Science Reporter Magazine Summary October 2023 for UPSC Exam
Science Reporter Magazine Summary October 2023 Edition
Lets dive into the October 2023 edition of Science Reporter Magazine, readers are welcomed into fresh insights & scientific discoveries. The Science Reporter Magazine October 2023 edition is your gateway to staying at the forefront of Science and Technology. Join us as we explore the detail summary of this edition, let’s start…
Article 1) AI Empowering Wood Forensics
The Significance of Wood and Its Challenges
- Wood is a material that is widely used in many different applications, like as furniture and buildings. But there’s growing concern about this precious natural resource being depleted as a result of problems like illicit logging, deforestation, and climate change.
- Determining the species of wood and where it originated is essential for both environmental preservation and product quality assurance.
- This is where wood forensics, which uses a variety of methods to examine the characteristics and provenance of wood, enters the picture.
Wood Forensics for Sustainable Management
- Wood forensics provides vital tools for cultural heritage preservation, illegal timber trade prevention, and sustainable forest management. But it frequently calls for specific equipment and expertise, which aren’t always easily accessible.
- Similar to how forensic botany uses plant sciences in criminal investigations, artificial intelligence (AI) can be useful in this situation.
- AI methods can improve wood identification precision and lower error rates.
Challenges in Wood Forensics
- Illegal logging and the flood of imported lumber are results of the growing demand for wood and wood products.
- Furthermore, many wood species especially tropical ones lack freely available reference data.
- The field of wood forensics encounters difficulties in distinguishing closely related species, individual branches within a tree, and variances in wood quality resulting from processing techniques and environmental factors.
- Certain forensic techniques, such as mass spectrometry and DNA analysis, call for specific tools and knowledge.
AI as a Solution in Wood Forensics
- A crucial way to overcome the main obstacles in wood forensics is using artificial intelligence.
- The accurate tracking of the original source of the timber is made possible by molecular markers and DNA fingerprinting of wood samples.
- DNA analysis is essential for linking defendants to unlawfully cut down trees since it can match the DNA in one wood product to another.
- Along supply chains, it also facilitates independent chain-of-custody verification.
Computer Vision and Wood Identification
- The creation of Computer Vision (CV) for wood identification is another significant advancement in the field of wood forensics.
- Based on pixel intensity, anatomical element arrangement, dispersion, and aggregation, an AI-based CV can comprehend wood science and identify wood species.
- Finding these variations is largely the result of machine learning.
The Future of Wood Forensics with AI
- AI has recently given rise to a technological basis for increasingly precise wood identification.
- Numerous field applications for CV-based wood identification are now feasible thanks to the integration of AI and contemporary communication technologies.
- Artificial intelligence has the capacity to quickly, correctly, and efficiently identify different species of hardwood and softwood in the near future, which will further advance the subject of wood forensics.
Article 2) Solutions to Sewage Water in Vishakapatnam
The Vizag Coastal Zone and Its Challenges
- Known as the 12th biggest port in the country, the Visakhapatnam (Vizag) coastal zone is located in Andhra Pradesh, India.
- But the water from city sewage is a serious problem for it. There is a significant amount of solid debris in this sewage water, including glass, metals, plastics, building supplies, electronics parts, clothes, and other domestic waste.
- The water’s turbid appearance suggests that there is a lot of liquid waste present, including paint, oil, grease, pesticides, residential wastewater, and industrial chemical waste like mercury, cadmium, and zinc.
- Because they cause nutrient enrichment, rising water temperatures, and toxic odors, these dangerous compounds pose a serious threat to the health of the marine ecosystem.
Environmental Impacts of Sewage Wastes
- There are serious ecological repercussions when sewage waste is present in the coastal zone of Vizag.
- Degradation of natural habitats, reduction of oxygen levels, disturbance of breeding processes, and promotion of illnesses are some of the ways it leads to the loss of biodiversity.
- Because plastic bags and bottles can entangle them and cause asphyxia, sea life is also impacted.
- In addition, the local population depends on marine life for their food and livelihood, which raises questions about the possibility that fish from untreated sewage discharge points may absorb heavy metals.
- Ingestion of infected fish by humans may lead to serious health complications.
Addressing the Issue: A Multi-Faceted Approach
- Reducing the environmental impact of sewage water in coastal areas necessitates a diverse strategy.
- In order to improve understanding of the need of proper sewage disposal and its consequences on the coastal ecosystem, public awareness and education are essential.
- Encouragement of appropriate waste disposal techniques is necessary to reduce pollution.
- To purify sewage before it is released into coastal waterways, well-designed wastewater treatment plants must be established and maintained.
- Tight regulations controlling the release of wastewater from cities and industries are required to protect the environment and preserve the coastal ecosystem.
- In order to evaluate the quality of the water and pinpoint possible sources of sewage pollution, regular surveillance and monitoring programs are essential in the coastal zone.
- Additionally, the direct impact of sewage water on these delicate ecosystems might be lessened by diverting it away from sensitive coastal areas and ecologically significant sites.
Way Forward: Innovation and Research
- To enhance sewage treatment procedures and lessen the influence of sewage water outflows on the environment, research and cutting-edge technology must be invested in.
- This dedication to technology development may open the door to more environmentally friendly sewage treatment in coastal areas, protecting the sensitive balance of the marine ecology and the health and welfare of nearby residents.
Article 3) Nanotechnology Derived Herbal Gel for Menopausal Women
Context:
- The menopause and related conditions can negatively impact women’s health.
- This is especially important in countries where menopausal women experience serious health issues that have an impact on their emotional, physical, and financial well-being.
Development of a Nano-Tech-Derived Herbal Gel
- A unique herbal gel made from nanotechnology has been created by researchers at Jamia Hamdard in New Delhi to alleviate symptoms related to various stages of menopause.
- This gel minimizes side effects and increases patient compliance by combining the advantages of botanicals with a dependable delivery system.
- It is a thoroughly studied and pharmaco-technically evaluated skin formulation.
Understanding Women’s Preferences and Needs
- An assessment of menopause-related symptoms, their effect on women’s quality of life (QoL), the need for therapies, and patient preferences for therapy were done using a survey.
- The findings showed that women were reluctant to take hormones, and gynecologists were also reluctant to recommend them for long-term usage throughout the menopausal transition.
- This revealed an “unmet need” in the treatment of menopause.
Herbal Approach with Black Cohosh
- The research team included the Black Cohosh extract in a patient-friendly formulation to fill the discovered gap.
- Black cohosh has a well-established reputation for helping women with menopause and women’s health; controlled trials have verified its safety and effectiveness.
- This plant is unique in that it does not have estrogenic side effects, making it safer to use over an extended period of time.
- The scientists synthesized an enhanced proportion of black cohosh and nanometrically encapsulated it in lipid carriers.
- A transgel containing lipidic carriers loaded with black cohosh is part of this improved formulation.
- The dermal route is used to introduce the active components into the bloodstream after application to the skin.
Advantages of the Gel
- The developed gel has a number of therapeutic benefits, such as being simple to prepare and apply and not causing drug interactions, which are common for this age bracket.
- By using skin application, problems with oral prescriptions such as pharmacotechnical restrictions, liver toxicity, hepatic metabolism, and systemic side effects are circumvented.
- It also reduces adulteration-related problems, which are a possibility with oral herbal formulations.
Article 4) Keystone Species: Regulators of the Ecosystem
Context:
- The incredible biodiversity of our planet, which includes a wide range of life forms from microscopic organisms to complex ecosystems that support humans, animals, and plants, is what makes it special.
- Just a small portion of the 8.7 million species thought to exist have been recognized. Certain species, such as keystone species, are essential to preserving the harmony and balance of the environment.
Keystone Species: Ecosystem Architects
- Ecologist Robert T. Paine first proposed the theory of keystone species in the 1960s. These species are distinguished by their disproportionately significant responsibilities in maintaining the ecosystem.
- These species have a significant impact on the composition and operation of the ecosystem. Their existence has a major effect on the habitat’s stability and biodiversity, frequently through complex relationships with other species.
Identifying Keystone Species
A number of factors aid in identifying these important species:
- Species Interactions: Look out species that have an impact on other people’s behavior and abundance.
- Ecosystem Function: Examine their contributions to important ecological processes such as habitat alteration and pollination.
- Disproportionate Impact: Their existence or absence has a major impact on the ecology, even if they are not the most abundant.
- Trophic Influence: Their place in the food chain and how it affects the number of other species.
- Sensitivity to Disturbances: Their capacity to preserve the stability of ecosystems and their reaction to changes in the environment.
- Research and Ecological Studies: Refer to the scientific literature and professional perspectives to find out what is considered important in particular ecosystems.
Keystone Species’ Impact and Consequences
The loss of a keystone species can lead to significant repercussions:
- Loss of Biodiversity: Interaction disruptions have the potential to cause dependent species to become extinct or decline, which would affect biodiversity as a whole.
- Altered Trophic Cascade: In the food chain, imbalances in the predator-prey dynamic can have unanticipated consequences.
- Habitat Degradation: Other reliant organisms may be impacted by habitat changes or the disappearance of keystone species’ adjustments.
- Changes in Ecosystem Functioning: interference with vital ecological processes like nitrogen cycling or pollination.
- Decreased Resilience: Loss of keystone species diminishes an ecosystem’s ability to rebound from shocks.




Conservation and Human Benefits
- Keystone species must be preserved for the sake of both the ecosystem and human welfare. Important ecosystem services that are necessary for agriculture and environmental balance are provided by these species, such as habitat building and pollination.
- By ensuring the continuation of these important functions, keystone species are recognized and protected, supporting the stability and well-being of ecosystems.
Article 5) In the Name of Afforestation
Context:
- Serious environmental problems have been plaguing the planet, most notably the effects of climate change. While extreme weather phenomena like cyclones, increasing temperatures, and erratic weather patterns garner public attention, they have also had a positive impact on human health and sparked awareness and action.
- Despite attempts to address the underlying cause the continuous release of gases, most notably Carbon Dioxide (CO2) from numerous businesses and vehicles mitigation techniques, which mainly target reducing greenhouse gas emissions, have not been successful.
Forests’ Crucial Role in Mitigating Global Warming
- In order to combat global warming, natural forests are crucial for providing oxygen and storing carbon. But ongoing deforestation has made it more difficult for them to absorb CO2.
- Particularly, savannah and tropical woods make a substantial contribution to the creation of oxygen. In addition to having an impact on carbon storage, the loss of forest cover hastens the process of global warming.
- In response, scientists and decision-makers are endorsing afforestation initiatives as a way to lessen the effects of global warming.
Challenges and Controversies in Afforestation Efforts
- Notwithstanding the rise in afforestation efforts, a recent editorial emphasized certain disadvantages. Even though it has many advantages, reforestation might backfire if the wrong species are planted.
- Examples include the introduction of non-native species, such as Prosopis juliflora, which have had a negative effect on soil texture and biodiversity in the area. Ecological harm has also resulted from the careless planting of native species in inappropriate settings.
The Need for Thoughtful Afforestation
- The need for a more deliberate approach to afforestation is emphasized in the editorial. Negative effects may result from planting native trees in locations where they aren’t naturally suited for them or without taking into account their natural distribution.
- Open natural environments are frequently invaded by forestry operations, which disturbs the distinctive flora and fauna that these habitats support.
Guidelines for Effective Afforestation
- A thorough understanding of the origins of plant species and their compatibility with local environments is essential for ensuring the success of afforestation initiatives.
- It is necessary to review research records and publications regarding species’ past occurrences in planting sites. Agricultural departments, biodiversity boards, and scientific organizations should work together to design and oversee afforestation initiatives.
- To avoid detrimental changes to the local ecosystem and biodiversity, monitoring must be done continuously.
The Balance Between Planting and Preservation
- It is highlighted that afforestation requires a cautious and informed approach, and that a deeper understanding of the environmental consequences of planting the wrong species is vital.
- It is imperative to give due regard to the habitat preferences and distribution patterns of species in order to mitigate any potential harm to nearby ecosystems.
- In the end, it’s critical to keep in mind that planting trees is about more than just quantity; it’s also about maintaining the local biodiversity and fostering a favorable microclimate.
In order to prevent global warming and maintain the delicate balance of local ecosystems and biodiversity, afforestation initiatives must carefully pick and install trees.
Article 6) The Endangered Ungulate of Western Ghats
Context:
- This article will discuss about Nilgiri Tahr, a native mountain goat species that is endangered, among the Western Ghats’ lush vegetation which is also found in Eravikulam National Park.
- These shy, sheep-like animals prefer to live in the upper, forested areas of the Ghats, particularly the grassy plateaus and stony slopes at higher altitudes of 1200–2600 meters.
Characteristics and Behavior of the Nilgiri Tahr
- With short, coarse hair and a bristling mane that varies in color from yellowish-brown to grey and features a dorsal midline stripe, the Nilgiri Tahr has a unique appearance.
- The males can be identified by their darker color and bigger size, and they also exhibit horn traits that indicate their age. Being nocturnal creatures, they are most active in the early morning and late afternoon.
- These animals reproduce all year round, with the monsoon season being the prime time for breeding.
- Females achieve sexual maturity at 16 months.

Nilgiri Tahr

Conservation Challenges and Efforts
- The Nilgiri Tahr is threatened by a number of factors, including habitat degradation, illicit poaching, and the effects of climate change, despite its distinctive characteristics.
- Because of their IUCN Red List classification as endangered, Indian wildlife regulations have implemented protective measures.
- The limited and vulnerable populations of these mountain ungulates are the focus of conservation efforts spearheaded by several wildlife associations and research institutions, with Eravikulam National Park and other sanctuaries providing vital protection.
Article 7) Endangered Water Tigers of the Himalayas
Context:
- The holy Ganges River has religious and cultural significance in addition to being a navigable river.
- The Golden Mahseer, a fish that is legendary in Indian river systems, especially those in the Himalayas, lives there.
- Since its discovery during the colonial era, this species has piqued the interest of fishermen all over the world. It is renowned for its remarkable size and distinctive golden scales.
The Golden Mahseer: A Cultural Icon:
- Since its discovery in 1822, the large freshwater fish known as the Golden Mahseer, or Tor putitora, has captivated anglers all over the world in the rivers of the Himalayas.
- Its elusiveness and golden scales make it a cultural icon in the environment of the Himalayan River, and local tales and myths emphasize its importance.
Curiosity and Research Beginnings:
- In order to trace the fish’s movements, the investigation started by tagging them with VHF radio tags.
- The team engaged with the rivers Kolhu and Kosi in an effort to comprehend and corroborate local legends about the fish’s behavior.
- The results of the research showed that the migration patterns of male and female Mahseers differed, verifying the fish’s dispersal during monsoons.
- Interestingly, the fish carefully chose houses upstream and downstream, indicating how important certain features of the water are to their environment.
Migration Stories and Research Objectives:
- According to local legend, the Golden Mahseer migrated upstream during the monsoon season in search of safe breeding sites in the Ganges’ crystal-clear waters.
- This served as the impetus for an innovative study on the tagging of freshwater fish in India that used VHF radio tags to track the movement patterns of the species.
Research Journey and Findings:
- On a sunny June 2019 day, the tagging experiment began, exposing Golden Mahseer’s initiating movements throughout the pre-monsoon season.
- Local stories were validated by the study, which saw dispersal during monsoons and variations in migration between male and female individuals.

Habitat Requirements and Conservation Challenges:
- The study highlighted the possible effects of changes to the river system by revealing the fish’s meticulous choice of residences based on water depth, temperature, and velocity.
- The migratory patterns of the Golden Mahseer are threatened by the shifting tides in the Himalayas, which are characterized by barrages, dams, sand mining, and water pollution.
Community-Based Conservation Needs:
- Reductions in catch sizes reported locally highlight the necessity of community-based conservation initiatives.
- It becomes imperative to raise awareness among the local populace in order to protect the Golden Mahseer and ensure that it has the ideal environment.
Research Implications and Future Scope:
- This study is the first attempt in India to use radio tagging to shed light on the migrations of Golden Mahseer.
- The results provide a framework for protecting the habitat of the species and establish the parameters for further studies on the migration of Mahseers in India.
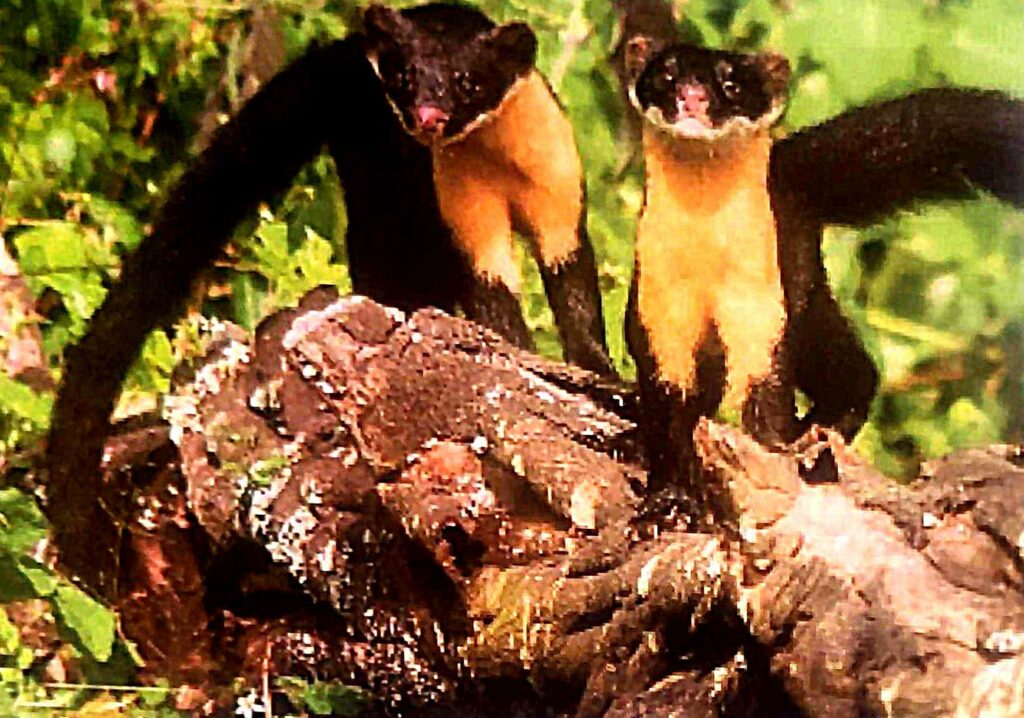
Article 8) Conserving the Nilgiri Martens
Habitat and Characteristics
- The Nilgiri Marten, which is also called the white-bellied marten, is a small carnivorous animal that is indigenous to the Nilgiri Hills in the Western Ghats of India.
- This elusive animal, which has a long tail, slim body, and dark brown or blackish-brown fur with a noticeable white patch on its chest and throat, finds refuge in Pampadum Shola National Park.
- The marten is primarily an arboreal animal that lives mostly in the forest canopy.
Population and Behavior
- They are opportunistic predators that feed on a wide range of food, including small mammals, birds, insects, reptiles, fruits, and nuts. Estimates place its number at about 1000 individuals.
- The Nilgiri Marten is a nocturnal, solitary animal whose behavior and ecology are poorly understood due to little research.
Indicator Species and Conservation Status
- The Nilgiri marten is an indicator species for the health of the forest ecosystem, but habitat loss, fragmentation, and hunting pressure have put it in jeopardy.
- The goal of conservation efforts is to save its natural habitat and guarantee its continued existence.
- The importance of the marten’s preservation for the environment as a whole is highlighted by its function as an indicator species.
Species Diversity of Martens
Mustelidae Family
- The family Mustelidae, which includes martens, is a broad category of omnivorous animals.
- The Nilgiri marten is a member of the genus Martes, which is found in colder climates.
- Since each species in the genus has distinct traits, adaptations, and geographic distributions, they all add to the marten family’s overall variety.
Ecological Peculiarities
- The Nilgiri Hills, home to the Nilgiri marten, have unusual ecological features that contribute to an environment that is distinct and multifaceted.
- The dense areas of evergreen trees scattered with grasslands make up the “montane shola forests” of the Nilgiri Hills, offering a varied home for a variety of animals.
- A plentiful supply of precipitation supports freshwater environments and aquatic life.
Sacred Groves and Diverse Landscapes
- Sacred groves, preserved for their religious and cultural value, serve as havens for flora and fauna, protecting biodiversity in the Nilgiri Hills.
- Mountains, valleys, plateaus, and grasslands are just a few of the region’s many landforms, which produce microhabitats that sustain distinct natural populations.
Conservation Status of Nilgiri Marten
Endangered Classification
- The IUCN Red List now lists the Nilgiri marten as Endangered because of habitat loss, fragmentation, poaching, and possible climate change effects. There are serious risks from human activities like habitat conversion and deforestation.
- To preserve the survival of the species, conservation measures include research projects, community involvement, wildlife protection legislation, and habitat protection.
Ongoing Threats and Climate Change
- The Nilgiri marten is threatened by occasional hunting, human encroachment, and climate change.
- The difficulties are made worse by habitat loss brought on by infrastructure development for ecotourism initiatives.
- Campaigns to raise awareness, research to meet the unique needs and challenges faced by the species, and habitat protection are examples of conservation strategies.
Conclusion
- The ecological significance of the Nilgiri marten in the Western Ghats is highlighted by its status as an indicator species.
- To secure the long-term survival of this rare and endangered species in the Nilgiri Hills, conservation activities must address habitat protection, human-wildlife conflicts, and persistent threats.
Article 9) Migratory Birds on Indian Postage Stamps
Spectacle of Migration
- India is home to both endemic and migratory birds, contributing to its great avian variety.
- Large groups of people travel long distances by air every year from Central Europe, Northern Asia, and Africa to India for their October to March winter holiday.
Migration Patterns
- India experiences a large influx of migratory birds over its length and breadth from October to March.
- The migration map is dominated by birds, including pintail ducks, garganeys, and white storks.
- These birds migrate across roughly 29 nations via three main flight routes: the Central Asian Flyway, the East Asian Flyway, and the East Asian-Australasian Flyway.
- They flee the severe circumstances in their home countries and seek refuge in India.
Ecological Significance
- One good sign of a healthy environment is the presence of migrating birds.
- These birds are essential for maintaining pest management, spreading seeds, and aiding in pollination.
- Their contributions highlight the crucial connection that migrating birds have to ecological balance.
Philately: Stamps as Conservation Messengers
Postal Commemoration
- Acknowledging the significance of migrating birds for the environment, the Indian Postal Department has released postage stamps featuring these avian guests.
- These stamps are effective instruments for raising public awareness of the value and beauty of migrating birds.
Special Covers and First Day Covers
- In addition to stamps, the Postal Service has released First Day Covers (FDC) and Special Covers (SC) honoring migrating birds, wildlife reserves, wetlands, and bird sanctuaries.
- The purpose of these campaigns is to raise public awareness of the value of protecting these natural treasures.

Conservation Efforts through Philately
- Numerous unique covers have been released to honor occasions and places that are important to migratory birds.
- Covers from Mangalajodi Marshland, Haripex-2006, and Magadikere Conservation Reserve are a few examples.
- These programs emphasize how important it is to preserve and safeguard these vital ecosystem contributors.

Urgency of Conservation
Threats to Migratory Birds
- Notwithstanding their vital ecological roles, migratory birds are threatened by poaching, habitat degradation, and hunting.
- Some species are on the verge of extinction due to population declines brought on by mass killings and habitat changes.
Moral Duty to Conserve
- When one considers how susceptible birds are to changes in their habitat, advocating for conservation becomes morally required.
- The pressing need to save these priceless creatures from extinction highlights the necessity of group efforts to guarantee migratory birds’ continuous presence in India’s natural tapestry.
Article 10) Quantum Technology: It’s Ramifications for the Future
Nobel Laureates in Quantum Technology
- Three pioneers of quantum technology applications—Alain Aspect, John Clauser, and Anton Zeilinger were given the 2022 Nobel Prize in Physics.
- This new field is a vital tool for modernization and digitalization since it promises unmatched information processing capabilities.
Global Quantum Race
- With significant investments being made in quantum research by nations like the USA, Canada, UK, and EU, quantum technology has become a global buzzword.
- China is ranked fifth in the world for investments in quantum technology, demonstrating the importance of this area globally.
National Quantum Mission (NQM): India’s Quantum Aspiration
Quantum Ecosystem in India
- The Union Cabinet authorized the National Quantum Mission (NQM) with funds totaling Rs. 6000 crores in order to establish India as a hub for quantum technologies.
- In order to become globally competitive, the purpose is to seed, nurture, and scale up research in quantum technologies and applications (QTA).
Mission Objectives
- The objectives of the NQM are delineated with the aim of augmenting comprehension and involvement in Quantum technology.
- The goal of the mission is to acquaint people with Quantum language and concepts before going into the subtleties of the technology.
Quantum Mechanics: Fundamentals and Implications
Quantum Basics
- ‘Quantum’ means ‘discrete,’ implying that matter or light exist as separate packets.
- By investigating events at subatomic scales, quantum mechanics turns theoretical study into revolutionary technological applications.
Quantum Applications
- Quantum technology has many uses, ranging from smart manufacturing and defense to drug development and healthcare.
- Its promise extends to effective supply chain management, optimal distribution of energy, and eco-friendly activities.
Main Areas of Quantum Research
Quantum Computing
- By using qubits and quantum superposition, quantum computing aims to surpass traditional computers in terms of speed and complexity by achieving quantum supremacy.
Quantum Simulation
- Research is driven by quantum simulations, which forecast material properties and get around the drawbacks of traditional modeling techniques.
Quantum Communication
- Secure information transfer is ensured via quantum communication, which uses quantum cryptography to thwart attacks by quantum computers.
Quantum Sensing
- Quantum sensing promises ultra-sensitive sensors that are orders of magnitude more sensitive than their modern counterparts.
Quantum Budget and Challenges
Global Spending
- Quantum research and technology development receive distinct funding from nations including the United States, China, and the European Union.
- With its breakthroughs in quantum-secured networks, China is the leader in public funding.
Quantum Challenge
- Redesigning policies to encourage quantum R&D, countries are putting a greater emphasis on industry-academia cooperation.
- Waiting it out is necessary due to the uncertainty surrounding the socio-economic and legal elements.
Future of Quantum Technology
Potential Applications
- Future uses for quantum technology include molecular design, secure communications, new materials, sophisticated algorithms for a variety of sectors, and precision equipment.
- Its revolutionary influence on the automotive, chemical, financial, and healthcare industries is still greatly expected.
The Journey Ahead
- The future will be shaped by quantum technology as its revolutionary effects on industries and realized potential are realized.
- The need of having a thorough understanding of the consequences and prospects of quantum technology is emphasized in the article’s conclusion.
Article 11) Quantum Entanglement: A Strange Feature of Quantum Physics
- The interrelated quantum states of particles, like photons or electrons, are described by quantum entanglement, an intriguing phenomenon observed in nature.
- Entangled particles violate the traditional limit of information transmission set by the speed of light by instantly linking the states of two particles, even if they are separated by great distances.
“Spooky Action at a Distance”
- Due to its seemingly instantaneous violation of the basic constraint that forbids information transmission faster than the speed of light, Albert Einstein nicknamed quantum entanglement “spooky action at a distance”.
- Even though Einstein was first skeptical, the phenomena was confirmed by later photon and electron studies.
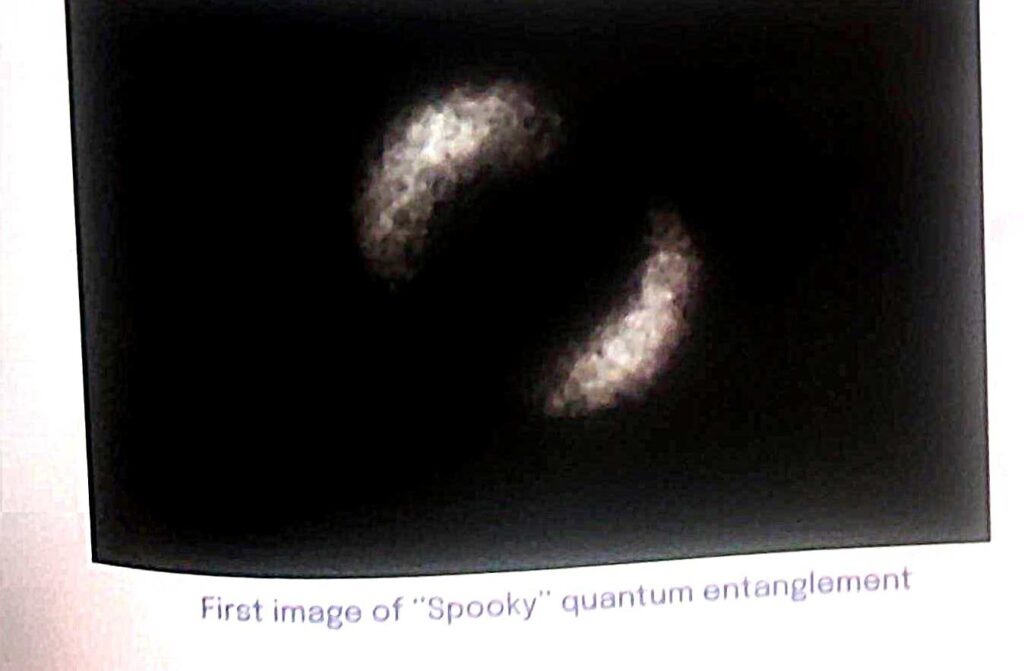
First Image Of “Spooky” Quantum Entanglement
Superposition and Entanglement
- Superposition, in which quantum particles concurrently exist in a mixture of two opposing states, is the foundation of quantum entanglement.
- Quantum mechanics was shaped by the fact that instantaneous information about a distant companion may be obtained by observing the state of a single entangled particle.
Historical Context and Key Contributors
Einstein’s Dispute
- A 1935 study by Albert Einstein and associates questioned the logic of quantum theory, especially as it related to entanglement.
- Albert Einstein’s well-known remark, “God does not play dice with the universe,” expresses his lack of faith.
- Nevertheless, the immediate connection between entangled particles was confirmed by other investigations.
Key Scientists
- Important contributions to the description and formalization of quantum entanglement have come from eminent figures including David Bohm, John Stuart Bell, John Clauser, and Alain Aspect.
- Through his emphasis on non-local interactions, John Bell’s work supported the existence of “spooky action at a distance.”
Experimental Validation
- Certain consequences of entanglement in local hidden-variable theories were shown to be non-reproducible, as demonstrated by experiments testing Bell’s inequalities, such as the CHSH inequality.
- Strong evidence of quantum strangeness was found in entangled photon experiments conducted by Clauser, Aspect, and Zeilinger.
Quantum Entanglement in Practice
Quantum Communication and Encryption
- Experimental tests of quantum entanglement for secure communication have demonstrated the long-distance teleportation of quantum information contained in entangled photons.
- Message security is guaranteed by entanglement in quantum communication.
Macroscopic Entanglement
- Quantum entanglement has been preserved at macroscopic dimensions greater than subatomic particles thanks to recent investigations.
- Establishing long-distance fiber optic cable connections between atoms paves the way for the eventual creation of a quantum internet.
Nobel Recognition and Beyond
- Aspect, Clauser, and Zeilinger were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2022 for their experimental demonstration of reality’s quantum character.
- A better understanding of the atomic nucleus is provided by ongoing nuclear science experiments that investigate the entanglement between various particles.
Future Implications and Applications
Quantum Technologies
- At the heart of quantum technologies is quantum entanglement, which makes possible applications like teleportation, quantum computing, and cryptography.
- Its potential uses span a wide range of industries, including early intervention and disease monitoring in medicine.
Quantum Internet
- A quantum internet is possible thanks to ongoing experiments with quantum entanglement.
- Particles that are entangled may act as information channels, transforming the speed and security of transmission.
Broader Applications
- Future uses of quantum entanglement extend beyond communication and computers to include nanotechnology, biology, and other technical developments.
- This basic quantum phenomena has far-reaching effects, as demonstrated by its capacity to influence not just the present but also the past, future, and past.
Article 12) Empowering Rural Women in STEM for Sustainable Agritech
Introduction: A Crucial Imperative for Development
- In addition to being a question of gender equality, empowering rural women is essential to maintaining sustainable development and food security.
- Given their crucial position as the backbone of the agricultural workforce, rural women’s empowerment, particularly in STEM ( Science, technology, Engineering, Mathematics) sectors, has become a critical issue in the quickly evolving global community.
Challenges Faced by Women in Agriculture
- Even though women contribute significantly to farming duties, they frequently face obstacles while trying to obtain necessary resources.
- The emphasis on agri-biotech procedures offers a chance to close the gender gap in science and technology, empowering women and resolving disparities.
Empowering Women Farmers: A Path to a Progressive India
- The empowerment of women farmers must be given top priority if India is to become progressive.
- Recognizing the vital role that agriculture plays in the nation’s economy, this entails giving people equal access to land ownership, financial resources, modern farming methods, and instruction on sustainable agriculture practices.
Role of STEM Education in Rural Empowerment
- A major factor in providing people with the skills required for the modern workforce is STEM education.
- Nonetheless, access to high-quality education and technology is difficult in rural places.
- Encouraging rural women to pursue STEM careers, especially in agri-biotech, can help them realize their full potential as catalysts.
Challenges in Agritech: Enhancing Efficiency and Productivity
Inefficient Supply Chain
- One of the issues facing agricultural technology, or agritech, is an ineffective supply chain with a lot of middlemen.
- The supply chain can be streamlined with the use of technology, which lowers expenses, waste, and delays.
Limited Financing Options
- Farmers, particularly those operating on a small scale, face challenges in obtaining adequate funding to invest in contemporary farming methods.
- This gap can be filled by creative finance arrangements that are adapted to the needs of farmers.
Inadequate Irrigation
- Outdated irrigation techniques affect crop productivity and lead to wasteful water use.
- Water efficiency can be improved by putting in place smart irrigation systems that make use of sensor and data analytics technologies.
Challenges of Farm Size
- Thanks to economies of scale, implementing sophisticated technologies is more difficult for smaller farms.
- Cooperatives that promote cooperation can assist smallholder farmers in reaping the benefits of group projects.
Eliminating Middlemen Through Agritech Platforms
- Price manipulation in agricultural transactions is frequently the result of middlemen’s involvement.
- By utilizing agritech platforms that provide direct communication between farmers and consumers, middlemen can be removed, resulting in an open market.
Addressing Climatic Variations with Technology
- Events with extreme weather can be dangerous for agriculture.
- Climate-smart crop varieties and precision agriculture are two examples of integrated technologies that help lessen the effects of climate-related issues.
Promoting Farm Mechanization for Productivity
- Productivity is hampered when farm mechanization is unavailable.
- Promoting mechanized farming equipment and training farmers can increase productivity and encourage the uptake of contemporary farming techniques.
Feminization of Indian Agriculture: Multifaceted Impacts
Causes and Impacts of Feminization
- Male migration to urban regions is one element contributing to the femininization of agriculture, as women are left to oversee agricultural operations.
- Although it provides economic empowerment, it also causes limited recognition, mental health problems, and cultural isolation.
Solutions for Empowering Women in Agriculture
- It takes a diversified strategy that combines awareness-raising, skill development, and education to empower women in agriculture.
- The goal of government programs like MKSP, NFSM, and Biotech-KISAN is to encourage women in the industry by offering training, financial assistance, and capacity building.
Government Initiatives for Women Empowerment
- A number of government programs, like as the MUDRA Yojana, Stand-Up India Scheme, and PMEGP, assist rural women in developing their entrepreneurial and financial independence.
- Programs for developing skills, such as PMKVY, are designed to close the gap between the supply and demand for skilled labor.
Innovative Solutions for Agricultural Empowerment
- The government’s dedication to the development of rural women is demonstrated by the implementation of a new agritech strategy that focuses on teaching women how to operate and repair drones.
- Drone technology makes it possible to monitor crops and manage pests efficiently.
Conclusion: Collaborative Strategies for Inclusive Development
- Governments, organizations, and educational institutions must work together to address issues in agritech and empower rural women in STEM professions.
- It is necessary to create comprehensive policies that support inclusivity and equal opportunities for advancement and innovation while attending to the particular requirements of rural women.
Article 13) Seaweed Farming
Versatility of Seaweeds: The ‘Medical Food’
- Macroscopic algae that flourish in maritime conditions are known as seaweeds, and they are a renewable resource with a wide range of uses. Known as the “medical food of the 21st century,” they are useful for chemicals, medications, food, and energy.
- Applications include those in the fields of agriculture, biomedicine, industry, nutrition, and personal care.
Industrial Applications: From Pharmaceuticals to Paper
- Seaweeds are widely used in many important industrial applications, such as processed food, cardboard, paint, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.
- Notable ingredients found in medications, cosmetics, and bone-replacement therapy include agar and carrageenan.
- Rich seaweed resources make the west and southeast shores of India, especially Tamil Nadu, perfect for large-scale seaweed production.
Biodiversity of Indian Seas: A Treasure Trove
- There are about 844 kinds of seaweed in India’s waters, with a standing stock estimated to be 58,715 tons.
- Brown, red, or green macrophytic benthic marine algae are the different types of seaweeds.
- With their combined length of approximately 8100 km, the west and southeast coasts are ideal for seaweed farming, particularly in Tamil Nadu.
Economically Important Seaweeds: A Resource for Various Industries
- 145 of the 221 commercially significant seaweeds are used as food, while 110 aid in the synthesis of phycocolloids.
- Agar is produced by farming Gelidiella acerosa, Gracilaria edulis, and Gracilaria dura, whereas carrageenan is produced by cultivating Kappaphycus alvarezii.
- Alginates are made from brown seaweeds such as Sargassum wightii and Turbinaria conoides.




Environmental Impact and Nutritional Value
- Seaweed farming offers advantages beyond just financial gain. By treating wastewater, reducing eutrophication, and enhancing the quality of coastal waters, it has a favorable environmental impact.
- Seaweeds, also referred to as sea vegetables, are a source of nutraceutical supplements with a range of health advantages since they are high in vitamins and minerals.
- They are rich in fiber, proteins, antioxidants, antibacterial agents, and vital amino acids.
Economic Potential and Sustainable Development
- The billion-dollar sector of seaweed cultivation is advancing environmentally friendly growth.
- India is well-positioned to transform its economy because to its vast coastline and ideal growing conditions.
- Due to its quick growth cycle, seaweed aquaculture has the potential to produce substantial revenue, which would be especially advantageous for coastal towns.
Challenges and Opportunities for Seaweed Farming
- Although seaweed farming has shown to have minimal effects on ecosystems, some effects have been documented.
- Extensive seaweed farming, when planned properly, can serve as a viable substitute for aquaculture sectors that have greater detrimental effects on the environment.
- The seaweed business in India has to grow sustainably, and this requires robust seed development, mass spore production, and inclusive economic growth.
Empowering Coastal Communities: A Path to Prosperity
- Growing seaweed has potential for inclusive development and is not only a business venture.
- It can also create livelihood opportunities, especially for women, and offer coastal communities an alternative source of income, particularly during fishing prohibitions.
- Establishing local-level institutions, raising awareness, and providing training are necessary for seaweed farming endeavors in India to be successful.
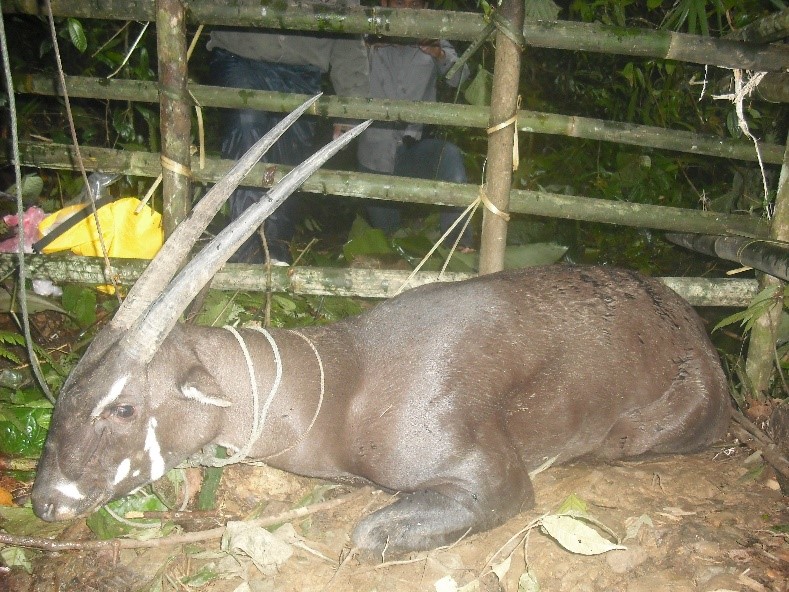
Article 14) The Asian Unicorn
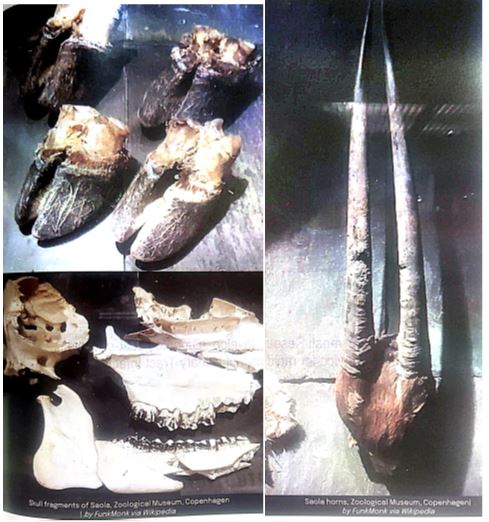
Mysterious Existence and Rarity
- The identity of the Saola, often known as the Asian unicorn, is still unknown.
- It is mostly found in the Annamite Range in Vietnam and Laos.
- This secretive species, which is critically endangered and has never been kept in captivity, has only been conclusively documented four times in the wild, although its incredible beauty and infrequent sightings have captivated scientists and nature enthusiasts.
Striking Appearance of the Asian Unicorn
- Falling under the genus Pseudoryx, saolas are a distinct species that resemble unicorns from mythology.
- Among their most distinctive characteristics are their sleek and elegant horns, which can grow up to 50 centimeters in length and are adorned on a bright chestnut coat.
- The saola is known as the “Asian Unicorn” because of its rarity and ability to live alone in harsh conditions; sightings are infrequent because of this.
Zoological Discovery and Conservation Challenges
- The remarkably long horns on the saola’s head, discovered in 1992 in north-central Vietnam during a collaborative survey, represented a startling zoological find.
- The most current shot of this reticent creature was taken in 2013; the first photos were taken in captivity in 1993.
- The saola, which has a population of less than 250, is severely threatened by hunting, the illegal fur trade, traditional medicine, and the eating of meat, which makes immediate conservation efforts essential.
Conservation Efforts and Collaborative Approach
- Devoted conservationists and groups are actively fighting to safeguard not only the animal but also its natural habitat in order to avert the sad extinction of the saola.
- Scientists and local people working together is seen to be essential to reducing risks caused by humans.
- Establishing sanctuaries and increasing public awareness are crucial elements of preservation that offer important insights into the behavioral patterns and ecological needs of the saola.
Hope for Survival and Global Engagement
- There is yet hope for the survival of the saola in spite of obstacles. International collaborations and raised public awareness can be extremely important to conservation efforts. Sustaining the saola and protecting this magnificent Asian unicorn for future generations requires us to support sustainable activities, protect habitats, and oppose illegal hunting.
News in Brief from Science Reporter Magazine October 2023 Edition
1) Robotic Gripping Device — Combo of Strength and Delicacy
- North Carolina State University researchers have created a novel robotic gripping tool with a wide range of applications.
- This novel gripper demonstrates incredible versatility: it can be used to pick up a drop of water with softness, lift 6.4 kg with strength, fold a cloth with dexterity, and handle microfilms that are 20 times thinner than a human hair with precision.
- The researchers have incorporated technology that allows the gripper to be controlled by electrical signals from forearm muscles, demonstrating its potential for integration with robotic prosthetics in addition to possible uses in manufacturing.
- The journal Nature Communications published the paper that described these developments.
2) IIT Guwahati Researchers develop 3D printed cost-effective device for rapid diagnosis of Urinary Tract Infection
- IIT Guwahati researchers have developed a quick, accurate, and reliable tool for urinary tract infection (UTI) detection.
- The type of infection in a patient may be determined in 5 minutes using this Point-of-Care Testing (POCT) prototype, which is a major advance over traditional detection methods that need several days and urine culture.
- The affordable device, which is expected to cost Rs 608 for manufacturing and Rs 25 for each sample test, solves the demand for effective UTI testing in rural areas that lack adequate facilities and where a large number of cases go undiagnosed.
- The journal “ACS Applied Bio Materials” has published the device’s specifications.
3) Scientists invent micrometres-thin battery charged by saline solution
- Researchers at Singapore’s Nanyang Technological University have developed a novel flexible battery that is as thin as a human cornea and is intended to power smart contact lenses.
- When submerged in saline solution, this biocompatible battery which lacks the cables and hazardous heavy metals present in traditional batteries stores electricity.
- The study, which was published in the journal Nano Energy, emphasizes the possibility of using human tears which include potassium and sodium ions—as a substitute power source.
- An extra hour of battery life was shown in tests using a simulated tear solution for each twelve-hour wearing cycle.
- Conventional charging of the battery with an external power source is another option.
4) Miniature battery to power tiny devices integrated into human tissues
- A new ‘droplet battery,’ developed by Oxford University researchers, is a miniature soft power source made by laying a chain of five nanoliter-sized droplets of conductive hydrogel.
- This hydrogel makes it possible to create tiny batteries that can power tiny devices incorporated into human tissues.
- It is made up of a 3D network of polymer chains with considerable water absorption.
- The development of small bio-integrated devices with therapeutic properties, such focused medication delivery and expedited wound healing, is one of the possible uses.
- The study, which highlights the battery’s potential applications in biology and medicine, was published in the journal Nature.