoring and control? Critically discuss the various issues involved. (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2014) |
ARTICLE 5: Advancements in Psychosurgery and the Mental Health Care Act, 2017: A Renewed Hope for Treatment-Resistant Mental Health Conditions

Introduction: The Mental Health Care Act, 2017
- The Mental Health Care Act of 2017 marks a significant milestone in India’s healthcare landscape, introducing transformative provisions to protect the rights of mental health patients.
- Among its notable provisions is the regulation of psychosurgery, a topic previously overlooked in earlier versions of the Act.
Recent Cases: Application of Psychosurgery
- Recent cases in India highlight the application of psychosurgery under the provisions of the Mental Health Care Act of 2017.
- These cases involve Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) procedures performed on individuals with chronic mental health conditions, showcasing the Act’s practical implications in addressing treatment-resistant cases.
Roots and Rise of Psychosurgery
- Psychosurgery, historically associated with treating psychiatric disorders, traces its roots back to pioneers like Antonio Egas Moniz and Gottilab Burckhardt.
- Despite early successes, the procedure faced ethical challenges, particularly its side effects and mortality rates.
- However, modern advancements, including refined techniques and minimally invasive procedures like DBS, have revitalised interest in surgical interventions for mental health conditions.
Psychosurgery vs. Pharmacology
- The decline of psychosurgery in the mid-20th century coincided with the rise of pharmacotherapy and Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) as safer and more effective treatments for psychiatric disorders.
- However, a significant portion of patients remained resistant to conventional treatments, necessitating the reconsideration of surgical interventions.
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) as a Promising Alternative
- DBS, initially successful in treating movement disorders, has emerged as a promising alternative for medication-resistant psychiatric conditions.
- Its minimally invasive nature and adjustable settings offer a safer and more effective approach compared to traditional psychosurgery, garnering attention for its potential in treating various mental health disorders.
Rights and Regulations: Guidelines for Psychosurgery
- International and national guidelines, including those set by the World Society for Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery and the Mental Health Care Act of 2017, emphasise the importance of ethical considerations and informed consent in psychosurgery.
- These guidelines outline strict procedural requirements, patient selection criteria, and post-operative monitoring to ensure the safety and efficacy of surgical interventions.
Challenges and Recommendations
- Despite the resurgence of surgical therapies for psychiatric disorders, challenges persist regarding ethical considerations, societal perceptions, and patient awareness.
- Experts advocate for a multidisciplinary approach to psychosurgery, integrating advancements in neuroscience, imaging technology, and pharmacology to ensure comprehensive and ethical patient care.
Conclusion
- The enactment of the Mental Health Care Act of 2017 and recent advancements in surgical interventions like DBS offer renewed hope for individuals with treatment-resistant mental health conditions while emphasising the importance of ethical guidelines and multidisciplinary collaboration in ensuring patient safety and well-being.
ARTICLE 6: Revolutionizing Pain Management: Exploring the Promise of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
Top of Form
Understanding Pain: An Introduction
- Pain is a universal experience that ranges from minor discomfort to debilitating agony.
- Defined by the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) as “an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, actual or potential tissue damage,” pain is a vital signal from the body, indicating that something is amiss.
- While acute pain typically fades with healing, chronic pain can persist for months or years, significantly impacting one’s quality of life.
Types of Pain and Their Impact
- There are two primary categories of pain: acute and chronic.
- Acute pain arises suddenly in response to injury or illness and diminishes as the body heals.
- Chronic pain, on the other hand, persists for extended periods and often poses significant challenges for patients, affecting their overall well-being.
- Conditions such as arthritis, migraines, fibromyalgia, and chronic regional pain syndrome exemplify the debilitating nature of chronic pain.
Managing Pain: Traditional Approaches
- Traditional pain management strategies encompass a range of interventions, including rest, heat and cold therapy, painkillers, distraction techniques, and emotional support.
- While these methods may offer temporary relief, chronic pain often recurs upon discontinuation of medication, highlighting the need for more comprehensive medical attention from specialists.
Understanding Pain Pathways: Nociceptors and Neural Signals
- Pain signals originate from nociceptors—specialised receptors for pain perception—distributed throughout the body.
- These signals travel to the brain via the spinal cord alongside non-painful sensory information such as touch and temperature.
- The gate control mechanism of pain, first proposed in the mid-sixties, regulates the transmission of pain signals, providing insights into pain modulation.
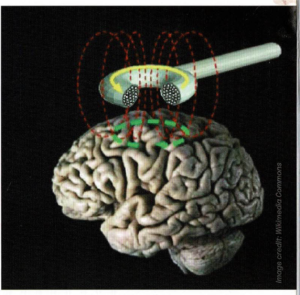
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS): A Novel Approach
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) emerges as a promising therapeutic modality for chronic pain management.
- TMS modulates neural activity by applying magnetic fields to specific brain regions non-invasively, potentially alleviating pain.
- The technique disrupts coordinated neural activity, reorganising the brain circuits associated with pain processing.
Mechanisms and Efficacy of TMS
- The precise mechanisms underlying TMS’s pain-relieving effects are still under investigation.
- Hypotheses suggest that TMS modulates neural networks involved in pain perception, stimulates the release of endogenous opioids, and alters brain connectivity and plasticity.
- Clinical trials have reported significant reductions in pain intensity and improved overall quality of life following TMS treatment.
Challenges and Future Directions
- While TMS shows promise as an alternative pain treatment, further research is necessary to optimise treatment protocols and identify patient subgroups who may benefit most from this therapy.
- Despite minimal side effects, ongoing refinement of TMS techniques and protocols is essential to enhance its efficacy and accessibility for individuals suffering from chronic pain.
Conclusion:
- Pain remains a complex and challenging aspect of healthcare, with TMS offering innovative possibilities for pain relief.
- As researchers continue to explore the mechanisms and applications of TMS, this technique can potentially improve the lives of individuals with chronic pain, offering hope for enhanced quality of life and well-being.
ARTICLE 7: National Centre for Disease Informatics and Research (NCDIR) Spearheads Cancer Surveillance Efforts in India through Innovative Digital ToolTop of Form
National Centre for Disease Informatics and Research (NCDIR):
- The Bengaluru-based NCDIR, operating under the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), is dedicated to creating and maintaining a national research database on cancer and other non-communicable diseases.
- This objective is facilitated by a web-based assessment and analysis tool called “Cancer Samiksha.”
Understanding Cancer Prevalence:
- Experts attribute the increasing prevalence of cancer to various factors such as growing life expectancy, adoption of Western lifestyles, stress, smoking, alcohol consumption, obesity, sedentary lifestyles, and environmental factors like prolonged radiation exposure.
Importance of Cancer Surveillance:
- Given the rising cancer burden, regular assessment and analysis are crucial for early diagnosis and treatment.
- As part of the Digital India Campaign, the healthcare sector has embraced digitisation, including establishing online cancer registries by the National Cancer Registry Programme (NCRP).
Evolution of NCRP:
- The NCRP, initiated in December 1981, operates a network of cancer registries categorised into population-based and hospital-based registries.
- Initially launched in three states, the program has expanded to encompass a wider geographic area, now including 38 population-based and 189 hospital-based cancer registries.
Data Collection and Utilisation:
- Population-based cancer registries collect data on new cancer cases from various sources, while hospital-based cancer registries focus on recording cancer patients’ information within hospital settings.
- The meticulously collected data undergoes rigorous scrutiny before publication.
Role in National Health Programs:
- The data generated by NCRP informs the National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Disease, and Stroke (NPCDCS) under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India.
- This data-driven approach aids in strategic planning, resource allocation, prevention programs, and impact assessment regarding cancer control measures.
Benefits and Implications:
- Effective cancer control necessitates early detection and treatment. The NCRP facilitates this process by providing vital insights for healthcare professionals to plan, establish treatment facilities, allocate resources, and assess the impact of cancer-related activities.
- Hospitals leverage registry data to enhance cancer care services, ensuring adherence to international standards throughout the data collection and analysis process.
ARTICLE 8: Unlocking the Potential of Northeast India: Shiitake Mushrooms Spearhead Economic Growth and Nutritional RenaissanceTop of Form
Unlocking the Potential of Northeast India:
- Northeast India, situated within the biodiverse “Indo-Burma” hotspot, holds significant promise for sustainable development by exploring local resources.
- With much of the region still practicing organic farming, there is growing interest among food entrepreneurs, particularly in the burgeoning mushroom market, driven by its nutritional and nutraceutical benefits.
Global Mushroom Market Dynamics:
- The global mushroom market has grown substantially, reaching $62.44 billion in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 9.8% by 2027.
- Leading players such as Button and Shiitake mushrooms dominate the market, with increasing demand fueled by factors like veganism.
- While China, the US, and Europe are key contributors, the Asia Pacific region, including India, holds significant revenue potential.
Shiitake Mushroom: A Rising Star:
- Shiitake, the second most popular edible mushroom globally, has garnered attention for its nutraceutical potential.
- Native to Southeast Asia, Shiitake’s demand has surged due to its health benefits, leading to its premium pricing in the market.
- With its conducive climate and habitat, Northeast India is poised to become a key player in Shiitake cultivation, offering economic opportunities for local farmers.
Empowering Local Communities:
- Cultivating Shiitake mushrooms in Northeast India can empower local farmers and boost the region’s economy.
- With its rich nutritional profile and potential medicinal properties, Shiitake holds promise for culinary purposes and as a source of mycoceuticals.
- Securing a Geographical Indication (GI) tag for Indian Shiitake could further enhance its marketability and create job opportunities.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Despite its potential, the Shiitake market in India faces challenges such as inadequate scientific validation, climatic variability, and logistical constraints.
- Overcoming these hurdles requires a concerted effort to educate farmers, invest in research, and adopt advanced cultivation techniques.
- Addressing food intolerance and allergenicity concerns is crucial for ensuring Shiitake’s safe consumption and commercial success.
Tapping into Future Opportunities:
- With ongoing research focusing on Shiitake’s health benefits, India has the potential to emerge as a global mushroom superpower.
- Scientific validation and market-driven strategies can propel Shiitake cultivation to new heights, driving economic growth and improving livelihoods.
- As the journey unfolds, opportunities for innovation and empowerment abound, positioning Shiitake as a key player in the global food market.
| PYQ: With reference to “Gucchi” sometimes mentioned in the news, consider the following statements: (2022) 1. It is a fungus. 2. It grows in some Himalayan forest areas. 3. It is commercially cultivated in the Himalayan foothills of north-eastern India. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 3 only (c) 1 and 2 (d) 2 and 3 Ans: (c) |
ARTICLE 9: Nanorespirocytes: Transforming Healthcare with Advanced Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology in Healthcare:
- Nanotechnology, with its potential applications in medicine, electronics, energy, and materials science, offers advanced disease detection and treatment tools in the healthcare sector.
- Respirocytes, an example of modern nanodevices, are being developed to detect disease markers and provide timely treatment, revolutionising conventional diagnostic and therapeutic techniques.
Respirocytes: Nanomachines for Oxygen Delivery:
- Respirocytes are artificial nanodevices designed to mimic the function of natural red blood cells, capable of carrying oxygen and carbon dioxide in the bloodstream.
- These spherical nanomachines, proposed by Robert A. Freitas, have a diameter of about 1 µm and can operate at extreme pressures, significantly outperforming natural red blood cells in oxygenation efficiency.
Medical Applications of Nanorespirocytes:
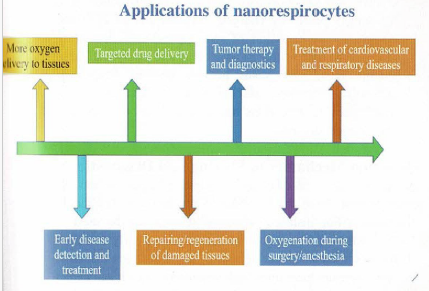
- Nanorespirocytes, also known as medical nanorobots, hold promise for treating conditions such as anaemia, ischemia, and carbon monoxide poisoning.
- By delivering oxygen more efficiently to tissues, they could enhance medical treatments and reduce the need for blood transfusions.
- Moreover, nanorespirocytes offer targeted drug delivery and tissue repair capabilities, potentially improving cancer therapy and regenerative medicine.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Nano-Respirocytes:
- The advantages of nanorespirocytes include better oxygen delivery, targeted drug delivery, tissue repair, improved disease diagnosis, and reduced need for blood transfusions.
- However, challenges such as safety concerns, regulatory barriers, manufacturing complexity, scalability issues, and public perception need to be addressed to ensure their successful development and adoption in medical science.
Future Prospects and Challenges:
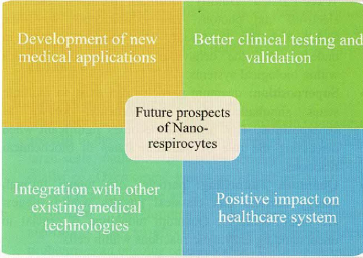
- Nanorespirocytes represent a significant advancement in medical science research, offering multifunctional treatment tools for various illnesses.
- While technological advancements continue, addressing the risks and uncertainties associated with nanotechnology is essential to ensure their safe and effective integration into healthcare practices.
Conclusion
- Overall, the development of nanorespirocytes exemplifies the transformative potential of nanotechnology in healthcare, promising novel approaches to disease diagnosis, treatment, and patient care.
- However, thorough research, regulatory oversight, and public engagement are necessary to navigate the complexities and realise the full benefits of this innovative technology.
| PYQ: There is some concern regarding the nanoparticles of some chemical elements that are used by the industry in the manufacture of various products. Why? (UPSC Prelims 2014) 1) They can accumulate in the environment and contaminate water and soil. 2) They can enter the food chains. 3) They can trigger the production of free radicals. Select the correct answer using the code given below. a) 1 and 2 only b) 3 only c) 1 and 3 only d) 1, 2 and 3 Answer: (d) |
ARTICLE 10: Exploring the Culinary Delights of Edible Flowers: Unveiling Nutritional Riches and Health Benefits
Exploring Edible Flowers
- Beyond their decorative allure, edible flowers serve as significant components of culinary traditions globally, renowned for their nutritional richness and medicinal attributes.
- Despite their potential, the utilisation of these flowers remains confined to specific regions, with many unaware of their benefits.
Red Cotton Tree (Bombax ceiba)

- This tree, found across Asia, yields flowers known for their nutritional content and purported health benefits.
- Commonly consumed as a vegetable dish, the flowers contain essential compounds like B-sitosterol and quercetin, contributing to their perceived health advantages.
Sunn Hemp (Crotalaria juncea)

- Sunn hemp, belonging to the Fabaceae family, offers edible buds for culinary purposes.
- Rich in calcium, phosphorus, and fibre, these buds provide nutritional value and gastronomic delight, especially when incorporated into various cuisines.
Banana Flower (Musa paradisiaca)

- Renowned for its medicinal properties, the banana flower boasts a robust nutritional profile featuring vital minerals and vitamins crucial for bodily functions.
- With its pink hue and sizable petals, this flower enhances visual appeal and adds flavour and nutrition to culinary creations.
Drumstick Tree (Moringa oleifera)

- Dubbed a ‘Superfood,’ drumstick flowers are celebrated for their dense nutrient composition, including many essential vitamins and minerals.
- Widely consumed in India, these flowers are prized for their culinary versatility and potential health benefits.
Mountain Ebony (Bauhinia variegata)

- The mountain ebony, or kachnar, is valued for its cooling properties, particularly during hot weather.
- Its flowers and buds, abundant in spring, are utilised in various culinary applications and are believed to offer health-enhancing properties in rural cuisines.
Field Pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo)

- Field pumpkin flowers, commonly known as Kaddu, are a staple in Indian cuisine, especially during the rainy season.
- Rich in Vitamin C and A, these flowers are delicious and contribute to overall health and well-being.
Conclusion
- Understanding these edible flowers’ nutritional significance and culinary potential can broaden culinary horizons and promote healthier dietary practices, enriching both gastronomic experiences and overall well-being.
| PYQ: Why is a plant called Prosopis juliflora often mentioned in the news? (2018) (a) Its extract is widely used in cosmetics. (b) It tends to reduce the biodiversity in the area in which it grows. (c) Its extract is used in the synthesis of pesticides. (d) None of the above Answer: (b) |
ARTICLE 11: Survival Strategies of Lithops: Mimicry, Water Storage, and Adaptability
Mimicry as a Survival Strategy
- Lithops, commonly known as “flowering stones,” have evolved a unique survival strategy by resembling small rocks, enabling them to evade herbivores during grazing periods.
- Native to Namibia and South Africa, their uncanny resemblance to sand and stones makes them incredibly difficult to spot, increasing their chances of survival by reducing the likelihood of being detected and consumed.
Beyond Appearance: Mimicry and Disguise
- The mimicry displayed by Lithops extends beyond their appearance.
- Known by various Afrikaans names based on their resemblance to miniature hoofprints, such as beeskloutjie (cattle hoof), skaappootjie (sheep hoof), or perdeklou (horse’s hoof), this further reinforces their disguise and enhances their chances of remaining undetected by potential herbivores.
Water Storage and Endurance
- Lithops are renowned for their exceptional water-storing capacity, allowing them to thrive in harsh, arid environments with limited moisture sources.
- Their ability to store water within specialised leaves enables them to endure prolonged periods of drought and survive in regions with scarce rainfall.
Scientific Interest and Research
- Lithops’ unique adaptations and survival strategies have attracted scientific interest, leading to studies exploring their physiological and ecological aspects.
- Research highlights their water storage capacity and ability to withstand arid conditions, providing insights into mechanisms that enable them to survive in challenging environments.
Adaptability and Responsiveness
- Another unique aspect of Lithops is their ability to change leaf colouration in response to environmental conditions.
- This adaptability demonstrates their responsiveness to their surroundings, allowing them to maximise their chances of survival in arid and challenging habitats by adjusting their appearance to blend in effectively.
Conclusion: Diverse Survival Mechanisms
- By mimicking rocks and possessing remarkable water-storing abilities, Lithops exemplify the plant kingdom’s incredible diversity of survival mechanisms.
- From camouflage to water conservation and adaptability, plants like Lithops showcase nature’s ingenuity in ensuring survival in diverse environments.
NEWS IN BRIEF
1) University of Washington Researchers Unveil Wireless Smart Thermal Earring: A Fusion of Fashion and Functionality

Development of Wireless Smart Thermal Earrings:
- Researchers from the University of Washington have introduced a breakthrough in wearable technology by developing a wireless smart thermal earring.
- The prototype, compact and comparable to the weight of a paperclip, is designed to monitor the temperature of the wearer’s earlobe continuously.
Compact Design and Long Battery Life:
- Despite its small size, the innovative device boasts a remarkable battery life of 28 days.
- It incorporates two sensors for temperature measurement, with one sensor attached to the wearer’s ear using a magnetic clip while the other hangs below the first sensor.
- This design ensures accurate and continuous monitoring of earlobe temperature.
Efficient Power Consumption:
- A notable feature of the wireless smart thermal earring is its efficient power consumption, allowing for prolonged use without frequent recharging.
- This efficiency enhances the practicality and usability of the device, making it suitable for everyday wear.
Integration with Fashion Trends
- In addition to its technological advancements, the researchers also considered the fashion aspect by exploring personalised designs for the earrings.
- By integrating the device with fashion trends, such as customisable designs, the earring serves a functional purpose and appeals to users’ aesthetic preferences.
Publication and Academic Recognition
- The research detailing the development of the wireless smart thermal earring was published in the Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, highlighting its significance in the field of wearable technology and its potential for further innovation and application.
2) MIT Engineers Develop Wearable Ultrasound Sticker for Early Disease Detection

- Engineers at MIT have created a postage stamp-sized wearable ultrasound sticker capable of monitoring the stiffness of deep internal organs.
- This innovative device is designed to detect early signs of diseases like liver and kidney failure and track the progression of solid tumours.
- The sticker can be conveniently worn on the skin, providing a non-invasive method for health monitoring.
- The development was published in Science Advances, showcasing its potential for early disease detection and monitoring.
3) IIT Jodhpur Engineers Develop Breakthrough ‘Make in India’ Breath Sensor for Disease Detection
Breakthrough in Breath Sensor Technology
- Researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology Jodhpur have achieved a significant milestone by developing the first “Make in India” human breath sensor.
- This sensor utilises metal oxides and nanosilicon and operates at room temperature, marking a notable technological advancement.
Application in Drunk Driving Cases
- The primary function of the developed breath sensor is to measure alcohol content in the breath, particularly in cases related to drunk driving.
- This capability addresses a crucial societal concern and contributes to efforts aimed at reducing alcohol-related accidents and fatalities on the roads.
Disease Characterisation Capabilities
- The enhanced sensor technology shows promise in the characterisation of diseases such as asthma, diabetic ketoacidosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, sleep apnea, and cardiac arrest.
- By monitoring the volatile organic compounds in a person’s breath, the sensor aids in early disease detection and monitoring, potentially improving patient outcomes and healthcare management.
Publication and Academic Recognition
- The research detailing the development and potential applications of the breath sensor was published in the journal IEEE Sensors Letters.
- This publication underscores the scientific significance of the innovation and its potential to address pressing societal challenges while advancing the sensor technology field.
4) Washington State University Researchers Develop Novel Surgical Implant to Combat Bacterial Infections
Innovative Surgical Implant Development:
- Researchers from Washington State University have introduced a novel surgical implant designed to combat bacterial infections.
- In laboratory tests, this implant demonstrated the ability to eliminate 87% of the bacteria responsible for staph infections while maintaining strength and compatibility with surrounding tissue, akin to existing implants.
- The International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing reported the findings detailing this breakthrough.
Potential for Improved Infection Control:
- The development of this surgical implant holds promise for significantly enhancing infection control in various common surgeries, including hip and knee replacements, performed worldwide daily.
- Bacterial colonisation of implants stands as a primary cause of their failure and adverse outcomes post-surgery. This novel implant could mitigate such risks and improve patient outcomes by effectively reducing bacterial presence.
Multifunctional Device for Enhanced Integration:
- Researchers highlight the multifunctionality of this implant, emphasising its potential for infection control and promoting integration with bone tissue.
- This dual functionality offers a significant advantage, as the implant addresses infection concerns and facilitates better integration with the surrounding tissue, promoting successful surgical outcomes and long-term implant stability.
Implications for Future Surgical Practices:
- The development of this innovative implant marks a significant step forward in surgical technology and infection control.
- Further research and refinement could revolutionise surgical practices by reducing the risk of post-operative infections and improving the overall success rates of surgeries, particularly those involving joint replacements.
- The potential impact of this advancement on patient care and healthcare outcomes is substantial, and warrants continued investigation and development.
