Yojana Summary May 2023 : Innovation In Space Tech
Innovation in space tech:
In India, Space exploration is the driving force for technological Innovation, as it has opened unprecedented opportunities for Research and Development(R&D). The pace of Innovation in space technology is rapid and transformative.
The Space Infrastructure in India has witnessed many technological innovations and actively pursuing the maiden human spaceflight mission– Gaganyaan, to send astronauts to space and safely return to the Earth.
On 21st November 1963, the first rocket took off from Thumba, a fishing hamlet near Thiruvananthapuram. However, the rocket payload, radar and computers required to launch the sounding rocket came from outside the country. This challenge was taken up by Indian scientists like Vikram Sarabhai and Satish Dhavan, which led to the development of India’s space program.
Development of India’s Space transportation system:
- Development of 1st gen vehicle: In the 1970s, the beginning of space transportation system with the development of solid propulsion-based sounding rockets capable of 30kg of payload at 120km altitude. Subsequently, they developed 1st generation vehicles, i.e., SLV, and ASLV, with induction of liquid propulsion technology.
- Development of 2nd gen vehicle: The integration of solid and liquid propulsion and development of various technologies in areas like aerodynamics, manufacturing, composites, mission simulation, and payload integration supported in the development of 2ndgeneration launch vehicles, i.e., PSLV with the capability of placing 1700kg payload in polar orbit.
- Development of 3rd gen vehicle: Indigenous development of a cryogenic propulsive engine is the major technology of leap in the development of 3rd generation rocket, i.e., GSLV with the capability of 2000kg payload in GTO (Geo-Synchronous transfer orbit).
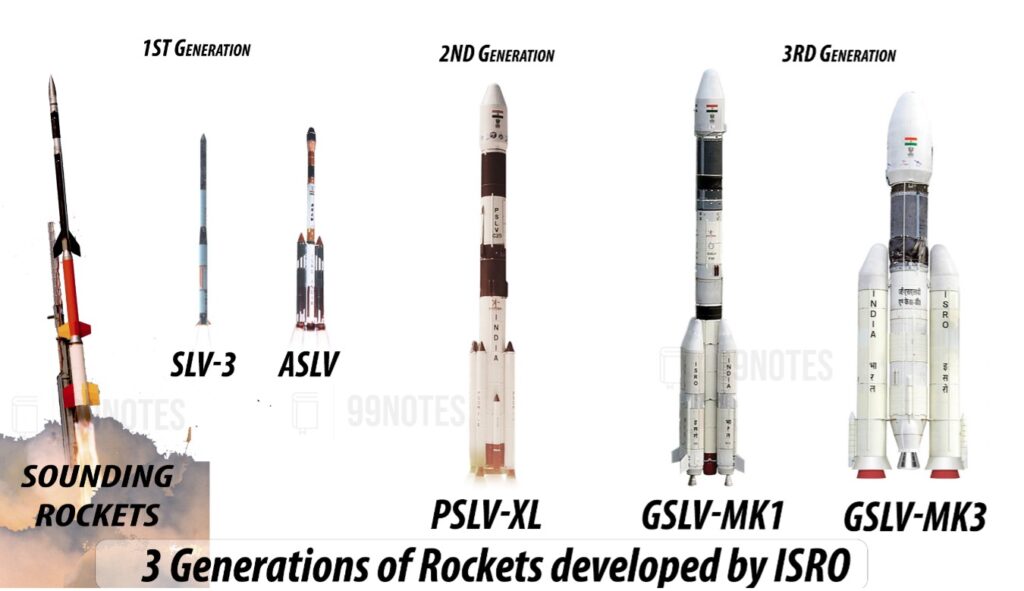
- There are few high throughput communication satellites that necessitated the development of advanced launching vehicles, i.e., LVM3 powered by the world’s 3rd largest solid boosters, high capacity liquid and cryogenic engines with the capability of putting 4000kg payload in GTO.
- The new family member of ISRO is SSLV, a three-stage launch vehicle with solid stages and a liquid propulsion-based trimming module made SSLV is capable of launching a 500kg satellite into a 500km planar orbit in a quick turn-around time.
Space infrastructure:
- India’s first satellite was ‘Aryabhata’ (Aryabhatta Spacecraft), named after famous astronomer ‘Aryabhata’, and was launched on 19th April 1970.
- Subsequently, experimental missions like BHASKARA and Apple were executed towards remote sensing, meteorology and communications technologies.
- Remote sensing has grown from a coarse resolution of 1km to a fine resolution of 28cm day & night all-weather capability. The communication transponders also grew from a mere single unit to 317 numbers.
- The ISRO has mastered the capability of making a satellite of 2000kg in 1kw to 6000kg with 14kw power.
- The present space infrastructure includes 25 Earth Observation, 22 Communication, 7 Navigation, 2 Space Science & Experimental Small and student satellites.
Space science and inter-planetary missions & applications:
- By the opening era of planetary explorations, ISRO gained confidence and technical expertise from satellites and launch vehicle technologies. As a result, they have successfully sailed to the moon and Mars in their very first respective attempts.
- Chanrayaan-1 was the first lunar orbiter mission that brought new changes in hosting international payloads, calibration, data interpretation etc., and successfully finding water on the moon.
- The Chandrayaan-2 mission was highly complex compared to its predecessor, consisting of an orbiter, Lunar Rover and lander craft.
- The first ever interplanetary mission to the red planet, called MOM (Mars orbiter mission), aka Mangalyaan by ISRO, made India the first Asian nation to reach Martian orbit.
- The spacecraft was monitored from ISTRAC, ISRO-Bengaluru, with support from the IDSN (Indian deep space network) antennae in Karnataka.
- The multi-wavelength space astronomy mission, ‘Astrosat’ (multi-wavelength observations in a single satellite), has served astronomers from nearly 50 countries.
- The EO (Earth observation) application is institutionalised across many user ministries/departments towards national security, Agro-forestry, disaster management, LULC, and decision-making support for major flagship support programmes of the government.
- Revolution in imaging technologies like Pushbroom, 3-tier imaging, SAR, GPR, TDI&VHR imaging etc., the domain of EO served to accomplish 47 missions with capabilities of spatial resolution from 1km to 28cm, temporal resolution of 24 days to 2.5 days, the spectral resolution of 7bits to 14bits.
Human space exploration:
- ISRO is actively pursuing the maiden human spaceflight mission, several R&D programmes related to space robotics- Vyommitra (Human-robot), lander and rover for Chandrayaan-3 mission space-based robotic manipulator 3d printing in space
- The affirmation of re-entry flight of crew module, i.e., CARE mission, pod abort test for crew escape systems, and testing of human-rated LV propulsive stages, i.e., solid boosters, liquid and cryo engines, has been successfully accomplished.
- A new test vehicle (TV) has been developed to test critical crew-associated systems and also conducted a major development of test IMAT of the crew module declaration system to simulate different failure conditions of the parachute system.
Startups Revolutionising India’s growth story:
Entrepreneurship is the main pillar of ‘Atmanibhar Bharat’ in India and is heading towards building a brighter future. In the last few years, India has become a hub for startups due to phenomenal disruptions in Innovation, technological advancements, and supportive government policies.
- On the 75th year of independence, Prime Minister Narendra Modi laid the goal of Amritkaal, i.e., the next 25 years ascend to new heights of prosperity for India and Indians.
- In 2016 the government launched the Startup India initiative to promote, transform, and nurture the ecosystem and empower startups along with budding entrepreneurs.
- The DPIIT (the Department of Promotion of Industry and internal trade) is the nodal Department for the startup ecosystem. In the past few years, Indian startups have raised an exceptionally good amount of funding. $25 billion have been raised in 2022 alone.
- Indian unicorn is flourishing in the fast-paced, dynamic ecosystem while developing innovative solutions and generating large-scale employment.
- In the past 4years, this number has increased exponentially, with a whopping 66% year-on-year growth in additional growth. Now India is home to over 108 unicorns and stands as the 2nd largest unicorn nation in the world.
- Startup India has introduced various schemes to simplify and facilitate the process of raising funds at both early and mature stages.
- A few government schemes support early-stage funding from angel investors and venture capital firms. One such scheme includes the Startup India seed fund scheme (SIFSS), which has an outlay of 945 crores It provides assistance for proof of concept, prototype development, product trials, market entry and commercialisation. By 2024(4 years), it is expected to support 3600 entrepreneurs through 300 incubators.
- The Fund of Funds scheme, launched in 2016, is committed to assisting startups financially. It supports the SEBI-registered AIFs, which in turn support individual startups. It has a corpus of 10,000 crores rupees dedicated to supporting and handholding startups at a mature stage.
- The credit guarantee scheme mainly aims at startups by providing credit guarantees to loans extended by the MIs to finance eligible borrowers, namely DPIIT– Recognised startups.
- This is just the beginning of the golden era of India as we have just entered
The potential of India’s Edtech sector:
The rapid adoption of EdTech (Education technology) can be attributed to the fast-paced digitalisation of India, the expansion of ICT infrastructure, and the accessibility of gadgets and data over the last 2 decades. India’s Edtech sector is one of the largest online Education in the world, with 400 startups operating across its various sub-sectors, and these are cumulatively raised more than $ 10 billion over the last decade.
What is EdTech?
- Edtech is the usage of technology-software and hardware to enhance teaching and learning, smartphones loaded with EdTech apps have now become synonymous with Education.
- EdTech enables everyone to get a consistent quality of Education, no matter their age or learning abilities.
- The needs of each student are different as per the pace and style with which they learn, availability and access to a robust ICT (information and communication technology) ecosystem.
India’s ICT Revolution:
- In FY 2022, the Indian ICT industry crossed $200 billion in total revenue, 5 million in total workforce and is predicted to spend $ 144 billion on ICT by the end of 2023.
- EDTech is an important sector in the industry’s transition from enterprise servicing to enterprise solution provision, and the service segment is expected to make up about 52% of this spending.
- The number of internet users between 2010-2022 increased by 10x from 92.5 million to 2 million and is expected to rise to 1.53 billion by 2040.
- The number of smartphone users between 2010-2022 increased by 27x from 34 million to 931 million and is expected to rise to 53 billion by 2040.
How does EdTech help Students:
Technology made Education affordable for all kinds of students and learners. Moreover, EdTech has enabled accessibility by reaching the remotest parts of India. There are 3 major benefits of Edtech for students include:
- Learning while playing: Gamified techniques used in EdTech, especially K-6, make concepts easier for students to understand and make learning fun.
- Classes anywhere and anytime: EdTEch reaches the remotest parts of Students can access these classes anytime and anywhere; working professionals can devote their free time to learning new skills.
- Access to quality teachers: According to ASER 2019, 30% of schools in India are privately managed. EdTech facilitates access to quality teachers in every town and village in India at the push of a few buttons in the mobile app.
Online and Offline Education:
- The cost of setting up classes in the traditional offline classroom cost structure includes rentals, utilities, and maintenance of the property as well as the cost of the teacher’s time. The students and their parents bear the brunt of all these costs.
- EdTech theoretically takes away all of that. In addition, lower infrastructure costs and larger student base help leverage economies of scale. This ultimately leads to lower costs for the end user.
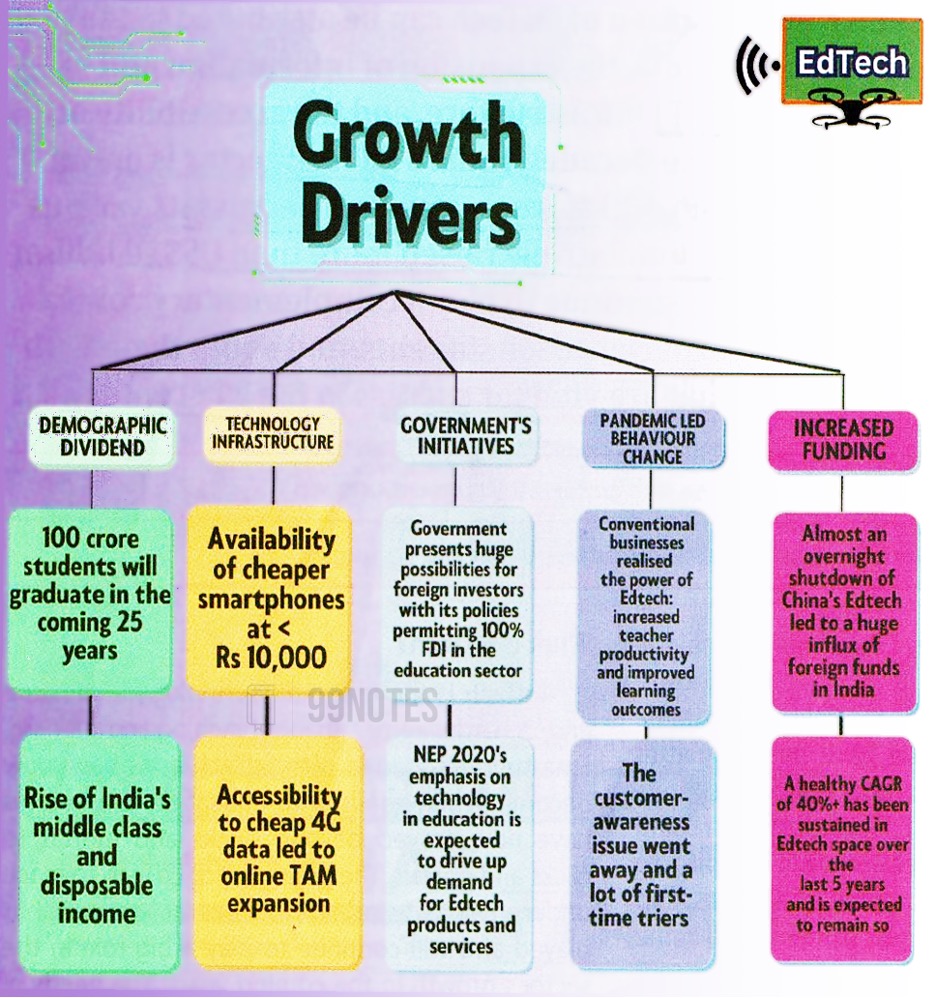
Key growth drivers:
- The growth of EdTech in India has been driven by the 5 key factors that are essential for its expansion and success. These include 1. Demographic dividend 2. Technology infrastructure 3. Government initiatives 4. Pandemic-led behavioural changes 5.Increased funding.
- The strength was about 300 million kids in k-12, out of whom 85-90 million have internet access. In addition, 40 million students are part of the Indian higher education system, as envisaged in the NEP 2020, when the GER will increase to 50% by 2035. This number will double to 80 million.
- There are a few government-launched programmes and initiatives to promote digital Education, such as SWAYAM, DIKSHA, e-pathshala, national broadband mission, and BharatNet have made EdTech easier to reach remote areas.
- The latest announcement by the finance minister in the Union Budget 2022 is of the national digital university (NDU). It offers regular degrees and mid-career certificate courses that will be recognised by employers and other universities too.
Challenges:
- EdTech conveys high potential, massive opportunities, and the ability to transform Education at various levels. However, it also presents several challenges that need to be considered as we Embrace EdTech products, platforms and services. Mainly three major challenges include:
- Psychological and social effects of online digital Education: online digital Education can have psychological and social effects on students. Lack of face-to-face interaction and socialisation opportunities can affect their mental health and social skills.
- Perception of parents: parents may have reservations about the effectiveness of EdTech and may prefer traditional classroom-based Education for their wards.
- Pupil-teacher ratio: Maintaining a low pupil-teacher ratio in online education programs is important to ensure that students receive personalised attention, support and mentorship from teachers.
Critical success factors:
During the pandemic, the importance of using digital tools such as networks, platforms, and apps for Education is accentuated, and students are gradually returning to face-to-face learning. As long as digital aids are deemed useful by students, the supply of EdTech will continue to create its own demand. To ensure the holistic impact of EdTech, it is very important to balance technology and traditional education methods. There are 3 critical success factors that can enhance this impact of EdTech include:
- Integrate practical work: EdTech programmes must integrate internships/apprenticeships as a part of the curriculum design.
- Create Multilingual content: According to the latest census, only 10% of the Indian population speaks English, and 45% speaks Hindi. It means nearly 45% of the population is not conversant with Hindi/English. Therefore, they need to focus on content creation in regional languages to ensure wider reach, usage, and relevance.
- Focus on holistic Education: providing holistic Education is one of the key objectives of NEP 2020. The core elements include Environmental responsibility, sustainable development at the planet level, self-reliance and patriotism at the national level, and community well-being at the societal level, which is integrated into the curriculum and overall design of the programmes.
Leveraging Technology for Transforming Healthcare:
Context:
Digital health captures a wide spectrum of technology–supported and operated health innovations and solutions. Mainly aims to provide healthcare services and interventions in an increasingly technologically sophisticated world. Advancements in digital applications have led to greater use of technology in providing healthcare services. The IoMT has combined the medical services and applications connecting to health IT systems that use diverse networking technologies.
What is digital health?
- The telemedicine practice guidelines issued by the union ministry of Health in March 2020 defined telemedicine as the delivery of health care services, where distance acts as a critical factor.
- The recent addition to the repository of health-related terminology is ‘digital health’. Various terms are being used, such as e-health, tele-health, tele-medicine, tele-consultations, health apps etc.
- It also defines the delivery and facilitation of health and health-related services, including medical care provider and patient, Education of health information services, and self-care via telecommunications and digital communication technologies, Mhealth (mobile health).
- The digital health application includes training, Education, skill development, and enhancement of the capacities of healthcare providers.
- The IoMT (internet of medical things) combined and loT (Internet of Things) uses range from telemedicine technology to improve communication between doctors and patients to decreasing the potential for exposure to contagious diseases.
Growth of digital health interventions:
- As per the precedence report, in May 2022, the global market size of digital health was estimated at USD 332.53 billion and expected to peak around USD 1,694.21 billion by 2032 showing a CAGR of 19.4%.
- One of the major advantages of telemedicine is that it can save time and effort, especially for rural patients, who need not travel long distances to obtain consultation and treatment.
- The Broad multidisciplinary framework of digital health is defined as the cultural transformation of how disruptive technologies that provide digital health and objective data accessible to both caregivers and patients.
- The quality of healthcare is provided to meet the goals of Antyodaya is to deliver quality services up to the last mile.
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi, in his 98th edition of ‘Mannkibaat’, addressed in Feb 2022 and launched the ‘eSanjeevani app’ for its extensive medical services via
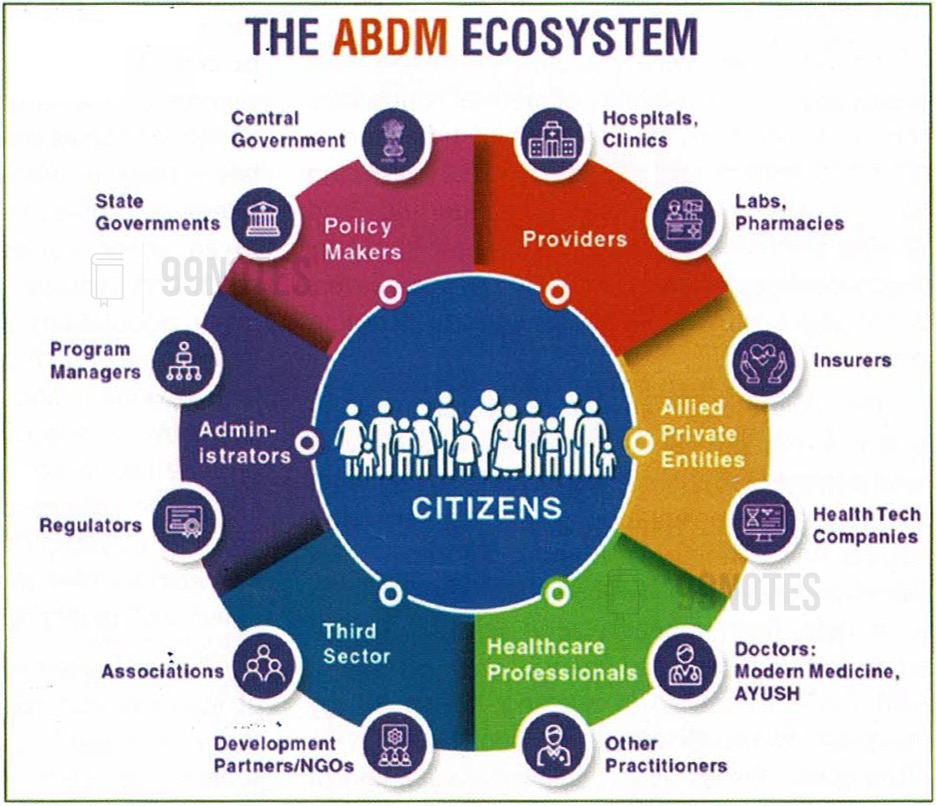
Ayushman Bharat digital mission (ABDM):
- ABDM is an integrated digital health infrastructure for the country, and Prime Minister launched this mission in September 2021. It aims to develop the backbone that is necessary to support it.
- It eventually connects the digital health solutions of hospitals across the country, simplifying the process of hospitals and increasing ease of living.
- An important part of ABDM is ABHA (Ayushman Bharat health account) contains a 14-digit number to uniquely identify a beneficiary as a participant in India’s digital healthcare Ecosystem.
- So far, over 18 crore ABHA IDs have been created, and 23.56 crore health records have been digitally linked under the ABDM.
- The services have been adopted by 365 hospitals within 5 months and helped over 5lakh patients save time. Currently, services live in 125 districts across 25 states/UTs in the country.
CoWIN:
- The CoWIN(covid Vaccine intelligence network) system was launched on 16th January 2021, provided the technological backbone to India’s Covid-19 vaccination programme and administered more than 220 crore doses.
- The platform provided up to six members to be registered under one mobile-number-linked account.
- The key feature of the CoWIN platform
- Blendered registration: Beneficiaries can register online or on-site at the vaccination centre
- Beneficiary book online at their convenience of time and choice of location
- Track vaccination schedule
- Instant digital vaccination certificate with certificate correction utility.
- Multilingual portal with 12 languages.
- Mobile application for their ease of use for vaccinators.
- Vaccine stock management
- Publishing of vaccine schedules in advance
- Real-time dashboards
- Tracking of AEFI
- Digital covid-19 vaccination certificate tracking and
- Facility wise coverage
- As of Feb 2023, more than 10croretele consultations have benefitted patients through medical and super specialists trained in telemedicine.
- Tele-MANAS (tele mental health assistance and networking across states) was launched on 10th October 2022. It aims to provide free telemental health services, including counselling and integrated medical and psychosocial interventions through video consultations.
NIKSHAY 2.0 portal(or ni-kshay):
- The president of India launched the Pradhan mantra TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan in September 2022.
- NIKSHAY 2.0 is a digital platform for community support for persons diagnosed with TB. The main purpose of this portal is to provide technological backup for the NIKSHAY scheme.
- As of 3rd March 2023, around 13.25 lakh TB patients were on treatment in the NI-kshay portal, and more than 69000 NI-kshay mitras were registered in this portal.
Conclusion:
- It has been widely acknowledged that digital health has the potential to bring about rapid, radical, and vast changes in not only healthcare services but also research and development in Pharma, medical devices, drugs and vaccination cold chain management, supply chain etc. digital health farms is one of the key priorities of the G20 India health track.
Transforming technology:
Context:
Quantum computing differs from traditional computing, which uses ‘bits’–binary digits of 0s and 1s to represent the information. In 2012, Serge Haroche and David Wineland were awarded the Nobel Prize in physics for their groundbreaking experimental methods enabling individual quantum systems’ measures and manipulation. This may transform the entire technology ecosystem. Long-term schemes of the Department of Science and Technology could possibly introduce strategic infrastructure and manpower training projects.
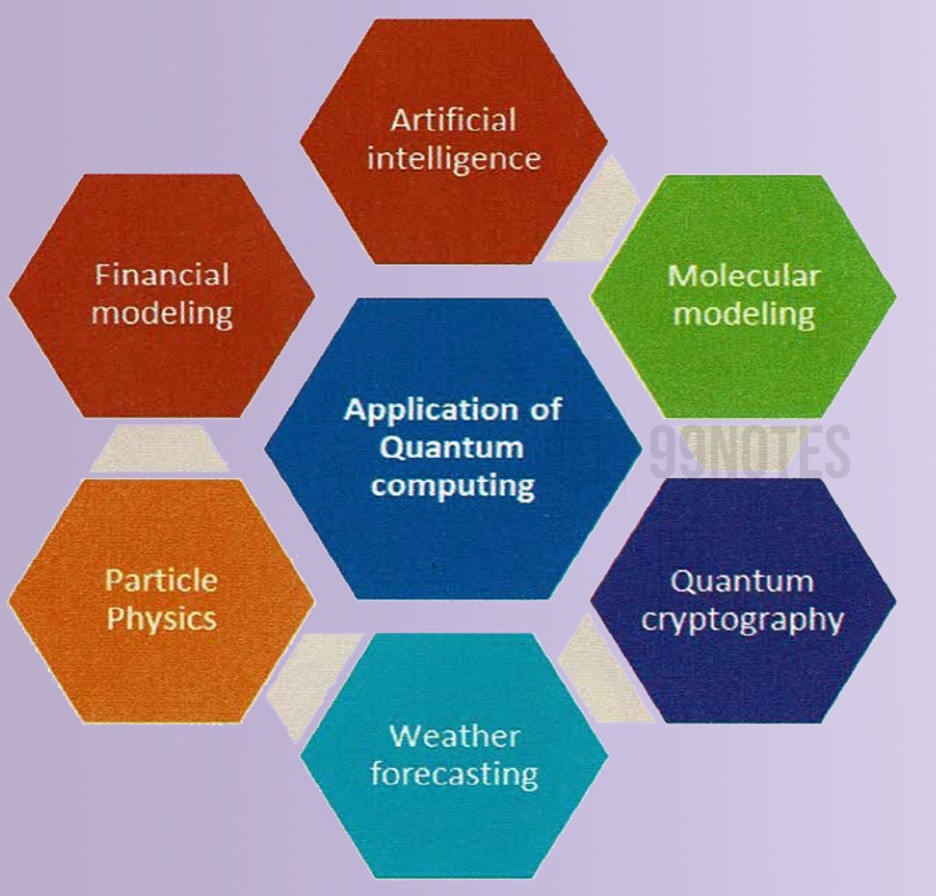
Impact of quantum computing:
Here are a few areas where the impact of quantum computing is likely to be felt:
- Faster data analysis in industrial data science –quantum computers can perform certain types of calculations significantly faster than classical computing logic.
- Improved machine learning outcome –machine learning algorithms are increasingly being used for predictive capabilities and enhanced data-driven decision-making.
- Improved optimisation for complex problems –quantum computers can potentially solve these problems much faster than classical computers, enabling more efficient optimisation of complex problems.
- Improved industrialisation – Realisation of industrial maturity levels such as industry 4.0 and beyond through platforms like digital twins would be enabled through quantum computing.
- Improved process efficiencies in digital transformation –it may result in faster process automation by analysing real-time data generated in the organisation process.
Implications for practice and policy:
- Quantum computing is an advanced area where research and development are still at a nascent stage.
- It needs to cover both hardware and software to further develop a homegrown quantum technology industry.
- The quantum computer also needs clear and sustained policy and governance since it deals with new levels of data and computation.
- Skill areas of data science, decision and machine learning are going to be intensely impacted in the near future by quantum computing.
- The realisation of digital healthcare and biomedical research would be strongly facilitated using quantum computing.
- Startups can generate huge opportunities that disperse the burden of economic welfare and employment from metro cities.
Conclusion:
- Quantum computing is an area that government must focus on because it will be heavily dependent on exploiting information assets within and outside organisations in the long term.
- This may enable the improved capability for leveraging and exploiting this domain for the benefit of citizens and the nation going forward.
AI chatbots’ future and challenges:
The recent emergence of chatbots is a clear indication of the incredible transformation that artificial intelligence is currently undergoing and creating. The new-age chatbot utilises AI and NLP (natural language processing) to simulate human-like conversations and automate responses to customer queries. You may remember that tiny window that suddenly appears at the bottom of the right of the webpage and inquires like, ‘May I help you?’ it’s a chatbot. This is not only limited to understanding the text only, but to another popular mode of interaction, Audio input with AI too.
Future of work:
- The way we work and create content is being revolutionised by chatbots. Recently a tech giant has announced the integration of a powerful generative AI technology into its various applications.
- New Capabilities have been introduced to search applications, including those handling queries in natural Language. The chatbot can automate a range of tasks across multiple apps.
- The race for AI chatbots is not limited to big tech companies, as hundreds of AI chatbots have been launched by companies of all sizes in the recent past.
- Ai chatbots can transform the healthcare sector by offering numerous services to both healthcare providers and patients.
- Customer service chatbots can be integrated into various digital channels like websites, social media platforms and messaging applications to help people with their Enquires and provide support.
- The banking sector uses AI chatbots as a way of reducing costs and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Challenges:
- The biggest concern about chatbots is that their increasing use can result in a considerable number of people losing their jobs since AI is gaining to match human output and intelligence.
- We have two schools of thought with differing views.
- One of them thinks that once the hype around it subsides, AI will be seen as the result of a natural process of development and Innovation.
- The second school of thought feels that the power and capabilities that AI can acquire over time are beyond what we visualise, especially considering the speed with which things are happening.
- There are other challenges, including their lack of emotional intelligence, improper responses due to misunderstandings, lack of empathy and their compromises on privacy.
- If we do not put a break on the uncontrolled development of AI, later, it can become a challenge for its creator itself.
5G-cyber security challenges:
The 5G is the latest global standard wireless communication with ultra-fast speed, launched in October 2022 and holds the promise of revolutionary changes in the way we communicate and consume content on the internet. The higher speed will potentially ensure lower latency rates and more reliability in mobile data communications. As per a recent survey, the 5G will enable $13.2 trillion of global economic output and support $ 22.3 million jobs.
Geopolitics of 5G:
- The majority of world telecom leaders may have taken the lead in developing 5G technology; the real thrust has come from the Chinese telecom companies.
- Chinese companies like Huawei and ZTE have been aggressively penetrating into new markets by commercialising the technology and offering it at cheaper rates than their competitors.
- The 5G will play a potential role in national development and economic growth. It can be undoubtedly regarded as a critical infrastructure.
- The 5G communication network will represent a valuable target for cyberattacks, including sabotage. Recently in November 2022, the US banned sales and imports of new communication networks.
5G and cyber threat landscape:
- The former UK Prime Minister Boris Johnson floated the idea of D-10, it’s a coalition of 10 democracies, to create an alternative supply for 5G and other emerging technologies.
- The quadrilateral security dialogue (Quad) members (India, Japan, Australia, and the US), too, have pledged interoperability and are working on 5G supplier diversification.
- Recent issues of cyber threat, in August 2020, a report from the Australian government and New Guinea’s national cyber security centre noted that the latter’s national data centre, built by a Chinese telecom company, had multiple cyber security issues which exposed confidential government data.
- The context of privacy risks like the Conversion of 4G to 5G networks require several similar antennas and base stations. This can allow location tracking of mobile phones or internet users inside and outside, compromising their privacy.
Conclusion:
- Organisations connecting to the 5G network must be aware of the evolving threat landscape and adopt security protocols accordingly. They must determine their threat posture and secure their infrastructure.
- Cyber hygiene – The understanding of safe practices in cyberspace – can help them to better tackle the threats and protect themselves.



