Yojana Summary: September, 2024 – Union Budget 2024-25
1. Public Finance And Development – Evaluation Of India’s Budgetary Priorities
Introduction
- The Indian Union Budget for 2024-25 presents a comprehensive roadmap for economic growth, inclusivity, and sustainability.
- With a primary focus on transforming agriculture, creating jobs, promoting self-sufficiency, enhancing human resources, and ensuring energy security, the budget sets ambitious goals for the coming years.
- This article breaks down the budget’s key areas, analysing the government’s initiatives to drive growth across various sectors.

Focus on Sustainable Agriculture
Promoting Eco-Friendly Farming Practices
- The budget sets a target of transitioning one crore farmers to natural farming over the next two years.
- 10,000 bio-input resource centres will be established to support this shift, promoting organic alternatives to chemical fertilisers.
- The government also aims to certify and brand natural farming products, enhancing market visibility for eco-friendly produce.
Towards Self-Sufficiency in Pulses and Oilseeds
- India currently relies on imports to meet domestic demand for pulses and oilseeds.
- The budget focuses on strengthening domestic production, storage, and marketing infrastructure to reduce this dependency.
- Self-sufficiency in these critical food commodities is expected to enhance India’s food security and reduce its import bills.
Improving Agricultural Productivity
- A Rs 1.52 lakh crore allocation for agriculture and allied sectors has been announced to boost productivity.
- Initiatives include developing climate-resilient crops, enhancing agricultural research, and promoting digital public infrastructure for farmers.
- The government plans to address inefficiencies in vegetable supply chains through the creation of large-scale clusters near consumption hubs.
Addressing Employment and Skilling Gaps
Boosting Employment Opportunities
- The Prime Minister’s Package for Employment and Skilling receives a Rs 2 lakh crore outlay, targeting 4.1 crore youth through five key schemes.
- The Employment Linked Incentive Schemes offer financial incentives to employers for creating jobs, particularly in manufacturing.
- Upgrading 1,000 ITIs (Industrial Training Institutes) and launching internship programs at top firms aim to enhance the employability of India’s workforce.
Skill Development Initiatives
- A Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) with an allocation of Rs 60,000 crore aims to provide skills training to 20 lakh youth.
- This scheme will ensure that ITIs remain aligned with industry demands, offering courses for emerging skills in high-demand sectors.
Additional Employment Measures
- Provisions for working women hostels and creches are included to support women in the workforce.
- The government introduces skilling loans and education loans, making it easier for youth to access training and job opportunities.

Investing in Human Resources and Social Justice
Prioritising Education and Healthcare
- The government has allocated Rs 1.2 lakh crore to education and Rs 3.8 lakh crore to healthcare, focusing on expanding access and improving quality.
- Education and healthcare systems are key to developing a healthy, skilled workforce, ready to meet the demands of a growing economy.
Empowering Marginalised Communities
- The budget places a strong emphasis on social justice, ensuring that vulnerable sections of society are covered under key welfare programs.
- An allocation of Rs 3 lakh crore is dedicated to schemes benefiting women, including education, healthcare, and skill development.
Affordable Housing for All
- Under the PM Awas Yojana, three crore houses will be constructed, providing affordable housing to millions of families.
- This initiative not only addresses the housing deficit but also stimulates the real estate and construction sectors, creating jobs and economic opportunities.
Strengthening Manufacturing and Service Sectors
Revitalising the MSME Sector
- The Credit Guarantee Scheme for MSMEs facilitates loans for machinery and equipment purchases, crucial for business expansion.
- The government lowers the turnover threshold for onboarding MSMEs onto the TReDS platform, increasing access to working capital.
Supporting Startups
- The budget’s abolition of the Angel Tax aims to stimulate investments in startups, fostering innovation and job creation in emerging industries.
Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme
- The PLI scheme continues to incentivize domestic manufacturing, helping industries achieve economies of scale and enhancing global competitiveness.
Urban Development and Energy Security
Transforming Urban Spaces
- The government aims to facilitate the creative redevelopment of cities, creating jobs and stimulating investment in urban regions.
- Transit-Oriented Development in 14 large cities is planned to promote sustainable urban growth, improve public transport, and create mixed-use corridors.
Affordable Urban Housing
- A Rs 10 lakh crore investment is allocated for building one crore houses for the urban poor, addressing affordable housing challenges in cities.
- Interest subsidies for affordable housing loans will help middle-class families secure homes in urban areas.
Securing Energy Future
- The budget prioritises a balanced approach to energy transition, aiming for renewable energy projects worth Rs 1.5 lakh crore.
- The government will promote nuclear energy research, partnering with the private sector to develop small and modular reactors.
Driving Infrastructure and Reforms
Investing in Capital Infrastructure
- The central government’s Rs 11.11 lakh crore capital expenditure push will stimulate infrastructure growth, encouraging states to follow suit.
- Private sector participation will be encouraged through policies such as viability gap funding and market-based financing frameworks.
Next Generation Economic Reforms
- A policy framework for next-generation reforms will focus on improving productivity and creating more efficient markets.
- State governments will be involved in the implementation of these reforms, ensuring seamless execution and uniform development.
Conclusion
- The Indian Union Budget 2024-25 outlines a forward-looking vision, with a balanced focus on agriculture, employment, human resources, urban development, and energy security.
- By addressing core issues like self-sufficiency in food, promoting eco-friendly farming, and enhancing skilling, the budget takes a holistic approach to growth.
- Infrastructural investments, urban renewal, and next-gen reforms are expected to drive sustained economic growth, while strong social welfare measures ensure inclusivity across all sections of society.
2. Inclusive Human Resource Development And Social Justice
Introduction
- The Indian Union Budget for 2024-25 is designed to promote inclusive growth, social justice, and economic development.
- It focuses on human resource development, employment generation, skilling, and support for various sectors.
- The budget emphasises modernization, reforms, and welfare programs aimed at creating an equitable and sustainable future for all citizens.
Focus on Human Capital Development
- The budget places a high priority on investing in education, skilling, and employment opportunities.
- Allocation for Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs):
- Rs 60,000 crore is earmarked for upgrading 1,000 ITIs, aiming to skill 20 lakh youth.
- This initiative aims to bridge the skill gap by aligning training with industry needs.
- Skilling Programs:
- A revised Model Skill Loan Scheme has been introduced to provide affordable loans for vocational training.
- Focus on modernization of ITIs to enhance employability and relevance in the modern job market.

Boosting Employment and Labor Reforms
- Employment-linked incentives form a key part of the budget’s job creation strategy.
- Employment Incentive Schemes:
- Scheme A: Provides a one-month wage subsidy to first-time employees to encourage their integration into the formal economy.
- Scheme B: Incentivizes employers in the manufacturing sector to hire new employees, boosting job creation.
- Scheme C: Offers EPFO contribution reimbursements to employers hiring new staff, reducing their financial burden and encouraging workforce expansion.
- Labor Reform Initiatives:
- Integration of the Eshram portal with other employment services to streamline job-seeking processes.
- Revamping of Shram Suvidha and Shram Shakti portals to improve user accessibility.
- Introduction of a comprehensive employment portal connecting job seekers with employers to improve employment outcomes.
Investments in Social Equity and Welfare
- The budget is rooted in ensuring social equity, with a strong emphasis on welfare schemes for marginalised sections.
- Women’s Empowerment Initiatives:
- Significant funding has been allocated for schemes promoting women’s participation in the workforce.
- Programs are designed to foster economic independence and upliftment of women across sectors.
- Tribal Welfare:
- The Pradhan Mantri Janjaya Unnat Gram Abhiyan is aimed at improving the socio-economic conditions of tribal communities.
- This initiative focuses on providing targeted support to bridge inequalities and ensure access to development opportunities.
Inclusive Development and Social Security
- A concerted effort has been made to ensure comprehensive social security through various government schemes.
- Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana:
- Aimed at ensuring food security for 80 crore citizens, particularly the underprivileged, through subsidised grain distribution.
- Expanded Coverage:
- The budget seeks to eliminate exclusion errors by covering all eligible beneficiaries under welfare programs.
- This ensures that the benefits of economic growth reach every corner of society, promoting inclusivity.
Economic Revitalization and Infrastructure
- Infrastructure development forms a critical part of the budget’s strategy for economic revival.
- Manufacturing and Investment Boost:
- Special focus on creating a favourable environment for investments in the manufacturing sector to stimulate job creation.
- The budget’s labour reforms aim to reduce compliance burdens and ease the process of doing business.
- Urban and Rural Infrastructure:
- Targeted investments in both urban development and rural infrastructure aim to improve connectivity, access to services, and quality of life.
Conclusion
- The Indian Union Budget 2024-25 prioritises inclusive growth, social justice, and employment generation, with a clear focus on skilling and workforce development.
- By integrating labour reforms, boosting employment-linked incentives, and ensuring social security for marginalised groups, the budget reflects the government’s commitment to equitable and sustainable growth.
- Through targeted investments in human capital and infrastructure, the budget lays the foundation for a transformed and inclusive India where opportunities are accessible to all sections of society.
3. A New Chapter In India’s Employment Story
Introduction
- The Indian Union Budget for 2024-25 outlines a comprehensive strategy aimed at fostering employment, skilling, and promoting the growth of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs).
- Several innovative schemes and reforms are introduced to address labour market challenges, job creation, and ease of doing business, which are crucial to India’s long-term economic growth.
Major Employment and Skilling Initiatives
- Prime Minister’s Employment Package
- A significant Rs 2 lakh crore package is introduced to benefit 4.1 crore youth.
- The initiative is focused on addressing youth unemployment, enhancing skill development, and generating jobs across various sectors.
- First Timers Scheme for New Workers
- This scheme is designed to support first-time employees by offering a one-month wage subsidy.
- Encourages the entry of new workers into the formal employment sector, benefiting 210 lakh youth.
- Aims to provide a financial cushion for both employees and employers to help integrate fresh talent into the workforce.
- Job Creation Incentives in Manufacturing
- A new scheme is aimed specifically at boosting job creation in the manufacturing sector, particularly targeting first-time employees.
- The government will reimburse employers for a portion of their Employees’ Provident Fund Organization (EPFO) contributions for new hires, encouraging workforce expansion.
- This initiative is expected to benefit 30 lakh youth by incentivizing companies to hire new workers and grow their operations.
Supporting Employers and MSMEs
- Financial Assistance for Employers
- The budget addresses the challenges faced by employers, especially small and medium enterprises (SMEs), by offering financial support.
- This initiative is aimed at reducing the financial burden on employers, making it easier for them to hire new employees, increase production, and expand their businesses.
- Revamped Shram Suvidha Portal
- The Shram Suvidha portal is streamlined to enhance compliance and ease of doing business for employers.
- By simplifying employment-related services, the portal helps businesses navigate regulatory obligations, thereby reducing their administrative burdens.
- Labor Reforms for a Conducive Business Environment
- The budget focuses on improving the overall business environment through labour reforms that promote ease of doing business.
- By integrating the eShram portal with existing platforms, the government is creating a centralised hub for workers seeking employment, training, and career guidance.
Enhancing Job Matching and Skilling
- National Career Services (NCS 2.0)
- The introduction of National Career Services (NCS 2.0) aims to bridge the gap between job seekers and employers by leveraging data-driven tools.
- NCS 2.0 is designed to help job seekers by providing end-to-end services, including career guidance and job placement.
- This platform ensures that job seekers remain competitive in the evolving labour market by connecting them with relevant opportunities.
- Commitment to Skilling and Upgradation
- Recognizing the importance of a skilled workforce, the government has prioritised skilling and upskilling initiatives to meet industry demands.
- A centrally sponsored scheme for skilling aims to benefit 20 lakh youth, focusing on areas like manufacturing, which require skilled labour to boost productivity and global competitiveness.
Impact on SMEs and the Economy
- Schemes for Job Creation and SME Support
- Specific schemes introduced in the budget aim to stimulate job creation in key sectors like manufacturing and support SMEs in their expansion efforts.
- These initiatives are crucial for strengthening SMEs, which form the backbone of India’s economy by generating employment and contributing to GDP growth.
- Revamped Samadhan Portal for Business Compliance
- The Samadhan portal has been revamped to enhance the ease of compliance, thereby reducing the administrative burden on businesses.
- This step is essential for creating a more conducive environment for investment and innovation, ultimately resulting in job creation and economic development.
Conclusion
- These reforms are expected to have a lasting impact on job creation, ease of doing business, and India’s overall economic development.
- With a focus on inclusive growth, the budget underscores the importance of skill development, labour reforms, and business-friendly policies in ensuring a sustainable and dynamic economic future for India.
4. Salaried Class And Consumers: Key To Viksit Bharat
Introduction
- The Indian Union Budget 2024-25 lays out a strategic roadmap for achieving a $10 trillion GDP by 2033 and a “developed country” status by 2047.
- A strong focus has been placed on key drivers of growth, including salaried individuals, consumers, employment generation, and boosting consumption.
Boosting Disposable Income and Consumption
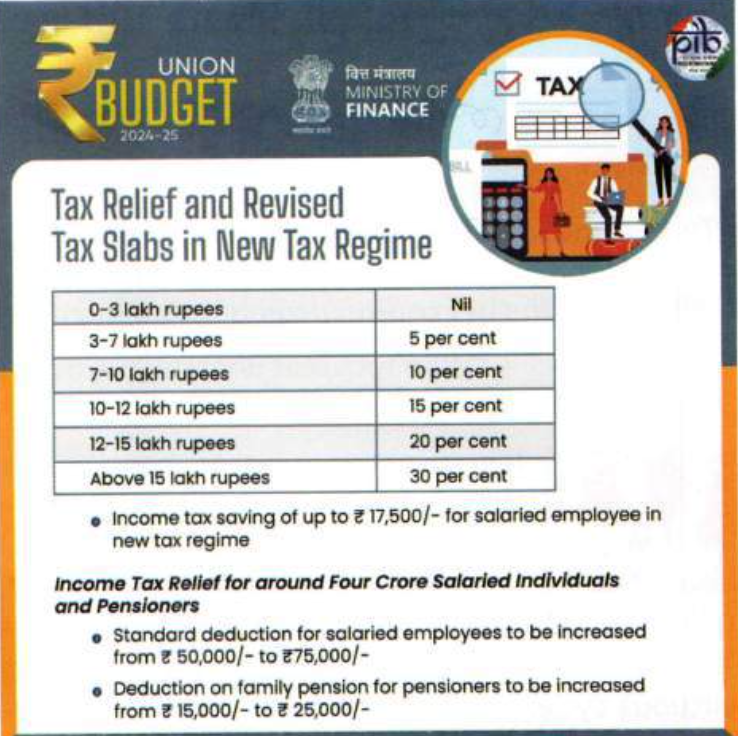
- Raising the Standard Deduction
- To increase disposable income for salaried individuals, the government has raised the standard deduction.
- This move is expected to provide financial relief to a significant portion of the working population, leading to increased spending capacity.
- Revised Tax Slabs
- Changes in tax slabs are introduced, ensuring that middle-income groups benefit from reduced taxes.
- These revisions aim to boost consumer spending by leaving more money in the hands of taxpayers, a critical step for driving domestic demand.
- Employment Linked Incentive (ELI) Scheme
- A new scheme, the Employment Linked Incentive (ELI), is introduced to promote job creation across industries.
- The ELI scheme links incentives to the number of jobs created by employers, encouraging businesses to hire more workers and contribute to overall employment growth.
Encouraging Job Creation in Manufacturing
- First Timers Scheme for New Employees
- A special scheme targeting first-time employees offers a one-month wage subsidy, encouraging new workers to join the formal sector.
- This initiative is expected to benefit 210 lakh youth, providing both financial support for employees and incentives for employers to expand their workforce.
- Incentivizing Job Creation in Manufacturing
- The budget introduces a direct benefit scheme for the manufacturing sector, offering reimbursement to employers for EPFO contributions for newly hired workers.
- With the government covering a portion of these costs, employers are incentivized to increase their workforce, creating additional jobs in this critical sector.
Consumer-Centric Measures for Economic Growth
- Reduction in Customs Duties
- The budget focuses on making imported goods more affordable by reducing customs duties on various items, benefiting consumers directly.
- This measure, combined with the planned Goods and Services Tax (GST) rate rationalisation, aims to lower prices, increase disposable income, and stimulate demand for goods and services.
- Supporting Consumer Confidence
- Measures such as increased disposable income through tax cuts and reduced prices through lower import duties are expected to boost consumer confidence.
- Higher confidence among consumers translates to increased spending, which in turn helps businesses grow, creating a positive feedback loop for economic expansion.
- Planning for GST Rate Rationalization
- The government has outlined plans to rationalise GST rates, ensuring that tax structures are streamlined and consumer-friendly.
- This move is designed to simplify taxation for consumers and businesses alike, fostering an environment that promotes consumption and economic growth.
Labor Reforms and Simplified Compliance
- Labour and Employment Reforms
- The budget highlights the integration of the eShram portal with other platforms to provide a comprehensive solution for workers seeking employment, skill development, and career guidance.
- This step is crucial for improving workforce participation and enhancing the ease of doing business by providing streamlined services to both employees and employers.
- Improved Business Environment
- With the introduction of revamped portals like Shram Suvidha, the government is focused on reducing the compliance burden on businesses.
- These improvements will help companies concentrate on growth and expansion, resulting in a more favourable environment for investment and innovation.
Conclusion
- By focusing on raising disposable incomes, creating employment opportunities, supporting SMEs, and promoting consumer spending, the budget sets the stage for sustained economic growth.
- Through these reforms, the government seeks to create a virtuous cycle of higher income, increased consumption, and enhanced business activity, all contributing to India’s overarching economic aspirations.
5. Productivity And Resilience In Agriculture
Introduction
- India’s agricultural sector is a cornerstone of its economy, engaging approximately 42.3% of the population and contributing 18.2% to the national GDP.
- The Indian government is committed to modernising agriculture to achieve its goal of becoming a developed nation by 2047.
- Significant budget allocations, like the Rs. 1.52 lakh crore for the Union Budget (2024-25), highlight the government’s prioritisation of agriculture and farmers’ welfare.
Role of Scientific Research
- Scientific research is pivotal for agricultural development, fostering innovation and addressing emerging challenges.
- India boasts one of the world’s largest agricultural research and education networks, aimed at enhancing productivity and resilience.
- Ongoing reviews of the agricultural research setup focus on climate-resilient varieties to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Emphasis on Digital Transformation
- Digital Empowerment of Farmers:
- The government is actively promoting digital technologies to improve efficiency and sustainability in agriculture.
- The establishment of Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for agriculture provides farmers access to vital information and services.
- Growth of Agri-Tech Startups:
- A robust digital ecosystem is emerging, supported by agri-tech startups, offering farmers tools to enhance productivity and market access.
Sustainable Farming Practices
- Natural Farming Initiatives:
- The government promotes natural farming that minimises chemical inputs and enhances soil health.
- This approach aims to reduce environmental pollution and improve agricultural system resilience.
- Organic Agriculture Promotion:
- Organic farming practices are being encouraged to foster sustainability and long-term productivity.
Value Chain and Community Development
- Investment in Value Chains:
- Government initiatives are aimed at improving infrastructure, storage, and market linkages for various agricultural products, reducing waste and increasing farmer income.
- Community Farming Initiatives:
- Support for community farms and producer organisations empowers small farmers through collective bargaining and access to markets.
Focus on Fisheries Sector
- The fisheries sector is prioritised for growth, with investments in aquaculture and processing facilities to enhance economic contributions.
- Promotion of sustainable practices in fisheries aims to improve food security and create employment opportunities.
Achievements in Agricultural Production
- Increased Output:
- Significant increases in production have been observed across commodities like vegetables, pulses, and oilseeds due to government initiatives and technological improvements.
- Record Foodgrain Production:
- Foodgrain production reached an all-time high in 2022-23, demonstrating the effectiveness of current agricultural strategies, despite a slight decline in 2023-24 due to adverse weather.
Challenges and Government Responses
- Addressing Self-Sufficiency:
- Despite progress, challenges remain in achieving self-sufficiency in pulses and oilseeds, prompting ongoing government measures to boost production.
- Infrastructure Development Needs:
- Investments in cold storage and processing facilities are essential to reduce post-harvest losses and improve market access.
- Resilience to Climate Change:
- Climate-smart agricultural practices and the development of drought-tolerant crop varieties are critical to enhancing the sector’s resilience against climate change.
Conclusion
- The Indian government’s multifaceted approach to transforming agriculture focuses on sustainability, resilience, and technological advancement.
- By investing in scientific research, digital empowerment, sustainable practices, and infrastructure development, India is well-positioned to meet its agricultural challenges.
- The commitment to fostering a prosperous agricultural sector not only supports the economy but also ensures food security and improved livelihoods for millions.
6. Innovation, Research And Development
Introduction
- The Indian Budget for 2024-25 marks a significant step forward in the country’s commitment to science, technology, health, and agriculture.
- The allocations reflect a holistic approach to fostering innovation, enhancing public welfare, and promoting sustainability.
- This article outlines the key allocations and initiatives in the budget, focusing on science and technology, health, and agriculture.
Enhanced Budgetary Allocation for Science, Technology, and Innovation (STI)
- Overall Increase: The budget for STI has been set at Rs. 79,641.55 crore, representing a 15.1% increase from the previous year.
- Ministry Allocations:
- The Department of Science and Technology received a 31% increase.
- The Department of Biotechnology saw a 42% increase.
- The Department of Scientific and Industrial Research received a 26% boost.
- Emerging Technologies Focus:
- Prioritisation of artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and biotechnology as crucial areas for economic growth.
- Acknowledgment of the societal challenges that these technologies can address.
Institutional Framework for Research
- Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF):
- The Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) aims to create a comprehensive research framework in India.
- Objective: Its primary goal is to efficiently coordinate human and material resources across various disciplines.
- Funding: The initiative has an allocation of one lakh crore rupees for private sector innovation, development, and research.
Innovation and Entrepreneurship Promotion
- Key Initiatives Launched:
- Critical Mineral Mission: Focused on enhancing the availability and sustainability of critical minerals for technological advancements.
- India AI Mission: Aimed at developing artificial intelligence capabilities within the country.
- PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana: Initiative to provide free electricity for solar energy in households.
Commitment to Clean Energy and Sustainability
- National Green Hydrogen Mission: Emphasises the transition to cleaner energy sources through hydrogen technology.
- Solar Energy Mission: Focuses on expanding solar energy capacity as a sustainable energy solution.
- The budget underscores the importance of sustainability in driving future economic growth.
Priorities in Health Sector
- Increased Health Budget: The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has received a significant funding increase to enhance healthcare services.
- Digital Health Focus:
- Establishment of the National Institute for Research in Digital Health and Data Science (NIRDHDS) with a notable increase in funding.
- Promotion of digital health initiatives to improve healthcare delivery and accessibility.
- Support for AYUSH Systems:
- Enhanced funding for Ayurveda, Yoga, Unani, Siddha, and Homeopathy (AYUSH) systems.
- Initiatives such as AYURGYAN and Ayurswasthay Yojana to promote traditional medicine.
Agricultural Advancements
- Increased Allocation for Agricultural Research:
- Significant funds allocated for agricultural research aimed at raising productivity and developing climate-resilient crops.
- Digital Infrastructure in Agriculture:
- Commitment to implementing Digital Public Infrastructure to streamline agricultural practices.
- Introduction of New Crop Varieties:
- Release of 109 new high-yielding and climate-resilient varieties of crops to enhance food security.
Conclusion
- The focus on innovation, sustainability, and the promotion of emerging technologies signals the government’s intent to position India as a leader in these crucial sectors.
- These initiatives are expected to drive economic growth, create employment opportunities, and address key societal challenges, significantly improving the quality of life for Indian citizens.
7. Energy Security
Introduction
- The Indian government is focusing on energy security to support the country’s rapidly growing economy.
- According to the Economic Survey 2023-24, India’s energy needs are expected to rise by 2 to 2.5 times by 2047.
- The government aims to diversify energy sources and enhance domestic production to meet increasing demand.
Current Energy Landscape
- Thermal Generation: As of June 2024, 54.5% of India’s power generation is derived from thermal sources (coal, gas, and diesel).
- Non-Fossil Fuels: The remaining 45.5% comes from non-fossil fuel sources, which include renewable energy and nuclear power.
- Nuclear power constitutes 1.8% of the total energy mix.

Challenges to Energy Security
- Heavy Dependence on Imports:
- India relies significantly on imports for petroleum products and critical minerals, creating vulnerabilities in energy security.
- Environmental Concerns:
- The current energy mix raises climate change issues, necessitating a transition to more sustainable energy sources.
Opportunities for Improvement
- Transition to Renewable Energy:
- The government actively promotes the use of renewable energy sources, particularly solar and wind power, to lessen reliance on fossil fuels and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Innovation in Coal Sector:
- Gasification technology offers a pathway to revolutionise coal utilisation, allowing for reduced dependence on imported natural gas while decreasing emissions.
Strategic Objectives of Energy Policy
- Ensuring Reliable Supply:
- Aims to provide a consistent and sustainable energy supply to cater to economic, social, and political demands.
- Diversification of Energy Sources:
- Focuses on creating a diversified energy mix to minimise risks associated with over-reliance on any single source.
- Commitment to Sustainability:
- Targets a transition toward cleaner energy to address environmental challenges and mitigate climate change impacts.
- Affordability for All:
- Strives to make energy accessible and affordable for every citizen, fostering social equity.
Initiatives to Achieve Energy Goals
- Investment in Renewable Projects:
- The government is increasing investments in solar, wind, and other renewable energy initiatives to bolster capacity and reduce emissions.
- Promoting Energy Efficiency:
- Encourages the adoption of energy-efficient technologies and practices to decrease overall consumption and enhance efficiency.
- Infrastructure Development:
- Expanding the energy grid and improving infrastructure to facilitate the integration of renewable sources into the energy mix.
- International Collaboration:
- Engaging in partnerships with other nations to enhance energy security and promote the adoption of clean energy technologies.
Conclusion: Towards a Sustainable Future
- By tackling the challenges and leveraging opportunities, India can secure its energy future while supporting sustainable development.
- A balanced approach to energy production and consumption will contribute significantly to a resilient economy and a cleaner environment.
- Achieving energy security is not only crucial for economic growth but also essential for social well-being and environmental sustainability, paving the way for a brighter future for India.
8. Fostering Infrastructure Development In India Through Fiscal Interventions
Introduction
- The Indian government has placed significant emphasis on infrastructure development in the budget for 2024-25.
- A substantial portion of total expenditure is allocated to various infrastructure projects, highlighting the government’s recognition of infrastructure’s vital role in driving economic growth, enhancing quality of life, and facilitating regional development.
Key Budget Highlights
- Increased Financial Allocation:
- The budget allocates Rs. 11,11,111 crore for infrastructure development, which represents 3.4% of the GDP.
- This allocation marks the highest level in recent years, reflecting a robust commitment to infrastructure.
- Enhanced Physical Connectivity:
- A focus on physical connectivity is evident, with significant investments planned for roadways, railways, airports, and ports.
- Roadway Development Initiatives:
- Plans are in place to upgrade the existing road network, improve connectivity, and decrease logistics costs, facilitating smoother transportation across the country.
- Railway Modernization Efforts:
- The budget includes funds specifically earmarked for modernising the railway sector, with investments in locomotives, wagons, and essential infrastructure improvements.
- Urban Development Focus:
- Allocations for urban development aim to enhance housing, infrastructure, and amenities, contributing to improved living conditions in urban areas.
Rationale Behind Infrastructure Investment
- Catalyst for Economic Growth:
- Infrastructure development serves as a crucial driver of economic growth, generating jobs, attracting investments, and enhancing operational efficiency.
- Social Upliftment:
- Investments in infrastructure can significantly elevate quality of life by improving access to essential services such as healthcare, education, and transportation.
- Balanced Regional Development:
- Infrastructure projects can help close the developmental gap between urban and rural areas, promoting equitable growth across the nation.
Challenges and Opportunities
- Funding Constraints:
- Despite the significant budget allocation, challenges remain in securing adequate funding for all proposed infrastructure projects.
- Environmental Considerations:
- Infrastructure development can lead to environmental issues, including deforestation and pollution.
- The government must ensure that projects are carried out sustainably to mitigate these impacts.
- Land Acquisition Complexities:
- Acquiring land for infrastructure projects can be a protracted and complicated process. Streamlining this process is essential for timely project implementation.
Conclusion: Unlocking India’s Potential
- By effectively addressing the challenges associated with infrastructure development and implementing comprehensive plans, the Indian government can maximise its demographic dividend.
- Robust infrastructure is not only fundamental for economic growth but also crucial for achieving a vision of a developed nation.
- Ultimately, the commitment to infrastructure development is expected to enhance overall societal well-being, facilitate economic progress, and promote sustainable regional development throughout India.
9. Focus On The Manufacturing And Services Sectors
Introduction
- The manufacturing and services sectors are crucial to India’s economic landscape, serving as the foundation for development and job creation.
- The Union Budget 2024-25 reflects the Indian government’s commitment to transforming the nation into a developed economy, encapsulated in the vision of “Vikas Bharat.”
- This article explores the significance of both sectors, the initiatives taken to bolster them, and their collective impact on India’s economic trajectory.
Importance of the Manufacturing Sector
- Manufacturing contributes approximately 16-17% to India’s GDP, marking it as a vital driver of economic growth.
- The sector is recognized for its job creation potential and its role in fostering innovation.
- India has the potential to emerge as a global manufacturing hub, with the capacity to export goods worth US$1 trillion by 2030.
Government Initiatives to Boost Manufacturing
- The government has introduced several key initiatives aimed at enhancing the manufacturing landscape:
- SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0: A program focused on improving manufacturing capabilities and fostering rapid transformation through Industry 4.0 technologies.
- New Credit Guarantee Scheme for MSMEs: Enables term loans without collateral or third-party guarantees, facilitating easier access to finance.
- Increased Mudra Loan Limits: Provides higher loan ceilings for entrepreneurs who have successfully repaid previous loans.
- Enhanced Trade Receivables Discounting System (TREDS): Reduced turnover thresholds for onboarding buyers to streamline payment processes for MSMEs.
- Credit Assessment Model Based on Digital Footprints: Utilises technology to evaluate the creditworthiness of MSMEs more accurately.
- E-Commerce Export Hubs: Establishes platforms to assist MSMEs and traditional artisans in selling products internationally.
- Incentives for Eco-Friendly Technologies: Offers subsidies and tax breaks to companies investing in sustainable practices.
The Services Sector as an Economic Engine
- The services sector accounts for over 50% of India’s GDP and experienced a growth rate of 9.1% in 2022-23.
- It contributed 55% to India’s Gross Value Added (GVA) at current prices in FY24.
- The sector is the leading destination for Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) inflows in India.
Government Strategies to Enhance the Services Sector
- The Indian government has implemented a series of initiatives designed to stimulate growth in the services sector:
- Skill India Program: Aims to skill and upskill 400 million people by 2022 to meet the demands of the evolving job market.
- Make in India Program: Aims to strengthen the manufacturing sector while also enhancing the services sector’s contribution.
- Union Budget 2024-25 Focus: Prioritises investments in digital infrastructure, workforce digital literacy, and seamless integration between manufacturing and services.
Growth Potential of Services Sector
- The services sector holds substantial growth potential due to several factors:
- High Employment Elasticity: The sector has demonstrated the ability to create jobs at a rapid pace.
- Improved Ease of Doing Business: The government’s commitment to simplifying regulations promotes a more conducive environment for service businesses.
- Increasing Demand for Services: Domestic and global markets are witnessing a rising demand for diverse services.
Key Data Points on Services Sector Performance
- In 2022-23, the services sector generated nearly half of the 8.12 million jobs created across the economy.
- Between October and December 2023, India’s services exports grew by 5.1% to USD 87.7 billion, contributing to a trade surplus of USD 44.9 billion.
Infrastructure Development as a Catalyst
- The budget emphasises substantial investments in infrastructure, a critical component for transforming India into a global manufacturing hub.
- Improved infrastructure could contribute an additional US$ 500 billion annually to the global economy by 2030, further enhancing India’s competitiveness on the world stage.
Conclusion
- The interdependence of manufacturing and services sectors is fundamental to India’s economic growth and development.
- By addressing challenges and leveraging growth opportunities, India is well-positioned to achieve its vision of “Vikas Bharat,” ensuring a sustainable and prosperous future for its citizens.




