13 June 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Analysis
1. Tackling the fatty liver disease epidemic
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Health |
| Context |
|
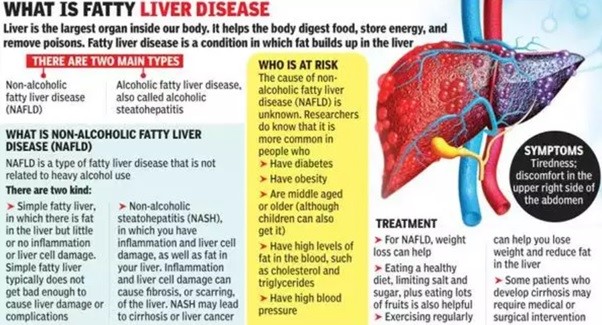
Introduction
- The theme for International Fatty Liver Day this year is ‘Act Now, Screen Today’.
- This theme highlights the urgent need for awareness and action against liver diseases, particularly non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Fatty liver disease is now reclassified as Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD).
Growing Burden
- MASLD is a growing global health issue, with prevalence estimated at 25-30% worldwide.
- In India, the prevalence among adults is 38.6%, and among obese children, it is around 36%.
- MASH (Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis) is expected to become the most common cause of chronic liver disease and the leading indication for liver transplantation.
Link with Metabolic Syndrome
- MASLD is closely linked with metabolic syndrome, including conditions like obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure, and abnormal cholesterol levels.
- Prevalence rates of MASLD in individuals with these conditions are alarmingly high: 55.5%-59.7% for diabetes, 64.6%-95% for obesity, and 73% for severe metabolic syndrome.
- Excessive consumption of carbohydrates, especially refined carbs and sugars, contributes to metabolic problems and insulin resistance.
- Insulin resistance leads to the conversion of excess glucose into fatty acids, which are stored in the liver, causing fatty liver and potentially progressing to more severe liver conditions.
Early Detection and Screening
- Fatty liver disease often goes undetected in its early stages due to the absence of symptoms.
- Early diagnosis is crucial and can be achieved through comprehensive health screenings.
- Key screening components include a thorough history, physical examination, blood tests, and an ultrasound of the abdomen.
- Physical examination should assess visceral fat through measurements like height, weight, body mass index (BMI), abdominal girth, and waist-to-hip ratio.
- Blood tests should cover cardio-metabolic risk factors, including blood count, sugar profile, blood lipid profile, liver function tests, and kidney tests.
Importance of Ultrasound
- An ultrasound of the abdomen is vital for screening liver disease and diagnosing fatty liver.
- Despite its importance, it is often missed or not included in health checks due to limited availability of radiologists and stringent regulatory approvals.
- In a study of 50,000 people, 33% had fatty liver as observed using an ultrasound, but only one in three had elevated liver enzymes in their blood test.
Advanced Liver Tests
- Liver fibrosis assessment, using technologies like vibration-controlled transient elastography, is crucial for detecting liver scarring.
- This non-invasive tool measures liver stiffness and helps assess early stages of liver fibrosis.
- Regular monitoring of liver fibrosis progression and response to treatment is essential.
Integrated Approach
- An integrated approach to detect and manage liver diseases at an early stage includes ultrasound, comprehensive metabolic screening, and elastography.
- Screening tests and their frequency should be personalised based on individual risk factors like family history, lifestyle, and pre-existing health conditions.
- Clinicians should avoid making generic assumptions based on age or physical markers alone.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Integrated strategies combining dietary modifications, regular physical activity, and effective weight management are necessary to mitigate liver disease risks.
- The liver is a ‘silent organ’ that does not show noticeable signs of damage until advanced stages.
- Awareness of lifestyle choices and their long-term impact on liver health is crucial.
Conclusion
- Taking active control of health through frequent screenings and conscious lifestyle choices is vital.
- The foundation for a happy life begins with good health, emphasising the importance of early detection and management of liver diseases.
| More information about non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): |
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the prevalence, risk factors, progression, and management strategies of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). How can early diagnosis and intervention mitigate its impact on public health? (250 Words /15 marks) |
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 9)






