9 November 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Analysis
1. The BRICS journey — gaining heft while in transition
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Context |
| The 2024 BRICS summit in Kazan highlighted the bloc’s resilience amid global conflicts, expanding membership and aiming to reform the international order for inclusivity.New partnerships signal BRICS’s growing influence in representing the Global South.India views BRICS as key to advancing strategic autonomy and fostering East-West relations. |
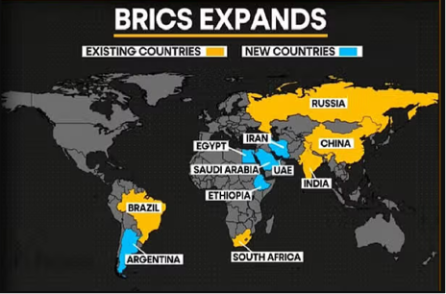
Background and Context
- The BRICS 2024 summit in Kazan, Russia, marked the 16th summit since the group’s inception in 2009.
- Initially comprising Brazil, Russia, India, and China, South Africa joined in 2011, giving BRICS its current form.
- The group faced challenges in its second decade due to COVID-19, the India-China Galwan Valley clash in 2020, and Russia’s conflict with NATO due to the Ukraine war, testing its unity and resilience.
Expansion and Global Representation
- BRICS expanded at the 15th summit in 2023, adding Saudi Arabia, the UAE, Iran, Egypt, and Ethiopia.
- Interest from 34 additional nations indicates BRICS’s appeal as a platform for emerging economies and developing countries, aiming to create a “Global Majority.”
- Thirteen more nations were invited to join as “partner states,” including Cuba, Algeria, Türkiye, Indonesia, and Kazakhstan, broadening BRICS’s demographic and economic reach.
| Core Mission and Characteristics of BRICS |
|
BRICS 2024 Summit Outcomes
- Political and Security Cooperation
- The declaration addressed the conflict in West Asia, criticising Israeli actions and calling for a ceasefire, hostage release, and a Palestinian state.
- In contrast, the Ukraine war received limited attention due to Russia’s BRICS leadership, with members reiterating calls for peaceful resolution.
- The summit opposed unilateral economic sanctions, highlighting their adverse impacts on human rights.
- Economic and Financial Cooperation
- The idea of a common currency remains under study, with the current focus on facilitating trade in local currencies between BRICS nations and partners.
- Saudi Arabia’s hesitance impacted funding expectations for the New Development Bank (NDB), leading to recommendations to enhance NDB operations without large capital inflows.
- Social and Cultural Collaboration
- The summit emphasised people-to-people exchanges in culture, sports, and civil society for long-term socio-economic development, aiming to foster closer connections across BRICS societies.
India’s Role and Perspective
- Strategic and Diplomatic Significance
- BRICS is among India’s six important plurilateral platforms, allowing it to promote global multipolarity, assert strategic autonomy, and support Global South interests.
- The summit facilitated a crucial India-China meeting, leading to border disengagement agreements and potentially improving bilateral ties.
- India values BRICS for enhancing its role as a bridge between East and West and North and South, expanding its diplomatic reach and influence.
- Outlook on BRICS Expansion
- While initially cautious about expansion, India now sees it as beneficial, provided it is managed carefully to strengthen BRICS’s influence.
- The group’s potential to foster East-West and North-South dialogues aligns with India’s geopolitical interests, reinforcing its position as a strategic global player.
Conclusion
- The Kazan summit underscored BRICS’s resilience and adaptability, with a vision to support inclusive global reforms rather than overhaul the current order.
- The addition of new members and partner states extends its influence, while India’s involvement and expanding diplomatic ties highlight BRICS’s significance as a balancing force in the international landscape.
| Practice Question: Discuss the evolving role of BRICS in promoting a multipolar world order, with a focus on recent expansions and India’s strategic objectives within the grouping. (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. Staying cool, but with clean tech, global collaborations
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Topic: GS3 – Environment – Environmental pollution and degradation |
| Context |
| As global temperatures rise, sustainable cooling solutions are critical to protecting vulnerable populations.The Quad nations, particularly India, are leading initiatives like the Wilmington Declaration to promote affordable, high-efficiency cooling technologies.Through partnerships and policies, India is positioning itself as a leader in climate-friendly cooling efforts worldwide. |
The Wilmington Declaration and Quad’s Commitment
- On September 21, 2024, Quad nations (Australia, India, Japan, and the U.S.) issued the Wilmington Declaration, reaffirming their dedication to sustainable energy and high-efficiency cooling solutions.
- This builds on the earlier India-U.S. roadmap to create secure, resilient global clean energy supply chains, focusing on affordable, energy-efficient cooling technologies in vulnerable areas.
India’s Leadership in Sustainable Cooling
- India has committed to significant investments in solar and cooling infrastructure across the Indo-Pacific region.
- In collaboration with the U.S., India aims to expand manufacturing capacities for high-efficiency air conditioners and ceiling fans, reducing the climate impact of cooling systems.
Cooling-Related Emissions: The Role of the Kigali Amendment
- The Montreal Protocol’s Kigali Amendment (2016) targets HFCs, potent greenhouse gases used in cooling systems, which could contribute to 0.52°C of warming by 2100 if unchecked.
- Aligning HFC reduction with energy efficiency improvements could achieve around two-thirds of potential greenhouse gas reductions by cutting electricity consumption.
Emissions Challenges: Indirect and Direct Impacts
- Indirect emissions from cooling systems powered by fossil fuels and direct emissions from harmful refrigerants both pose climate risks.
- Many countries lack integrated efficiency and refrigerant standards, and outdated, inefficient cooling appliances still dominate several markets, creating environmental and energy challenges.
India’s Need for a Mission-Mode Approach
- India’s extreme heat, with temperatures reaching 50°C, underscores the need for efficient cooling to protect public health, preserve food and medicines, and maintain industrial processes.
- Projections indicate that by 2030, 160-200 million Indians may face life-threatening heatwaves annually, with productivity, health, and food security at risk due to extreme heat.
India’s Cooling Action Plan (ICAP)
- India ratified the Kigali Amendment in 2021, committing to cut HFC use by 85% by 2047.
- The India Cooling Action Plan (ICAP) sets a target for a 20%-25% reduction in cooling demand and a shift to low-global warming potential (GWP) refrigerants.
- Establishing a national mission for sustainable cooling with cross-sectoral collaboration and inter-ministerial coordination is essential to address these challenges.
Global Partnerships and the Role of COP29
- The Quad’s initiatives and the U.S.-India partnership focus on deploying affordable, high-efficiency cooling solutions, with equitable access being critical for regions most in need.
- COP28 (Dubai) saw 63 countries pledge a 68% reduction in cooling emissions by 2050 under the Global Cooling Pledge, aiming to provide cooling access to 3.5 billion people and save $17 trillion in energy costs.
- COP29 must build on this by increasing global commitments, expanding partnerships, and scaling up sustainable cooling technology access.
India as a Global Leader in Cooling Solutions
- India’s proactive approach through ICAP positions it as a leader in climate-friendly cooling solutions, ensuring thermal comfort and supporting climate goals.
- By addressing its cooling needs, India can protect its population from rising temperatures while leading international efforts to combat climate change through sustainable cooling.
| PYQ: Discuss global warming and mention its effects on the global climate. Explain the control measures to bring down the level of greenhouse gases which cause global warming, in the light of the Kyoto Protocol, 1997. (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2022) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of sustainable cooling solutions in the context of climate change. Analyse India’s role in global cooling initiatives such as the Wilmington Declaration and the India Cooling Action Plan (ICAP). (250 Words /15 marks) |





